Abstract
Chronic exposure to drugs of abuse alters brain reward circuits and produces functional changes in the dopamine (DA) system. However, it is not known whether these changes are directly related to drug-driven behaviors or whether they simply are adaptive responses to long-term drug exposure. Here, we combined the rat model of cocaine self-administration with brain slice electrophysiology to identify drug-use related alterations in the neuromodulatory effects of DA in the oval bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (ovBST), a robust DA terminal field. Long–Evans rats self-administered cocaine intravenously (0.75 mg/kg/injection) for an average of 15 d, on reward-lean or -rich schedules of reinforcement. Brain slice recordings conducted 20 h after the last self-administration session revealed a reversal of the neuromodulatory effect of DA on GABAA-IPSCs. Specifically, the effect of DA switched from a D2-mediated decrease in drug-naive rats to a D1-receptor-mediated increase in GABAA-IPSC in cocaine self-administering rats. Furthermore, the switch in DA modulation of GABAA-IPSC remained after a 30 d withdrawal period. In contrast, this switch was not observed after the acquisition phase of cocaine self-administration, when rats received cocaine passively, or in rats maintaining sucrose self-administration. Therefore, our study reveals a reversal in the effects of DA on inhibitory transmission, from reduction to enhancement, in the ovBST of cocaine self-administering rats. This change was unique to voluntary intake of cocaine and maintained after a withdrawal period, suggesting a mechanism underlying the maintenance of cocaine self-administration and perhaps craving during drug-free periods.
Introduction
Chronic and voluntary intake of drugs of abuse in animals has different neurological consequences than passive intake of the same substances or intake of natural rewards, such as sucrose (Dumont et al., 2005; Martin et al., 2006; Chen et al., 2008; You et al., 2008; Caillé et al., 2009; Kalant, 2010). For example, rats with a history of cocaine or nicotine self-administration demonstrate enhanced (in magnitude or duration) AMPA-mediated responses in several areas of the brain reward system, but these changes are not seen in rats self-administering a natural reward or when drug intake is passive (Dumont et al., 2005; Martin et al., 2006; Chen et al., 2008; You et al., 2008; Caillé et al., 2009; Kalant, 2010). Interestingly, it is currently unknown whether such neural changes specific to voluntary drug intake also occur in the brain dopamine (DA) system. DA is a potent modulator of both excitatory and inhibitory synaptic transmission, and the dopamine system is a preferential target for most drugs of abuse (Wise, 1996; Nicola et al., 2000). Passive in vivo (experimenter-administered) exposure to psychostimulants or opioids produces a variety of neuroadaptations in the effects of DA on synaptic transmission and neuronal activity (Higashi et al., 1989; Bonci and Williams, 1996; Beurrier and Malenka, 2002; Li and Kauer, 2004). However, these neuroadaptations have not been linked to drug self-administration behaviors, a necessary step to verify their involvement in addiction.
Here we sought to determine whether cocaine self-administration would produce specific alterations in the neuromodulatory effects of DA in the oval subregion of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (ovBST), which is characterized by a high density of tyrosine hydroxylase-positive terminals, DARPP-32, and D2-like DA receptors (D2Rs) (Deutch et al., 1988; Gustafson and Greengard, 1990; Schalling et al., 1990; Phelix et al., 1992; Scibilia et al., 1992; Freedman and Cassell, 1994; Hasue and Shammah-Lagnado, 2002; Meloni et al., 2006; Krawczyk et al., 2011). We have previously shown that DA causes a D2R-dependent reduction of GABAA-mediated inhibitory transmission in the ovBST of drug-naive rats (Krawczyk et al., 2011). Our study also demonstrated that the ovBST was largely devoid of D1-like DA receptors, an intriguing finding given that intra-ovBST microinjections of the D1R antagonist SCH-23390 reduce cocaine and ethanol self-administration in dependent rats (Epping-Jordan et al., 1998; Eiler et al., 2003). Therefore, we hypothesize that cocaine self-administration may be accompanied by functional alterations of DA receptors in the ovBST.
To test this hypothesis, we combined cocaine self-administration paradigms and brain slice electrophysiology in rats. We observed a D2R-to-D1R switch in the ovBST that resulted in a reversal (from decrease to enhancement) in the modulatory effects of DA on GABAA-mediated synaptic transmission only in rats with a prolonged history of cocaine self-administration. This switch in the neuromodulatory effects of DA was maintained after a 30 d drug-free period, suggesting that D1R-mediated increase in ovBST GABAA-mediated synaptic transmission may contribute to the maintenance, craving, and perhaps, relapse to cocaine intake.
Materials and Methods
Subjects.
One hundred thirty-one male Long–Evans rats (Charles River Laboratories) weighing 250–300 g were housed individually in a climate-controlled colony room. The rats were maintained on a 12 h reversed light/dark cycle (9:00 A.M. lights off–9:00 P.M. lights on) with all behavioral testing occurring during the dark phase. The rats were allowed to acclimatize to surroundings for a minimum of 3 d. Rat chow and water were provided ad libitum in the home cages and in the test chambers for the duration of the experimental sessions. All the experiments were conducted in accordance with the Canadian Council on Animal Care guidelines for use of animals in experiments and approved by the Queen's University Animal Care Committee.
Surgeries.
Fifty-eight rats were weighed and anesthetized with isoflurane (2–3%, 5 L/min). We used manufactured indwelling catheters for intrajugular cannulations (Model IVSA28, Camcath). The end of the tubing was inserted 32 mm into the right jugular vein, toward the right atria, and tied with 4-0 suturing silks. The rest of the tubing was fed subcutaneously to back-mounted 28 ga stainless steel cannulae. All incisions were closed with 4-0 absorbable suturing silk. Upon surgery completion and recovery from anesthesia, the rats were returned to the colony room. The rats received Anafen (5 mg/kg) injections, subcutaneously, for 3 d postoperatively and also received fruits to supplement normal chow diet during recovery. Intravenous cannulae were flushed daily with a sterile heparin–saline solution (20 IU heparin/ml) to prevent clots and conserve patency.
Acquisition of operant behaviors.
Behavioral testing for sucrose or cocaine self-administration was conducted in operant chambers, each equipped with a house light, a response lever with cue light, and a food dispenser for sucrose pellet reinforcement (Med Associates). Rats were placed in the operant chambers for daily 4 h sessions. Rats learned sucrose- or cocaine-reinforced operant responding on a fixed ratio-1 (FR-1) schedule of reinforcement where each lever press illuminated the cue light and delivered the reward, either one sucrose pellet (75 mg) or a cocaine-HCl infusion (0.75 mg/kg in 0.12 ml of sterile saline over 4 s). Upon each reward delivery, the lever was retracted for 20 s, during which the cue light remained illuminated; no additional responses could occur during this holding period. Training was considered acquired when the rats responded 25 times, in a titrated fashion (infusions or pellet delivery at regular time intervals), for 3 consecutive days.
Experimental groups.
Rats were assigned to seven experimental groups: control (n = 45), sucrose (n = 28), acquisition (n = 10), cocainePR (n = 32), yoked (n = 10), withdrawal (n = 3), and cocaineFR1 (n = 3). Rats in the control group were singly housed and age-matched to behaviorally trained rats. Rats in the acquisition group were killed for recordings 20 h following reaching criteria for acquisition of cocaine self-administration. These rats self-administered cocaine (0.75 mg/kg/injection) for 5 ± 1 d on an FR-1 schedule. Rats in the sucrose and cocainePR groups graduated to a progressive ratio schedule of reinforcement (PR) in which lever pressing to obtain each subsequent reward increased according to the following equation: Response Ratio= 5e(injection number×0.2) − 5 (Richardson and Roberts, 1996). Rats in the cocainePR and sucrose groups remained on the PR schedule of reinforcement for 16 ± 2 and 19 ± 3 d, respectively (two-tailed Student's t test on days on PR: t(61) = 0.74, p = 0.75). At this chosen dose of cocaine (0.75 mg/kg/injection), rats from both the cocainePR (71.2 ± 6.5 presses, n = 32) and sucrose (53.5 ± 7.9 presses, n = 28) groups reached a similar breaking point (two-tailed Student's t test on final ratio pressing: t(61) = −1.71, p = 0.09). A group of rats receiving cocaine passively (yoked) was included in the study to dissociate the neural mechanisms underlying drug-taking behavior from the neuroadaptations produced by chronic exposure to cocaine (Dumont et al., 2005). Accordingly, yoked rats received cocaine in exactly the same amount and frequency as their self-administering cocainePR counterparts. Levers were not available but reward delivery was also signaled by a 20 s cue light illumination. To determine potential neural long-term changes due to cocaine self-administration, rats assigned to the withdrawal group self-administered cocaine for 15 d under the PR schedule and were then withdrawn from training for 30 d. Finally, rats assigned to the cocaineFR1 group were not graduated to the PR schedule but rather remained on an FR-1 schedule for 15 d following acquisition. We used this group to control for the switch from reward-rich (FR-1) to -lean (PR) schedules.
Brain slices preparation and electrophysiology.
Approximately 20 h after the end of their last training session, rats were anesthetized with isoflurane and their brains rapidly removed. Coronal slices (250 μm) containing the BST were prepared in a physiological solution containing (in mm) 126 NaCl, 2.5 KCl, 1.2 MgCl2, 6 CaCl2, 1.2 NaH2PO4, 25 NaHCO3, and 11 d-glucose at 15°C. Slices were incubated at 34°C for 60 min and transferred to a chamber that was constantly perfused (3 ml/min) with physiological solution maintained at 34°C and equilibrated with 95% O2/5% CO2. Whole-cell voltage-clamp recordings were made using microelectrodes filled with a solution containing (in mm) 70 K+-gluconate, 80 KCl, 1 EGTA, 5 HEPES, 2 MgATP, 0.3 GTP, and 1 P-creatine. All recordings were restricted to the ovBST, and more precisely, to the dorsal half of the ovBST (Fig. 1A). The exact anteroposterior coordinates representing the brain slice used vary slightly between brain atlases [−0.26 mm and −0.12 mm according to Swanson (2003) and Paxinos and Watson (2005), respectively] (Fig. 1A). In practice, we used the slices where the posterior part of the anterior commissure (ac) decussates but where the lateral extensions of the ac are still present. We thus recorded from a maximum of two slices per rat (four hemisections/rat) for consistent localization of the recordings. Recordings were restricted laterally to an imaginary vertical line that would run through the lateral ventricle. In addition, recordings were restricted to the area of the dorsolateral BST located dorsal to the halfway point between the tip of the lateral ventricle and the top of the ac (Fig. 1A). Postsynaptic currents were evoked by local fiber stimulation with tungsten bipolar electrodes while ovBST neurons were voltage clamped at −70 mV. Stimulating electrodes were placed in the ovBST, 100–500 μm lateral (IPSC) or dorsal (EPSC) from the recorded neurons (Fig. 1A), and paired electrical stimuli (10–100 μA, 0.1 ms duration, 20 Hz) were applied at 0.1 Hz. GABAA-IPSC and AMPA-EPSC were pharmacologically isolated with DNQX (50 μm) and picrotoxin (100 μm), respectively. Recordings were made using a Multiclamp 700B amplifier and a Digidata 1440A (Molecular Devices Scientific). Data were acquired and analyzed with Axograph X running on Apple computers. GABAA-IPSCs were measured in all seven groups of rats, whereas AMPA-EPSCs were only investigated in control, sucrose, and cocainePR rats. Since pilot studies showed no effect of Cocaine self-administration on DA or NA modulation of AMPA-EPSC, we reasoned that results from yoked, withdrawal, acquisition, and cocaineFR1 groups would be of limited interest.
Figure 1.
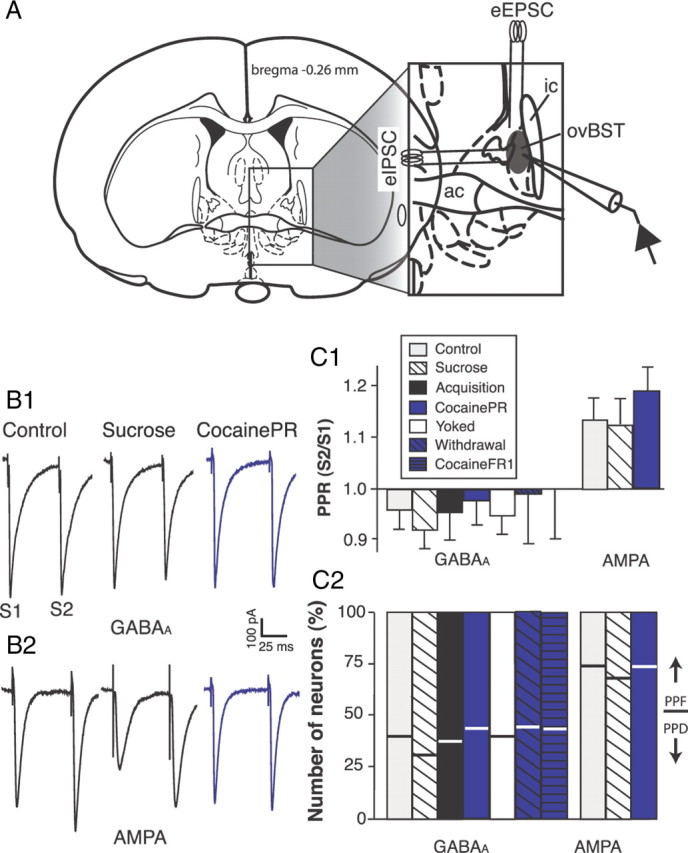
Brain slice recordings of evoked whole-cell postsynaptic currents in the rat ovBST. A, Schematic illustration of the experimental procedures for ovBST (shaded area in the inset) GABAA-IPSC and AMPA-EPSC measurements. B, Representative traces showing evoked whole-cell GABAA-IPSC (B1) and AMPA-EPSC (B2) in brain slices from three representative experimental groups. Two electrical stimuli were applied at 50 ms interval to calculate PPRs (S2/S1). C1, Bar graph summarizing PPR50 ms of evoked GABAA-IPSC and AMPA-EPSC. C2, Bar graph summarizing the incidence of ovBST neurons displaying PPF (bottom part of bars) or PPD (top part of bars).
Drugs.
Stock solution of DA (10 mm), NA (10 mm), quinpirole (1 mm), and SCH-23390 (10 mm) were prepared in double-distilled water. Stock solution of DNQX (100 mm), SKF-81297 (1 mm), sulpiride (1 mm), and yohimbine (1 mm), were prepared in DMSO (100%). Each drug was further dissolved in the physiological solutions at the desired concentration and the final DMSO concentration never exceeded 0.1%. Cocaine-HCl was dissolved at 2.5 mg/ml in sterile saline and pH was adjusted to 7.3 with NaOH. All drugs were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich or Tocris Biosciences except cocaine-HCl (Medisca).
Statistical analysis.
We measured drug-induced change in postsynaptic current (PSC) peak amplitude from baseline in percentage ([(Peak amplitudedrug − Peak amplitudebaseline)/Peak amplitudebaseline] × 100) 5–10 min after bath application of the drugs. We assessed drug effects using two-tailed t tests with hypothesized values of 0 [H0: ΔGABAA-IPSC (%) = 0]. We minimized type I error with a Bonferroni-adjusted α level (α = 0.05/number of t tests). We calculated paired-pulse ratios (PPRs) by dividing the second (S2) by the first (S1) peak amplitude that we normalized to baseline. We calculated peak amplitudes for S1 and S2 from a baseline value measured immediately before the stimulus artifacts. We assessed drug effects on PPR using two-tailed t tests with hypothesized values of 1 [H0: ΔPPR (Normalized) = 1]. We minimized type I error with a Bonferroni-adjusted α level (α = 0.05/number of t tests). We used multiple t tests because we only measured the full dose–response effect in control, sucrose, and cocainePR rats. We analyzed the coefficient of variation (CV) by plotting r [(1/CVdrug2)/(1/CVbaseline2)] against π (Peak amplitudedrug/Peak amplitudebaseline) and computed bivariate linear fits of r by π (Faber and Korn, 1991). We used one-way ANOVAs to compare multiple means and conducted appropriate statistical tests for multiple comparisons (indicated in Results and figures) when ANOVAs deemed significance. All statistical analyses were done with JMP 9.0 (SAS Institute).
Results
Measures of synaptic transmission in the rat ovBST (Fig. 1)
Local fiber electrical stimulation reproducibly evoked GABAA-IPSCs and AMPA-EPSCs (Fig. 1). To determine the probability of neurotransmitter release (Pr) across the different groups, we measured and compared the paired-pulse ratio (PPR50 ms) of evoked GABAA-IPSC and AMPA-EPSC (Fig. 1C1). Evoked GABAA-IPSC predominantly displayed a slight and similar depression (PPD) in all seven groups of rats (F(6,178) = 0.79, p = 0.58), a feature characteristic of a population of synapses with high Pr. In contrast, the PPR50 ms of evoked AMPA-EPSC resulted in paired-pulse facilitation (PPF) in control, sucrose, and cocainePR groups (F(2,140) = 0.71, p = 0.49). AMPA-EPSC from acquisition and yoked groups was not studied, because maintenance of cocaine self-administration did not produce any measurable changes at excitatory synapses (see Fig. 5). Altogether, PPR analyses revealed no treatment effects on the probability of neurotransmitter release in the ovBST.
Figure 5.
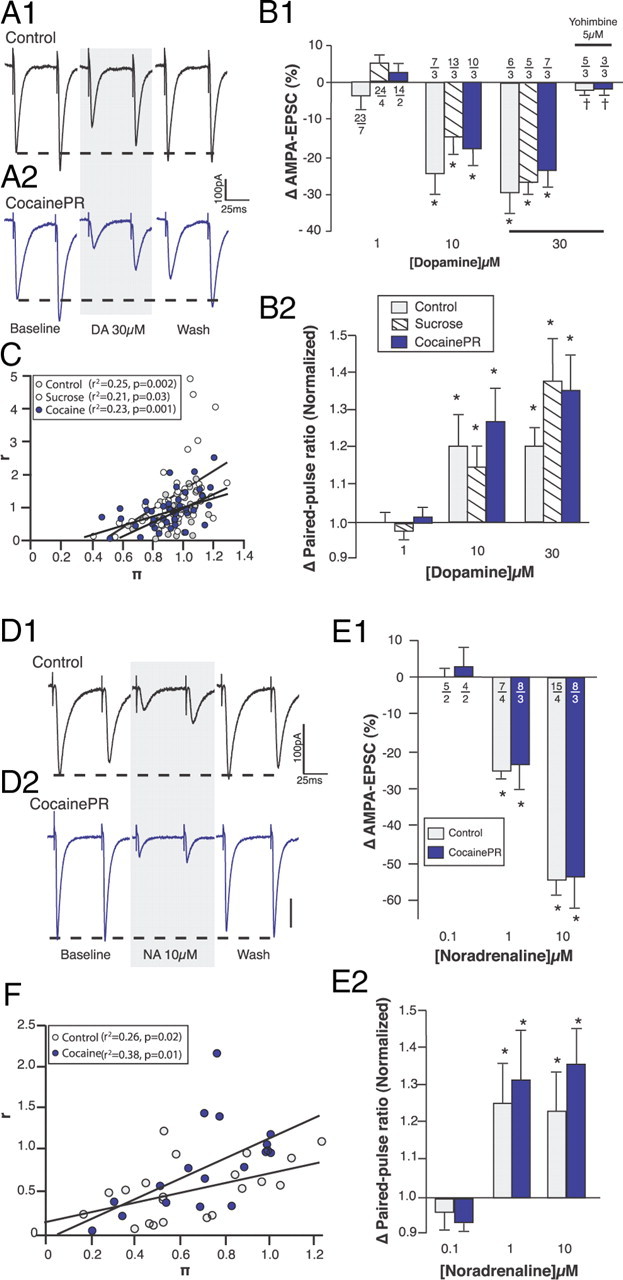
Effect of DA on AMPA-EPSC. A, Representative traces showing the effect of DA on evoked AMPA-EPSC in the ovBST of control (A1) and cocainePR (A2) rats. B, Bar graphs summarizing the effect of DA on the change in amplitude (B1) and PPR (B2) of evoked AMPA-EPSC. *Significantly different from 0 (amplitude) or 1 (PPR); two-tailed Student's t tests, p < 0.005. C, Dot plot showing CV analyses of the effect of DA (1–30 μm) on evoked AMPA-EPSC. D, Representative traces showing the effect of NA on evoked AMPA-EPSC in the ovBST of control (D1) and cocainePR (D2) rats. E, Bar graphs summarizing the effects of NA on the change in amplitude (E1) and paired-pulse ratios (E2) of evoked AMPA-EPSC. *Significantly different from 0 (amplitude) or 1 (PPR); two-tailed Student's t tests, p < 0.001. F, Dot plot showing CV analyses of the effect of NA (0.1–10 μm) on evoked AMPA-EPSC in both control and cocainePR groups.
Neuromodulatory effects of DA on inhibitory synaptic transmission (Fig. 2)
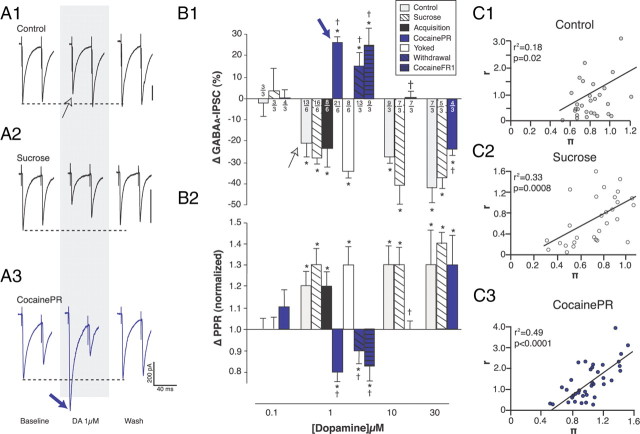
Figure 2.
Effects of DA on GABAA-IPSC. A, Representative traces showing the effects of bath-applied DA on the amplitude of evoked GABAA-IPSC in brain slices from control (A1), sucrose (A2), and cocainePR (A3) rats. B, Bar graphs summarizing the effect of DA on the amplitude (B1) and PPR (B2) of evoked GABAA-IPSC. *Significantly different from 0 (amplitude) or 1 (PPR); two-tailed Student's t tests, p < 0.001. †Significantly different from control, sucrose, acquisition, and yoked; one-way ANOVA, p < 0.01. Numbers indicate the number of neurons (above) and rats (below), respectively. C, Dot plots summarizing CV analyses of the effects of DA (0.1–30 μm) on evoked GABAA-IPSC in brain slices from control (C1), sucrose (C2), and cocainePR (C3) rats. Dot plots show r [(1/CVdrug2)/(1/CVbaseline2)] as a function of π (Peak amplitudedrug/Peak amplitudebaseline).
As previously reported (Krawczyk et al., 2011), bath application of DA (0.1–30 μm) decreased the amplitude of evoked GABAA-IPSC in a reversible and dose-dependent manner in the ovBST of control rats (Fig. 2A1,B1). At DA concentrations that decreased GABAA-IPSC, we observed statistically significant increases in PPR50 ms, suggesting that DA acts presynaptically (Fig. 2B2) (Zucker, 1989). Confirming the PPR, a CV analysis revealed a significant positive correlation, further supporting the idea that DA acts presynaptically (Fig. 2C1) (Faber and Korn, 1991). At 1 μm, DA produced a similar presynaptic reduction in GABAA-IPSC in the ovBST of sucrose, acquisition, and yoked rats (Fig. 2). In contrast, in cocainePR rats, exposure to 1 μm DA caused a significant presynaptic increase in the amplitude of GABAA-IPSC (Fig. 2A3,B,C3). This effect was dose specific, however, because 10 μm DA did not produce any effect in cocainePR rats, and 30 μm DA produced a reduction in GABAA-IPSC amplitude in cocainePR rats, although significantly smaller than in the control and sucrose groups (Fig. 2B1). At concentrations lower than 0.1 μm, DA did not change GABAA-IPSC amplitude in control, sucrose, or cocainePR rats (data not shown). We further confirmed that the switch in the neuromodulatory effects of DA (1 μm) on GABAA-IPSC also occurred in rats self-administering cocaine on a reward-rich schedule of reinforcement. Accordingly, in rats that remained on an FR-1 schedule (cocaineFR1), DA 1 μm presynaptically increased the amplitude of GABAA-IPSC (2B1, B2). We also investigated whether the effects of DA on GABAA-IPSC would remain altered during withdrawal and saw that indeed, DA enhanced the amplitude of GABAA-IPSC after a 30 d withdrawal period (Fig. 2B1,B2).
DA receptors (Figs. 3, 4)
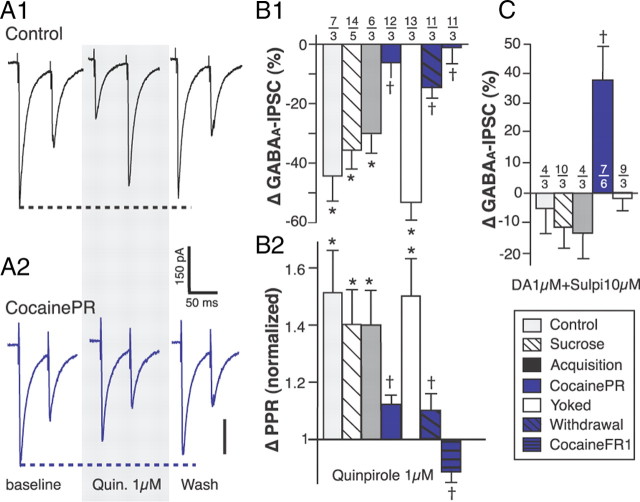
Figure 3.
D2R-mediated effects of DA on GABAA-IPSC. A, Representative traces showing the effects of the D2R agonist quinpirole (1 μm) on evoked GABAA-IPSC in brain slices from control (A1) and cocainePR (A2) rats. B, Bar graph summarizing the effect of quinpirole on amplitude (B1) and PPR (B2) of GABAA-IPSC. C, Bar chart summarizing the effect of DA (1 μm) on the amplitude of evoked GABAA-IPSC in the presence of the D2R antagonist sulpiride (10 μm). *Significantly different from 0 (amplitude) or 1 (PPR); two-tailed Student's t tests, p < 0.001. †Significantly different from control, sucrose, acquisition, and yoked; one-way ANOVA, p < 0.05. Numbers indicate the number of neurons (above) and rats (below), respectively.
Figure 4.
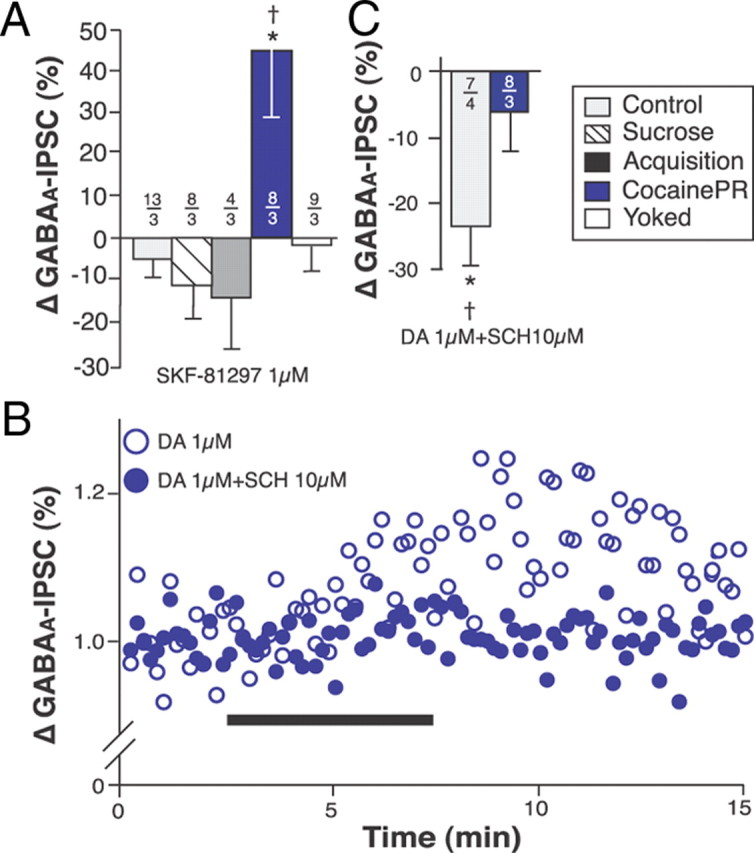
D1R-mediated effects of DA on GABAA-IPSC. A, Bar graph summarizing the effects of the D1R agonist SKF-81297 on the amplitude of GABAA-IPSC. B, Dot plot (representative experiment) showing the effect of DA on the amplitude of GABAA-IPSC as a function of time in the absence (open circles) or presence (closed circles) of the D1R antagonist SCH-23390 (10 μm). Black bar indicates bath application of DA. C, Bar chart summarizing the effect of DA (1 μm) on the amplitude of evoked GABAA-IPSC in the presence of the D1R antagonist SCH-23390 (10 μm). *Significantly different from 0 (amplitude) or 1 (PPR); two-tailed Student's t tests, p < 0.001. †Significantly different from all other groups; one-way ANOVA, p < 0.05. Numbers indicate the number of neurons (above) and rats (below), respectively.
In the control, sucrose, acquisition and yoked groups, the effect of DA on GABAA-IPSC was mediated by D2-like DA receptors (D2R). Consistent with this, the D2R agonist quinpirole (1 μm) mimicked the effects of DA on GABAA-IPSC and the D2R antagonist sulpiride (10 μm) blocked DA-induced reduction in GABAA-IPSC amplitude in these groups of rats (Fig. 3). PPR analyses suggest that D2R are located presynaptically (Fig. 3B2). In contrast, quinpirole had almost no effect on GABAA-IPSC in cocainePR, withdrawal, and cocaineFR1 rats (Fig. 3B). In slices from the cocainePR group, the D1R agonist SKF-81297 (1 μm) increased the amplitude of GABAA-IPSC (Fig. 4). Noticeably, the effect of SKF-81297 on GABAA-IPSC amplitude in the cocainePR group was similar to the effect of 1 μm DA 5–10 min after bath application, but it did not plateau until ∼30 min after application (data not shown). These results suggest a persistent D1R-mediated response specific to cocainePR rats. Finally, the D1R antagonist SCH-23390 (10 μm) completely abolished the effect of DA (1 μm) in cocainePR rats, but had no effect in the control group (Fig. 4B,C).
Neuromodulatory effects of DA on excitatory synaptic transmission (Fig. 5)
As we previously reported (Krawczyk et al., 2011), bath application of DA (0.1–30 μm), reversibly and dose-dependently decreased the amplitude of evoked AMPA-EPSC in the ovBST of control rats (Fig. 5A1,B1). PPR50 ms and CV analyses suggest that this is a presynaptic effect (Fig. 5B2,C) (Zucker, 1989). However, DA was 10 times less potent at reducing the amplitude of AMPA-EPSC than at reducing that of GABAA-IPSC (Figs. 2B1, 5B1) (Krawczyk et al., 2011). Furthermore, SKF-81297 and quinpirole, D1R and D2R agonists, respectively, did not affect AMPA-EPSC amplitude in control rats (Table 1). In contrast, the α2-adrenergic receptor (α2R) antagonist yohimbine (5 μm) completely blocked the effect of DA on AMPA-EPSC (Fig. 5B1) (Krawczyk et al., 2011), and noradrenaline (NA) was three times more potent than DA at presynaptically reducing AMPA-EPSC (Fig. 5B1,E1). The effects of DA, NA, and DA agonists on AMPA-EPSC were similar in control, sucrose, and cocainePR rats (Fig. 5, Table 1). These data suggest that the effect of DA on excitatory synaptic transmission is mediated by α2R (Zhang et al., 1999; Cornil et al., 2002; Zhang and Ordway, 2003; Cornil and Ball, 2008; Guiard et al., 2008; Krawczyk et al., 2011) and that α2Rs are not functionally altered with operant responding for either a pharmacological or natural reward.
Table 1.
Effects of DA receptor agonists on the amplitude of evoked AMPA-EPSCs in the ovBST
| SKF-81297 |
Quinpirole |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 μm | 1 μm | 0.1 μm | 1 μm | |
| Control | −6.0 ± 2.3 (9) | −6.5 ± 4.3 (6) | −1.5 ± 2.5 (7) | −0.6 ± 2.2 (8) |
| Sucrose | −1.2 ± 3.2 (14) | −2.8 ± 3.8 (14) | −1.6 ± 2.1 (13) | −8.9 ± 3.9 (9) |
| CocainePR | −2.9 ± 2.8 (12) | −2.5 ± 2.0 (13) | −5.6 ± 2.8 (15) | −0.9 ± 4.3 (8) |
Values are ΔAMPA-EPSC (percentage); n values are given in parentheses.
Discussion
DA decreases GABAA-mediated inhibitory transmission in the rat ovBST by activating presynaptic D2R (Krawczyk et al., 2011; this study). Here we show, however, that DA causes a D1R-mediated increase in GABAA inhibitory transmission in the rat ovBST during maintenance of cocaine self-administration, a change that remained after a 30 d drug-free period. Thus, the effect of DA on GABAA-mediated inhibitory transmission in the ovBST is reversed and the DA receptor subtype is altered in the rat ovBST during maintenance of cocaine self-administration. This switch is specific for maintenance of cocaine self-administration, and is not observed after acquisition of cocaine self-administration, during maintenance of sucrose self-administration, or when cocaine delivery is not contingent upon lever pressing. We conclude that this switch in the neuromodulatory effect of DA in the ovBST is likely a feature of drug-driven behaviors since it did not occur in rats self-administering sucrose. This observation contrasted slightly with our previous report demonstrating that operant responding for sucrose increases AMPA-mediated currents, albeit by a lesser magnitude than cocaine and in the ventrolateral BST (Dumont et al., 2005). Thus, this novel result significantly expands our understanding of the neural circuits and mechanisms involved in chronic drug intake in a preclinical setting.
Dysfunctional D2R in cocaine self-administering rats
The switch from a D2R-dependent reduction of GABAA-mediated inhibitory transmission to a D1R-mediated increase in GABAA inhibitory transmission was associated with decreased D2R and de novo D1R activity. Decreased D2R function correlates with increased vulnerability to the reinforcing and addictive properties of cocaine in animal models and humans (Volkow et al., 1990, 1993; Morgan et al., 2002; Nader et al., 2002, 2006; Dalley et al., 2007). Thus, the present study extends this observation to another DA terminal field, the ovBST, and to the experimental context of maintenance of, and protracted withdrawal from, cocaine self-administration. This D2R dysfunction associated with drug abuse may be linked to fewer receptors, uncoupling of receptor–effector pathways, or other mechanisms of desensitization (Namkung and Sibley, 2004; Namkung et al., 2009). In the current experimental model, D2R dysfunction was rescued by adenylate cyclase (AC) activation with bath application of forskolin (data not shown). This suggests that cocaine self-administration decreases the D2R-AC/PKA response in the ovBST, and that this effect is pharmacologically reversible, in vitro. This model may be of particular interest because D2R dysfunction and decrease in D2R binding sites in rhesus monkeys (Moore et al., 1998; Nader et al., 2002) are specifically associated with cocaine self-administration. We showed that D2R was not restored following a 30 d withdrawal period. Future studies could investigate whether D2R hypofunction remains after longer detoxification periods. Furthermore, whether interventions aimed at stimulating D2R function in the reward circuit increase the capacity for abstinence from addictive drugs could also be tested.
De novo D1R function in cocaine self-administering rats
D2R function in the ovBST was intact during acquisition of cocaine self-administration, suggesting that D2R dysfunction may play a role in the transition to compulsive drug use (Deroche-Gamonet et al., 2004; Vanderschuren and Everitt, 2004; Johnson and Kenny, 2010). De novo D1R function, which was specifically observed in the ovBST during maintenance of cocaine self-administration, could also play a role in the transition to compulsive drug use. In rhesus monkeys, cocaine self-administration is associated with an increase in D1R binding activity in the shell of the nucleus accumbens, an extended amygdala structure closely related and robustly connected to the ovBST (Dong et al., 2001b; Nader et al., 2002). Furthermore, virtually no immunostaining or functional D1R could be detected in the ovBST of drug-naive rats (Krawczyk et al., 2011). These results are consistent with the idea that cocaine self-administration promotes the expression of the D1R gene or receptor trafficking to the membrane surface. This could be facilitated by a direct protein–protein interaction between D1R and NMDA receptors, a phenomenon previously observed in heterologous cellular models and dissociated hippocampal neurons (Pei et al., 2004). D1R hypersensitivity has also been reported in animal models of DA depletion. For example, D1R hypersensitivity involves a switch in intracellular signaling pathways in dopamine-depleted striatum (Gerfen et al., 2002). Additional studies are required to investigate whether any of these mechanisms are involved in the maintenance of cocaine self-administration, relapse to cocaine intake, or incubation of cocaine craving.
Consequence of DA receptor switch on ovBST function
We observed reduced D2R and increased D1R activity (at GABA synapses) in rats maintaining cocaine self-administration, which may consequently increase GABAergic tone in the ovBST. This DA-mediated increase in inhibitory tone in the ovBST should result in a net decrease in output of ovBST projection neurons. The ovBST is exclusively populated with GABA neurons that coexpress CRF, neurotensin, somatostatin, enkephalin, and/or dynorphin (Ju et al., 1989; Moga et al., 1989; Veinante et al., 1997; Day et al., 1999) and should exert an inhibitory effect on afferent targets. The ovBST targets includes brain areas within (e.g., fusiform BST) and outside the BST (e.g., nucleus accumbens shell, lateral hypothalamus, retrorubral field, parabrachial nucleus, central amygdala) (Dong et al., 2001a). The current study did not examine the consequences of DA-mediated increase in GABAA-mediated transmission on the ovBST neural network. However, a previous study showed that microinjection of a GABAA receptor antagonist into the dorsolateral BST reduced GABAergic tone and ethanol self-administration in rats (Hyytiä and Koob, 1995). Because dorsolateral BST D1R blockade also reduced cocaine self-administration (Epping-Jordan et al., 1998), it seems reasonable to suggest that D1-mediated increase in ovBST GABAergic tone contributes to drug-driven operant behaviors. Consistent with the hypothesis that DA may decrease ovBST output in cocaine-dependent rats and promote motivated behaviors, systemic injection of anorexinergic agents triggers the expression of the protein Fos (an indicator of neuronal activation) in the ovBST (Bonaz et al., 1993; Li et al., 1994; Li and Rowland, 1995; Rowland et al., 1996). Together, this evidence suggests that ovBST neuronal activity inversely correlates with motivated behaviors.
DA modulation of excitatory synaptic transmission in the ovBST
DA reduces excitatory synaptic transmission mediated by AMPA ionotropic receptors in the ovBST by cross-activating presynaptic α2R, a mechanism that is not altered by cocaine self-administration [see Fig. 5 and Krawczyk et al. (2011)]. It is worth mentioning that in rats chronically exposed to psychostimulants (in an experimenter-controlled manner), there are increases in D1R-mediated modulation of excitatory transmission in the nucleus accumbens (Higashi et al., 1989; Beurrier and Malenka, 2002; Li and Kauer, 2004). Although an increase in D1R function was also observed in the ovBST of cocainePR rats in our study, these receptors seemed restricted to inhibitory transmission, showing a remarkable distinction with ventral striatum areas. Importantly, DA (at concentrations 10 times higher than required to modulate inhibitory transmission) may still modulate excitatory synaptic transmission in the ovBST. Cocaine may promote this mechanism by producing large DA transients in the BST (Carboni et al., 2000). The behavioral significance of this potential effect of DA on ovBST AMPA currents is, however, unknown and may be difficult to evaluate experimentally.
Neural mechanisms underlying voluntary cocaine intake
The rodent model of stimulant self-administration has been a relatively good predictor of human substance abuse behavior (Deroche-Gamonet et al., 2004; Vanderschuren and Everitt, 2004; Panlilio, 2010). Our previous brain slice patch-clamp studies using this model demonstrated that alteration in synaptic plasticity of excitatory synapses in the ventrolateral portion of the BST correlated with cocaine self-administration, but not with passive (or noncontingent) cocaine intake (Dumont et al., 2005). Similar results reported in the nucleus accumbens suggest that the neurological mechanisms associated with voluntary and passive exposure to drugs of abuse are fundamentally different, and that it is critical to understand and differentiate these mechanisms to distinguish addictive behavior from adaptation to chronic drug exposure (Martin et al., 2006; Chen et al., 2008).
Role of ovBST D1R in drug-driven operant behaviors
Previous studies showed that intra-ovBST D1R blockade reduces cocaine- and ethanol- but not sucrose-driven operant behaviors in rats (Epping-Jordan et al., 1998; Eiler et al., 2003). We previously demonstrated the absence of D1R immunostaining and function in the ovBST of drug-naive rats, a result that contrasts with behavioral studies. Here we reconcile the physiological, anatomical, and behavioral data by showing de novo D1R function in cocaine-dependent rats. Altogether, our study adds to growing evidence supporting a role for the dorsal BST in drug-taking behaviors and relapse to drug seeking after drug-free periods (Epping-Jordan et al., 1998; Walker et al., 2000; Erb et al., 2001; Leri et al., 2002; Eiler et al., 2003).
In summary, we identified a switch in DA regulation of GABAA-IPSC in the ovBST that was specifically associated with cocaine self-administration and remained after a 30 d drug-free period. This drug and behavior-induced switch was associated with dysfunctional presynaptic D2R signaling as well as de novo D1R responses. Furthermore, the switch was not observed with passive drug exposure or self-administration of a natural reward, revealing a potential target for the management of substance abuse. Although D1R antagonists are associated with adverse effects that preclude their use in drug addiction therapy, identifying and characterizing D1R downstream signaling pathways may reveal interesting therapeutic alternatives (Nann-Vernotica et al., 2001).
Footnotes
This project was supported by a Canadian Institutes of Health Research operating grant (MOP-79277), The J.P. Bickell Foundation, and Queen's University. We thank Cindy Chiang, Darya Ianovskaia, Adam Schizkoske, and Robert Iaccino for technical support. We thank Drs. Mary C. Olmstead, Richard J. Beninger, Martin Paré, and Scott Hayton for providing feedback on the project and manuscript.
References
- Beurrier C, Malenka RC. Enhanced inhibition of synaptic transmission by dopamine in the nucleus accumbens during behavioral sensitization to cocaine. J Neurosci. 2002;22:5817–5822. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-14-05817.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonaz B, De Giorgio R, Taché Y. Peripheral bombesin induces c-fos protein in the rat brain. Brain Res. 1993;600:353–357. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)91397-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonci A, Williams JT. A common mechanism mediates long-term changes in synaptic transmission after chronic cocaine and morphine. Neuron. 1996;16:631–639. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80082-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caillé S, Guillem K, Cador M, Manzoni O, Georges F. Voluntary nicotine consumption triggers in vivo potentiation of cortical excitatory drives to midbrain dopaminergic neurons. J Neurosci. 2009;29:10410–10415. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2950-09.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carboni E, Silvagni A, Rolando MT, Di Chiara G. Stimulation of in vivo dopamine transmission in the bed nucleus of stria terminalis by reinforcing drugs. J Neurosci. 2000;20:RC102. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-20-j0002.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen BT, Bowers MS, Martin M, Hopf FW, Guillory AM, Carelli RM, Chou JK, Bonci A. Cocaine but not natural reward self-administration nor passive cocaine infusion produces persistent LTP in the VTA. Neuron. 2008;59:288–297. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.05.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornil CA, Ball GF. Interplay among catecholamine systems: dopamine binds to alpha2-adrenergic receptors in birds and mammals. J Comp Neurol. 2008;511:610–627. doi: 10.1002/cne.21861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornil CA, Balthazart J, Motte P, Massotte L, Seutin V. Dopamine activates noradrenergic receptors in the preoptic area. J Neurosci. 2002;22:9320–9330. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-21-09320.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalley JW, Fryer TD, Brichard L, Robinson ES, Theobald DE, Lääne K, Peña Y, Murphy ER, Shah Y, Probst K, Abakumova I, Aigbirhio FI, Richards HK, Hong Y, Baron JC, Everitt BJ, Robbins TW. Nucleus accumbens D2/3 receptors predict trait impulsivity and cocaine reinforcement. Science. 2007;315:1267–1270. doi: 10.1126/science.1137073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day HE, Curran EJ, Watson SJ, Jr, Akil H. Distinct neurochemical populations in the rat central nucleus of the amygdala and bed nucleus of the stria terminalis: evidence for their selective activation by interleukin-1beta. J Comp Neurol. 1999;413:113–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deroche-Gamonet V, Belin D, Piazza PV. Evidence for addiction-like behavior in the rat. Science. 2004;305:1014–1017. doi: 10.1126/science.1099020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutch AY, Goldstein M, Baldino F, Jr, Roth RH. Telencephalic projections of the A8 dopamine cell group. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;537:27–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb42095.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong HW, Petrovich GD, Swanson LW. Topography of projections from amygdala to bed nuclei of the stria terminalis. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2001a;38:192–246. doi: 10.1016/s0165-0173(01)00079-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong HW, Petrovich GD, Watts AG, Swanson LW. Basic organization of projections from the oval and fusiform nuclei of the bed nuclei of the stria terminalis in adult rat brain. J Comp Neurol. 2001b;436:430–455. doi: 10.1002/cne.1079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont EC, Mark GP, Mader S, Williams JT. Self-administration enhances excitatory synaptic transmission in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. Nat Neurosci. 2005;8:413–414. doi: 10.1038/nn1414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiler WJ, 2nd, Seyoum R, Foster KL, Mailey C, June HL. D1 dopamine receptor regulates alcohol-motivated behaviors in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis in alcohol-preferring (P) rats. Synapse. 2003;48:45–56. doi: 10.1002/syn.10181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epping-Jordan MP, Markou A, Koob GF. The dopamine D-1 receptor antagonist SCH 23390 injected into the dorsolateral bed nucleus of the stria terminalis decreased cocaine reinforcement in the rat. Brain Res. 1998;784:105–115. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(97)01190-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erb S, Salmaso N, Rodaros D, Stewart J. A role for the CRF-containing pathway from central nucleus of the amygdala to bed nucleus of the stria terminalis in the stress-induced reinstatement of cocaine seeking in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2001;158:360–365. doi: 10.1007/s002130000642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber DS, Korn H. Applicability of the coefficient of variation method for analyzing synaptic plasticity. Biophys J. 1991;60:1288–1294. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82162-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman LJ, Cassell MD. Distribution of dopaminergic fibers in the central division of the extended amygdala of the rat. Brain Res. 1994;633:243–252. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(94)91545-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerfen CR, Miyachi S, Paletzki R, Brown P. D1 dopamine receptor supersensitivity in the dopamine-depleted striatum results from a switch in the regulation of ERK1/2/MAP kinase. J Neurosci. 2002;22:5042–5054. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-12-05042.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guiard BP, El Mansari M, Blier P. Cross-talk between dopaminergic and noradrenergic systems in the rat ventral tegmental area, locus ceruleus, and dorsal hippocampus. Mol Pharmacol. 2008;74:1463–1475. doi: 10.1124/mol.108.048033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson EL, Greengard P. Localization of DARPP-32 immunoreactive neurons in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis and central nucleus of the amygdala: co-distribution with axons containing tyrosine hydroxylase, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide, and calcitonin gene-related peptide. Exp Brain Res. 1990;79:447–458. doi: 10.1007/BF00229315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasue RH, Shammah-Lagnado SJ. Origin of the dopaminergic innervation of the central extended amygdala and accumbens shell: a combined retrograde tracing and immunohistochemical study in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 2002;454:15–33. doi: 10.1002/cne.10420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi H, Inanaga K, Nishi S, Uchimura N. Enhancement of dopamine actions on rat nucleus accumbens neurones in vitro after methamphetamine pre-treatment. J Physiol. 1989;408:587–603. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyytiä P, Koob GF. GABAA receptor antagonism in the extended amygdala decreases ethanol self-administration in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1995;283:151–159. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(95)00314-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson PM, Kenny PJ. Dopamine D2 receptors in addiction-like reward dysfunction and compulsive eating in obese rats. Nat Neurosci. 2010;13:635–641. doi: 10.1038/nn.2519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ju G, Swanson LW, Simerly RB. Studies on the cellular architecture of the bed nuclei of the stria terminalis in the rat: II. Chemoarchitecture. J Comp Neurol. 1989;280:603–621. doi: 10.1002/cne.902800410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalant H. What neurobiology cannot tell us about addiction. Addiction. 2010;105:780–789. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.2009.02739.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krawczyk M, Georges F, Sharma R, Mason X, Berthet A, Bézard E, Dumont EC. Double-dissociation of the catecholaminergic modulation of synaptic transmission in the oval bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. J Neurophysiol. 2011;105:145–153. doi: 10.1152/jn.00710.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leri F, Flores J, Rodaros D, Stewart J. Blockade of stress-induced but not cocaine-induced reinstatement by infusion of noradrenergic antagonists into the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis or the central nucleus of the amygdala. J Neurosci. 2002;22:5713–5718. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-13-05713.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li BH, Rowland NE. Effects of vagotomy on cholecystokinin- and dexfenfluramine-induced Fos-like immunoreactivity in the rat brain. Brain Res Bull. 1995;37:589–593. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(95)00045-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li BH, Spector AC, Rowland NE. Reversal of dexfenfluramine-induced anorexia and c-Fos/c-Jun expression by lesion in the lateral parabrachial nucleus. Brain Res. 1994;640:255–267. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(94)91881-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y, Kauer JA. Repeated exposure to amphetamine disrupts dopaminergic modulation of excitatory synaptic plasticity and neurotransmission in nucleus accumbens. Synapse. 2004;51:1–10. doi: 10.1002/syn.10270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M, Chen BT, Hopf FW, Bowers MS, Bonci A. Cocaine self-administration selectively abolishes LTD in the core of the nucleus accumbens. Nat Neurosci. 2006;9:868–869. doi: 10.1038/nn1713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meloni EG, Gerety LP, Knoll AT, Cohen BM, Carlezon WA., Jr Behavioral and anatomical interactions between dopamine and corticotropin-releasing factor in the rat. J Neurosci. 2006;26:3855–3863. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4957-05.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moga MM, Saper CB, Gray TS. Bed nucleus of the stria terminalis: cytoarchitecture, immunohistochemistry, and projection to the parabrachial nucleus in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1989;283:315–332. doi: 10.1002/cne.902830302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore RJ, Vinsant SL, Nader MA, Porrino LJ, Friedman DP. Effect of cocaine self-administration on dopamine D2 receptors in rhesus monkeys. Synapse. 1998;30:88–96. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-2396(199809)30:1<88::AID-SYN11>3.0.CO;2-L. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D, Grant KA, Gage HD, Mach RH, Kaplan JR, Prioleau O, Nader SH, Buchheimer N, Ehrenkaufer RL, Nader MA. Social dominance in monkeys: dopamine D2 receptors and cocaine self-administration. Nat Neurosci. 2002;5:169–174. doi: 10.1038/nn798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nader MA, Daunais JB, Moore T, Nader SH, Moore RJ, Smith HR, Friedman DP, Porrino LJ. Effects of cocaine self-administration on striatal dopamine systems in rhesus monkeys: initial and chronic exposure. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2002;27:35–46. doi: 10.1016/S0893-133X(01)00427-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nader MA, Morgan D, Gage HD, Nader SH, Calhoun TL, Buchheimer N, Ehrenkaufer R, Mach RH. PET imaging of dopamine D2 receptors during chronic cocaine self-administration in monkeys. Nat Neurosci. 2006;9:1050–1056. doi: 10.1038/nn1737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namkung Y, Sibley DR. Protein kinase C mediates phosphorylation, desensitization, and trafficking of the D2 dopamine receptor. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:49533–49541. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M408319200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namkung Y, Dipace C, Urizar E, Javitch JA, Sibley DR. G protein-coupled receptor kinase-2 constitutively regulates D2 dopamine receptor expression and signaling independently of receptor phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:34103–34115. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.055707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nann-Vernotica E, Donny EC, Bigelow GE, Walsh SL. Repeated administration of the D1/5 antagonist ecopipam fails to attenuate the subjective effects of cocaine. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2001;155:338–347. doi: 10.1007/s002130100724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicola SM, Surmeier J, Malenka RC. Dopaminergic modulation of neuronal excitability in the striatum and nucleus accumbens. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2000;23:185–215. doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.23.1.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panlilio LV. Stimulant self-administration. In: Olmstead MC, editor. Animal models of drug addiction. New York: Springer; 2010. pp. 57–81. [Google Scholar]
- Paxinos G, Watson C. In: The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. 5 Ed. Paxinos G, Watson C, editors. San Diego: Academic; 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Pei L, Lee FJ, Moszczynska A, Vukusic B, Liu F. Regulation of dopamine D1 receptor function by physical interaction with the NMDA receptors. J Neurosci. 2004;24:1149–1158. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3922-03.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelix CF, Liposits Z, Paull WK. Monoamine innervation of bed nucleus of stria terminalis: an electron microscopic investigation. Brain Res Bull. 1992;28:949–965. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(92)90218-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson NR, Roberts DC. Progressive ratio schedules in drug self-administration studies in rats: a method to evaluate reinforcing efficacy. J Neurosci Methods. 1996;66:1–11. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(95)00153-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowland NE, Bellinger LL, Li BH, Mendel VE. Satietin: Fos mapping of putative brain sites of action. Brain Res. 1996;717:189–192. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(96)00073-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalling M, Djurfeldt M, Hökfelt T, Ehrlich M, Kurihara T, Greengard P. Distribution and cellular localization of DARPP-32 mRNA in rat brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1990;7:139–149. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(90)90091-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scibilia RJ, Lachowicz JE, Kilts CD. Topographic nonoverlapping distribution of D1 and D2 dopamine receptors in the amygdaloid nuclear complex of the rat brain. Synapse. 1992;11:146–154. doi: 10.1002/syn.890110208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson LS. In: Brain maps: structure of the rat brain. Swanson LS, editor. San Diego: Academic; 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Vanderschuren LJ, Everitt BJ. Drug seeking becomes compulsive after prolonged cocaine self-administration. Science. 2004;305:1017–1019. doi: 10.1126/science.1098975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veinante P, Stoeckel ME, Freund-Mercier MJ. GABA- and peptide-immunoreactivities co-localize in the rat central extended amygdala. Neuroreport. 1997;8:2985–2989. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199709080-00035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkow ND, Fowler JS, Wolf AP, Schlyer D, Shiue CY, Alpert R, Dewey SL, Logan J, Bendriem B, Christman D. Effects of chronic cocaine abuse on postsynaptic dopamine receptors. Am J Psychiatry. 1990;147:719–724. doi: 10.1176/ajp.147.6.719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkow ND, Fowler JS, Wang GJ, Hitzemann R, Logan J, Schlyer DJ, Dewey SL, Wolf AP. Decreased dopamine D2 receptor availability is associated with reduced frontal metabolism in cocaine abusers. Synapse. 1993;14:169–177. doi: 10.1002/syn.890140210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker JR, Ahmed SH, Gracy KN, Koob GF. Microinjections of an opiate receptor antagonist into the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis suppress heroin self-administration in dependent rats. Brain Res. 2000;854:85–92. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(99)02288-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise RA. Neurobiology of addiction. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1996;6:243–251. doi: 10.1016/s0959-4388(96)80079-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- You ZB, Wang B, Zitzman D, Wise RA. Acetylcholine release in the mesocorticolimbic dopamine system during cocaine seeking: conditioned and unconditioned contributions to reward and motivation. J Neurosci. 2008;28:9021–9029. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0694-08.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang W, Ordway GA. The alpha2C-adrenoceptor modulates GABA release in mouse striatum. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2003;112:24–32. doi: 10.1016/s0169-328x(03)00026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang W, Klimek V, Farley JT, Zhu MY, Ordway GA. alpha2C adrenoceptors inhibit adenylyl cyclase in mouse striatum: potential activation by dopamine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999;289:1286–1292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker RS. Short-term synaptic plasticity. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1989;12:13–31. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.12.030189.000305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]