Abstract
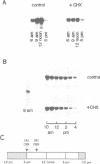
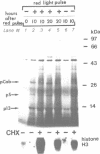
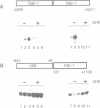
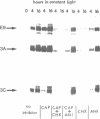
We have investigated the effects of protein synthesis inhibitors on light-induced expression of two plant nuclear genes, Cab and rbcS, in wheat, pea and transgenic tobacco. Light activation of these two genes is very sensitive to cycloheximide, an inhibitor of cytoplasmic protein synthesis but not to chloramphenicol, an inhibitor of organellar protein synthesis. Studies with chimeric gene constructs in transgenic tobacco seedlings show that cycloheximide exerts its effect at the transcriptional level. As a control, we show that the expression of the cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) 35S promoter is enhanced by cycloheximide treatment, irrespective of the coding sequence used. Escape-time analyses with green wheat seedlings show that the cycloheximide block for Cab gene expression is after the primary signal transduction step linked to phytochrome photoconversion. Our results suggest that phytochrome activation of Cab and rbcS is mediated by a labile protein factor(s) synthesized on cytoplasmic ribosomes.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altus M. S., Pearson D., Horiuchi A., Nagamine Y. Inhibition of protein synthesis in LLC-PK1 cells increases calcitonin-induced plasminogen-activator gene transcription and mRNA stability. Biochem J. 1987 Mar 1;242(2):387–392. doi: 10.1042/bj2420387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batschauer A., Apel K. An inverse control by phytochrome of the expression of two nuclear genes in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Eur J Biochem. 1984 Sep 17;143(3):593–597. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08411.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst D., Oesterhelt D. Purified phytochrome influences in vitro transcription in rye nuclei. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3075–3078. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02261.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fluhr R., Kuhlemeier C., Nagy F., Chua N. H. Organ-specific and light-induced expression of plant genes. Science. 1986 May 30;232(4754):1106–1112. doi: 10.1126/science.232.4754.1106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fluhr Robert, Moses Phyllis, Morelli Giorgio, Coruzzi Gloria, Chua Nam-Hai. Expression dynamics of the pea rbcS multigene family and organ distribution of the transcripts. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2063–2071. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04467.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giuliano G., Pichersky E., Malik V. S., Timko M. P., Scolnik P. A., Cashmore A. R. An evolutionarily conserved protein binding sequence upstream of a plant light-regulated gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7089–7093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J., Nebert D. W. Autoregulation plus upstream positive and negative control regions associated with transcriptional activation of the mouse P1(450) gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7269–7288. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. J., Kay S. A., Chua N. H. Sequence-specific interactions of a pea nuclear factor with light-responsive elements upstream of the rbcS-3A gene. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2543–2549. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02542.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. J., Yong M. H., Cuozzo M., Kano-Murakami Y., Silverstein P., Chua N. H. Binding site requirements for pea nuclear protein factor GT-1 correlate with sequences required for light-dependent transcriptional activation of the rbcS-3A gene. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4035–4044. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03297.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman L. S., Thompson W. F., Briggs W. R. Different Red Light Requirements for Phytochrome-Induced Accumulation of cab RNA and rbcS RNA. Science. 1984 Dec 21;226(4681):1447–1449. doi: 10.1126/science.226.4681.1447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keith B., Chua N. H. Monocot and dicot pre-mRNAs are processed with different efficiencies in transgenic tobacco. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2419–2425. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04516.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhlemeier C., Strittmatter G., Ward K., Chua N. H. The Pea rbcS-3A Promoter Mediates Light Responsiveness but not Organ Specificity. Plant Cell. 1989 Apr;1(4):471–478. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.4.471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linial M., Gunderson N., Groudine M. Enhanced transcription of c-myc in bursal lymphoma cells requires continuous protein synthesis. Science. 1985 Dec 6;230(4730):1126–1132. doi: 10.1126/science.2999973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lissemore J. L., Quail P. H. Rapid transcriptional regulation by phytochrome of the genes for phytochrome and chlorophyll a/b-binding protein in Avena sativa. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4840–4850. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy F., Boutry M., Hsu M. Y., Wong M., Chua N. H. The 5'-proximal region of the wheat Cab-1 gene contains a 268-bp enhancer-like sequence for phytochrome response. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2537–2542. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02541.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. P., Utz P. J., Durand D. B., Toole J. J., Emmel E. A., Crabtree G. R. Identification of a putative regulator of early T cell activation genes. Science. 1988 Jul 8;241(4862):202–205. doi: 10.1126/science.3260404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson J., VAN Montagu M., Herrera-Estrella L. Photosynthesis-associated gene families: differences in response to tissue-specific and environmental factors. Science. 1986 Jul 4;233(4759):34–38. doi: 10.1126/science.233.4759.34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sive H. L., Heintz N., Roeder R. G. Regulation of human histone gene expression during the HeLa cell cycle requires protein synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2723–2734. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theologis A., Huynh T. V., Davis R. W. Rapid induction of specific mRNAs by auxin in pea epicotyl tissue. J Mol Biol. 1985 May 5;183(1):53–68. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90280-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timko M. P., Kausch A. P., Castresana C., Fassler J., Herrera-Estrella L., Van den Broeck G., Van Montagu M., Schell J., Cashmore A. R. Light regulation of plant gene expression by an upstream enhancer-like element. Nature. 1985 Dec 12;318(6046):579–582. doi: 10.1038/318579a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]