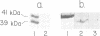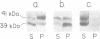Abstract
The solubilized D2-dopamine receptor from bovine striatum exhibits high and low affinity states for dopaminergic agonists. Guanine nucleotides and pertussis toxin convert the solubilized receptor from a high affinity state to a low one. A D2-receptor preparation partially purified by affinity chromatography on a haloperidol adsorbent, exhibited agonist-stimulated GTPase activity. [32P]ADP-ribosylation by pertussis toxin of this receptor preparation resulted in the specific labeling of two protein bands corresponding to mol. wts of 39 and 41 kd, in SDS-PAGE. Association of these G-proteins with the receptor was specifically inhibited by Gpp(NH)p. Immunoblot analysis of these G-proteins indicated that the 41- and 39-kd protein bands are analogous to brain Gi and Go respectively. These experiments demonstrate that two distinct pertussis toxin-sensitive G-proteins are functionally associated with bovine striatum D2-dopamine receptor.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brandt D. R., Ross E. M. GTPase activity of the stimulatory GTP-binding regulatory protein of adenylate cyclase, Gs. Accumulation and turnover of enzyme-nucleotide intermediates. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):266–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canonico P. L., Valdenegro C. A., Macleod R. M. Dopamine inhibits 32P incorporation into phosphatidylinositol in the anterior pituitary gland of the rat. Endocrinology. 1982 Jul;111(1):347–349. doi: 10.1210/endo-111-1-347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. M., Bier-Laning C. M., Halford M. K., Ahlijanian M. K., Zahniser N. R. Dopamine, acting through D-2 receptors, inhibits rat striatal adenylate cyclase by a GTP-dependent process. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Feb;29(2):113–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cote T. E., Frey E. A., Grewe C. W., Kebabian J. W. Evidence that the D-2 dopamine receptor in the intermediate lobe of the rat pituitary gland is associated with an inhibitory guanyl nucleotide component. J Neural Transm Suppl. 1983;18:139–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cote T. E., Frey E. A., Sekura R. D. Altered activity of the inhibitory guanyl nucleotide-binding component (Ni) induced by pertussis toxin. Uncoupling of Ni from receptor with continued coupling of Ni to the catalytic unit. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):8693–8698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delbeke D., Dannies P. S. Stimulation of the adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate and the Ca2+ messenger systems together reverse dopaminergic inhibition of prolactin release. Endocrinology. 1985 Aug;117(2):439–446. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-2-439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elazar Z., Kanety H., David C., Fuchs S. Purification of the D-2 dopamine receptor from bovine striatum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Oct 14;156(1):602–609. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80885-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elazar Z., Kanety H., Schreiber M., Fuchs S. Anti-idiotypes against a monoclonal anti-haloperidol antibody bind to dopamine receptor. Life Sci. 1988;42(20):1987–1993. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(88)90498-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enjalbert A., Sladeczek F., Guillon G., Bertrand P., Shu C., Epelbaum J., Garcia-Sainz A., Jard S., Lombard C., Kordon C. Angiotensin II and dopamine modulate both cAMP and inositol phosphate productions in anterior pituitary cells. Involvement in prolactin secretion. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4071–4075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita N., Nakahiro M., Fukuchi I., Saito K., Yoshida H. Effects of pertussis toxin on D2-dopamine receptor in rat striatum: evidence for coupling of Ni regulatory protein with D2-receptor. Brain Res. 1985 May 6;333(2):231–236. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91576-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gierschik P., Milligan G., Pines M., Goldsmith P., Codina J., Klee W., Spiegel A. Use of specific antibodies to quantitate the guanine nucleotide-binding protein Go in brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2258–2262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith P., Gierschik P., Milligan G., Unson C. G., Vinitsky R., Malech H. L., Spiegel A. M. Antibodies directed against synthetic peptides distinguish between GTP-binding proteins in neutrophil and brain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14683–14688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris-Warrick R. M., Hammond C., Paupardin-Tritsch D., Homburger V., Rouot B., Bockaert J., Gerschenfeld H. M. An alpha 40 subunit of a GTP-binding protein immunologically related to Go mediates a dopamine-induced decrease of Ca2+ current in snail neurons. Neuron. 1988 Mar;1(1):27–32. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90206-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingram C. D., Bicknell R. J., Mason W. T. Intracellular recordings from bovine anterior pituitary cells: modulation of spontaneous activity by regulators of prolactin secretion. Endocrinology. 1986 Dec;119(6):2508–2518. doi: 10.1210/endo-119-6-2508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel J. M., Jaquet P., Vincent J. D. The electrical properties of isolated human prolactin-secreting adenoma cells and their modification by dopamine. Endocrinology. 1985 Oct;117(4):1448–1455. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-4-1448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Judd A. M., Koike K., Schettini G., Login I. S., Hewlett E. L., Yasumoto T., MacLeod R. M. Dopamine decreases 7315a tumor cell prolactin release induced by calcium mobilization. Endocrinology. 1985 Sep;117(3):1215–1221. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-3-1215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Oinuma M., Kusakabe K., Ui M. A new GTP-binding protein in brain tissues serving as the specific substrate of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. FEBS Lett. 1987 Mar 23;213(2):353–358. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81521-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacey M. G., Mercuri N. B., North R. A. Dopamine acts on D2 receptors to increase potassium conductance in neurones of the rat substantia nigra zona compacta. J Physiol. 1987 Nov;392:397–416. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G. Techniques used in the identification and analysis of function of pertussis toxin-sensitive guanine nucleotide binding proteins. Biochem J. 1988 Oct 1;255(1):1–13. doi: 10.1042/bj2550001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumby S., Pang I. H., Gilman A. G., Sternweis P. C. Chromatographic resolution and immunologic identification of the alpha 40 and alpha 41 subunits of guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):2020–2026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer E. J., Lok J. M., Wolf L. G. Purification and properties of the inhibitory guanine nucleotide regulatory unit of brain adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14222–14229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohara K., Haga K., Berstein G., Haga T., Ichiyama A., Ohara K. The interaction between D-2 dopamine receptors and GTP-binding proteins. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Mar;33(3):290–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onali P., Olianas M. C., Gessa G. L. Characterization of dopamine receptors mediating inhibition of adenylate cyclase activity in rat striatum. Mol Pharmacol. 1985 Aug;28(2):138–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzi M., D'Agostini F., Da Prada M., Spano P. F., Haefely W. E. Dopamine D2 receptor stimulation decreases the inositol trisphosphate level of rat striatal slices. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Apr 14;136(2):263–264. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90724-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki K., Sato M. A single GTP-binding protein regulates K+-channels coupled with dopamine, histamine and acetylcholine receptors. Nature. 1987 Jan 15;325(6101):259–262. doi: 10.1038/325259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman P., Watanabe M., Grigoriadis D., Tedesco J. L., George S. R., Svensson U., Nilsson J. L., Neumeyer J. L. Dopamine D2 receptor binding sites for agonists. A tetrahedral model. Mol Pharmacol. 1985 Nov;28(5):391–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senogles S. E., Benovic J. L., Amlaiky N., Unson C., Milligan G., Vinitsky R., Spiegel A. M., Caron M. G. The D2-dopamine receptor of anterior pituitary is functionally associated with a pertussis toxin-sensitive guanine nucleotide binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4860–4867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley D. R., Creese I. Regulation of ligand binding to pituitary D-2 dopaminergic receptors. Effects of divalent cations and functional group modification. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4957–4965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds S. H., Strange P. G., Hall A. W., Taylor R. J. Guanine nucleotide effects on agonist binding at D2 dopamine receptors in bovine anterior pituitary. Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 Mar 1;35(5):731–735. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90239-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds S. H., Strange P. G. Inhibition of inositol phospholipid breakdown by D2 dopamine receptors in dissociated bovine anterior pituitary cells. Neurosci Lett. 1985 Oct 10;60(3):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90588-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegel A. M. Signal transduction by guanine nucleotide binding proteins. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1987 Jan;49(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(87)90058-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoof J. C., Kebabian J. W. Two dopamine receptors: biochemistry, physiology and pharmacology. Life Sci. 1984 Dec 3;35(23):2281–2296. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(84)90519-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson P. T., Gershoni J. M., Hawrot E., Lentz T. L. Binding of alpha-bungarotoxin to proteolytic fragments of the alpha subunit of Torpedo acetylcholine receptor analyzed by protein transfer on positively charged membrane filters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2553–2557. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]