Abstract
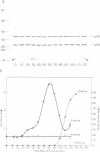
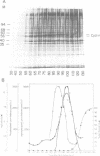
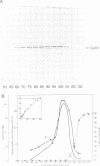
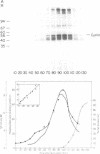
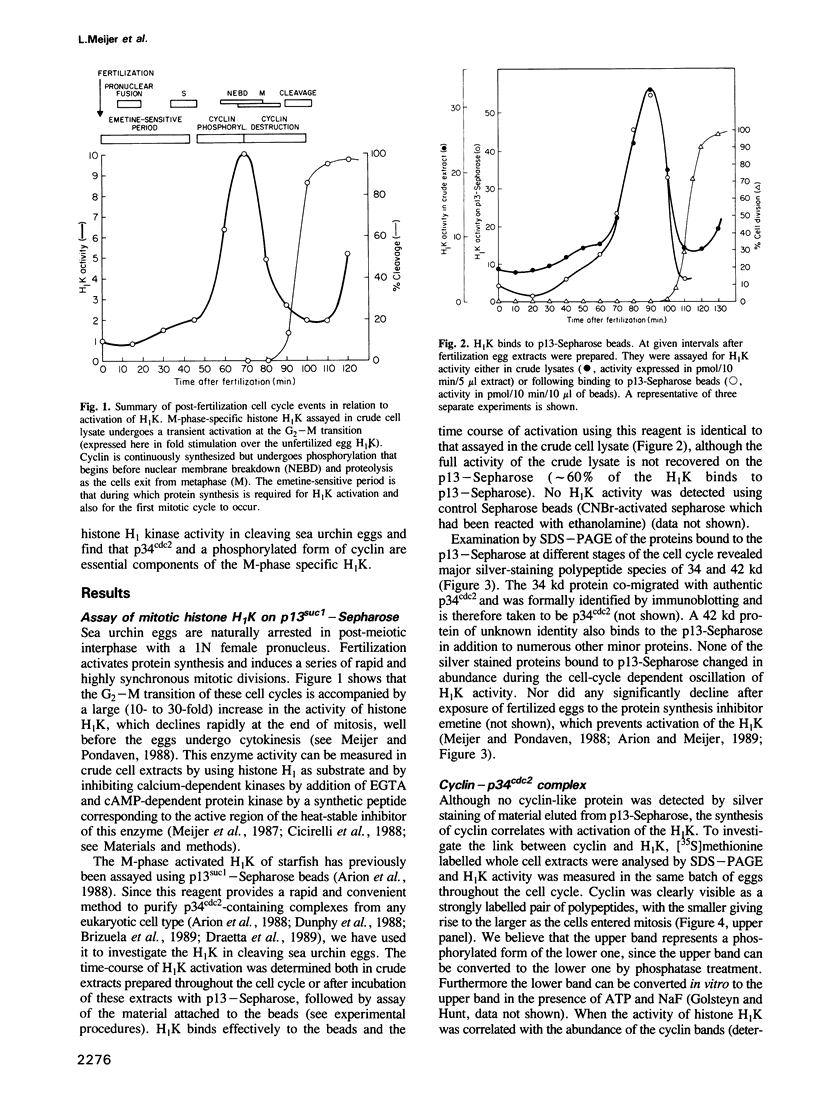
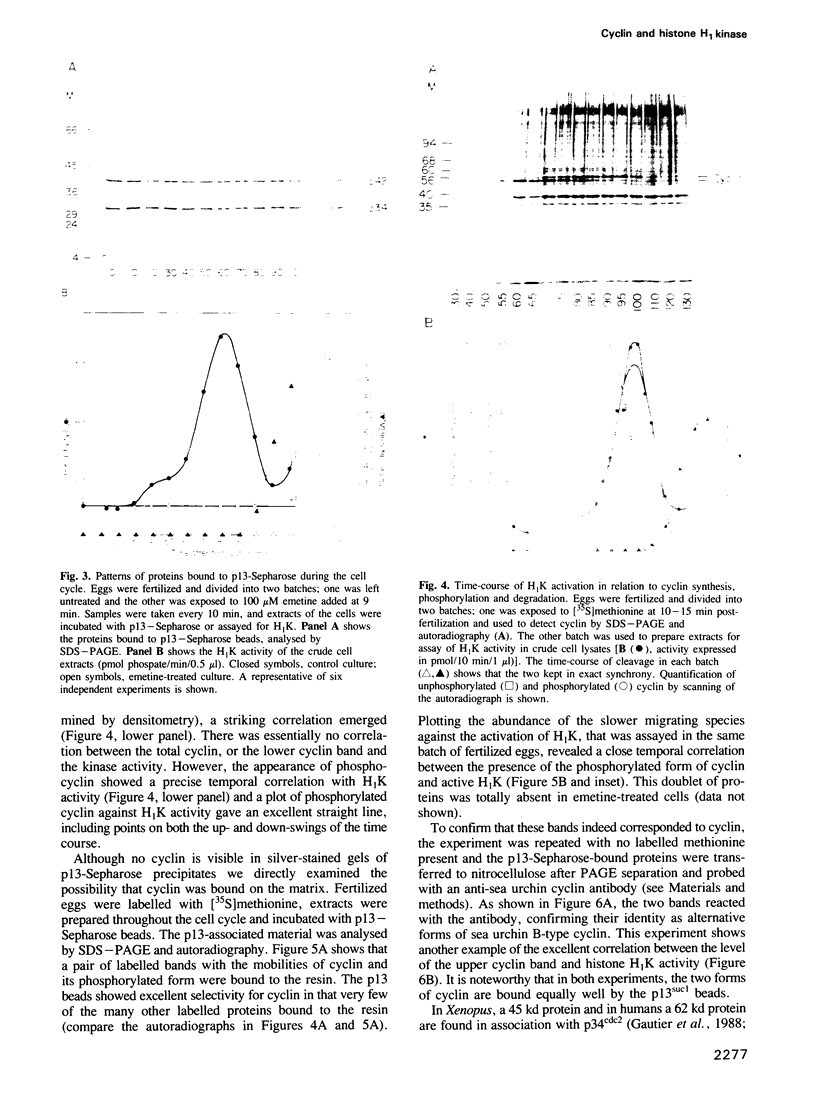
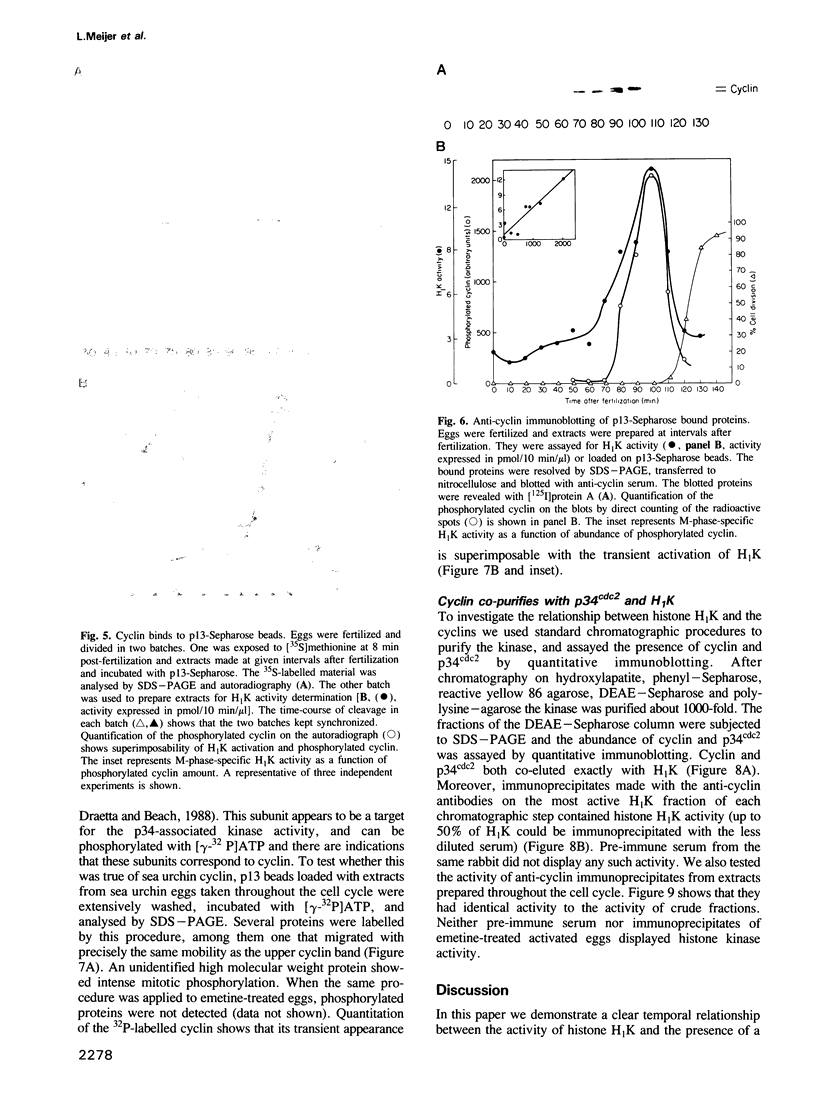
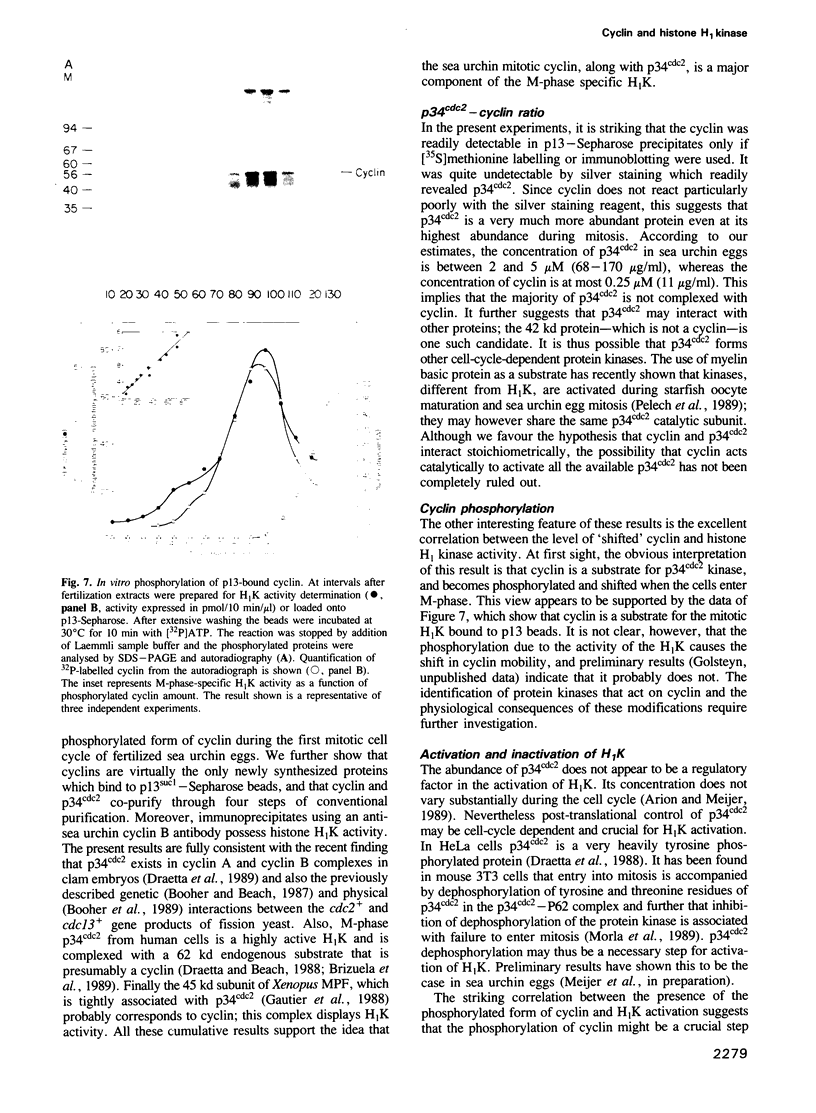
A so-called 'growth-associated' or 'M-phase specific' histone H1 kinase (H1K) has been described in a wide variety of eukaryotic cell types; p34cdc2 has previously been shown to be a catalytic subunit of this protein kinase. In fertilized sea urchin eggs the activity of H1K oscillates during the cell division cycle and there is a striking temporal correlation between H1K activation and the accumulation of a phosphorylated form of cyclin. H1K activity declines in parallel with proteolytic cyclin destruction of the end of the first cell cycle. By virtue of the high affinity of the fission yeast p13suc1 for the p34cdc2 protein, H1K strongly binds to p13-Sepharose beads. Cyclin, p34cdc2 and H1K co-purify on this affinity reagent as well as through several conventional chromatographic procedures. Anticyclin antibodies immunoprecipitate the M-phase specific H1K in crude extracts or in purified fractions. Sea urchin eggs appear to contain much less cyclin than p34cdc2, suggesting that p34cdc2 may interact with other proteins. These results demonstrate that cyclin and p34cdc2 are major components of the M-phase specific H1K.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arion D., Meijer L., Brizuela L., Beach D. cdc2 is a component of the M phase-specific histone H1 kinase: evidence for identity with MPF. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):371–378. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90060-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booher R., Beach D. Interaction between cdc13+ and cdc2+ in the control of mitosis in fission yeast; dissociation of the G1 and G2 roles of the cdc2+ protein kinase. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3441–3447. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02667.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booher R., Beach D. Involvement of cdc13+ in mitotic control in Schizosaccharomyces pombe: possible interaction of the gene product with microtubules. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2321–2327. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03075.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury E. M., Inglis R. J., Matthews H. R. Control of cell division by very lysine rich histone (F1) phosphorylation. Nature. 1974 Feb 1;247(5439):257–261. doi: 10.1038/247257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brizuela L., Draetta G., Beach D. p13suc1 acts in the fission yeast cell division cycle as a component of the p34cdc2 protein kinase. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3507–3514. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02676.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicirelli M. F., Pelech S. L., Krebs E. G. Activation of multiple protein kinases during the burst in protein phosphorylation that precedes the first meiotic cell division in Xenopus oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):2009–2019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cyclin in fission yeast. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):738–740. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)90933-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cyclin in fission yeast. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):738–740. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)90933-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Beach D. Activation of cdc2 protein kinase during mitosis in human cells: cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation and subunit rearrangement. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):17–26. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90175-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Brizuela L., Potashkin J., Beach D. Identification of p34 and p13, human homologs of the cell cycle regulators of fission yeast encoded by cdc2+ and suc1+. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):319–325. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90227-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Luca F., Westendorf J., Brizuela L., Ruderman J., Beach D. Cdc2 protein kinase is complexed with both cyclin A and B: evidence for proteolytic inactivation of MPF. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):829–838. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90687-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Piwnica-Worms H., Morrison D., Druker B., Roberts T., Beach D. Human cdc2 protein kinase is a major cell-cycle regulated tyrosine kinase substrate. Nature. 1988 Dec 22;336(6201):738–744. doi: 10.1038/336738a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Brizuela L., Beach D., Newport J. The Xenopus cdc2 protein is a component of MPF, a cytoplasmic regulator of mitosis. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):423–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90205-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Rosenthal E. T., Youngblom J., Distel D., Hunt T. Cyclin: a protein specified by maternal mRNA in sea urchin eggs that is destroyed at each cleavage division. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):389–396. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90420-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Norbury C., Lohka M., Nurse P., Maller J. Purified maturation-promoting factor contains the product of a Xenopus homolog of the fission yeast cell cycle control gene cdc2+. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):433–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90206-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardie D. G., Matthews H. R., Bradbury E. M. Cell-cycle dependence of two nuclear histone kinase enzyme activities. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jun 15;66(1):37–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10422.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohmann P. Phosphorylation of H1 histones. Mol Cell Biochem. 1983;57(1):81–92. doi: 10.1007/BF00223526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labbe J. C., Lee M. G., Nurse P., Picard A., Doree M. Activation at M-phase of a protein kinase encoded by a starfish homologue of the cell cycle control gene cdc2+. Nature. 1988 Sep 15;335(6187):251–254. doi: 10.1038/335251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labbé J. C., Picard A., Karsenti E., Dorée M. An M-phase-specific protein kinase of Xenopus oocytes: partial purification and possible mechanism of its periodic activation. Dev Biol. 1988 May;127(1):157–169. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90197-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake R. S., Salzman N. P. Occurrence and properties of a chromatin-associated F1-histone phosphokinase in mitotic Chinese hamster cells. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 5;11(25):4817–4826. doi: 10.1021/bi00775a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. G., Nurse P. Complementation used to clone a human homologue of the fission yeast cell cycle control gene cdc2. Nature. 1987 May 7;327(6117):31–35. doi: 10.1038/327031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohka M. J., Hayes M. K., Maller J. L. Purification of maturation-promoting factor, an intracellular regulator of early mitotic events. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3009–3013. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews H. R., Huebner V. D. Nuclear protein kinases. Mol Cell Biochem. 1984;59(1-2):81–99. doi: 10.1007/BF00231306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer L., Pelech S. L., Krebs E. G. Differential regulation of histone H1 and ribosomal S6 kinases during sea star oocyte maturation. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 1;26(24):7968–7974. doi: 10.1021/bi00398a063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer L., Pondaven P. Cyclic activation of histone H1 kinase during sea urchin egg mitotic divisions. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Jan;174(1):116–129. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90147-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minshull J., Blow J. J., Hunt T. Translation of cyclin mRNA is necessary for extracts of activated xenopus eggs to enter mitosis. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):947–956. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90628-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin synthesis drives the early embryonic cell cycle. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):275–280. doi: 10.1038/339275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Solomon M. J., Kirschner M. W. The role of cyclin synthesis and degradation in the control of maturation promoting factor activity. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):280–286. doi: 10.1038/339280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelech S. L., Meijer L., Krebs E. G. Characterization of maturation-activated histone H1 and ribosomal S6 kinases in sea star oocytes. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 1;26(24):7960–7968. doi: 10.1021/bi00398a062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunt T. Molecular cloning and characterization of the mRNA for cyclin from sea urchin eggs. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):2987–2995. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02604.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quirin-Stricker C. Histone H1 kinase from mouse plasmacytoma. Further characterization and molecular structure. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jul 16;142(2):317–322. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08288.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quirin-Stricker C., Schmitt M. Purification and characterization of a specific histone H1 protein kinase from mouse plasmacytoma. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Aug;118(1):165–172. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05500.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I., Hadwiger J. A., Lörincz A. T. Protein kinase activity associated with the product of the yeast cell division cycle gene CDC28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4055–4059. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal E. T., Hunt T., Ruderman J. V. Selective translation of mRNA controls the pattern of protein synthesis during early development of the surf clam, Spisula solidissima. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):487–494. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90635-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlepper J., Knippers R. Nuclear protein kinases from murine cells. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Dec 1;60(1):209–220. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb20993.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. D., Glaccum M. B., Fischer E. H., Krebs E. G. Primary-structure requirements for inhibition by the heat-stable inhibitor of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1613–1616. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simanis V., Nurse P. The cell cycle control gene cdc2+ of fission yeast encodes a protein kinase potentially regulated by phosphorylation. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):261–268. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90390-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standart N., Minshull J., Pines J., Hunt T. Cyclin synthesis, modification and destruction during meiotic maturation of the starfish oocyte. Dev Biol. 1987 Nov;124(1):248–258. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90476-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson K. I., Farrell K. M., Ruderman J. V. The clam embryo protein cyclin A induces entry into M phase and the resumption of meiosis in Xenopus oocytes. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):861–870. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90801-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westendorf J. M., Swenson K. I., Ruderman J. V. The role of cyclin B in meiosis I. J Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;108(4):1431–1444. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.4.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodford T. A., Pardee A. B. Histone H1 kinase in exponential and synchronous populations of Chinese hamster fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 5;261(10):4669–4676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu R. S., Panusz H. T., Hatch C. L., Bonner W. M. Histones and their modifications. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1986;20(2):201–263. doi: 10.3109/10409238609083735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeilig C. E., Langan T. A. Studies on the mechanism of activation of mitotic histone H1 kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Aug 14;95(3):1372–1379. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91625-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]