Abstract
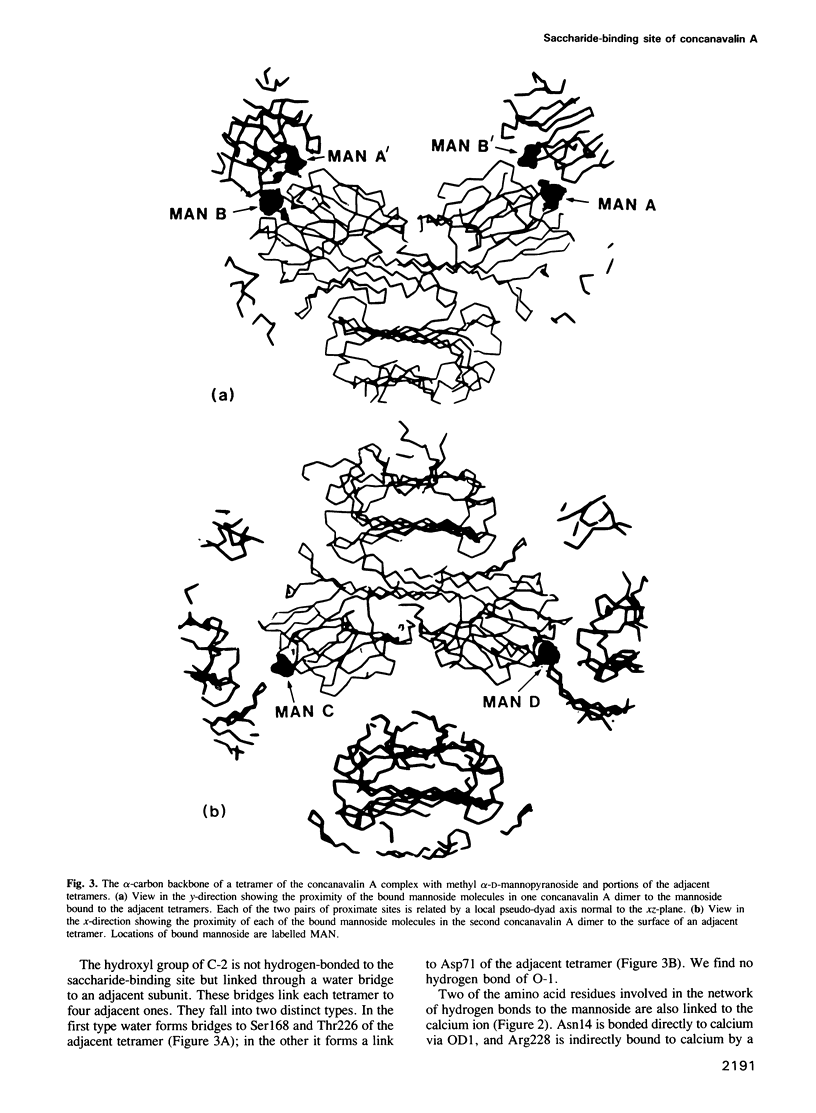
A complex of concanavalin A with methyl alpha-D-mannopyranoside has been crystallized in space group P212121 with a = 123.9 A, b = 129.1 A and c = 67.5 A. X-ray diffraction intensities to 2.9 A resolution have been collected on a Xentronics/Nicolet area detector. The structure has been solved by molecular replacement where the starting model was based on refined coordinates of an I222 crystal of saccharide-free concanavalin A. The structure of the saccharide complex was refined by restrained least-squares methods to an R-factor value of 0.19. In this crystal form, the asymmetric unit contains four protein subunits, to each of which a molecule of mannoside is bound in a shallow crevice near the surface of the protein. The methyl alpha-D-mannopyranoside molecule is bound in the C1 chair conformation 8.7 A from the calcium-binding site and 12.8 A from the transition metal-binding site. A network of seven hydrogen bonds connects oxygen atoms O-3, O-4, O-5 and O-6 of the mannoside to residues Asn14, Leu99, Tyr100, Asp208 and Arg228. O-2 and O-1 of the mannoside extend into the solvent. O-2 is hydrogen-bonded through a water molecule to an adjacent asymmetric unit. O-1 is not involved in any hydrogen bond and there is no fixed position for its methyl substituent.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernstein F. C., Koetzle T. F., Williams G. J., Meyer E. F., Jr, Brice M. D., Rodgers J. R., Kennard O., Shimanouchi T., Tasumi M. The Protein Data Bank: a computer-based archival file for macromolecular structures. J Mol Biol. 1977 May 25;112(3):535–542. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer C. F., Sternlicht H., Marcus D. M., Grollman A. P. Interactions of saccharides with concanavalin A. Mechanism of binding of alpha- and beta-methyl D-glucopyranoside to concanavalin A as determined by 13C nuclear magnetic resonance. Biochemistry. 1973 Oct 23;12(22):4448–4457. doi: 10.1021/bi00746a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham B. A., Wang J. L., Waxdal M. J., Edelman G. M. The covalent and three-dimensional structure of concanavalin A. II. Amino acid sequence of cyanogen bromide fragment F3. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 25;250(4):1503–1512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dani M., Manca F., Rialdi G. Calorimetric study of concanavalin A binding to saccharides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jan 30;667(1):108–117. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(81)90071-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M., Cunningham B. A., Reeke G. N., Jr, Becker J. W., Waxdal M. J., Wang J. L. The covalent and three-dimensional structure of concanavalin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2580–2584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer J., Kaufman H. W., Kalb A. J. An x-ray crystallographic study of concanavalin A. J Mol Biol. 1970 Mar 14;48(2):365–366. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90169-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardman K. D., Agarwal R. C., Freiser M. J. Manganese and calcium binding sites of concanavalin A. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):69–86. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90513-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardman K. D., Ainsworth C. F. Structure of concanavalin A at 2.4-A resolution. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 19;11(26):4910–4919. doi: 10.1021/bi00776a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardman K. D., Ainsworth C. F. Structure of the concanavalin A-methyl alpha-D-mannopyranoside complex at 6-A resolution. Biochemistry. 1976 Mar 9;15(5):1120–1128. doi: 10.1021/bi00650a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacrot B., Cusack S., Dianoux A. J., Engelman D. M. Inelastic neutron scattering analysis of hexokinase dynamics and its modification on binding of glucose. Nature. 1982 Nov 4;300(5887):84–86. doi: 10.1038/300084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalb A. J., Levitzki A. Metal-binding sites of concanavalin A and their role in the binding of alpha-methyl d-glucopyranoside. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(4):669–672. doi: 10.1042/bj1090669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalb A. J., Lustig A. The molecular weight of concanavalin A. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Oct 21;168(2):366–367. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(68)90161-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quiocho F. A. Carbohydrate-binding proteins: tertiary structures and protein-sugar interactions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:287–315. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.001443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeke G. N., Jr, Becker J. W., Edelman G. M. The covalent and three-dimensional structure of concanavalin A. IV. Atomic coordinates, hydrogen bonding, and quaternary structure. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 25;250(4):1525–1547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoham M., Yonath A., Sussman J. L., Moult J., Traub W., Kalb A. J. Crystal structure of demetallized concanavalin A: the metal-binding region. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jun 25;131(2):137–155. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturtevant J. M. Heat capacity and entropy changes in processes involving proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2236–2240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villafranca J. J., Viola R. E. The use of 13C spin lattice relaxation times to study the interaction of alpha-methyl-D-glucopyranoside with concanavalin A. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Feb;160(2):465–468. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90422-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yariv J., Kalb A. J., Levitzki A. The interaction of concanavalin A with methyl alpha-D-glucopyranoside. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Sep 3;165(2):303–305. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(68)90063-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yariv J., Kalb A. J., Papiz M. Z., Helliwell J. R., Andrews S. J., Habash J. Properties of a new crystal form of the complex of concanavalin A with methyl alpha-D-glucopyranoside. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 5;195(3):759–760. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90198-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]