Abstract
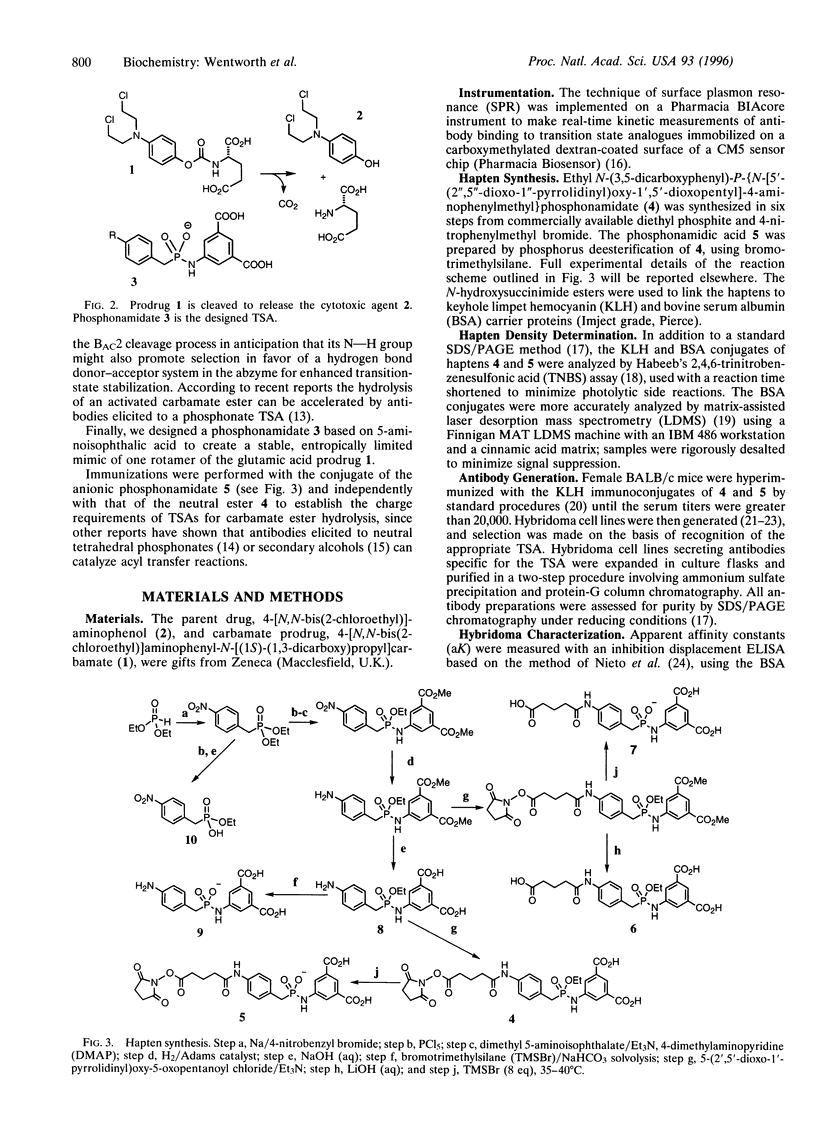
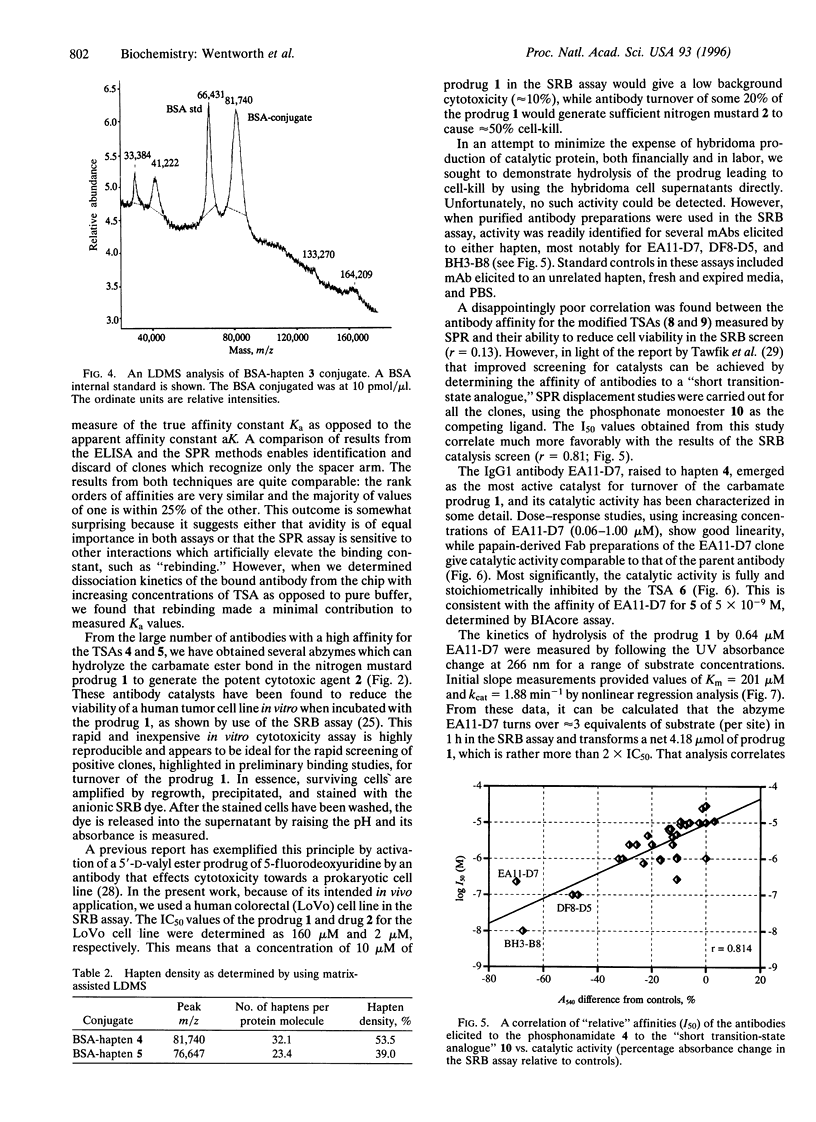
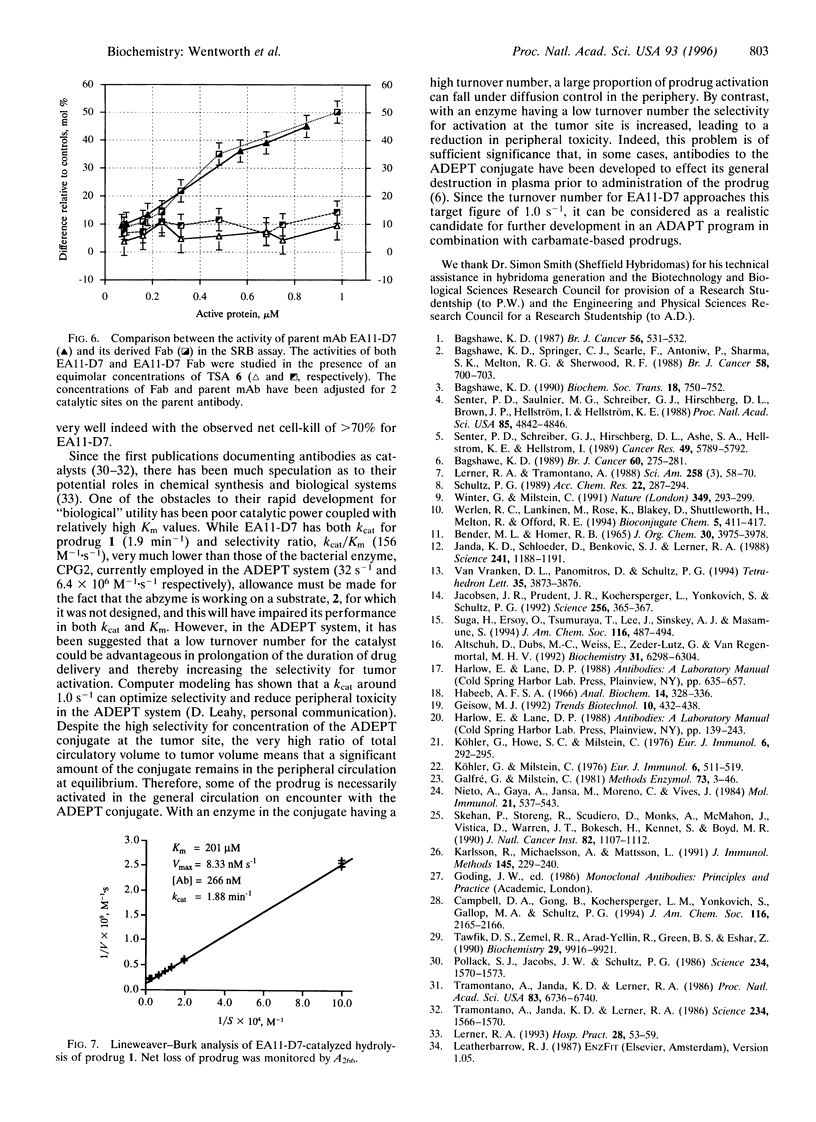
Antibody-directed enzyme prodrug therapy, ADEPT, is a recent approach to targeted cancer chemotherapy intended to diminish the nonspecific toxicity associated with many commonly used chemotherapeutic agents. Most ADEPT systems incorporate a bacterial enzyme, and thus their potential is reduced because of the immunogenicity of that component of the conjugate. This limitation can be circumvented by the use of a catalytic antibody, which can be "humanized," in place of the bacterial enzyme catalyst. We have explored the scope of such antibody-directed "abzyme" prodrug therapy, ADAPT, to evaluate the potential for a repeatable targeted cancer chemotherapy. We report the production of a catalytic antibody that can hydrolyze the carbamate prodrug 4-[N,N-bis(2-chloroethyl)]aminophenyl-N-[(1S)-(1,3- dicarboxy)propyl]carbamate (1) to generate the corresponding cytotoxic nitrogen mustard (Km = 201 microM, kcat = 1.88 min-1). In vitro studies with this abzyme, EA11-D7, and prodrug 1 lead to a marked reduction in viability of cultured human colonic carcinoma (LoVo) cells relative to appropriate controls. In addition, we have found a good correlation between antibody catalysis as determined by this cytotoxicity assay in vitro and competitive binding studies of candidate abzymes to the truncated transition-state analogue ethyl 4-nitrophenylmethylphosphonate. This cell-kill assay heralds a general approach to direct and rapid screening of antibody libraries for catalysts.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschuh D., Dubs M. C., Weiss E., Zeder-Lutz G., Van Regenmortel M. H. Determination of kinetic constants for the interaction between a monoclonal antibody and peptides using surface plasmon resonance. Biochemistry. 1992 Jul 14;31(27):6298–6304. doi: 10.1021/bi00142a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagshawe K. D. Antibody directed enzymes revive anti-cancer prodrugs concept. Br J Cancer. 1987 Nov;56(5):531–532. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1987.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagshawe K. D. Antibody-directed enzyme/prodrug therapy (ADEPT). Biochem Soc Trans. 1990 Oct;18(5):750–752. doi: 10.1042/bst0180750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagshawe K. D., Springer C. J., Searle F., Antoniw P., Sharma S. K., Melton R. G., Sherwood R. F. A cytotoxic agent can be generated selectively at cancer sites. Br J Cancer. 1988 Dec;58(6):700–703. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1988.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagshawe K. D. The First Bagshawe lecture. Towards generating cytotoxic agents at cancer sites. Br J Cancer. 1989 Sep;60(3):275–281. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1989.270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfrè G., Milstein C. Preparation of monoclonal antibodies: strategies and procedures. Methods Enzymol. 1981;73(Pt B):3–46. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)73054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisow M. J. Mass measurement at high molecular weight--new tools for biotechnologists. Trends Biotechnol. 1992 Dec;10(12):432–441. doi: 10.1016/0167-7799(92)90293-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habeeb A. F. Determination of free amino groups in proteins by trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid. Anal Biochem. 1966 Mar;14(3):328–336. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90275-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen J. R., Prudent J. R., Kochersperger L., Yonkovich S., Schultz P. G. An efficient antibody-catalyzed aminoacylation reaction. Science. 1992 Apr 17;256(5055):365–367. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5055.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janda K. D., Schloeder D., Benkovic S. J., Lerner R. A. Induction of an antibody that catalyzes the hydrolysis of an amide bond. Science. 1988 Sep 2;241(4870):1188–1191. doi: 10.1126/science.3413482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson R., Michaelsson A., Mattsson L. Kinetic analysis of monoclonal antibody-antigen interactions with a new biosensor based analytical system. J Immunol Methods. 1991 Dec 15;145(1-2):229–240. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90331-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Howe S. C., Milstein C. Fusion between immunoglobulin-secreting and nonsecreting myeloma cell lines. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Apr;6(4):292–295. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Derivation of specific antibody-producing tissue culture and tumor lines by cell fusion. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Jul;6(7):511–519. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner R. A. Catalytic antibodies: the concept and the promise. Hosp Pract (Off Ed) 1993 Jul 15;28(7):53–59. doi: 10.1080/21548331.1993.11442820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner R. A., Tramontano A. Catalytic antibodies. Sci Am. 1988 Mar;258(3):58-60, 65-70. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0388-58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieto A., Gaya A., Jansa M., Moreno C., Vives J. Direct measurement of antibody affinity distribution by hapten-inhibition enzyme immunoassay. Mol Immunol. 1984 Jun;21(6):537–543. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(84)90070-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack S. J., Jacobs J. W., Schultz P. G. Selective chemical catalysis by an antibody. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1570–1573. doi: 10.1126/science.3787262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senter P. D., Saulnier M. G., Schreiber G. J., Hirschberg D. L., Brown J. P., Hellström I., Hellström K. E. Anti-tumor effects of antibody-alkaline phosphatase conjugates in combination with etoposide phosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4842–4846. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senter P. D., Schreiber G. J., Hirschberg D. L., Ashe S. A., Hellström K. E., Hellström I. Enhancement of the in vitro and in vivo antitumor activities of phosphorylated mitomycin C and etoposide derivatives by monoclonal antibody-alkaline phosphatase conjugates. Cancer Res. 1989 Nov 1;49(21):5789–5792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skehan P., Storeng R., Scudiero D., Monks A., McMahon J., Vistica D., Warren J. T., Bokesch H., Kenney S., Boyd M. R. New colorimetric cytotoxicity assay for anticancer-drug screening. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1990 Jul 4;82(13):1107–1112. doi: 10.1093/jnci/82.13.1107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tawfik D. S., Zemel R. R., Arad-Yellin R., Green B. S., Eshhar Z. Simple method for selecting catalytic monoclonal antibodies that exhibit turnover and specificity. Biochemistry. 1990 Oct 23;29(42):9916–9921. doi: 10.1021/bi00494a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tramontano A., Janda K. D., Lerner R. A. Catalytic antibodies. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1566–1570. doi: 10.1126/science.3787261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tramontano A., Janda K. D., Lerner R. A. Chemical reactivity at an antibody binding site elicited by mechanistic design of a synthetic antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6736–6740. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werlen R. C., Lankinen M., Rose K., Blakey D., Shuttleworth H., Melton R., Offord R. E. Site-specific conjugation of an enzyme and an antibody fragment. Bioconjug Chem. 1994 Sep-Oct;5(5):411–417. doi: 10.1021/bc00029a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter G., Milstein C. Man-made antibodies. Nature. 1991 Jan 24;349(6307):293–299. doi: 10.1038/349293a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]