Abstract
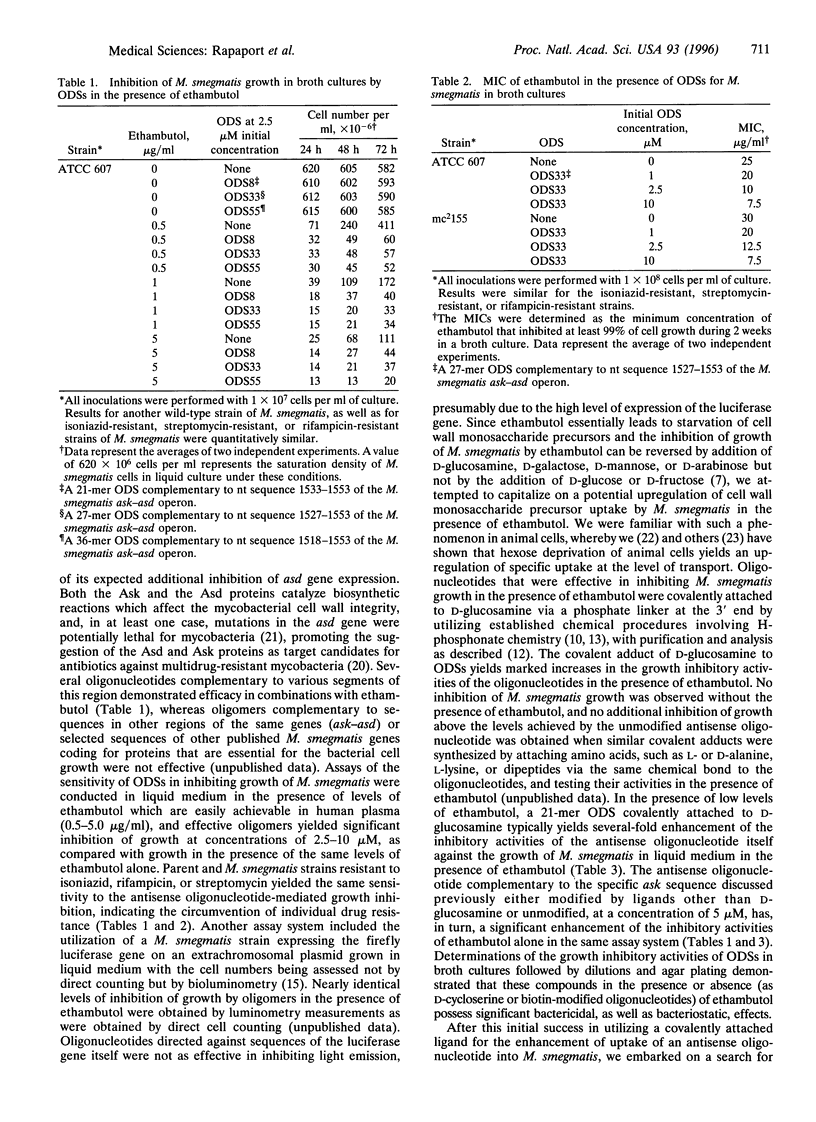
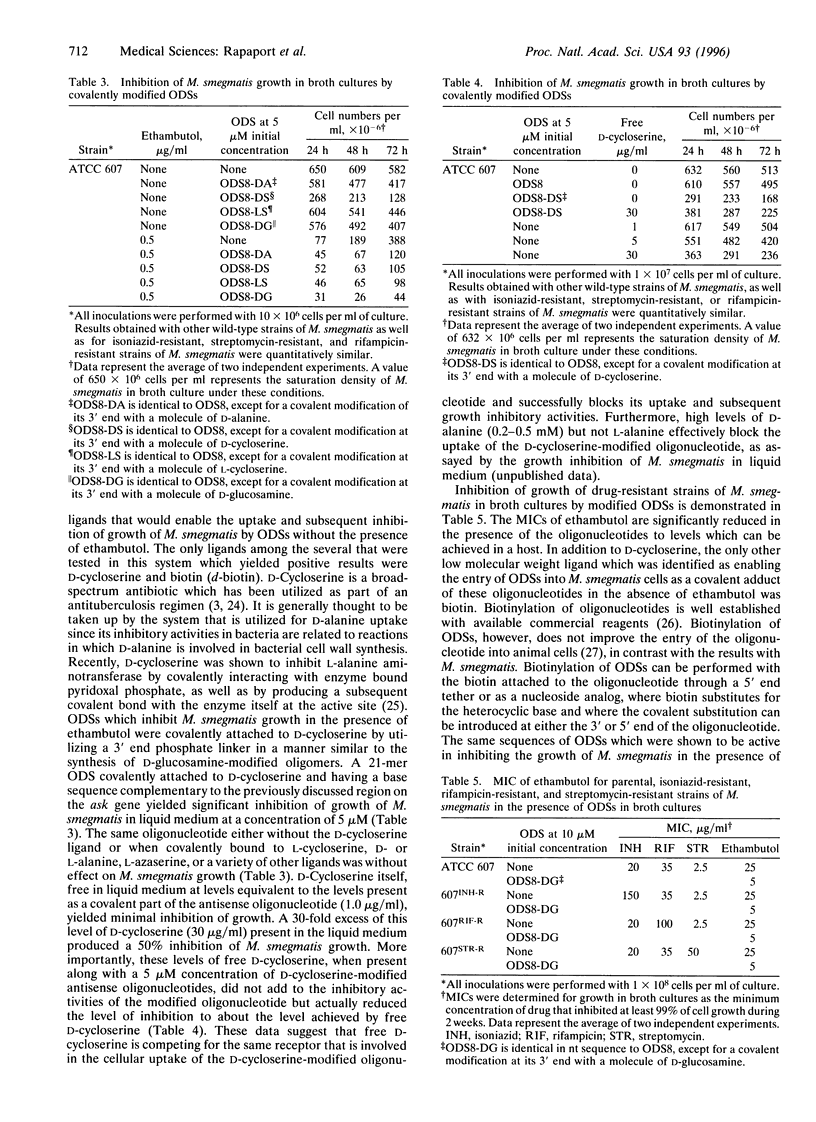
Strains of Mycobacterium smegmatis, a mycobacterium which shares genetic sequences, grows more rapidly, and is nonpathogenic in man as compared with Mycobacterium tuberculosis, were utilized for the initial development of new antimycobacterial therapy. Drug-resistant strains of M. smegmatis which are known to arise in a manner identical to the emergence of drug-resistant strains of M. tuberculosis were isolated and utilized as models for the antimycobacterial activities of modified and unmodified oligodeoxynucleotide phosphorothioates in broth cultures. Under normal conditions, oligodeoxynucleotide phosphorothioates do not enter mycobacteria, and several strategies were successfully utilized to afford entry of oligonucleotides into the mycobacterial cells. One involved the presence of very low levels of ethambutol, which enables the entry of oligonucleotides into mycobacteria because of its induced alterations in the cell wall, and another involved the utilization of oligonucleotides covalently attached to a D-cycloserine molecule, whereby entry into the mycobacterial cell is achieved by a receptor-mediated process. Another low molecular weight, covalently attached ligand that enabled the entry and subsequent antimycobacterial activities of oligodeoxynucleotide phosphorothioates in the absence of a cell wall modifying reagent was biotin. Significant sequence-specific growth inhibition of wild-type, as well as of drug-resistant, M. smegmatis was obtained by modified oligonucleotides complementary in sequence to a specific region of the mycobacterium aspartokinase (ask) gene when utilized in combinations with ethambutol (as compared to ethambutol alone) or as D-cycloserine or biotin covalent adducts without the presence of any other cytotoxic or cytostatic agent.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alland D., Kalkut G. E., Moss A. R., McAdam R. A., Hahn J. A., Bosworth W., Drucker E., Bloom B. R. Transmission of tuberculosis in New York City. An analysis by DNA fingerprinting and conventional epidemiologic methods. N Engl J Med. 1994 Jun 16;330(24):1710–1716. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199406163302403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee A., Dubnau E., Quemard A., Balasubramanian V., Um K. S., Wilson T., Collins D., de Lisle G., Jacobs W. R., Jr inhA, a gene encoding a target for isoniazid and ethionamide in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Science. 1994 Jan 14;263(5144):227–230. doi: 10.1126/science.8284673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beltinger C., Saragovi H. U., Smith R. M., LeSauteur L., Shah N., DeDionisio L., Christensen L., Raible A., Jarett L., Gewirtz A. M. Binding, uptake, and intracellular trafficking of phosphorothioate-modified oligodeoxynucleotides. J Clin Invest. 1995 Apr;95(4):1814–1823. doi: 10.1172/JCI117860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cirillo J. D., Barletta R. G., Bloom B. R., Jacobs W. R., Jr A novel transposon trap for mycobacteria: isolation and characterization of IS1096. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(24):7772–7780. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.24.7772-7780.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cirillo J. D., Weisbrod T. R., Pascopella L., Bloom B. R., Jacobs W. R., Jr Isolation and characterization of the aspartokinase and aspartate semialdehyde dehydrogenase operon from mycobacteria. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Feb;11(4):629–639. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00342.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heifets L. B., Iseman M. D., Lindholm-Levy P. J. Ethambutol MICs and MBCs for Mycobacterium avium complex and Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Dec;30(6):927–932. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.6.927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heym B., Cole S. T. Isolation and characterization of isoniazid-resistant mutants of Mycobacterium smegmatis and M. aurum. Res Microbiol. 1992 Sep;143(7):721–730. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(92)90067-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heym B., Honoré N., Truffot-Pernot C., Banerjee A., Schurra C., Jacobs W. R., Jr, van Embden J. D., Grosset J. H., Cole S. T. Implications of multidrug resistance for the future of short-course chemotherapy of tuberculosis: a molecular study. Lancet. 1994 Jul 30;344(8918):293–298. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)91338-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffner S. E., Källenius G., Beezer A. E., Svenson S. B. Studies on the mechanisms of the synergistic effects of ethambutol and other antibacterial drugs on Mycobacterium avium complex. Acta Leprol. 1989;7 (Suppl 1):195–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iseman M. D. Treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. N Engl J Med. 1993 Sep 9;329(11):784–791. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199309093291108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs W. R., Jr, Barletta R. G., Udani R., Chan J., Kalkut G., Sosne G., Kieser T., Sarkis G. J., Hatfull G. F., Bloom B. R. Rapid assessment of drug susceptibilities of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by means of luciferase reporter phages. Science. 1993 May 7;260(5109):819–822. doi: 10.1126/science.8484123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs W. R., Jr, Kalpana G. V., Cirillo J. D., Pascopella L., Snapper S. B., Udani R. A., Jones W., Barletta R. G., Bloom B. R. Genetic systems for mycobacteria. Methods Enzymol. 1991;204:537–555. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)04027-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letsinger R. L., Zhang G. R., Sun D. K., Ikeuchi T., Sarin P. S. Cholesteryl-conjugated oligonucleotides: synthesis, properties, and activity as inhibitors of replication of human immunodeficiency virus in cell culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6553–6556. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martineau R., Kohlbacher M., Shaw S. N., Amos H. Enhancement of hexose entry into chick fibroblasts by starvation: differential effect on galactose and glucose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3407–3411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metelev V., Agrawal S. Ion-exchange high-performance liquid chromatography analysis of oligodeoxyribonucleotide phosphorothioates. Anal Biochem. 1992 Feb 1;200(2):342–346. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(92)90476-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padmapriya A. A., Tang J., Agrawal S. Large-scale synthesis, purification, and analysis of oligodeoxynucleotide phosphorothioates. Antisense Res Dev. 1994 Fall;4(3):185–199. doi: 10.1089/ard.1994.4.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramazeilles C., Mishra R. K., Moreau S., Pascolo E., Toulmé J. J. Antisense phosphorothioate oligonucleotides: selective killing of the intracellular parasite Leishmania amazonensis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 16;91(17):7859–7863. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.17.7859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapaport E., Christopher C. W., Svihovec S. K., Ullrey D., Kalckar H. M. Selective high metabolic lability of uridine, guanosine and cytosine triphosphates in response to glucose deprivation and refeeding of untransformed and polyoma virus-transformed hamster fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1979 Nov;101(2):229–235. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041010205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rastogi N., David H. L. Mode of action of antituberculous drugs and mechanisms of drug resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Res Microbiol. 1993 Feb;144(2):133–143. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(93)90028-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rastogi N., Goh K. S., David H. L. Enhancement of drug susceptibility of Mycobacterium avium by inhibitors of cell envelope synthesis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 May;34(5):759–764. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.5.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silve G., Valero-Guillen P., Quemard A., Dupont M. A., Daffe M., Laneelle G. Ethambutol inhibition of glucose metabolism in mycobacteria: a possible target of the drug. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Jul;37(7):1536–1538. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.7.1536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloan R., Elliott R. J. D-cycloserine as an affinity ligand for L-alanine aminotransferase in aqueous two-phase systems. Biochem Soc Trans. 1994 Feb;22(1):32S–32S. doi: 10.1042/bst022032s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small P. M., Hopewell P. C., Singh S. P., Paz A., Parsonnet J., Ruston D. C., Schecter G. F., Daley C. L., Schoolnik G. K. The epidemiology of tuberculosis in San Francisco. A population-based study using conventional and molecular methods. N Engl J Med. 1994 Jun 16;330(24):1703–1709. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199406163302402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama K., Armstrong E. L., Kunugi K. A., Kilburn J. O. Inhibition by ethambutol of mycolic acid transfer into the cell wall of Mycobacterium smegmatis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Aug;16(2):240–242. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.2.240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama K., Kilburn J. O. Inhibition of synthesis of arabinogalactan by ethambutol in Mycobacterium smegmatis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Sep;33(9):1493–1499. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.9.1493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



