Abstract
Drugs that target microtubules are potent inhibitors of angiogenesis but their mechanism of action is not well understood. To explore this, we treated human umbilical vein endothelial cells with paclitaxel, vinblastine, and colchicine and measured the effects on microtubule dynamics and cell motility. In general, lower drug concentrations suppressed microtubule dynamics and inhibited cell migration whereas higher concentrations were needed to inhibit cell division; but, surprisingly, large drug-dependent differences were seen in the relative concentrations needed to inhibit these two processes. Suppression of microtubule dynamics did not significantly affect excursions of lamellipodia away from the nucleus or prevent cells from elongating; but, it did inhibit retraction of the trailing edges that are normally enriched in dynamic microtubules, thereby limiting cell locomotion. Complete removal of microtubules with a high vinblastine concentration caused a loss of polarity that resulted in roundish rather than elongated cells, rapid but non-directional membrane activity, and little cell movement. The results are consistent with a model in which more static microtubules stabilize the leading edge of migrating cells while more dynamic microtubules locate to the rear where they can remodel and allow tail retraction. Suppressing microtubule dynamics interferes with tail retraction, but removal of microtubules destroys the asymmetry needed for cell elongation and directional motility. The prediction that suppressing microtubule dynamics might be sufficient to prevent angiogenesis was supported by showing that low concentrations of paclitaxel could prevent the formation of capillary-like structures in an in vitro tube formation assay.
Keywords: motility, angiogenesis, cell division, tubulin, paclitaxel, vinblastine, colchicine
Introduction
Tumor growth depends on the formation of blood vessels that bring nutrients and oxygen to the cells, a process known as angiogenesis. When angiogenesis is inhibited, tumor size is limited and in most cases serious pathology is averted (1). Based on these observations, considerable effort has gone into identifying inhibitors of angiogenesis that can be used to treat patients with cancer. However, this approach has thus far met with only limited success (2). In order to advance this treatment option, it will be necessary to further understand the mechanisms involved in human angiogenesis and the mechanisms by which inhibitors interfere with the angiogenic process.
Drugs that target the microtubule cytoskeleton are potent inhibitors of angiogenesis, but the mechanisms by which they act are not well understood. Microtubules are dynamic polymers that alternate between periods of growth and shortening interrupted by pauses during which there is no net change in length. This behavior, termed dynamic instability, allows microtubules to probe their environment and remodel in response to cytoplasmic or extracellular signals (3, 4). Microtubule-targeted drugs suppress dynamic behavior regardless of whether they act like vinblastine and colchicine (structures shown in supplementary Fig. S1) to inhibit microtubule assembly, or they act like paclitaxel to stabilize microtubules (5). It traditionally has been thought that these drugs inhibit both cell division and cell migration by suppressing microtubule dynamics, but recent work indicates that low drug concentrations are sufficient to suppress dynamics and inhibit cell migration yet much higher drug concentrations are needed to block cell division (6, 7). The link between suppression of dynamics and inhibition of cell migration appears to hold for many cultured cell lines; but in the case of vascular endothelial cells it has been reported that microtubule dynamics are stimulated rather than suppressed by low concentrations of paclitaxel or vinflunine and this stimulation causes inhibition of cell migration (8, 9). To further explore the influence of microtubule-acting drugs on cell migration, we examined the dose-dependent effects of paclitaxel, colchicine, and vinblastine on dynamic instability and migration of primary human vascular endothelial cells (HUVEC). Our results indicate that the drugs suppress microtubule dynamics in parallel with inhibition of cell migration by interfering with the ability of microtubules to remodel in the trailing edge. The drug concentrations that suppressed microtubule dynamics and inhibited cell migration also inhibited the ability of the cells to form capillary-like tubes on Matrigel.
Materials and Methods
Materials
Medium 199, penicillin/streptomycin/glutamine, Hank's Buffered Saline Solution, trypsin-EDTA, lymphoprep 1077, trypsin, and 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride (DAPI) and Alexa 488-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG were from Invitrogen Life Technologies (Carlsbad, CA, USA). Porcine gelatin, vinblastine, colcemid and tubulin antibody DM1A were from Sigma-Aldrich Chemicals (St. Louis, MO, USA). Paclitaxel was obtained from cytoskeleton (Denver, CO, USA) and all other chemicals were from BDH (Toronto, Canada). The ibidi dishes and chambers are from ibidi (Munich, Germany) and plastic ware was from VWR International (West Chester, PA, USA) or Becton Dickinson (Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA).
Endothelial cell isolation
Endothelial cells were isolated from human umbilical cords (Foothills Hospital, Calgary, Canada) as described (10). They were grown on a matrix of 0.2% gelatin and maintained in M199 with 20% human serum. First passage endothelial cells were used in all experiments and the purity and differentiated status of the endothelial cells was confirmed by staining with VE-cadherin to identify endothelial cell junctions and von Wildebrand factor to identify Weibel-Palade bodies. The University of Calgary Conjoint Health Research Ethics Board approved all procedures requiring human subjects.
Mitotic index
Endothelial cells were grown on glass coverslips coated with 2% gelatin and 25 μM fibronectin for 24 h and microtubule inhibitors were added for an additional 24 h. The cells were fixed in 2% paraformaldehyde for 10 min, permeabilized in HBSS containing 0.5% Triton X-100, stained with DAPI for 30 min, washed in HBSS buffer for another 30 min, and then observed under a fluorescence microscope with a 40X, N.A. 0.60 objective. The mitotic index was calculated as the percentage of cells that had condensed chromosomes.
Immunofluorescence
Endothelial cells grown to 70% confluence on glass coverslips coated with 2% gelatin and 25 μM fibronectin were washed in PBS and pre-extracted with microtubule stabilizing buffer (20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 6.8), 1mM MgCl2, 2mM EGTA, 0.5% Nonidet P40, and 4 μM paclitaxel) at 4 °C for 1 min. They were then fixed in methanol at −20 °C for 10 min and stained with DM1A mouse monoclonal antibody to α-tubulin (Sigma Aldrich) for 1 h. The coverslips were washed and counterstained for 1 h with Alexa 488-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (Invitrogen) that included 1 μg/ml DAPI. After the final wash, the coverslips were mounted on slides with Prolong Gold mounting medium (Invitrogen). The images were captured with a 100X, N.A. 1.35 objective using a wide field microscope (Olympus) equipped with a CCD camera.
Endothelial cell migration and membrane activity
Endothelial cells were grown on 35 mm tissue culture dishes coated with gelatin and fibronectin until they reached confluence. A scratch was then introduced across the middle of the monolayer and the migration of the cells into the wound was monitored over time with the aid of a microscope equipped with a 37 °C incubator and CCD camera. Images of cells moving into a wound were captured starting at 1 h and continued every 15 min for a total of 12 h using a 4X, N.A. 0.16 objective on a wide field microscope (Olympus). Image stacks were imported into Image J using the LOCI bioformats importer plugin. Cells were tracked with the manual tracking plugin tool by recording the XY coordinates of the nucleus. To quantify membrane activity, images of migrating cells were captured 1 min apart using a 10X, N.A. 0.30 phase objective and imported into Image J. The distances of leading and trailing membrane edges from a fixed point in the nucleus were measured and plotted over time to generate life history plots of membrane positions. The results were quantified by averaging the changes in distance that occurred during each 1 min interval.
Angiogenesis
Endothelial cells were plated at approximately 80% of confluence on ibidi-bottom angiogenesis μ-slides coated with 10 μl of Matrigel and incubated in presence and absence of microtubule inhibitors. After 5 h, tube formation was monitored using phase contrast microscopy with a 4X, N.A. 0.16 objective. Calcein (2 μg/ml) was the added to fluorescently label the living cells. After 30 min, the medium was replaced and images were collected using either a 4X, N.A. 0.16 or 10X, N.A. 0.30 objective.
Live cell Imaging of microtubules
Endothelial cells grown on either ibidi 35 mm dishes or in ibidi 8 well plates were transfected with GFP-MAP4 using HUVEC JetPEI according to manufacturers instructions. 24 h following transfection, endothelial cells were transferred to phenol red-free medium prior to imaging. Images were captured every 5 s for 4 min, giving a total of 50 image frames. Microtubule dynamics were calculated by using ImageJ software as previously described (6, 11).
Statistics
All experiments were performed at least three times and statistical differences were determined using either a student’s t-test (two groups) or ANOVA with the appropriate post-test (more than two groups). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM and p < 0.05 was considered significant.
Results
Paclitaxel, colchicine, and vinblastine differ in their relative abilities to inhibit cell migration versus cell division
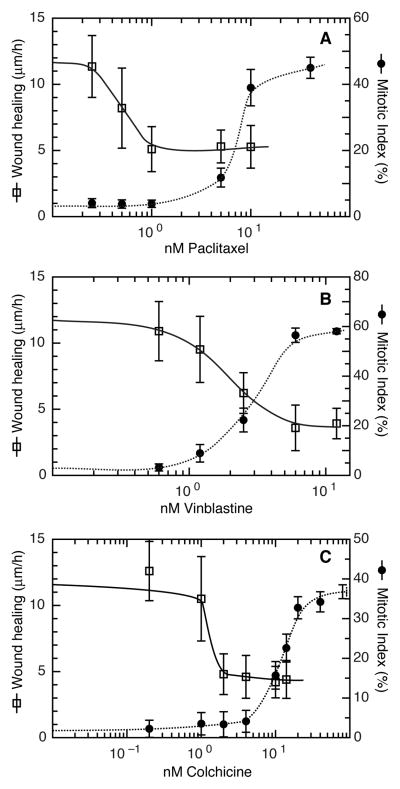
Using a variety of cultured cell lines, we previously reported that cell migration could be inhibited at lower concentrations of microtubule-targeted drugs than were needed to inhibit cell division (6). To test whether this relationship would also hold true for primary cells, we isolated fresh HUVEC and treated them with paclitaxel, colchicine, or vinblastine to examine the relative abilities of the drugs to inhibit cell migration and cell division. We found that paclitaxel inhibited cell migration at a 15.6-fold lower concentration than was needed to inhibit cell division (IC50 migration = 0.48 nM; IC50 cell division = 7.5 nM) (Fig. 1A). Thus, paclitaxel selectively inhibited HUVEC migration at concentrations that had no effect on cell division. In contrast, vinblastine inhibited cell migration and cell division at similar concentrations, with only a 1.6-fold difference in the IC50 values for migration and cell division (IC50 migration = 1.9 nM; IC50 cell division = 3.1 nM) (Fig. 1B). Colchicine showed an intermediate phenotype with a 7.9-fold difference in IC50 values (IC50 migration = 1.4 nM; IC50 cell division = 11.0 nM) (Fig. 1C). In all cases, migration was inhibited at lower concentrations than cell division in HUVEC, yet the separation of IC50 values varied considerably among the drugs. The molecular basis for this variation is unknown but is under active investigation.
Figure 1. The effect of microtubule inhibitors on cell proliferation and cell migration.
Paclitaxel (A), vinblastine (B), and colchicine (C) were tested for their ability to inhibit cell migration using a wound healing scratch assay (open squares, solid lines) and for their ability to block cell division measured as a rise in the mitotic index (solid circles, dotted lines).
Paclitaxel, vinblastine, and colchicine suppress microtubule dynamics in vascular endothelial cells
Microtubule inhibitors were reported to increase microtubule dynamics in HMEC-1 cells and HUVEC and the increases were tied to the inhibition of cell motility (8, 9). These results are in contradiction to the findings in most other cell types in which drug treatment has been reported to suppress microtubule dynamics (12). To directly address this discrepancy in primary cultures of HUVEC, we transfected the cells with EGFP-MAP4 to label the microtubules for live cell imaging experiments. Microtubule dynamics were then determined by measuring microtubule length every five seconds in the presence or absence of different concentrations of paclitaxel, vinblastine or colchicine. The concentrations used were based on the IC50 values for migration and cell division as shown in Fig. 1.
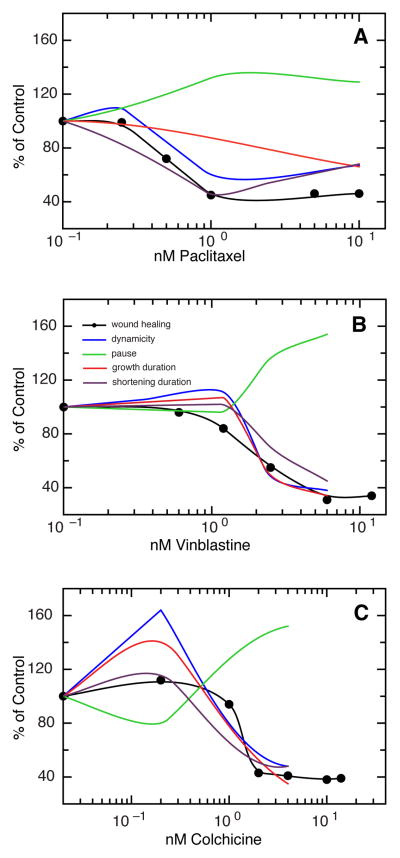
We found that all three drugs had dose-dependent effects on microtubule dynamics in HUVEC. Many parameters that influence dynamic instability were altered (Table S1, S2, and S3). Figure 2 shows that all three drugs significantly decreased the time microtubules spent either growing or shrinking, resulting in an increase in microtubules in a paused state. This resulted in a significant decrease in overall dynamicity, a parameter that serves as a measure for how quickly microtubules can remodel (Fig 2). In contrast to other cell lines, the drugs had limited effects on catastrophe, and growth and shrinkage rates (Tables S1, S2, and S3) in HUVEC. Drug-induced suppression of dynamicity consistently paralleled drug-induced suppression of cell motility.
Figure 2. Changes in select parameters of dynamic instability in cells treated with microtubule inhibitors.
HUVEC were transfected with EGFP-MAP4 and microtubule behavior was measured in varying concentrations of paclitaxel (A), vinblastine (B), and colchicine (C). The plots show the effects of drugs on various parameters of dynamic instability (colored lines) superimposed on the drug effects on cell motility determined from a wound healing scratch assay (solid circles, black line).
An exception to these general observations occurred with colchicine. At very low concentrations (0.2 nM) colchicine increased dynamicity, but dynamics were then suppressed as the concentration was increased (Fig. 2C). Importantly, cell migration was only inhibited at colchicine concentrations that suppressed dynamics. Overall, the results indicated that suppression of microtubule dynamics is associated with inhibition of endothelial cell migration and is likely to be responsible, at least in part, for the known anti-angiogenic effects of microtubule inhibitors (13).
Dynamic microtubules are enriched in the trailing edge of migrating cells
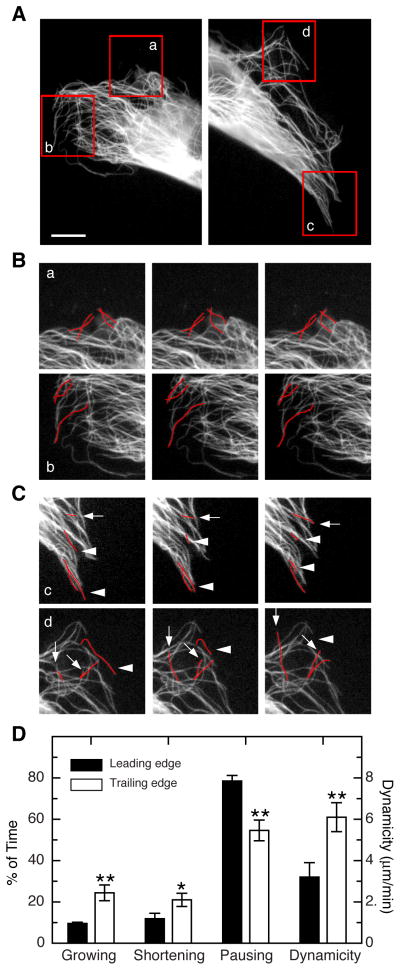
Locomotion begins with the extension of a lamellipodium that causes the cell to elongate, and is followed by retraction of the trailing edge to produce net forward movement. To better understand how dynamic microtubules are distributed during this process, GFP-MAP4-transfected HUVEC were observed by fluorescence time-lapse microscopy while moving into a scratch wound. One such cell is shown in Fig. 3. The leading edge is shown at the left and the trailing edge is shown at the right with areas monitored by time lapse outlined in red boxes labeled a–d (Fig. 3A). As shown in Fig. 3B, microtubules at the leading edge were relatively static with little growth or shortening during the 20 second time period that is shown. In contrast, both regions in the trailing edge showed significant numbers of microtubules that either grew (arrows) or shortened (arrowheads) during the same time period (Fig. 3C). In addition to spending more time growing and shortening, microtubules in the trailing edge spent less time in a paused state (54.6% trailing versus 78.5% leading) and their overall dynamicity was about twofold higher (6.1 trailing versus 3.2 leading) (Fig. 3D and Table S4). A significant number of microtubules in the tail regions shortened rapidly beyond the reference point from where our measurements started. Those microtubules were not included in our calculation of the parameters of dynamic instability listed in Table S4 because our calculations, like those of others who carry out these kinds of measurements, typically exclude microtubules that fail to exist for at least 120 s. Microtubules exhibiting such extended depolymerization were nearly absent in the leading edge of the cell and so our data actually underestimate the large differences in dynamics that exist between the leading and trailing edges of migrating cells. These data suggest that dynamic microtubules are specifically needed in the tail region to allow cell movement.
Figure 3. Asymmetric distribution of dynamic microtubules.
(A) HUVEC cell migrating into a scratch wound. The cell was transfected with EGFP-MAP4 to visualize the microtubules. Left panel shows the leading edge and the right panel shows the trailing edge. Areas that were monitored by time lapse are outlined in red. Scale bar = 7 μm. (B) Time lapse sequences of regions a and b from the leading edge. Photographs shown are 10 s apart. A few microtubules are traced in red to aid the viewer. (C) Time lapse sequences of regions c and d from the trailing edge. Photographs shown are 10 s apart. In contrast to the static microtubules at the leading edge, many of the microtubules in the trailing edge were seen to grow (arrows) or shorten (arrowheads). (D) Quantification of the percent of the time microtubules were growing, shortening, or pausing at the leading or trailing edges of the cell. The calculated dynamicity of the microtubules is also plotted on a separate scale. All the differences shown between the leading and trailing edges were found to be significant. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.
Suppressing dynamics inhibits tail retraction
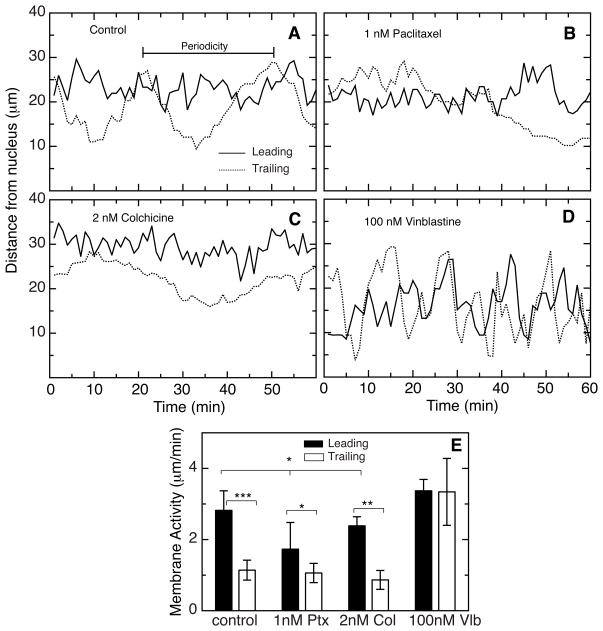
An asymmetric distribution of dynamic microtubules has been previously observed in migrating epithelial and fibroblast cell lines and is consistent with proposed a model in which dynamics are required to allow microtubule remodeling during tail retraction (14, 15). It is also possible, however, that microtubule assembly and disassembly are needed to regulate the activity of lamellipodia (16). To test this possibility we examined temporal membrane excursions in migrating HUVEC. This was done by measuring the distance between the cell membrane and the nucleus at either the leading or trailing edge of the cells and obtaining “life histories” of the two membrane edges. In untreated cells there was a clear difference in the membrane excursions between the leading and trailing edges (Fig. 4A and Movie 1). There were frequent excursions ranging from a few micrometers to over 10 micrometers at the leading edge and the membrane activity, which we define as the average rate of displacement of the membrane from the nucleus, was 2.8 ± 0.5 μm/min (Fig. 4E). The trailing edge displayed similar but shorter excursions with a membrane activity of 1.1 ± 0.3 μm/min. Superimposed on the shorter excursions at the trailing edge, however, there was a larger periodic increase and decrease in the distance from the nucleus with an average time between peaks of 26.4 ± 3.1 minutes that we interpret as stretching and release of the cell posterior as the cell moves forward. In support of this interpretation, direct observation of the stretching and release of the trailing edge of migrating HUVEC in time lapse movies gave an average value of 25.3 ± 5.8 min, a time that matched well to the periodicity we saw in the life history plots.
Figure 4. Membrane activity in HUVEC.
A time-lapse series of images taken 1 min apart were analyzed by measuring the distance of the leading (solid line) and trailing (dotted line) edges from the nucleus. Untreated cells (A), cells treated with 1 nM paclitaxel to suppress microtubule dynamics (B), cells treated with 2 nM colchicine to suppress microtubule dynamics (C) and cells treated with 100 nM vinblastine to eliminate the microtubules (D) are shown. Both edges exhibited relatively rapid fluctuations in the distance of the membrane from the nucleus. However, the trailing edge of control cells (dotted line in panel A) also exhibited a periodic rise and fall that we interpret as stretching and release of the trailing edge during cell migration. We define the time between successive peaks as the periodicity. Membrane activity, defined as the average rate of membrane displacement from the nucleus is plotted in (E). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.
Addition of 1 nM paclitaxel to suppress microtubule dynamics caused a small reduction in the length of excursions and membrane activity at the leading edge, but had little or no effect on the smaller excursions or membrane activity seen at the trailing edge (Figs. 4B, 4E, and Movie 2). However, the larger 26.4 minute average periodicity normally seen for the trailing membrane could no longer be measured within the 60 minute observation time of these measurements. Large excursions were still seen suggesting that the cell was able to stretch in the direction of movement, but the peaks were broader and the distance between peaks was extended. Similar changes were seen by observing time lapse video (Movie 2) where tail retraction appeared to be incomplete and the average time between successive tail retractions increased to 50.3 ± 5.5 min. Treating the cells with colchicine at a low concentration that suppresses microtubule dynamics produced similar results (Fig. 4C and 4E).
Although microtubule dynamics did not appear to play a major role in regulating membrane activity at the leading and trailing edges, the possibility remained that the physical presence of microtubules might be needed for membrane activity, perhaps by transporting vesicles to sites of membrane growth as has been suggested by others (17, 18). We tested this possibility by treating HUVEC with 100 nM vinblastine, a concentration that eliminated the microtubule cytoskeleton (Fig. S2). Contrary to the idea that microtubules are needed to facilitate membrane growth during lamellipodial extension, we observed that HUVEC lacking microtubules had even more membrane activity than control (Figs. 4D, 4E, and Movie 3). In addition, the difference in membrane activity between the leading and trailing edges seen in control cells was lost and the periodicity attributed to cell stretching was also lost. These changes are consistent with a model in which microtubules are needed for cell polarity and tail retraction but not for membrane activity.
Microtubules are needed for directional cell movement
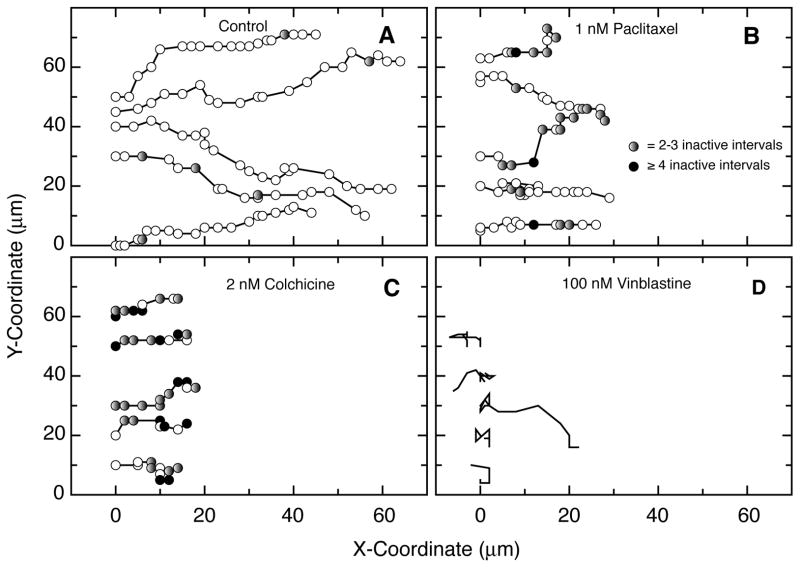
The ability of low drug concentrations to suppress microtubule dynamics and inhibit cell migration but not cell elongation suggested that the cells should still move in a directional manner, albeit more slowly. On the other hand, the loss of polarity in cells treated with a high concentration of vinblastine to eliminate the microtubule network suggested that the cells would lose directional cell motility. To test these predictions, individual cells were tracked in a wound healing assay and the results are shown in Fig. 5. Untreated HUVEC were seen to move predominantly and continuously in the direction of the wound (Fig. 5A). As predicted, cells treated with 1 nM paclitaxel (Fig. 5B) or 2 nM colchicine (Fig. 5C) to suppress microtubule dynamics continued to move predominantly in the direction of the wound, but their progress was much slower and contained “rests” during which there was no net movement between measurements. Cells treated with 100 nM vinblastine to eliminate microtubules appeared to be more static; but as predicted, when they did move the direction was random (Fig. 5D).
Figure 5. Migration paths of individual cells.
Time lapse movies of HUVEC moving into a scratch wound were analyzed by plotting the nuclear positions of individual cells at 15 min intervals. The direction of the wound is towards the right. (A) Untreated cells. Circles represent the position of the nucleus at time zero and every 15 min thereafter. (B) Cells treated with 1 nM paclitaxel to suppress microtubule dynamics. Shaded circles indicate the lack of any movement for one or more 15 min intervals. Gray, no change in position for 2–3 15-min intervals; black, no change in position for 4 or more 15-min intervals. (C) Cells treated with 2 nM colchicine to suppress microtubule dynamics. Shaded circles have the same meaning as in the previous panel. (D) Cells treated with 100 nM vinblastine to eliminate the microtubules. Circles were omitted because of extensive overlap.
Suppression of microtubule dynamics inhibits endothelial tube formation
The ability of low dose microtubule inhibitors to suppress microtubule dynamics and inhibit the migration of HUVEC suggested that they may also be able to inhibit angiogenesis at concentrations that cause minimal toxicity. To test effects on angiogenesis, we used an in vitro tube formation assay that mimics the ability of endothelial cells to reorganize into capillary-like structures on a three-dimensional Matrigel matrix (19). An example of the capillary-like network formed by untreated HUVEC in a 5 h time span is shown in Fig. 6A. When paclitaxel was included at a concentration that suppresses microtubule dynamics, far fewer endothelial tubes were seen (Fig. 6B). The images were quantified by measuring the total length of the tubes or the area occupied by tubes in 10 randomly chosen microscopic fields. Both methods gave very similar results showing that paclitaxel inhibited the ability of HUVEC to form tubes by 88% (Fig. 6C) (for tube length: 559 ± 25.2 μm for control versus 68.4 ± 2.5 μm for paclitaxel treated; p < 0.001; for percent area occupied by the tubes: 49.3 ± 1.1 for control versus 5.7 ± 0.9 for paclitaxel treated; p < 0.001). A dose response curve for the percent change in tube length at different concentrations of paclitaxel is depicted in Fig. 6C showing a close correlation between inhibition of wound healing and tube formation. A similar association between inhibition of cell migration and tube formation was obtained using low concentrations of colchicine (data not shown) suggesting that the relationship is not tied to the choice of microtubule inhibitor. The results indicate that suppression of microtubule dynamics can inhibit the generation of tube-like structures that have predictive value for the ability of endothelial cells to form capillaries.
Figure 6. In vitro angiogenesis assay showing capillary-like tube formation on Matrigel.
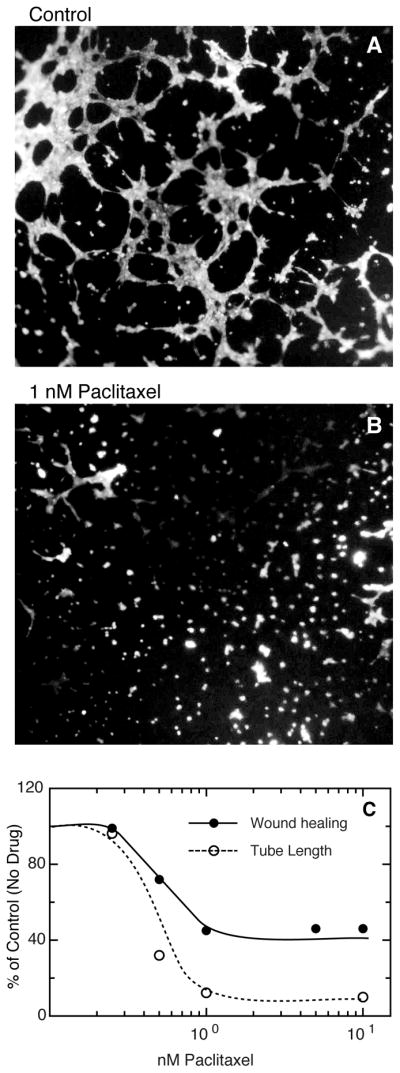
HUVEC were plated at a sub-confluent density on Matrigel and their ability to form tubes was measured after 5 h without (A) and with (B) 1 nM paclitaxel. The cells were stained with calcein for 30 min and observed with the aid of a 4X fluorescence objective. Quantification of tube formation by measuring tube length or area gave similar results that are plotted in panel (C) as a function of paclitaxel concentration. Closed circles and solid line, drug effects on cell migration using a wound healing assay; open circles and dotted line, drug effects on tube formation.
Discussion
The ability of microtubule-targeted drugs to inhibit angiogenesis has previously been reported, but the mechanism by which they act has remained controversial (see (13) for review). Liao et al. suggested that the drugs might be inhibiting cell migration by suppressing microtubule dynamics (20) and later studies confirmed this prediction in multiple cultured cell lines(6, 21–23). However, it has also been reported that in contrast to these other cell lines, microtubule dynamics were increased rather than decreased when HUVEC and HMEC-1 cells were treated with low concentrations of vinflunine or paclitaxel (8, 9). Further complicating interpretations of published studies is the widely held perception that drug concentrations able to suppress microtubule dynamics also inhibit cell proliferation (24). This perception was recently shown to be incorrect and paved the way towards explaining earlier reports that non-toxic concentrations of microtubule inhibitors can effectively inhibit angiogenesis (6, 7, 11).
Because there is a possibility that various cell lines might respond differently to drug treatment, we decided to test the effects of microtubule inhibitors on cells that are as close to the in vivo situation as possible. With this in mind, we isolated fresh HUVEC from human umbilical cords, cultured them in human serum, and used them within days of isolation. The cells were found to be highly motile in scratch assays and their migration was reduced by treating with relatively low concentrations of microtubule inhibitors. At the low drug concentrations that slowed motility, there was little or no effect on cell division but the results were highly drug dependent suggesting that it may be possible to find compounds that can efficiently inhibit cell migration with relatively little systemic toxicity due to blocking cell division.
To explore the mechanism by which low drug concentrations inhibit cell migration, we examined dose-dependent drug effects on microtubule behavior. Microtubules are known to exhibit stochastic episodes of growth and shortening interspersed with paused periods in which there is no net change in length. This behavior has been called dynamic instability and is believed to underlie the ability of microtubules to quickly remodel and adapt to changing cellular conditions (3, 4). Virtually all drugs that bind to microtubules have been shown to suppress this dynamic behavior in a variety of established cell lines (24). In agreement, we found that paclitaxel, vinblastine, and colchicine also suppress dynamics in primary cultures of HUVEC. Our results contrast with reports that microtubule dynamics increase in vascular endothelial cells lines that are drug treated (8, 9). The reasons for this discrepancy are unknown. However, we find the agreement of our data with the many other cell lines that have been examined to be a satisfying result that negates the need to postulate a different mechanism at work in the vasculature. Interestingly, we did find a small increase in microtubule dynamics in HUVEC treated with colchicine. The concentration that produced this effect, however, was insufficient to retard cell motility. Motility was inhibited by higher concentrations of colchicine in concert with a suppression of microtubule dynamics. Thus, even when drugs produce an increase in dynamics, those changes do not correlate with inhibition of cell migration.
To explain the role of microtubule dynamics in cell motility, we considered two possible models. Others have suggested that rac-GTP, a stimulator of lamellipodial activity, may be displaced from tubulin heterodimers when microtubules assemble, making it available to stimulate the actin polymerization needed to extend lamellipodia (25). However, this model appears to be incompatible with the observation that lamellipodial activity increased when microtubules were depolymerized at high drug concentrations (see Fig. 4). We therefore favor a second model based on the idea that microtubules can act as “struts” that physically oppose contractile forces generated by actin/myosin filaments (14, 26, 27).
This model predicts that a chemical gradient or other directional signal would induce a cascade of events resulting in the stabilization of microtubules at one end of a cell. This would allow consolidation of any membrane extension at this edge of the cell before contractile forces could return the cell to a rounded morphology. A continuation of this process following further membrane extensions (whether random or induced) would lead to a gradual extension of the cell in the direction of the chemical signal. Eventually, stresses on the cell resulting from stretching would have to be relieved by releasing the trailing edge and allowing the cell to return to a more rounded morphology before beginning another cycle of cell stretching. The retraction of the trailing edge, however, is dependent upon the ability of microtubules in the region to remodel. By suppressing the dynamic behavior of microtubules, low concentrations of microtubule inhibitors interfere with the remodeling, inhibit the ability of the cells to retract their tails, and slow the movement of the cells toward the chemical signal.
Microtubule targeted drugs blocked cell migration in a scratch assay by 50% (Fig. 1) and blocked tube formation in a 3D matrix by almost 90% (Fig. 6). The ability of microtubule targeted drugs to inhibit cell migration and angiogenesis in these in vitro assays begs the question of why these same drugs have not been more effective in treating patients with cancer. We believe the answer lies in part on the protocols used to administer the drugs. Traditionally, microtubule inhibitors have been given to patients at maximum tolerated doses; i.e., high concentrations that produce significant toxicity. At these concentrations, the drugs interfere with mitotic spindle function and inhibit cell division. These activities were recently shown to result from the ability of these drugs to affect the stability of microtubule attachment to spindle poles and not by their ability to suppress microtubule dynamics as previously thought (7). Although inhibition of cell migration and angiogenesis also occurs under these conditions, the toxicity resulting from high dose regimens necessitates the cessation of treatment to allow bone marrow recovery. During this recovery period, tumor cell growth and angiogenesis resume as well.
A better strategy to target angiogenesis is continuous treatment with a low, non-cytotoxic drug concentration. Using concentrations greater than the minimum needed to inhibit cell migration will engage other drug actions such as inhibition of cell proliferation without producing any further decrease in cell motility (and angiogenesis). Our data suggest that the effectiveness of a low drug strategy will be highly drug dependent. As we have shown, microtubule inhibitors can have different relative potencies for inhibiting cell migration versus cell division. This is because the drugs target two separate microtubule characteristics: microtubule dynamics that are needed for cell migration, and stability of microtubule attachment to spindle poles that affects mitotic spindle function and cell division (6, 11). Thus, currently available drugs should be screened for their relative potencies in inhibiting these two distinct activities. Given our finding that paclitaxel requires a 15-fold increase in the concentration needed to inhibit cell division versus cell migration and the fact that drugs are currently optimized for their effects on mitosis rather than cell motility, it is likely that compounds that are even better at inhibiting cell migration versus cell division may exist. We are currently screening new drug derivatives in an attempt to isolate such compounds.
With an optimized drug, preferably one that can be given orally to patients on an outpatient basis, it should be theoretically possible to keep tumor growth and metastasis under control using continuous treatment that has little or no side effects beyond those associated with inhibition of angiogenesis. In fact, metronomic therapy with the current generation of mitotic inhibitors has already been attempted and some trials have met with success (28–31). However, it is not clear that the drugs selected for those trials were best suited for inhibiting angiogenesis, used at the proper concentration, or administered in the most effective way. Thus, results so far are encouraging, but much work remains in order to optimize the strategy.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Jen Amon and Dr. Pina Colarusso in the Live Cell Imaging Facility of the Snyder Institute for Chronic Disease at the University of Calgary for assistance with imaging and the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology at the Foothills Hospital for providing human umbilical cords. Dr. K.D. Patel is an Alberta Innovates: Health Solutions Medical Scientist.
The abbreviations used are
- HUVEC
human umbilical vein endothelial cells
- DAPI
4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride
Footnotes
This work was supported by NIH Grant CA85935 (F. Cabral), an operating grant from the Canadian Institutes for Health Research MOP-14180 (K. Patel), and an infrastructure grant from the Canadian Foundation for Innovation (K. Patel).
The authors have no conflicting financial interests.
References
- 1.Naumov GN, Akslen LA, Folkman J. Role of angiogenesis in human tumor dormancy: animal models of the angiogenic switch. Cell Cycle. 2006;5:1779–87. doi: 10.4161/cc.5.16.3018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Cao Y. Antiangiogenic cancer therapy: why do mouse and human patients respond in a different way to the same drug? Int J Dev Biol. 2011;55:557–62. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.103236yc. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kirschner M, Mitchison T. Beyond self-assembly: from microtubules to morphogenesis. Cell. 1986;45:329–42. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90318-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Mitchison T, Kirschner MW. Dynamic instability of microtubules. Nature. 1984;312:237–42. doi: 10.1038/312237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Amos LA. What tubulin drugs tell us about microtubule structure and dynamics. Sem Cell Devel Biol. 2011;22:916–26. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2011.09.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Yang H, Ganguly A, Cabral F. Inhibition of cell migration and cell division correlates with distinct effects of microtubule inhibiting drugs. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:32242–50. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.160820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ganguly A, Cabral F. New insights into mechanisms of resistance to microtubule inhibitors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011;1816:164–71. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2011.06.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Pasquier E, Honore S, Pourroy B, Jordan MA, Lehmann M, Briand C, et al. Antiangiogenic concentrations of paclitaxel induce an increase in microtubule dynamics in endothelial cells but not in cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2005;65:2433–40. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-2624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Pourroy B, Honore S, Pasquier E, Bourgarel-Rey V, Kruczynski A, Briand C, et al. Antiangiogenic concentrations of vinflunine increase the interphase microtubule dynamics and decrease the motility of endothelial cells. Cancer Res. 2006;66:3256–63. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-3885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ganguly A, Zhang H, Sharma R, Parsons S, Patel KD. Isolation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells and their use in the study of neutrophil transmigration under flow conditions. J Vis Exp. 2012;66:e4032. doi: 10.3791/4032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ganguly A, Yang H, Cabral F. Paclitaxel dependent cell lines reveal a novel drug activity. Mol Cancer Ther. 2010;9:2914–23. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-10-0552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Dumontet C, Jordan MA. Microtubule-binding agents: a dynamic field of cancer therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010;9:790–803. doi: 10.1038/nrd3253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Schwartz EL. Antivascular actions of microtubule-binding drugs. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:2594–601. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ganguly A, Yang H, Sharma R, Patel KD, Cabral F. The role of microtubules and their dynamics in cell migration. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:43359–69. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.423905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Salaycik KJ, Fagerstrom CJ, Murthy K, Tulu US, Wadsworth P. Quantification of microtubule nucleation, growth and dynamics in wound-edge cells. J Cell Sci. 2005;118:4113–22. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kaverina I, Straube A. Regulation of cell migration by dynamic microtubules. Sem Cell Devel Biol. 2011;22:968–74. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2011.09.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Bershadsky AD, Futerman AH. Disruption of the Golgi apparatus by brefeldin A blocks cell polarization and inhibits directed cell migration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994;91:5686–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.12.5686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Rodionov VI, Gyoeva FK, Tanaka E, Bershadsky AD, Vasiliev JM, Gelfand VI. Microtubule-dependent control of cell shape and pseudopodial activity is inhibited by the antibody to kinesin motor domain. J Cell Biol. 1993;123:1811–20. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.6.1811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Auerbach R, Lewis R, Kubai L, Akhtar N. Angiogenesis assays: a critical overview. Clin Chem. 2003;49:32–40. doi: 10.1373/49.1.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Liao G, Nagasaki T, Gundersen GG. Low concentrations of nocodazole interfere with fibroblast locomotion without significantly affecting microtubule level: implications for the role of dynamic microtubules in cell locomotion. J Cell Sci. 1995;108:3473–83. doi: 10.1242/jcs.108.11.3473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ganguly A, Cabral F. The arresting action of microtubules in cell motility. Cell Cycle. 2011;10:2614–5. doi: 10.4161/cc.10.16.16593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ganguly A, Yang H, Cabral F. Class III β-tubulin counteracts the ability of paclitaxel to inhibit cell migration. Oncotarget. 2011;2:368–77. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Mikhailov A, Gundersen GG. Relationship between microtubule dynamics and lamellipodium formation revealed by direct imaging of microtubules in cells treated with nocodazole or Taxol. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1998;41:325–40. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0169(1998)41:4<325::AID-CM5>3.0.CO;2-D. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Jordan MA, Wilson L. Microtubules as a target for anticancer drugs. Nature Reviews. 2004;4:253–65. doi: 10.1038/nrc1317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Waterman-Storer CM, Salmon ED. Positive feedback interactions between microtubule and actin dynamics during cell motility. Curr opin Cell Biol. 1999;11:61–7. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(99)80008-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Brangwynne CP, MacKintosh FC, Kumar S, Geisse NA, Talbot J, Mahadevan L, et al. Microtubules can bear enhanced compressive loads in living cells because of lateral reinforcement. J Cell Biol. 2006;173:733–41. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200601060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ingber DE. Tensegrity I. Cell structure and hierarchical systems biology. J Cell Sci. 2003;116:1157–73. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Andre N, Pasquier E, Gentet JC, Kamen BA. Looking at the seemingly contradictory role of vinblastine in anaplastic large-cell lymphoma from a metronomic perspective. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:e90–91. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.32.2883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Briasoulis E, Pappas P, Puozzo C, Tolis C, Fountzilas G, Dafni U, et al. Dose-ranging study of metronomic oral vinorelbine in patients with advanced refractory cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:6454–61. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-0970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Lee SJ, Ghosh SC, Han HD, Stone RL, Bottsford-Miller J, Shen DY, et al. Metronomic activity of CD44-targeted hyaluronic acid-paclitaxel in ovarian carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18:4144–21. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-3250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Pasquier E, Honore S, Braguer D. Microtubule-targeting agents in angiogenesis: where do we stand? Drug Resist Updat. 2006;9:74–86. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2006.04.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.