Abstract
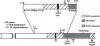
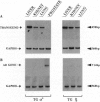
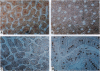
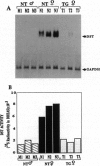
The rodent liver displays marked age- and sex-dependent changes in androgen sensitivity due to the sexually dimorphic and temporally programmed expression of the androgen receptor (AR) gene. We have altered this normal phenotype by constitutive overexpression of the rat AR transgene in the mouse liver by targeting it via the human phenylalanine hydroxylase (hPAH) gene promoter. These transgenic animals in their heterozygous state produce an approximately 30-fold higher level of the AR in the liver as compared with the nontransgenic control. Androgen inactivation via sulfonation of the hormone by dehydroepiandrosterone sulfotransferase (DST), an androgen-repressible enzyme, also contributes to the age- and sex-dependent regulation of hepatic androgen sensitivity. DST has a broad range of substrate specificity and is responsible for the age- and sex-specific activation of certain polycyclic aromatic hepatocarcinogens as well, by converting them to electrophilic sulfonated derivatives. In the transgenic female, the hepatic expression of DST was approximately 4-fold lower than in normal females, a level comparable to that in normal males. The hPAH-AR mice will serve as a valuable model for studying the sex- and age-invariant expression of liver-specific genes, particularly those involved in the activation of environmental hepatocarcinogens such as the aromatic hydrocarbons.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bingham P. M., Scott M. O., Wang S., McPhaul M. J., Wilson E. M., Garbern J. Y., Merry D. E., Fischbeck K. H. Stability of an expanded trinucleotide repeat in the androgen receptor gene in transgenic mice. Nat Genet. 1995 Feb;9(2):191–196. doi: 10.1038/ng0295-191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. S., Kokontis J., Liao S. T. Structural analysis of complementary DNA and amino acid sequences of human and rat androgen receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7211–7215. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee B., Majumdar D., Ozbilen O., Murty C. V., Roy A. K. Molecular cloning and characterization of cDNA for androgen-repressible rat liver protein, SMP-2. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):822–825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee B., Song C. S., Kim J. M., Roy A. K. Androgen and estrogen sulfotransferases of the rat liver: physiological function, molecular cloning, and in vitro expression. Chem Biol Interact. 1994 Jun;92(1-3):273–279. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(94)90069-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demyan W. F., Song C. S., Kim D. S., Her S., Gallwitz W., Rao T. R., Slomczynska M., Chatterjee B., Roy A. K. Estrogen sulfotransferase of the rat liver: complementary DNA cloning and age- and sex-specific regulation of messenger RNA. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Apr;6(4):589–597. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.4.1374839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falany C. N., Wilborn T. W. Biochemistry of cytosolic sulfotransferases involved in bioactivation. Adv Pharmacol. 1994;27:301–329. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(08)61037-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guiochon-Mantel A., Lescop P., Christin-Maitre S., Loosfelt H., Perrot-Applanat M., Milgrom E. Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of the progesterone receptor. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3851–3859. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04954.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffery S., Carter N. D., Clark R. G., Robinson I. C. The episodic secretory pattern of growth hormone regulates liver carbonic anhydrase III. Studies in normal and mutant growth-hormone-deficient dwarf rats. Biochem J. 1990 Feb 15;266(1):69–74. doi: 10.1042/bj2660069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen E. V., Suzuki T., Kawashima T., Stumpf W. E., Jungblut P. W., DeSombre E. R. A two-step mechanism for the interaction of estradiol with rat uterus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Feb;59(2):632–638. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.2.632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemppainen J. A., Lane M. V., Sar M., Wilson E. M. Androgen receptor phosphorylation, turnover, nuclear transport, and transcriptional activation. Specificity for steroids and antihormones. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):968–974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubahn D. B., Moyer J. S., Golding T. S., Couse J. F., Korach K. S., Smithies O. Alteration of reproductive function but not prenatal sexual development after insertional disruption of the mouse estrogen receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11162–11166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini M. A., Majumdar D., Chatterjee B., Roy A. K. Alpha 2u-globulin in modified sebaceous glands with pheromonal functions: localization of the protein and its mRNA in preputial, meibomian, and perianal glands. J Histochem Cytochem. 1989 Feb;37(2):149–157. doi: 10.1177/37.2.2463299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini M. A., Song C. S., Rao T. R., Chatterjee B., Roy A. K. Spatio-temporal expression of estrogen sulfotransferase within the hepatic lobule of male rats: implication of in situ estrogen inactivation in androgen action. Endocrinology. 1992 Sep;131(3):1541–1546. doi: 10.1210/endo.131.3.1380444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. A. Sulfonation in chemical carcinogenesis--history and present status. Chem Biol Interact. 1994 Jun;92(1-3):329–341. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(94)90074-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata K., Ozawa S., Miyata M., Shimada M., Gong D. W., Yamazoe Y., Kato R. Isolation and expression of a cDNA encoding a male-specific rat sulfotransferase that catalyzes activation of N-hydroxy-2-acetylaminofluorene. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 25;268(33):24720–24725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda H., Nojima H., Watanabe N., Watabe T. Sulphotransferase-mediated activation of the carcinogen 5-hydroxymethyl-chrysene. Species and sex differences in tissue distribution of the enzyme activity and a possible participation of hydroxysteroid sulphotransferases. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Sep 15;38(18):3003–3009. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90008-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Sandgren E. P., Avarbock M. R., Allen D. D., Brinster R. L. Heterologous introns can enhance expression of transgenes in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):478–482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Power R. F., Mani S. K., Codina J., Conneely O. M., O'Malley B. W. Dopaminergic and ligand-independent activation of steroid hormone receptors. Science. 1991 Dec 13;254(5038):1636–1639. doi: 10.1126/science.1749936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prins G. S., Birch L., Greene G. L. Androgen receptor localization in different cell types of the adult rat prostate. Endocrinology. 1991 Dec;129(6):3187–3199. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-6-3187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy A. K., Chatterjee B. Androgen action. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 1995;5(2):157–176. doi: 10.1615/critreveukargeneexpr.v5.i2.30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy A. K., Chatterjee B., Demyan W. F., Milin B. S., Motwani N. M., Nath T. S., Schiop M. J. Hormone and age-dependent regulation of alpha 2u-globulin gene expression. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1983;39:425–461. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571139-5.50015-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy A. K., Chatterjee B. Sexual dimorphism in the liver. Annu Rev Physiol. 1983;45:37–50. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.45.030183.000345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy A. K. Early events in the steroidal regulation of alpha2mu globulin in rat liver. Evidence for both androgenic and estrogenic induction. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Mar 1;73(2):537–543. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11348.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarlett C. O., Robins D. M. In vivo footprinting of an androgen-dependent enhancer reveals an accessory element integral to hormonal response. Mol Endocrinol. 1995 Apr;9(4):413–423. doi: 10.1210/mend.9.4.7659085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz A. G., Whitcomb J. M., Nyce J. W., Lewbart M. L., Pashko L. L. Dehydroepiandrosterone and structural analogs: a new class of cancer chemopreventive agents. Adv Cancer Res. 1988;51:391–424. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60227-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan P. J., Buchanan J. M., Anselmo V. C., Martin P. M. Equilibrium: the intracellular distribution of steroid receptors. Nature. 1979 Dec 6;282(5739):579–582. doi: 10.1038/282579a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song C. S., Rao T. R., Demyan W. F., Mancini M. A., Chatterjee B., Roy A. K. Androgen receptor messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) in the rat liver: changes in mRNA levels during maturation, aging, and calorie restriction. Endocrinology. 1991 Jan;128(1):349–356. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-1-349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Supakar P. C., Jung M. H., Song C. S., Chatterjee B., Roy A. K. Nuclear factor kappa B functions as a negative regulator for the rat androgen receptor gene and NF-kappa B activity increases during the age-dependent desensitization of the liver. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jan 13;270(2):837–842. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.2.837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Supakar P. C., Song C. S., Jung M. H., Slomczynska M. A., Kim J. M., Vellanoweth R. L., Chatterjee B., Roy A. K. A novel regulatory element associated with age-dependent expression of the rat androgen receptor gene. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 15;268(35):26400–26408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surh Y. J., Liem A., Miller E. C., Miller J. A. Age- and sex-related differences in activation of the carcinogen 7-hydroxymethyl-12-methylbenz[a]anthracene to an electrophilic sulfuric acid ester metabolite in rats. Possible involvement of hydroxysteroid sulfotransferase activity. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 Jan 15;41(2):213–221. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90479-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan J. A., Joseph D. R., Quarmby V. E., Lubahn D. B., Sar M., French F. S., Wilson E. M. The rat androgen receptor: primary structure, autoregulation of its messenger ribonucleic acid, and immunocytochemical localization of the receptor protein. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Dec;2(12):1276–1285. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-12-1276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso J. Y., Sun X. H., Kao T. H., Reece K. S., Wu R. Isolation and characterization of rat and human glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase cDNAs: genomic complexity and molecular evolution of the gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 11;13(7):2485–2502. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.7.2485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter C. A., Nasr-Schirf D., Luna V. J. Identification of transgenic mice carrying the CAT gene with PCR amplification. Biotechniques. 1989 Nov-Dec;7(10):1065–1070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., DeMayo J. L., Hahn T. M., Finegold M. J., Konecki D. S., Lichter-Konecki U., Woo S. L. Tissue- and development-specific expression of the human phenylalanine hydroxylase/chloramphenicol acetyltransferase fusion gene in transgenic mice. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):15105–15110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watabe T., Ogura K., Satsukawa M., Okuda H., Hiratsuka A. Molecular cloning and functions of rat liver hydroxysteroid sulfotransferases catalysing covalent binding of carcinogenic polycyclic arylmethanols to DNA. Chem Biol Interact. 1994 Jun;92(1-3):87–105. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(94)90056-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J. Interactions of hepatic cytochromes P-450 with steroid hormones. Regioselectivity and stereospecificity of steroid metabolism and hormonal regulation of rat P-450 enzyme expression. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Jan 1;37(1):71–84. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90756-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]