Abstract
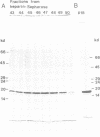
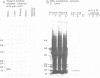
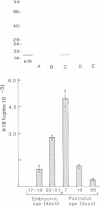
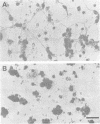
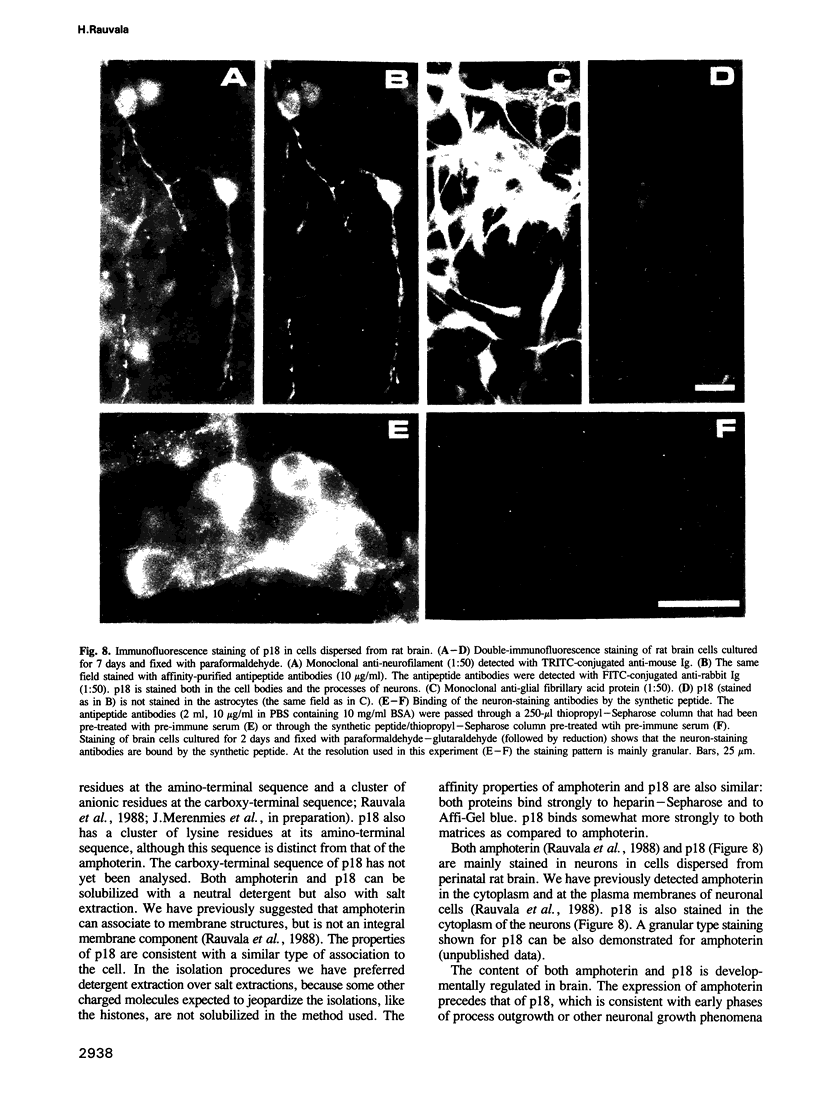
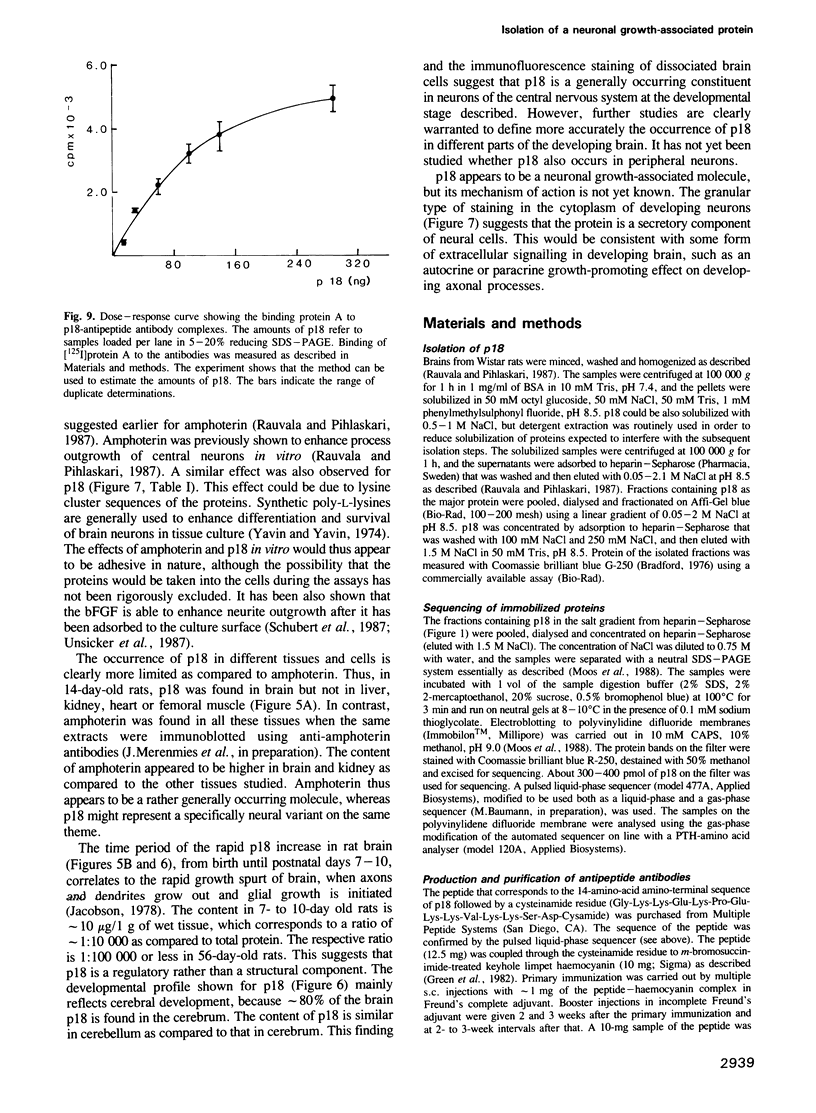
An 18-kd heparin-binding protein (p18) was isolated from perinatal rat brain. Although the protein closely resembles the fibroblast growth factors in its strong binding to heparin and in its apparent molecular mass, it has a distinct structure. This was concluded from the amino-terminal sequence analysis that identified a unique structure containing a cluster of lysine residues. Antipeptide antibodies were raised in rabbits according to the sequence analysis and affinity purified using a synthetic peptide. The antibodies were shown to bind specifically to p18, which was immunochemically distinct from the basic fibroblast growth factor. The antipeptide antibodies detected p18 in brain but not in liver, kidney, heart or skeletal muscle. The content of the protein was shown to undergo a remarkable developmental change corresponding to the time period of rapid sprouting of axons and dendrites in brain. The content of p18 was rapidly increased at the time of birth until the postnatal age of approximately 1 week, after which it was decreased to values less than 10% in young adults as compared to the content found in perinatal rats. p18 also enhanced neurite outgrowth in brain neurons in vitro. The protein was stained in neurons in cells dispersed from perinatal brain. The properties of p18 suggest that it has a role in the growth and maturation of brain.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg D. K. New neuronal growth factors. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1984;7:149–170. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.07.030184.001053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delli Bovi P., Curatola A. M., Kern F. G., Greco A., Ittmann M., Basilico C. An oncogene isolated by transfection of Kaposi's sarcoma DNA encodes a growth factor that is a member of the FGF family. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):729–737. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90331-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E. Enzyme immunoassay ELISA and EMIT. Methods Enzymol. 1980;70(A):419–439. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)70067-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esch F., Baird A., Ling N., Ueno N., Hill F., Denoroy L., Klepper R., Gospodarowicz D., Böhlen P., Guillemin R. Primary structure of bovine pituitary basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF) and comparison with the amino-terminal sequence of bovine brain acidic FGF. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6507–6511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Bialecki H., Greenburg G. Purification of the fibroblast growth factor activity from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 25;253(10):3736–3743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N., Alexander H., Olson A., Alexander S., Shinnick T. M., Sutcliffe J. G., Lerner R. A. Immunogenic structure of the influenza virus hemagglutinin. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90202-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klagsbrun M., Shing Y. Heparin affinity of anionic and cationic capillary endothelial cell growth factors: analysis of hypothalamus-derived growth factors and fibroblast growth factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):805–809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klagsbrun M., Smith S., Sullivan R., Shing Y., Davidson S., Smith J. A., Sasse J. Multiple forms of basic fibroblast growth factor: amino-terminal cleavages by tumor cell- and brain cell-derived acid proteinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1839–1843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moos M., Jr, Nguyen N. Y., Liu T. Y. Reproducible high yield sequencing of proteins electrophoretically separated and transferred to an inert support. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6005–6008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscatelli D., Joseph-Silverstein J., Manejias R., Rifkin D. B. Mr 25,000 heparin-binding protein from guinea pig brain is a high molecular weight form of basic fibroblast growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5778–5782. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse A. G., Polak J. M. Bifunctional reagents as vapour- and liquid-phase fixatives for immunohistochemistry. Histochem J. 1975 Mar;7(2):179–186. doi: 10.1007/BF01004561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauvala H., Merenmies J., Pihlaskari R., Korkolainen M., Huhtala M. L., Panula P. The adhesive and neurite-promoting molecule p30: analysis of the amino-terminal sequence and production of antipeptide antibodies that detect p30 at the surface of neuroblastoma cells and of brain neurons. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2293–2305. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauvala H., Pihlaskari R. Isolation and some characteristics of an adhesive factor of brain that enhances neurite outgrowth in central neurons. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16625–16635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert D., Ling N., Baird A. Multiple influences of a heparin-binding growth factor on neuronal development. J Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;104(3):635–643. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.3.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer A., Brewer M. T., Thompson R. C., Moscatelli D., Presta M., Rifkin D. B. A form of human basic fibroblast growth factor with an extended amino terminus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Apr 29;144(2):543–550. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80001-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoenen H., Edgar D. Neurotrophic factors. Science. 1985 Jul 19;229(4710):238–242. doi: 10.1126/science.2409599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unsicker K., Reichert-Preibsch H., Schmidt R., Pettmann B., Labourdette G., Sensenbrenner M. Astroglial and fibroblast growth factors have neurotrophic functions for cultured peripheral and central nervous system neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5459–5463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanier M. T., Holm M., Ohman R., Svennerholm L. Developmental profiles of gangliosides in human and rat brain. J Neurochem. 1971 Apr;18(4):581–592. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb11988.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yavin E., Yavin Z. Attachment and culture of dissociated cells from rat embryo cerebral hemispheres on polylysine-coated surface. J Cell Biol. 1974 Aug;62(2):540–546. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.2.540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida T., Miyagawa K., Odagiri H., Sakamoto H., Little P. F., Terada M., Sugimura T. Genomic sequence of hst, a transforming gene encoding a protein homologous to fibroblast growth factors and the int-2-encoded protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7305–7309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhan X., Bates B., Hu X. G., Goldfarb M. The human FGF-5 oncogene encodes a novel protein related to fibroblast growth factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3487–3495. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]