Abstract
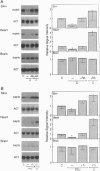
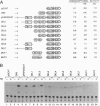
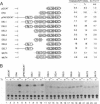
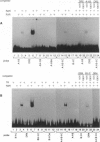
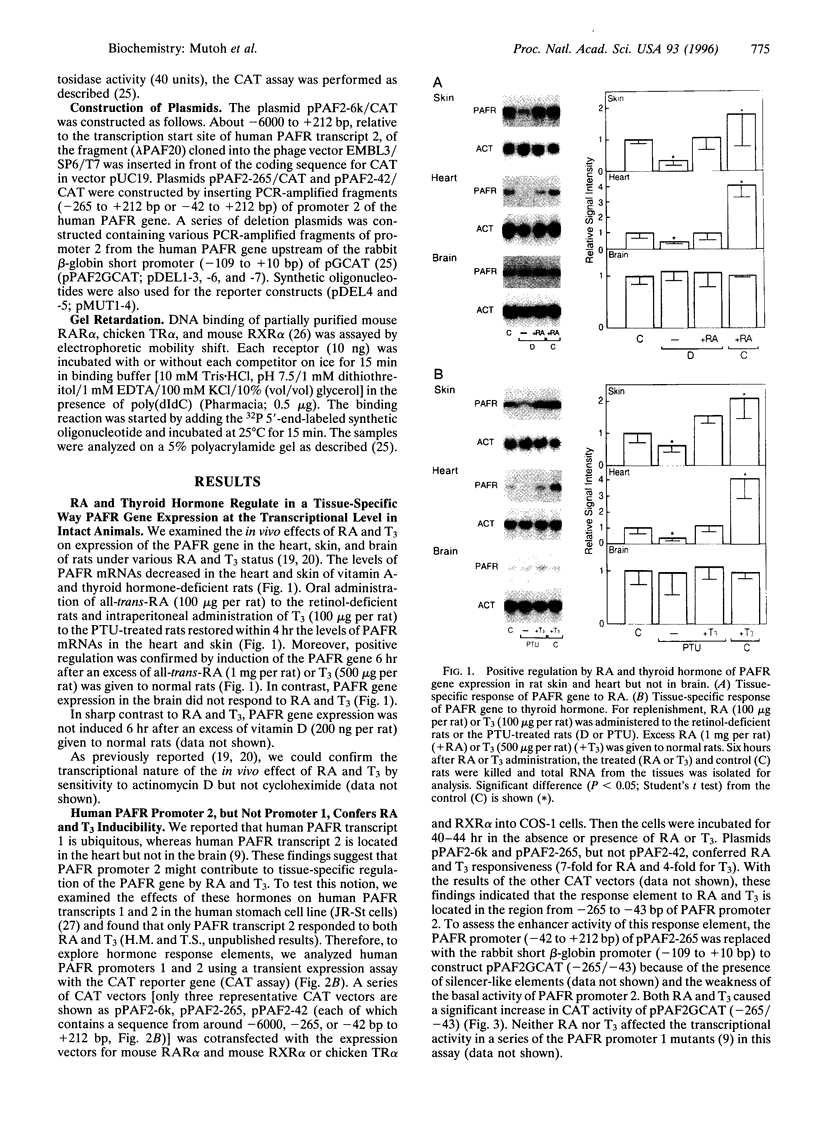
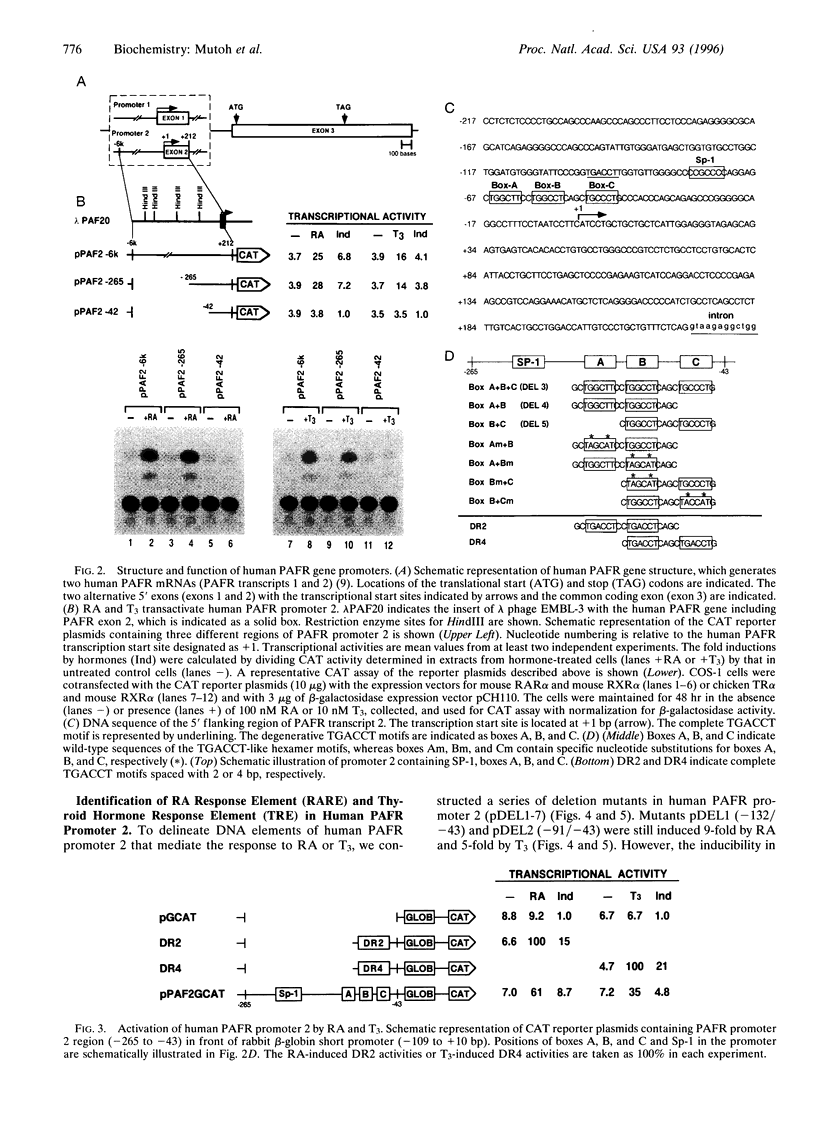
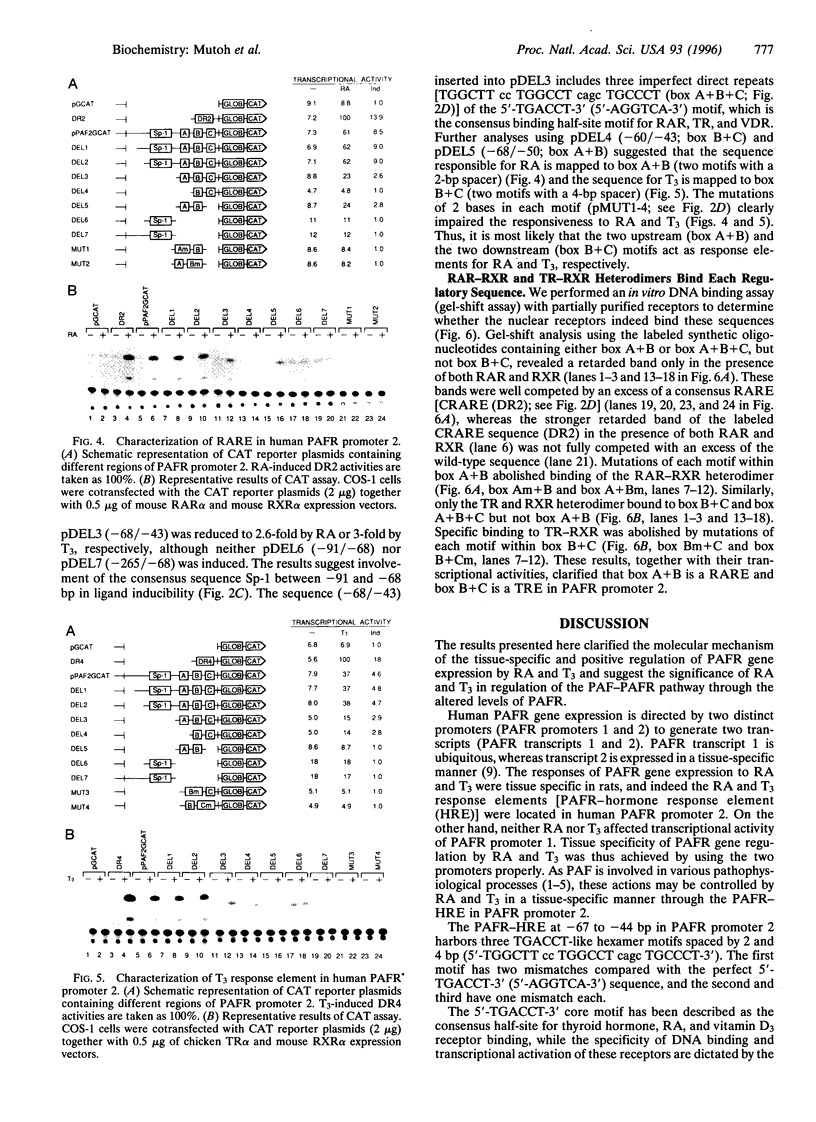
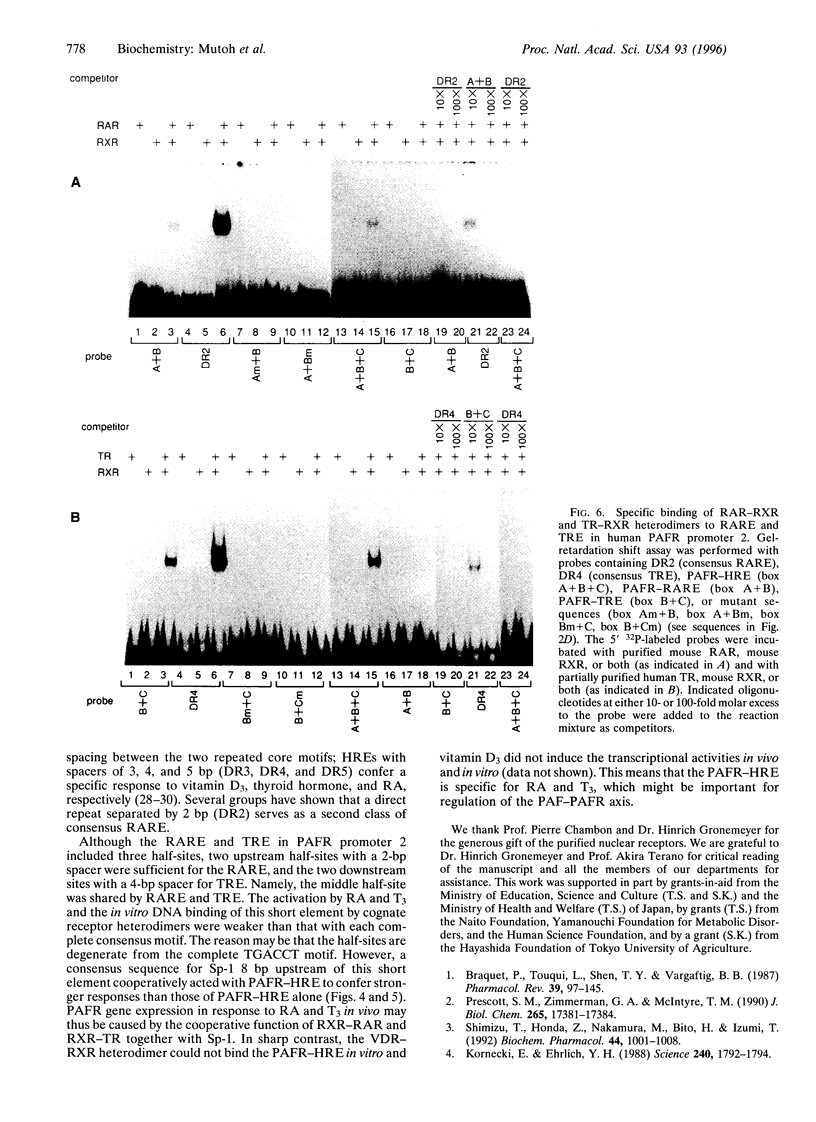
We have studied the effects of retinoic acid (RA) and thyroid hormone (3,3',5-triiodothyronine; T3) on platelet-activating factor receptor (PAFR) gene expression in intact rats and the ability of two human PAFR gene promoters (PAFR promoters 1 and 2) to generate two transcripts (PAFR transcripts 1 and 2). Northern blotting showed that RA and T3 regulated PAFR gene expression only in rat tissues that express PAFR transcript 2. Functional analysis of the human PAFR promoter 2 revealed that responsiveness to RA and T3 was conferred through a 24-bp element [PAFR-hormone response element (HRE) located from -67 to -44 bp of the transcription start site, whereas PAFR promoter 1 did not respond to these hormones. The PAFR-HRE is composed of three direct repeated TGACCT-like hexamer motifs with 2-and 4-bp spaces, and the two upstream and two downstream motifs were identified as response elements for RA and T3. Thus, the PAF-PAFR pathway is regulated by the PAFR level altered by a tissue-specific response to RA and T3 through the PAFR-HRE of the PAFR promoter 2.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bito H., Nakamura M., Honda Z., Izumi T., Iwatsubo T., Seyama Y., Ogura A., Kudo Y., Shimizu T. Platelet-activating factor (PAF) receptor in rat brain: PAF mobilizes intracellular Ca2+ in hippocampal neurons. Neuron. 1992 Aug;9(2):285–294. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90167-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braquet P., Touqui L., Shen T. Y., Vargaftig B. B. Perspectives in platelet-activating factor research. Pharmacol Rev. 1987 Jun;39(2):97–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambon P. The retinoid signaling pathway: molecular and genetic analyses. Semin Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;5(2):115–125. doi: 10.1006/scel.1994.1015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z. P., Shemshedini L., Durand B., Noy N., Chambon P., Gronemeyer H. Pure and functionally homogeneous recombinant retinoid X receptor. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 14;269(41):25770–25776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennert G., Lotan R. Effects of retinoic acid on the immune system: stimulation of T killer cell induction. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Jan;8(1):23–29. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguère V. Retinoic acid receptors and cellular retinoid binding proteins: complex interplay in retinoid signaling. Endocr Rev. 1994 Feb;15(1):61–79. doi: 10.1210/edrv-15-1-61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass C. K. Differential recognition of target genes by nuclear receptor monomers, dimers, and heterodimers. Endocr Rev. 1994 Jun;15(3):391–407. doi: 10.1210/edrv-15-3-391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda Z., Nakamura M., Miki I., Minami M., Watanabe T., Seyama Y., Okado H., Toh H., Ito K., Miyamoto T. Cloning by functional expression of platelet-activating factor receptor from guinea-pig lung. Nature. 1991 Jan 24;349(6307):342–346. doi: 10.1038/349342a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito S., Camussi G., Tetta C., Milgrom F., Andres G. Hyperacute renal allograft rejection in the rabbit. The role of platelet-activating factor and of cationic proteins derived from polymorphonuclear leukocytes and from platelets. Lab Invest. 1984 Aug;51(2):148–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamei Y., Kawada T., Kazuki R., Ono T., Kato S., Sugimoto E. Vitamin D receptor gene expression is up-regulated by 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Jun 30;193(3):948–955. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato S., Mano H., Kumazawa T., Yoshizawa Y., Kojima R., Masushige S. Effect of retinoid status on alpha, beta and gamma retinoic acid receptor mRNA levels in various rat tissues. Biochem J. 1992 Sep 15;286(Pt 3):755–760. doi: 10.1042/bj2860755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato S., Tora L., Yamauchi J., Masushige S., Bellard M., Chambon P. A far upstream estrogen response element of the ovalbumin gene contains several half-palindromic 5'-TGACC-3' motifs acting synergistically. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):731–742. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90148-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornecki E., Ehrlich Y. H. Neuroregulatory and neuropathological actions of the ether-phospholipid platelet-activating factor. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1792–1794. doi: 10.1126/science.3381103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan S., Bhuyan U. N., Talwar G. P., Ramalingaswami V. Effect of vitamin A and protein-calorie undernutrition on immune responses. Immunology. 1974 Sep;27(3):383–392. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leid M., Kastner P., Lyons R., Nakshatri H., Saunders M., Zacharewski T., Chen J. Y., Staub A., Garnier J. M., Mader S. Purification, cloning, and RXR identity of the HeLa cell factor with which RAR or TR heterodimerizes to bind target sequences efficiently. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):377–395. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90478-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkovský M., Edwards A. J., Hunt R., Palmer L., Medawar P. B. T-cell-mediated enhancement of host-versus-graft reactivity in mice fed a diet enriched in vitamin A acetate. Nature. 1983 Mar 24;302(5906):338–340. doi: 10.1038/302338a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mano H., Mori R., Ozawa T., Takeyama K., Yoshizawa Y., Kojima R., Arao Y., Masushige S., Kato S. Positive and negative regulation of retinoid X receptor gene expression by thyroid hormone in the rat. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional controls by thyroid hormone. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 21;269(3):1591–1594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutoh H., Bito H., Minami M., Nakamura M., Honda Z., Izumi T., Nakata R., Kurachi Y., Terano A., Shimizu T. Two different promoters direct expression of two distinct forms of mRNAs of human platelet-activating factor receptor. FEBS Lett. 1993 May 10;322(2):129–134. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81552-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutoh H., Ishii S., Izumi T., Kato S., Shimizu T. Platelet-activating factor (PAF) positively auto-regulates the expression of human PAF receptor transcript 1 (leukocyte-type) through NF-kappa B. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Dec 15;205(2):1137–1142. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.2784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutoh H., Kume K., Sato S., Kato S., Shimizu T. Positive and negative regulations of human platelet-activating factor receptor transcript 2 (tissue-type) by estrogen and TGF-beta 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Dec 15;205(2):1130–1136. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.2783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura M., Honda Z., Izumi T., Sakanaka C., Mutoh H., Minami M., Bito H., Seyama Y., Matsumoto T., Noma M. Molecular cloning and expression of platelet-activating factor receptor from human leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20400–20405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott S. M., Zimmerman G. A., McIntyre T. M. Platelet-activating factor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17381–17384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu T., Honda Z., Nakamura M., Bito H., Izumi T. Platelet-activating factor receptor and signal transduction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1992 Sep 25;44(6):1001–1008. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(92)90360-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto T., Tsuchimochi H., McGregor C. G., Mutoh H., Shimizu T., Kurachi Y. Molecular cloning and characterization of the platelet-activating factor receptor gene expressed in the human heart. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Dec 15;189(2):617–624. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)92245-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terano A., Nakada R., Mutoh H., Hiraishi H., Ota S., Shiina S., Shimada T., Itoh Y., Kimura K., Shiga J. Characterization of a newly established cell line (JR-St) derived from human gastric signet ring cell cancer, producing tumor markers. Gastroenterol Jpn. 1991 Feb;26(1):7–13. doi: 10.1007/BF02779502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Verneuil H., Metzger D. The lack of transcriptional activation of the v-erbA oncogene is in part due to a mutation present in the DNA binding domain of the protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 11;18(15):4489–4497. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.15.4489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]