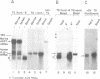
Abstract
Mice that are transgenic for human beta zero-thalassemic beta-globin alleles were generated in order to study how beta zero-thalassemic mutations affect beta-globin RNA metabolism in erythroid tissues. Three thalassemic alleles were studied, each of which harbors either a frameshift or a nonsense mutation. These mutations result in the premature termination of beta-globin mRNA translation and an abnormally low level of beta-globin mRNA in the peripheral blood of thalassemic patients. Comparative studies of mice that express any of the beta zero-thalassemic transgenes with mice that express a normal human beta-globin transgene demonstrated that all three thalassemic mRNAs are metabolized in erythroid tissues abnormally. RNA blotting and S1 nuclease transcript mapping revealed for each thalassemic transgene that (i) the full-length mRNA is abnormally short-lived and (ii) in addition to full-length mRNA, three more stable yet smaller RNAs are present. These smaller RNAs are polyadenylated and lack the mRNA 5' end.
Full text
PDF
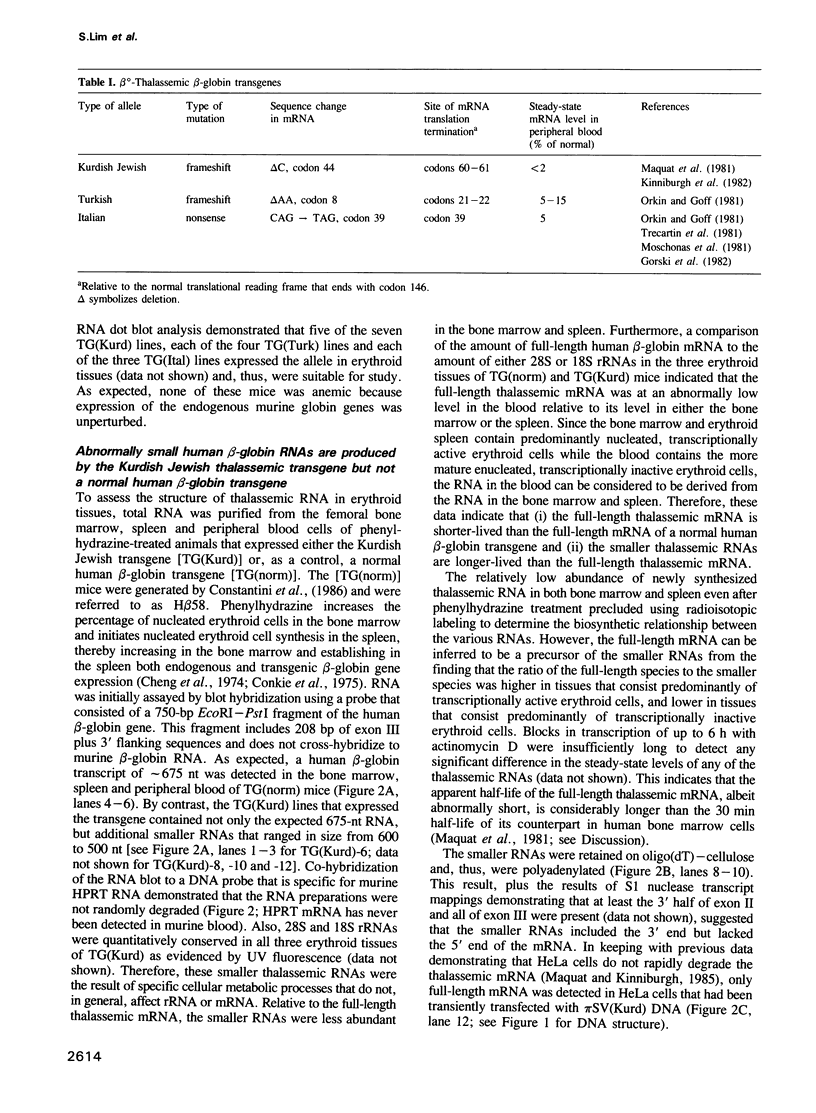
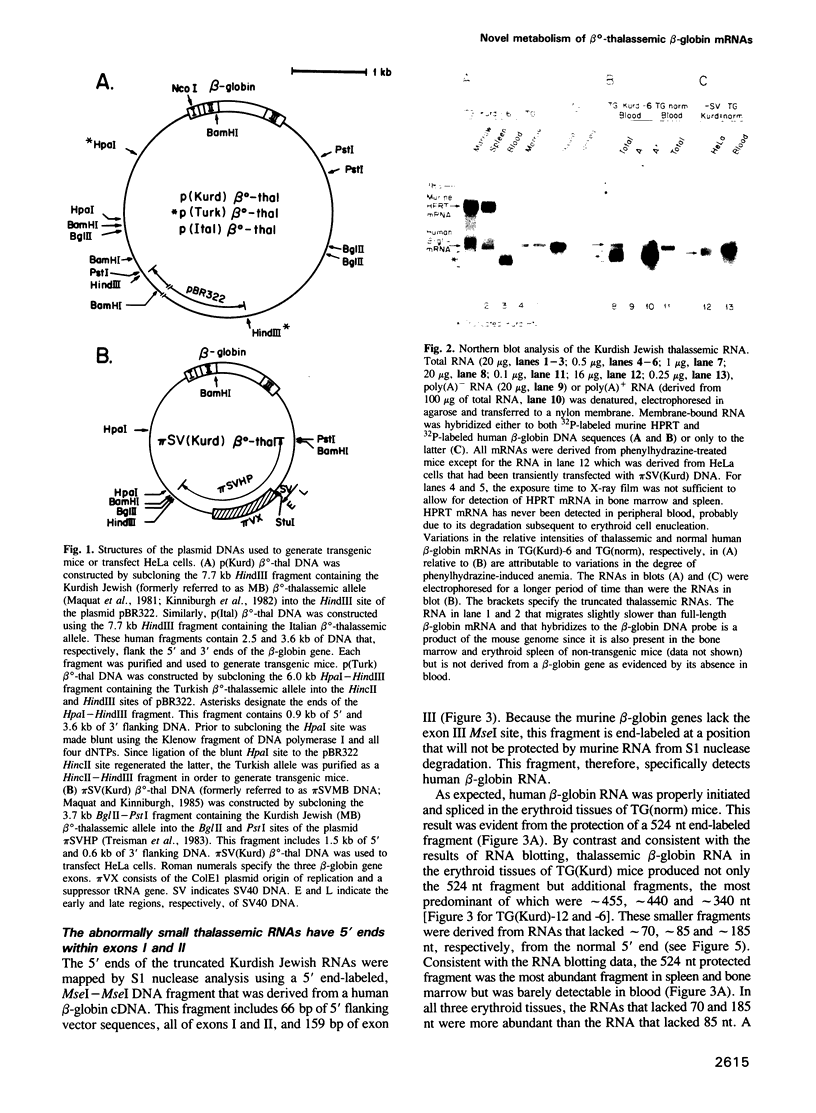




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baserga S. J., Benz E. J., Jr Nonsense mutations in the human beta-globin gene affect mRNA metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2056–2060. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann B., Potash M. J., Köhler G. Consequences of frameshift mutations at the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus of the mouse. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):351–359. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03636.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behringer R. R., Hammer R. E., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D., Townes T. M. Two 3' sequences direct adult erythroid-specific expression of human beta-globin genes in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7056–7060. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Spliced early mRNAs of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1274–1278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinster R. L., Chen H. Y., Trumbauer M. E., Yagle M. K., Palmiter R. D. Factors affecting the efficiency of introducing foreign DNA into mice by microinjecting eggs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4438–4442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. W., Thomas C. A., Jr Recovery of DNA segments from agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jan 15;101(2):339–341. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90197-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng T., Polmar S. K., Kazazian H. H., Jr Isolation and characterization of modified globin messenger ribonucleic acid from erythropoietic mouse spleen. J Biol Chem. 1974 Mar 25;249(6):1781–1786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conkie D., Kleiman L., Harrison P. R., Paul J. Increase in the accumulation of globin mRNA in immature erythroblasts in response to erythropoietin in vivo or in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Jul;93(2):315–324. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90456-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costantini F., Chada K., Magram J. Correction of murine beta-thalassemia by gene transfer into the germ line. Science. 1986 Sep 12;233(4769):1192–1194. doi: 10.1126/science.3461564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daar I. O., Maquat L. E. Premature translation termination mediates triosephosphate isomerase mRNA degradation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):802–813. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. W., Ruddle F. H. DNA-mediated genetic transformation of mouse embryos and bone marrow--a review. Gene. 1985;33(2):121–136. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90087-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski J., Fiori M., Mach B. A new nonsense mutation as the molecular basis for beta thalassaemia. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jan 25;154(3):537–540. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(82)80012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoekema A., Kastelein R. A., Vasser M., de Boer H. A. Codon replacement in the PGK1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: experimental approach to study the role of biased codon usage in gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2914–2924. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinniburgh A. J., Maquat L. E., Schedl T., Rachmilewitz E., Ross J. mRNA-deficient beta o-thalassemia results from a single nucleotide deletion. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Sep 25;10(18):5421–5427. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.18.5421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kollias G., Wrighton N., Hurst J., Grosveld F. Regulated expression of human A gamma-, beta-, and hybrid gamma beta-globin genes in transgenic mice: manipulation of the developmental expression patterns. Cell. 1986 Jul 4;46(1):89–94. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90862-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang K. M., Spritz R. A. Cloning specific complete polyadenylylated 3'-terminal cDNA segments. Gene. 1985;33(2):191–196. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90093-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losson R., Lacroute F. Interference of nonsense mutations with eukaryotic messenger RNA stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5134–5137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magram J., Chada K., Costantini F. Developmental regulation of a cloned adult beta-globin gene in transgenic mice. Nature. 1985 May 23;315(6017):338–340. doi: 10.1038/315338a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maquat L. E., Kinniburgh A. J. A beta zero-thalassemic beta-globin RNA that is labile in bone marrow cells is relatively stable in HeLa cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 25;13(8):2855–2867. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.8.2855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maquat L. E., Kinniburgh A. J., Beach L. R., Honig G. R., Lazerson J., Ershler W. B., Ross J. Processing of human beta-globin mRNA precursor to mRNA is defective in three patients with beta+-thalassemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4287–4291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maquat L. E., Kinniburgh A. J., Rachmilewitz E. A., Ross J. Unstable beta-globin mRNA in mRNA-deficient beta o thalassemia. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):543–553. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90396-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. W., Konecki D. S., Brennand J., Caskey C. T. Structure, expression, and mutation of the hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2147–2151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moschonas N., de Boer E., Grosveld F. G., Dahl H. H., Wright S., Shewmaker C. K., Flavell R. A. Structure and expression of a cloned beta o thalassaemic globin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Sep 11;9(17):4391–4401. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.17.4391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H., Goff S. C. Nonsense and frameshift mutations in beta 0-thalassemia detected in cloned beta-globin genes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 10;256(19):9782–9784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H., Kazazian H. H., Jr The mutation and polymorphism of the human beta-globin gene and its surrounding DNA. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:131–171. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.001023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pachter J. S., Yen T. J., Cleveland D. W. Autoregulation of tubulin expression is achieved through specific degradation of polysomal tubulin mRNAs. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90155-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez F., Starkman D., Bank A., Kerem H., Cividalli G., Rachmilewitz E. A. Absence of beta mRNA in beta0-thalassemia in Kurdish Jews. Blood. 1978 Oct;52(4):735–739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J. A precursor of globin messenger RNA. J Mol Biol. 1976 Sep 15;106(2):403–420. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90093-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J., Pizarro A. Human beta and delta globin messenger RNAs turn over at different rates. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jul 5;167(3):607–617. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80101-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townes T. M., Lingrel J. B., Chen H. Y., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. Erythroid-specific expression of human beta-globin genes in transgenic mice. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1715–1723. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03841.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trecartin R. F., Liebhaber S. A., Chang J. C., Lee K. Y., Kan Y. W., Furbetta M., Angius A., Cao A. beta zero thalassemia in Sardinia is caused by a nonsense mutation. J Clin Invest. 1981 Oct;68(4):1012–1017. doi: 10.1172/JCI110323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Green M. R., Maniatis T. cis and trans activation of globin gene transcription in transient assays. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7428–7432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trudel M., Magram J., Bruckner L., Costantini F. Upstream G gamma-globin and downstream beta-globin sequences required for stage-specific expression in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):4024–4029. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.4024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Sweet R., Sim G. K., Wold B., Pellicer A., Lacy E., Maniatis T., Silverstein S., Axel R. Transformation of mammalian cells with genes from procaryotes and eucaryotes. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]