Abstract
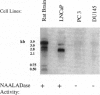
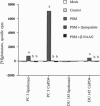
This report demonstrates that the investigational prostatic carcinoma marker known as the prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSM) possesses hydrolytic activity with the substrate and pharmacologic properties of the N-acetylated alpha-linked acidic dipeptidase (NAALADase). NAALADase is a membrane hydrolase that has been characterized in the mammalian nervous system on the basis of its catabolism of the neuropeptide N-acetylaspartylglutamate (NAAG) to yield glutamate and N-acetylaspartate and that has been hypothesized to influence glutamatergic signaling processes. The immunoscreening of a rat brain cDNA expression library with anti-NAALADase antisera identified a 1428-base partial cDNA that shares 86% sequence identity with 1428 bases of the human PSM cDNA [Israeli, R. S., Powell, C. T., Fair, W. R. & Heston, W.D.W. (1993) Cancer Res. 53, 227-230]. A cDNA containing the entire PSM open reading frame was subsequently isolated by reverse transcription-PCR from the PSM-positive prostate carcinoma cell line LNCaP. Transient transfection of this cDNA into two NAALADase-negative cell lines conferred NAAG-hydrolyzing activity that was inhibited by the NAALADase inhibitors quisqualic acid and beta-NAAG. Thus we demonstrate a PSM-encoded function and identify a NAALADase-encoding cDNA. Northern analyses identify at least six transcripts that are variably expressed in NAALADase-positive but not in NAALADase-negative rat tissues and human cell lines; therefore, PSM and/or related molecular species appear to account for NAAG hydrolysis in the nervous system. These results also raise questions about the role of PSM in both normal and pathologic prostate epithelial-cell function.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdel-Nabi H., Wright G. L., Gulfo J. V., Petrylak D. P., Neal C. E., Texter J. E., Begun F. P., Tyson I., Heal A., Mitchell E. Monoclonal antibodies and radioimmunoconjugates in the diagnosis and treatment of prostate cancer. Semin Urol. 1992 Feb;10(1):45–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J. Classification of peptidases. Methods Enzymol. 1994;244:1–15. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(94)44003-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger U. V., Carter R. E., Coyle J. T. The immunocytochemical localization of N-acetylaspartyl glutamate, its hydrolysing enzyme NAALADase, and the NMDAR-1 receptor at a vertebrate neuromuscular junction. Neuroscience. 1995 Feb;64(4):847–850. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(95)92578-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger U. V., Carter R. E., McKee M., Coyle J. T. N-acetylated alpha-linked acidic dipeptidase is expressed by non-myelinating Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system. J Neurocytol. 1995 Feb;24(2):99–109. doi: 10.1007/BF01181553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakely R. D., Coyle J. T. The neurobiology of N-acetylaspartylglutamate. Int Rev Neurobiol. 1988;30:39–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakely R. D., Robinson M. B., Thompson R. C., Coyle J. T. Hydrolysis of the brain dipeptide N-acetyl-L-aspartyl-L-glutamate: subcellular and regional distribution, ontogeny, and the effect of lesions on N-acetylated-alpha-linked acidic dipeptidase activity. J Neurochem. 1988 Apr;50(4):1200–1209. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb10593.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson Z., Salt T. E. The effects of N-acetylaspartylglutamate and distribution of N-acetylaspartylglutamate-like immunoreactivity in the rat somatosensory thalamus. Neuroscience. 1988 Jun;25(3):899–906. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90043-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollmann M., Heinemann S. Cloned glutamate receptors. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1994;17:31–108. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.17.030194.000335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horoszewicz J. S., Kawinski E., Murphy G. P. Monoclonal antibodies to a new antigenic marker in epithelial prostatic cells and serum of prostatic cancer patients. Anticancer Res. 1987 Sep-Oct;7(5B):927–935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israeli R. S., Miller W. H., Jr, Su S. L., Powell C. T., Fair W. R., Samadi D. S., Huryk R. F., DeBlasio A., Edwards E. T., Wise G. J. Sensitive nested reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction detection of circulating prostatic tumor cells: comparison of prostate-specific membrane antigen and prostate-specific antigen-based assays. Cancer Res. 1994 Dec 15;54(24):6306–6310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israeli R. S., Powell C. T., Corr J. G., Fair W. R., Heston W. D. Expression of the prostate-specific membrane antigen. Cancer Res. 1994 Apr 1;54(7):1807–1811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israeli R. S., Powell C. T., Fair W. R., Heston W. D. Molecular cloning of a complementary DNA encoding a prostate-specific membrane antigen. Cancer Res. 1993 Jan 15;53(2):227–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones H. E., Sillito A. M. The action of the putative neurotransmitters N-acetylaspartylglutamate and L-homocysteate in cat dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus. J Neurophysiol. 1992 Sep;68(3):663–672. doi: 10.1152/jn.1992.68.3.663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keil M., Wetterauer U., Heite H. J. Glutamic acid concentration in human semen--its origin and significance. Andrologia. 1979 Sep-Oct;11(5):385–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0272.1979.tb02224.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny A. J., Maroux S. Topology of microvillar membrance hydrolases of kidney and intestine. Physiol Rev. 1982 Jan;62(1):91–128. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1982.62.1.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto A., Nishiyama K., Nakanishi H., Uratsuji Y., Nomura H., Takeyama Y., Nishizuka Y. Studies on the phosphorylation of myelin basic protein by protein kinase C and adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12492–12499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letarte M., Vera S., Tran R., Addis J. B., Onizuka R. J., Quackenbush E. J., Jongeneel C. V., McInnes R. R. Common acute lymphocytic leukemia antigen is identical to neutral endopeptidase. J Exp Med. 1988 Oct 1;168(4):1247–1253. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.4.1247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu B., Maher R. J., Hannun Y. A., Porter A. T., Honn K. V. 12(S)-HETE enhancement of prostate tumor cell invasion: selective role of PKC alpha. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1994 Aug 3;86(15):1145–1151. doi: 10.1093/jnci/86.15.1145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopes A. D., Davis W. L., Rosenstraus M. J., Uveges A. J., Gilman S. C. Immunohistochemical and pharmacokinetic characterization of the site-specific immunoconjugate CYT-356 derived from antiprostate monoclonal antibody 7E11-C5. Cancer Res. 1990 Oct 1;50(19):6423–6429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyerhoff J. L., Carter R. E., Yourick D. L., Slusher B. S., Coyle J. T. Activity of a NAAG-hydrolyzing enzyme in brain may affect seizure susceptibility in genetically epilepsy-prone rats. Epilepsy Res Suppl. 1992;9:163–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyerhoff J. L., Carter R. E., Yourick D. L., Slusher B. S., Coyle J. T. Genetically epilepsy-prone rats have increased brain regional activity of an enzyme which liberates glutamate from N-acetyl-aspartyl-glutamate. Brain Res. 1992 Oct 9;593(1):140–143. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)91276-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radloff R., Bauer W., Vinograd J. A dye-buoyant-density method for the detection and isolation of closed circular duplex DNA: the closed circular DNA in HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 May;57(5):1514–1521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.5.1514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlings N. D., Barrett A. J. Evolutionary families of metallopeptidases. Methods Enzymol. 1995;248:183–228. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(95)48015-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson M. B., Blakely R. D., Couto R., Coyle J. T. Hydrolysis of the brain dipeptide N-acetyl-L-aspartyl-L-glutamate. Identification and characterization of a novel N-acetylated alpha-linked acidic dipeptidase activity from rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14498–14506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson M. B., Blakely R. D., Coyle J. T. Quisqualate selectively inhibits a brain peptidase which cleaves N-acetyl-L-aspartyl-L-glutamate in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Nov 4;130(3):345–347. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90291-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein J. D., Tsai G., Kuncl R. W., Clawson L., Cornblath D. R., Drachman D. B., Pestronk A., Stauch B. L., Coyle J. T. Abnormal excitatory amino acid metabolism in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 1990 Jul;28(1):18–25. doi: 10.1002/ana.410280106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekiguchi M., Okamoto K., Sakai Y. Excitatory action of N-acetylaspartylglutamate on Purkinje cells in guinea pig cerebellar slices: an intrasomatic study. Brain Res. 1987 Oct 13;423(1-2):23–33. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90820-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekiguchi M., Okamoto K., Sakai Y. Low-concentration N-acetylaspartylglutamate suppresses the climbing fiber response of Purkinje cells in guinea pig cerebellar slices and the responses to excitatory amino acids of Xenopus laevis oocytes injected with cerebellar mRNA. Brain Res. 1989 Mar 13;482(1):87–96. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90545-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serval V., Barbeito L., Pittaluga A., Cheramy A., Lavielle S., Glowinski J. Competitive inhibition of N-acetylated-alpha-linked acidic dipeptidase activity by N-acetyl-L-aspartyl-beta-linked L-glutamate. J Neurochem. 1990 Jul;55(1):39–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb08818.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serval V., Galli T., Cheramy A., Glowinski J., Lavielle S. In vitro and in vivo inhibition of N-acetyl-L-aspartyl-L-glutamate catabolism by N-acylated L-glutamate analogs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Mar;260(3):1093–1100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipp M. A., Vijayaraghavan J., Schmidt E. V., Masteller E. L., D'Adamio L., Hersh L. B., Reinherz E. L. Common acute lymphoblastic leukemia antigen (CALLA) is active neutral endopeptidase 24.11 ("enkephalinase"): direct evidence by cDNA transfection analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):297–301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slusher B. S., Robinson M. B., Tsai G., Simmons M. L., Richards S. S., Coyle J. T. Rat brain N-acetylated alpha-linked acidic dipeptidase activity. Purification and immunologic characterization. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):21297–21301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slusher B. S., Tsai G., Yoo G., Coyle J. T. Immunocytochemical localization of the N-acetyl-aspartyl-glutamate (NAAG) hydrolyzing enzyme N-acetylated alpha-linked acidic dipeptidase (NAALADase). J Comp Neurol. 1992 Jan 8;315(2):217–229. doi: 10.1002/cne.903150208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai G. C., Stauch-Slusher B., Sim L., Hedreen J. C., Rothstein J. D., Kuncl R., Coyle J. T. Reductions in acidic amino acids and N-acetylaspartylglutamate in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis CNS. Brain Res. 1991 Aug 9;556(1):151–156. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90560-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai G., Forloni G., Robinson M. B., Stauch B. L., Coyle J. T. Calcium-dependent evoked release of N-[3H]acetylaspartylglutamate from the optic pathway. J Neurochem. 1988 Dec;51(6):1956–1959. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb01186.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai G., Passani L. A., Slusher B. S., Carter R., Baer L., Kleinman J. E., Coyle J. T. Abnormal excitatory neurotransmitter metabolism in schizophrenic brains. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1995 Oct;52(10):829–836. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1995.03950220039008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai G., Stauch B. L., Vornov J. J., Deshpande J. K., Coyle J. T. Selective release of N-acetylaspartylglutamate from rat optic nerve terminals in vivo. Brain Res. 1990 Jun 4;518(1-2):313–316. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90989-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt K. W., Lee P. J., M'Timkulu T., Chan W. P., Loor R. Human prostate-specific antigen: structural and functional similarity with serine proteases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3166–3170. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westbrook G. L., Mayer M. L., Namboodiri M. A., Neale J. H. High concentrations of N-acetylaspartylglutamate (NAAG) selectively activate NMDA receptors on mouse spinal cord neurons in cell culture. J Neurosci. 1986 Nov;6(11):3385–3392. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-11-03385.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodgett J. R., Gould K. L., Hunter T. Substrate specificity of protein kinase C. Use of synthetic peptides corresponding to physiological sites as probes for substrate recognition requirements. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Nov 17;161(1):177–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10139.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wroblewska B., Wroblewski J. T., Saab O. H., Neale J. H. N-acetylaspartylglutamate inhibits forskolin-stimulated cyclic AMP levels via a metabotropic glutamate receptor in cultured cerebellar granule cells. J Neurochem. 1993 Sep;61(3):943–948. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03606.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann H. Signalling via ATP in the nervous system. Trends Neurosci. 1994 Oct;17(10):420–426. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(94)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]