Abstract
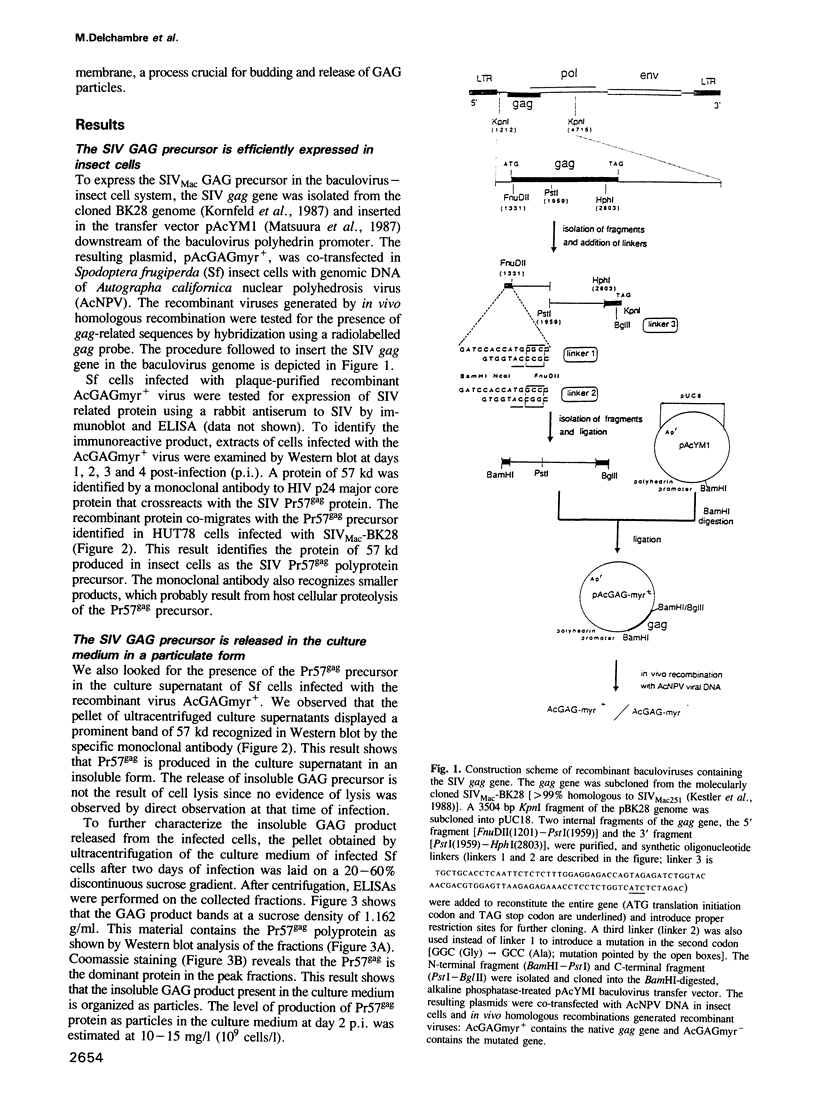
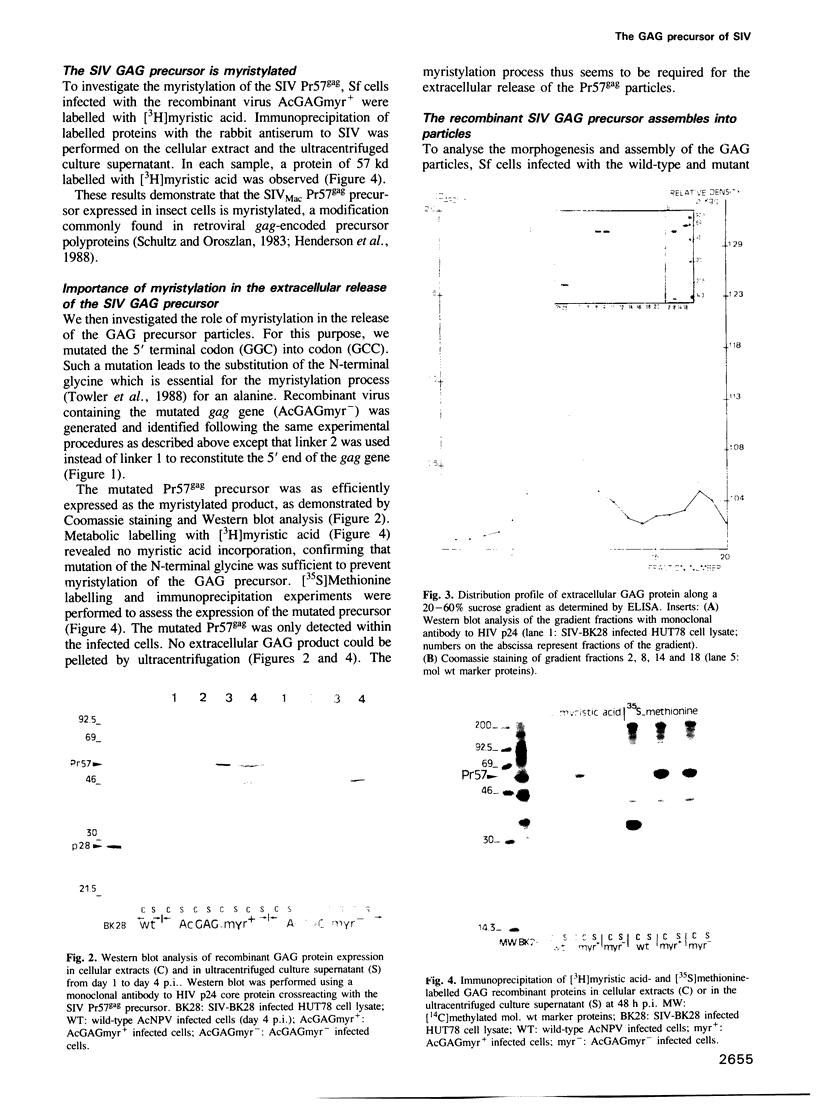
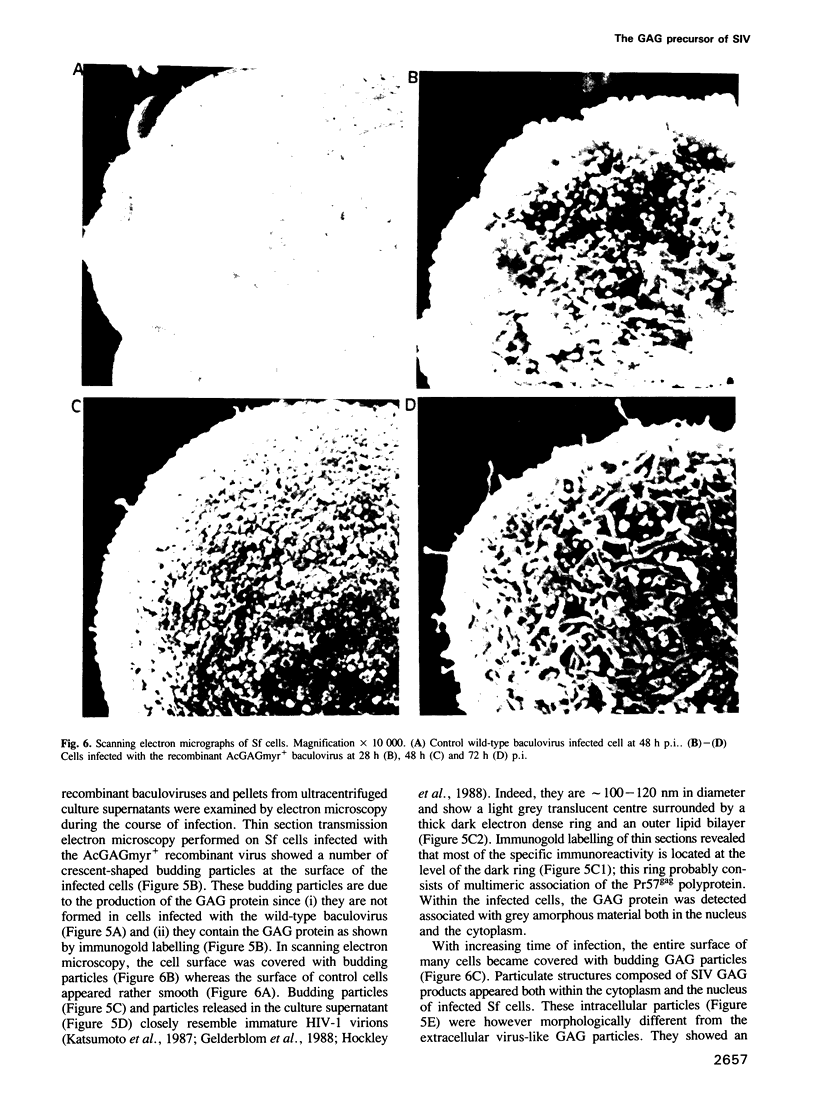
To examine the potential role of the GAG precursor polyprotein in morphogenesis and assembly of the simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV), we have expressed the gag gene of SIVMac using a baculovirus expression vector. Infection of insect cells with recombinant virus containing the entire gag gene results in high expression of the GAG precursor protein, Pr57gag. The recombinant protein is myristylated and is released in the culture supernatant in an insoluble particulate form. A point mutation in the N-terminal glycine codon (Gly----Ala) inhibits myristylation. This mutated product is highly expressed but is not found in the culture supernatant. Electron microscopy and immunogold labelling of infected cells show that the native Pr57gag protein assembles into 100-120 nm virus-like particles that bud from the cell plasma membrane and are released in the culture supernatant. The unmyristylated protein also assembles into particulate structures which only accumulate inside the cells. These results demonstrate that the unprocessed GAG precursor of SIV can spontaneously assemble into particles in the absence of other viral proteins. Myristylation of the Pr57gag precursor is necessary for its association with the cell plasma membrane, for budding and for extracellular release.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carstens E. B., Tjia S. T., Doerfler W. Infection of Spodoptera frugiperda cells with Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus I. Synthesis of intracellular proteins after virus infection. Virology. 1979 Dec;99(2):386–398. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti L., Guyader M., Alizon M., Daniel M. D., Desrosiers R. C., Tiollais P., Sonigo P. Sequence of simian immunodeficiency virus from macaque and its relationship to other human and simian retroviruses. Nature. 1987 Aug 6;328(6130):543–547. doi: 10.1038/328543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desrosiers R. C. Simian immunodeficiency viruses. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:607–625. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.003135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Laskey R. A. Protein import into the cell nucleus. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:367–390. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franchini G., Gurgo C., Guo H. G., Gallo R. C., Collalti E., Fargnoli K. A., Hall L. F., Wong-Staal F., Reitz M. S., Jr Sequence of simian immunodeficiency virus and its relationship to the human immunodeficiency viruses. Nature. 1987 Aug 6;328(6130):539–543. doi: 10.1038/328539a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. E., Benveniste R. E., Sowder R., Copeland T. D., Schultz A. M., Oroszlan S. Molecular characterization of gag proteins from simian immunodeficiency virus (SIVMne). J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2587–2595. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2587-2595.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockley D. J., Wood R. D., Jacobs J. P., Garrett A. J. Electron microscopy of human immunodeficiency virus. J Gen Virol. 1988 Oct;69(Pt 10):2455–2469. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-10-2455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafatos F. C., Jones C. W., Efstratiadis A. Determination of nucleic acid sequence homologies and relative concentrations by a dot hybridization procedure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1541–1552. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katona I. M., Urban J. F., Jr, Scher I., Kanellopoulos-Langevin C., Finkelman F. D. Induction of an IgE response in mice by Nippostrongylus brasiliensis: characterization of lymphoid cells with intracytoplasmic or surface IgE. J Immunol. 1983 Jan;130(1):350–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsumoto T., Hattori N., Kurimura T. Maturation of human immunodeficiency virus, strain LAV, in vitro. Intervirology. 1987;27(3):148–153. doi: 10.1159/000149733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kestler H. W., 3rd, Li Y., Naidu Y. M., Butler C. V., Ochs M. F., Jaenel G., King N. W., Daniel M. D., Desrosiers R. C. Comparison of simian immunodeficiency virus isolates. Nature. 1988 Feb 18;331(6157):619–622. doi: 10.1038/331619a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl N. E., Emini E. A., Schleif W. A., Davis L. J., Heimbach J. C., Dixon R. A., Scolnick E. M., Sigal I. S. Active human immunodeficiency virus protease is required for viral infectivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4686–4690. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld H., Riedel N., Viglianti G. A., Hirsch V., Mullins J. I. Cloning of HTLV-4 and its relation to simian and human immunodeficiency viruses. Nature. 1987 Apr 9;326(6113):610–613. doi: 10.1038/326610a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu A. H., Soong M. M., Wong P. K. Maturation of Moloney murine leukemia virus. Virology. 1979 Feb;93(1):269–274. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90297-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura Y., Possee R. D., Overton H. A., Bishop D. H. Baculovirus expression vectors: the requirements for high level expression of proteins, including glycoproteins. J Gen Virol. 1987 May;68(Pt 5):1233–1250. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-5-1233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. K. Baculoviruses as gene expression vectors. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:177–199. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.001141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papsidero L. D., Sheu M., Ruscetti F. W. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1-neutralizing monoclonal antibodies which react with p17 core protein: characterization and epitope mapping. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):267–272. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.267-272.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rein A., McClure M. R., Rice N. R., Luftig R. B., Schultz A. M. Myristylation site in Pr65gag is essential for virus particle formation by Moloney murine leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7246–7250. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. S., Hunter E. Myristylation is required for intracellular transport but not for assembly of D-type retrovirus capsids. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1045–1053. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1045-1053.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz A. M., Oroszlan S. In vivo modification of retroviral gag gene-encoded polyproteins by myristic acid. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):355–361. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.355-361.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seppälä I., Sarvas H., Péterfy F., Mäkelä O. The four subclasses of IgG can be isolated from mouse serum by using Protein A-Sepharose. Scand J Immunol. 1981 Oct;14(4):335–342. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1981.tb00573.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields A., Witte W. N., Rothenberg E., Baltimore D. High frequency of aberrant expression of Moloney murine leukemia virus in clonal infections. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):601–609. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90245-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. E., Kalderon D., Roberts B. L., Colledge W. H., Edge M., Gillett P., Markham A., Paucha E., Richardson W. D. The nuclear location signal. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1985 Oct 22;226(1242):43–58. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1985.0078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. E., Summers M. D., Fraser M. J. Production of human beta interferon in insect cells infected with a baculovirus expression vector. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;3(12):2156–2165. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.12.2156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. H. Evidence for a precursor-product relationship between intracytoplasmic A particles and mouse mammary tumour virus cores. J Gen Virol. 1978 Oct;41(1):193–200. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-41-1-193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens E. B., Compans R. W. Assembly of animal viruses at cellular membranes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:489–516. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.002421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towler D. A., Gordon J. I., Adams S. P., Glaser L. The biology and enzymology of eukaryotic protein acylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:69–99. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A. Finding the anti-oncogene. Sci Am. 1988 Sep;259(3):44–51. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0988-44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellink J., van Kammen A. Proteases involved in the processing of viral polyproteins. Brief review. Arch Virol. 1988;98(1-2):1–26. doi: 10.1007/BF01321002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinaka Y., Ishigame K., Ohno T., Kageyama S., Shibata K., Luftig R. B. Preparations enriched for "immature" murine leukemia virus particles that remain in tissue culture fluids are deficient in Pr65gag proteolyic activity. Virology. 1980 Jan 15;100(1):130–140. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90559-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]