Abstract
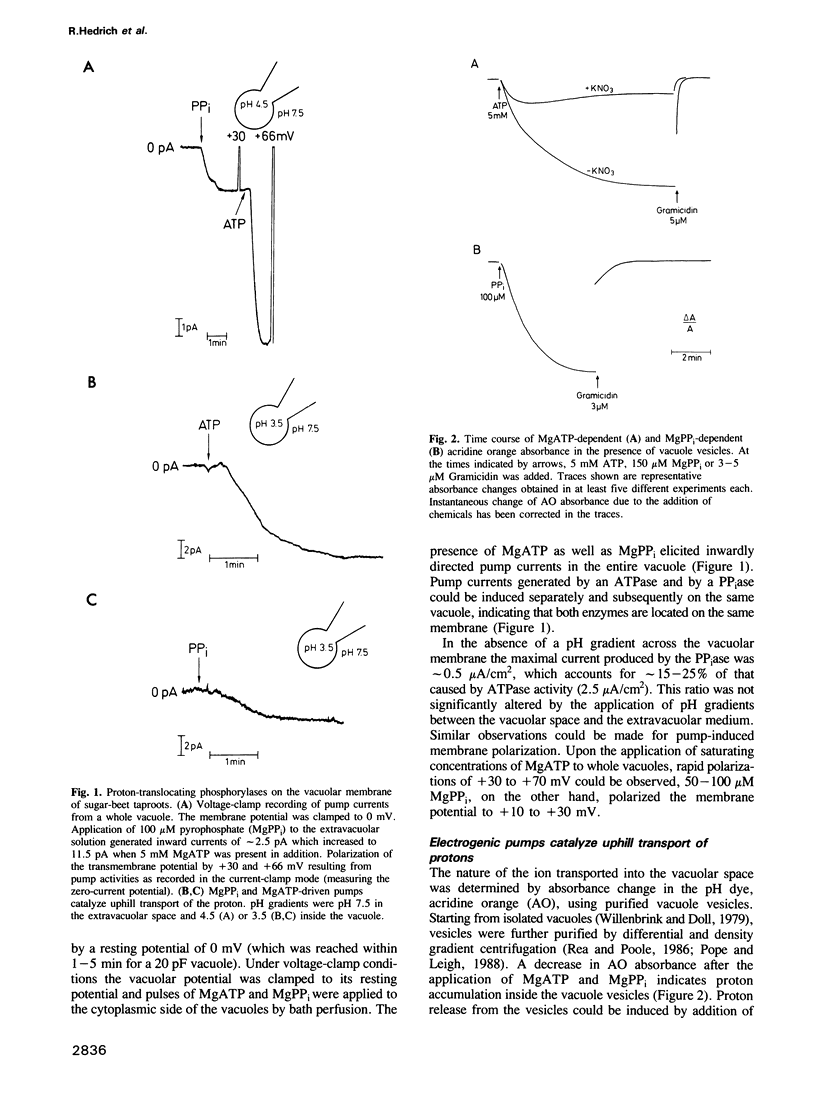
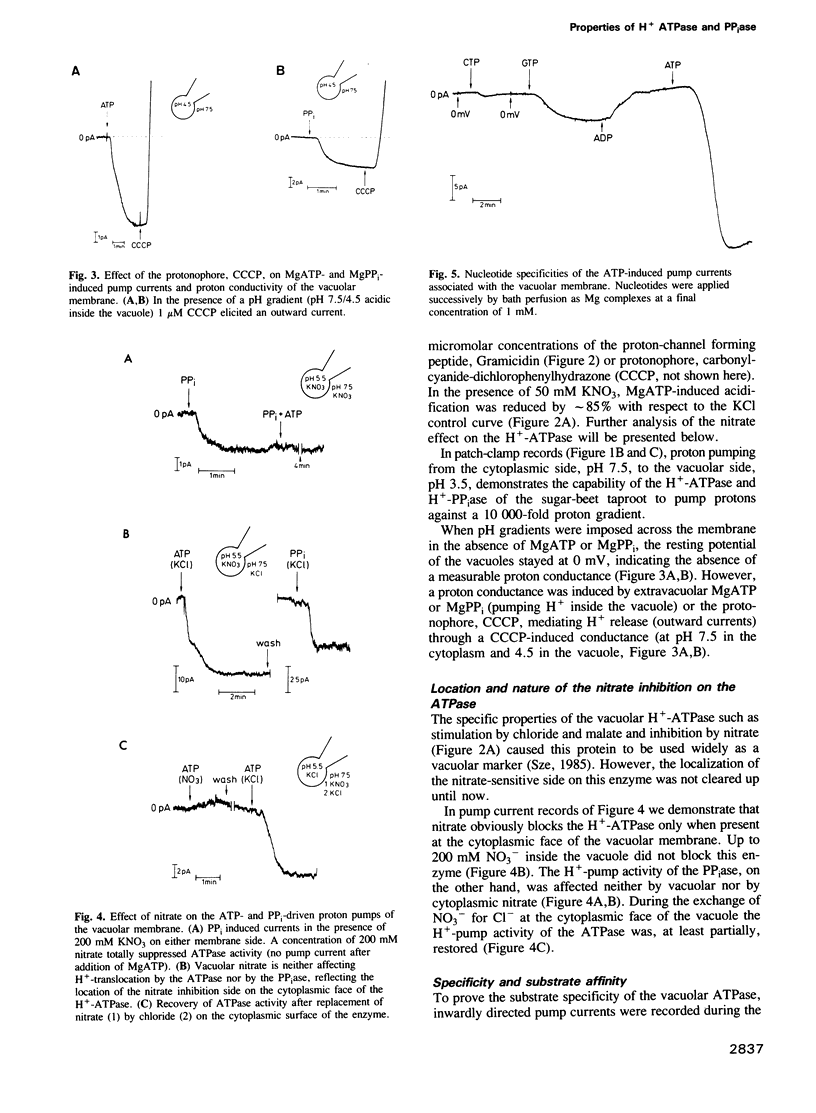
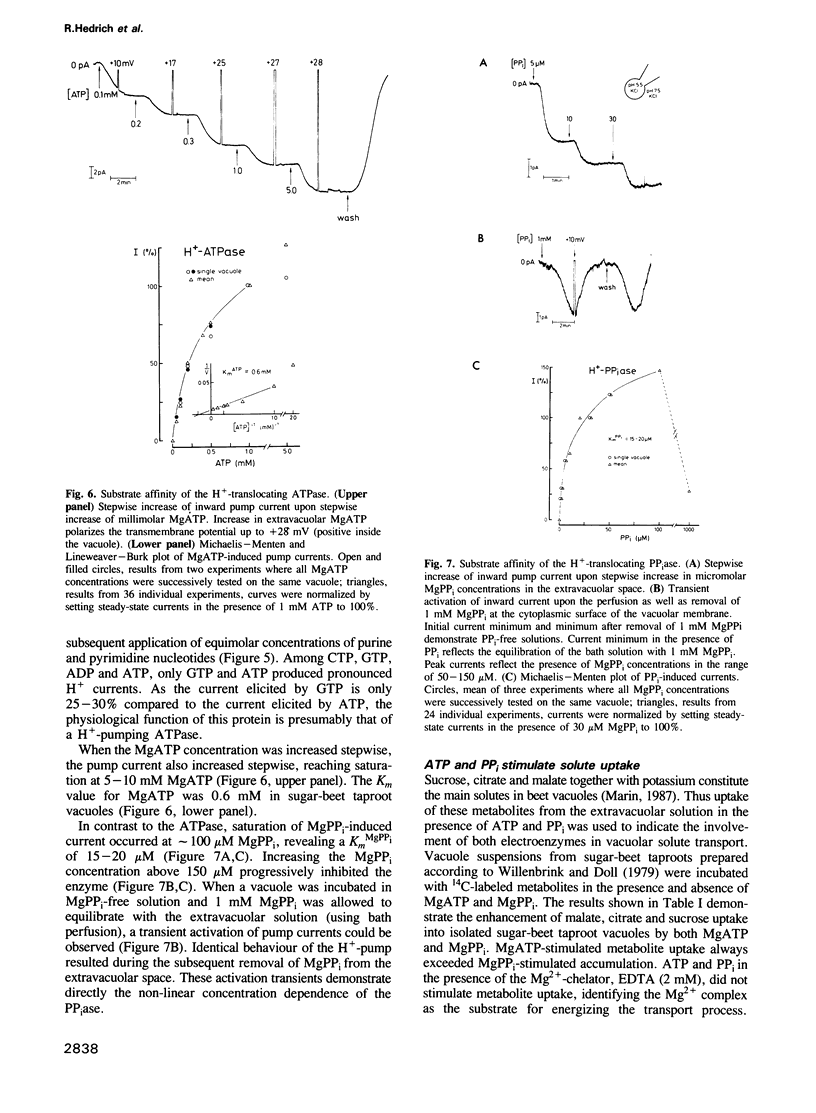
The electrical properties of the vacuolar-lysosomal H+ pumps were studied by direct measurement of the pump currents using the whole-cell configuration of the patch-clamp technique. Both pumps, the proton-translocating ATPase and pyrophosphatase, when activated by MgATP or inorganic Mg pyrophosphate (MgPP(i)), transport protons into the vacuole and polarize the membrane potential (positive inside the vacuole). Accumulation of protons in the lumen of vacuole vesicles was monitored by absorbance changes of the pH probe, acridine orange. The electrochemical gradient provided by both the ATPase and pyrophosphatase stimulates effectively the uptake of various metabolites such as malate, citrate and sucrose. The maximal current density produced by the ATPase was about 2.5 microA/cm2 and about 0.5 microA/cm2 for the pyrophosphatase. K(m)ATP was 0.6 mM; K(m)PPi was 15-20 microM with progressive inhibition above 150 microM. At a cytoplasmic pH of 7.5 both enzymes were capable of pumping protons against a 10,000-fold concentration gradient (pH 3.5 inside the vacuole). Proton current produced by the ATPase was blocked reversibly by extravacuolar NO(3)- only.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Al-Awqati Q. Proton-translocating ATPases. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:179–199. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.001143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentrup F. W., Gogarten-Boekels M., Hoffmann B., Gogarten J. P., Baumann C. ATP-dependent acidification and tonoplast hyperpolarization in isolated vacuoles from green suspension cells of Chenopodium rubrum L. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2431–2433. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadsby D. C., Kimura J., Noma A. Voltage dependence of Na/K pump current in isolated heart cells. Nature. 1985 May 2;315(6014):63–65. doi: 10.1038/315063a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhardt R., Stitt M., Heldt H. W. Subcellular Metabolite Levels in Spinach Leaves : Regulation of Sucrose Synthesis during Diurnal Alterations in Photosynthetic Partitioning. Plant Physiol. 1987 Feb;83(2):399–407. doi: 10.1104/pp.83.2.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harikumar P., Reeves J. P. The lysosomal proton pump is electrogenic. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10403–10410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrich R., Kurkdjian A. Characterization of an anion-permeable channel from sugar beet vacuoles: effect of inhibitors. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3661–3666. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03247.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafaire A. V., Schwarz W. Voltage dependence of the rheogenic Na+/K+ ATPase in the membrane of oocytes of Xenopus laevis. J Membr Biol. 1986;91(1):43–51. doi: 10.1007/BF01870213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson N. Structure, Function, and Evolution of Proton-ATPases. Plant Physiol. 1988 Jan;86(1):1–3. doi: 10.1104/pp.86.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson N., Taiz L. The evolution of H+-ATPases. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Mar;14(3):113–116. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90134-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasi-Caldogno F., Pugliarello M. C., De Michelis M. I. Electrogenic transport of protons driven by the plasma membrane ATPase in membrane vesicles from radish : biochemical characterization. Plant Physiol. 1985 Jan;77(1):200–205. doi: 10.1104/pp.77.1.200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rea P. A., Poole R. J. Chromatographic resolution of h-translocating pyrophosphatase from h-translocating ATPase of higher plant tonoplast. Plant Physiol. 1986 May;81(1):126–129. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.1.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder J. I. K+ transport properties of K+ channels in the plasma membrane of Vicia faba guard cells. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Nov;92(5):667–683. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.5.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuurmans Stekhoven F., Bonting S. L. Transport adenosine triphosphatases: properties and functions. Physiol Rev. 1981 Jan;61(1):1–76. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano E. E., Zeiger E., Hagiwara S. Red light stimulates an electrogenic proton pump in Vicia guard cell protoplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):436–440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitt M., Lilley R. M., Heldt H. W. Adenine nucleotide levels in the cytosol, chloroplasts, and mitochondria of wheat leaf protoplasts. Plant Physiol. 1982 Oct;70(4):971–977. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.4.971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



