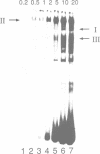
Abstract
Human c-fos expression is subject to tight transcriptional control. The gene is expressed at a high, constitutive level in some cell types and at a very low, but rapidly inducible level in many others. Induction of transcription by serum growth factors is mediated by the serum response element (SRE) to which at least two transcription factors, p67SRF and p62, bind. In this paper it is demonstrated that the low basal level of transcription is mediated through p67SRF bound to the SRE and that high, constitutive expression is observed when binding is prohibited. In this situation, an AP-1 consensus binding site adjacent to the SRE permits transactivation of the gene. Thus three levels of c-fos expression, induced, repressed and constitutive, appear to be determined by occupation of the SRE by p67SRF and its interaction with other proteins.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bender A., Sprague G. F., Jr MAT alpha 1 protein, a yeast transcription activator, binds synergistically with a second protein to a set of cell-type-specific genes. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):681–691. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90326-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavrier P., Janssen-Timmen U., Mattéi M. G., Zerial M., Bravo R., Charnay P. Structure, chromosome location, and expression of the mouse zinc finger gene Krox-20: multiple gene products and coregulation with the proto-oncogene c-fos. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):787–797. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu R., Boyle W. J., Meek J., Smeal T., Hunter T., Karin M. The c-Fos protein interacts with c-Jun/AP-1 to stimulate transcription of AP-1 responsive genes. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):541–552. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90076-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Van Beveren C., Verma I. M. Viral and cellular fos proteins are complexed with a 39,000-dalton cellular protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):167–172. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Distel R. J., Ro H. S., Rosen B. S., Groves D. L., Spiegelman B. M. Nucleoprotein complexes that regulate gene expression in adipocyte differentiation: direct participation of c-fos. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):835–844. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90621-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisch T. M., Prywes R., Roeder R. G. An AP1-binding site in the c-fos gene can mediate induction by epidermal growth factor and 12-O-tetradecanoyl phorbol-13-acetate. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1327–1331. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franza B. R., Jr, Sambucetti L. C., Cohen D. R., Curran T. Analysis of Fos protein complexes and Fos-related antigens by high-resolution two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Oncogene. 1987 May;1(2):213–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goutte C., Johnson A. D. a1 protein alters the DNA binding specificity of alpha 2 repressor. Cell. 1988 Mar 25;52(6):875–882. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90429-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Hermanowski A. L., Ziff E. B. Effect of protein synthesis inhibitors on growth factor activation of c-fos, c-myc, and actin gene transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1050–1057. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai T. W., Liu F., Allegretto E. A., Karin M., Green M. R. A family of immunologically related transcription factors that includes multiple forms of ATF and AP-1. Genes Dev. 1988 Oct;2(10):1216–1226. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.10.1216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halazonetis T. D., Georgopoulos K., Greenberg M. E., Leder P. c-Jun dimerizes with itself and with c-Fos, forming complexes of different DNA binding affinities. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):917–924. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90147-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes T. E., Sengupta P., Cochran B. H. The human c-fos serum response factor and the yeast factors GRM/PRTF have related DNA-binding specificities. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1713–1722. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera R. E., Shaw P. E., Nordheim A. Occupation of the c-fos serum response element in vivo by a multi-protein complex is unaltered by growth factor induction. Nature. 1989 Jul 6;340(6228):68–70. doi: 10.1038/340068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keleher C. A., Goutte C., Johnson A. D. The yeast cell-type-specific repressor alpha 2 acts cooperatively with a non-cell-type-specific protein. Cell. 1988 Jun 17;53(6):927–936. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)90449-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruijer W., Cooper J. A., Hunter T., Verma I. M. Platelet-derived growth factor induces rapid but transient expression of the c-fos gene and protein. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):711–716. doi: 10.1038/312711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushtai G., Barzilay J., Feldman M., Eisenbach L. The c-fos proto-oncogene in murine 3LL carcinoma clones controls the expression of MHC genes. Oncogene. 1988 Feb;2(2):119–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König H., Ponta H., Rahmsdorf U., Büscher M., Schönthal A., Rahmsdorf H. J., Herrlich P. Autoregulation of fos: the dyad symmetry element as the major target of repression. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2559–2566. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08394.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lech K., Anderson K., Brent R. DNA-bound Fos proteins activate transcription in yeast. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):179–184. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90506-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. A., Hai T. Y., SivaRaman L., Thimmappaya B., Hurst H. C., Jones N. C., Green M. R. A cellular protein, activating transcription factor, activates transcription of multiple E1A-inducible adenovirus early promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8355–8359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Mitchell P., Tjian R. Purified transcription factor AP-1 interacts with TPA-inducible enhancer elements. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90612-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung S., Miyamoto N. G. Point mutational analysis of the human c-fos serum response factor binding site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 11;17(3):1177–1195. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.3.1177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason I., Murphy D., Hogan B. L. Expression of c-fos in parietal endoderm, amnion and differentiating F9 teratocarcinoma cells. Differentiation. 1985;30(1):76–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1985.tb00516.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montminy M. R., Bilezikjian L. M. Binding of a nuclear protein to the cyclic-AMP response element of the somatostatin gene. Nature. 1987 Jul 9;328(6126):175–178. doi: 10.1038/328175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. I., Cohen D. R., Hempstead J. L., Curran T. Mapping patterns of c-fos expression in the central nervous system after seizure. Science. 1987 Jul 10;237(4811):192–197. doi: 10.1126/science.3037702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Bravo R., Burckhardt J., Curran T. Induction of c-fos gene and protein by growth factors precedes activation of c-myc. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):716–720. doi: 10.1038/312716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Verma I. M., Adamson E. D. Expression of c-onc genes: c-fos transcripts accumulate to high levels during development of mouse placenta, yolk sac and amnion. EMBO J. 1983;2(5):679–684. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01484.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabeppu Y., Ryder K., Nathans D. DNA binding activities of three murine Jun proteins: stimulation by Fos. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):907–915. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90146-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K., Shore D. Transcriptional regulation in the yeast life cycle. Science. 1987 Sep 4;237(4819):1162–1170. doi: 10.1126/science.3306917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman C., Runswick M., Pollock R., Treisman R. Isolation and properties of cDNA clones encoding SRF, a transcription factor that binds to the c-fos serum response element. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):989–1003. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90244-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passmore S., Maine G. T., Elble R., Christ C., Tye B. K. Saccharomyces cerevisiae protein involved in plasmid maintenance is necessary for mating of MAT alpha cells. J Mol Biol. 1988 Dec 5;204(3):593–606. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90358-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piette J., Yaniv M. Two different factors bind to the alpha-domain of the polyoma virus enhancer, one of which also interacts with the SV40 and c-fos enhancers. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1331–1337. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02372.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Cohen D. R., Curran T., Bos T. J., Vogt P. K., Bohmann D., Tjian R., Franza B. R., Jr Fos-associated protein p39 is the product of the jun proto-oncogene. Science. 1988 May 20;240(4855):1010–1016. doi: 10.1126/science.3130660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Voulalas P. J., Franza B. R., Jr, Curran T. Fos and Jun bind cooperatively to the AP-1 site: reconstitution in vitro. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1687–1699. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Lamph W. W., Kamps M., Verma I. M. fos-associated cellular p39 is related to nuclear transcription factor AP-1. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):553–560. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90077-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Sisson J. C., Verma I. M. Transcriptional autoregulation of the proto-oncogene fos. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):314–319. doi: 10.1038/334314a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Verma I. M. Modulation of c-fos gene transcription by negative and positive cellular factors. Nature. 1987 Apr 2;326(6112):507–510. doi: 10.1038/326507a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schirm S., Jiricny J., Schaffner W. The SV40 enhancer can be dissected into multiple segments, each with a different cell type specificity. Genes Dev. 1987 Mar;1(1):65–74. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröter H., Shaw P. E., Nordheim A. Purification of intercalator-released p67, a polypeptide that interacts specifically with the c-fos serum response element. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10145–10158. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönthal A., Büscher M., Angel P., Rahmsdorf H. J., Ponta H., Hattori K., Chiu R., Karin M., Herrlich P. The Fos and Jun/AP-1 proteins are involved in the downregulation of Fos transcription. Oncogene. 1989 May;4(5):629–636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönthal A., Herrlich P., Rahmsdorf H. J., Ponta H. Requirement for fos gene expression in the transcriptional activation of collagenase by other oncogenes and phorbol esters. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):325–334. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90195-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seedorf K., Krämmer G., Dürst M., Suhai S., Röwekamp W. G. Human papillomavirus type 16 DNA sequence. Virology. 1985 Aug;145(1):181–185. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90214-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setoyama C., Frunzio R., Liau G., Mudryj M., de Crombrugghe B. Transcriptional activation encoded by the v-fos gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3213–3217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw P. E., Bohmann D., Sergeant A. The SV40 enhancer influences viral late transcription in vitro and in vivo but not on replicating templates. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3247–3252. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04073.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw P. E., Schröter H., Nordheim A. The ability of a ternary complex to form over the serum response element correlates with serum inducibility of the human c-fos promoter. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):563–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90579-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Identification of a protein-binding site that mediates transcriptional response of the c-fos gene to serum factors. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):567–574. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90882-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Transient accumulation of c-fos RNA following serum stimulation requires a conserved 5' element and c-fos 3' sequences. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):889–902. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90285-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber F., de Villiers J., Schaffner W. An SV40 "enhancer trap" incorporates exogenous enhancers or generates enhancers from its own sequences. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):983–992. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildeman A. G., Sassone-Corsi P., Grundström T., Zenke M., Chambon P. Stimulation of in vitro transcription from the SV40 early promoter by the enhancer involves a specific trans-acting factor. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3129–3133. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02269.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson T., Treisman R. Fos C-terminal mutations block down-regulation of c-fos transcription following serum stimulation. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4193–4202. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03316.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Villiers J., Olson L., Tyndall C., Schaffner W. Transcriptional 'enhancers' from SV40 and polyoma virus show a cell type preference. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 20;10(24):7965–7976. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.24.7965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]