Abstract
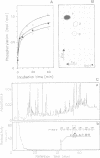
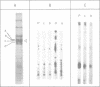
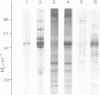
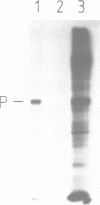
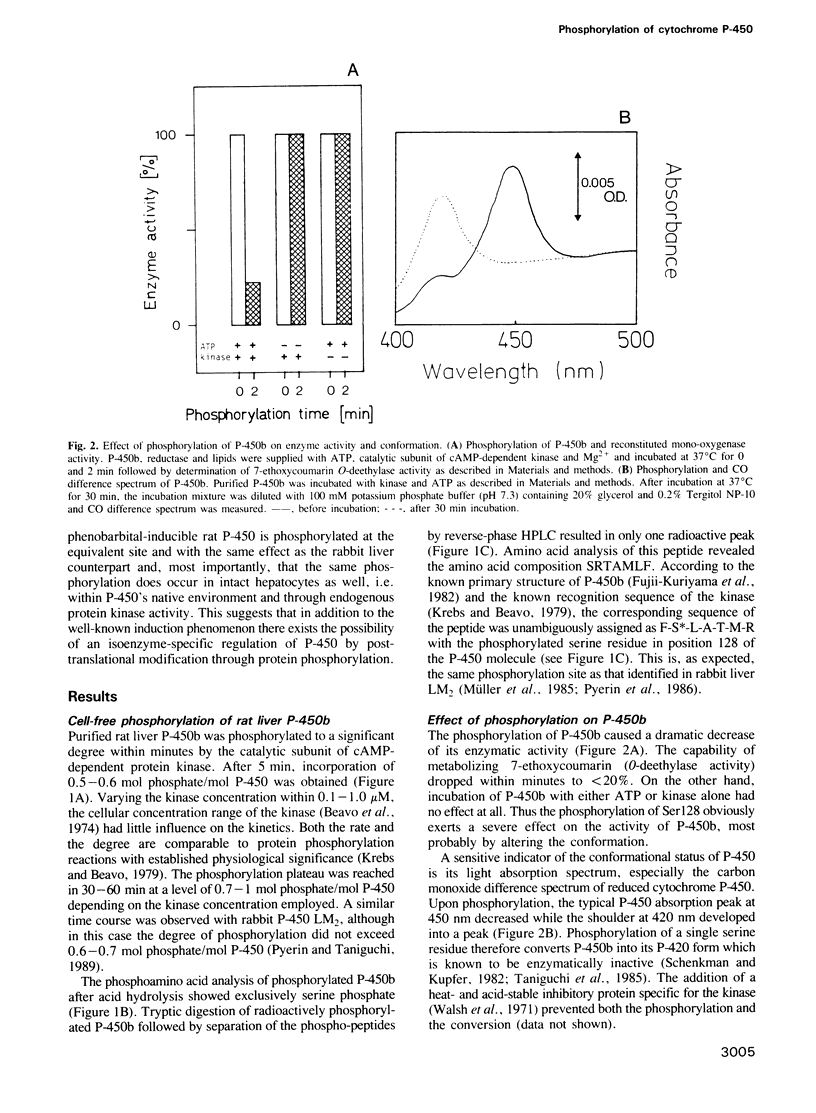
The major phenobarbital-inducible cytochrome P-450 purified from rat liver, a member of family II of the cytochrome P-450 gene superfamily, is rapidly phosphorylated by cAMP-dependent protein kinase. The phosphorylation reaches greater than 0.5 mol phosphate/mol P-450 after 5 min and is accompanied by a decrease in enzyme activity. The serine residue in position 128 was shown to be the sole phosphorylation site and a conformational change of the protein was indicated by a shift of the carbon monoxide difference spectrum of the reduced cytochrome from 450 to 420 nm. Comparison of amino acid sequences of various cytochrome P-450 families revealed a highly conserved arginine residue in the immediate vicinity of the phosphorylated serine residue which constitutes the kinase recognition sequence. It also revealed that only the members of the cytochrome P-450 family II carry this kinase recognition sequence. To find out whether this phosphorylation also occurs in vivo, the exchangeable phosphate pool of intact hepatocytes derived from phenobarbital-pretreated rats was labeled with 32Pi followed by an incubation of the cells with the membrane-permeating dibutyryl-cAMP or with the adenylate cyclase stimulator glucagon to activate endogenous kinase. As a result, a microsomal polypeptide with the same electrophoretic mobility as cytochrome P-450 became strongly labeled. Peptide mapping and immunoprecipitation with monospecific antibodies identified this protein as the major phenobarbital-inducible cytochrome P-450. It becomes phosphorylated at the same serine residues as in the cell-free phosphorylation.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beavo J. A., Bechtel P. J., Krebs E. G. Activation of protein kinase by physiological concentrations of cyclic AMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3580–3583. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cánepa E. T., Llambías E. B., Grinstein M. Effect of glucose on induction of delta-aminolevulinic acid synthase, ferrochelatase and cytochrome P-450 hemoproteins in isolated rat hepatocytes by phenobarbital and lead. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Aug 16;841(2):186–194. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(85)90020-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalet C., Clair P., Daujat M., Fort P., Blanchard J. M., Maurel P. Complete sequence of cytochrome P450 3c cDNA and presence of two mRNA species with 3' untranslated regions of different lengths. DNA. 1988 Jan-Feb;7(1):39–46. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England P. J., Walsh D. A. A rapid method for the measurement of [gamma-32P]ATP specific radioactivity in tissue extracts and its application to the study of 32Pi uptake in perfused rat heart. Anal Biochem. 1976 Oct;75(2):429–435. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90096-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOUTS J. R. Interaction of drugs and hepatic microsomes. Fed Proc. 1962 Nov-Dec;21:1107–1111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Mizukami Y., Kawajiri K., Sogawa K., Muramatsu M. Primary structure of a cytochrome P-450: coding nucleotide sequence of phenobarbital-inducible cytochrome P-450 cDNA from rat liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2793–2797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funae Y., Imaoka S. Simultaneous purification of multiple forms of rat liver microsomal cytochrome P-450 by high-performance liquid chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Oct 17;842(2-3):119–132. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(85)90193-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J., Kimura S., Song B. J., Pastewka J., Gelboin H. V., Hardwick J. P. Sequence of two related P-450 mRNAs transcriptionally increased during rat development. An R.dre.1 sequence occupies the complete 3' untranslated region of a liver mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 15;261(23):10667–10672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J., Matsunaga T., Nagata K., Meyer U. A., Nebert D. W., Pastewka J., Kozak C. A., Gillette J., Gelboin H. V., Hardwick J. P. Debrisoquine 4-hydroxylase: characterization of a new P450 gene subfamily, regulation, chromosomal mapping, and molecular analysis of the DA rat polymorphism. DNA. 1987 Apr;6(2):149–161. doi: 10.1089/dna.1987.6.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoh O. An improved algorithm for matching biological sequences. J Mol Biol. 1982 Dec 15;162(3):705–708. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90398-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haniu M., Armes L. G., Yasunobu K. T., Shastry B. A., Gunsalus I. C. Amino acid sequence of the Pseudomonas putida cytochrome P-450. II. Cyanogen bromide peptides, acid cleavage peptides, and the complete sequence. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12664–12671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardwick J. P., Song B. J., Huberman E., Gonzalez F. J. Isolation, complementary DNA sequence, and regulation of rat hepatic lauric acid omega-hydroxylase (cytochrome P-450LA omega). Identification of a new cytochrome P-450 gene family. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):801–810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemann F. S., Ozols J. The covalent structure of rabbit phenobarbital-induced cytochrome P-450. Partial amino acid sequence and order of cyanogen bromide peptides. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14988–14999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi Y., Yoshioka H., Yamane M., Gotoh O., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Complete nucleotide sequence of two steroid 21-hydroxylase genes tandemly arranged in human chromosome: a pseudogene and a genuine gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2841–2845. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutterer F., Dressler K., Greim H., Czygan P., Schaffner F., Popper H. Effect of cyclic AMP on the phenobarbital induced increase in cytochrome P-450 and hypertrophy of the endoplasmic reticulum of the rat liver. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1975;58(00):117–126. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-9026-2_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalb V. F., Woods C. W., Turi T. G., Dey C. R., Sutter T. R., Loper J. C. Primary structure of the P450 lanosterol demethylase gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. DNA. 1987 Dec;6(6):529–537. doi: 10.1089/dna.1987.6.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato R., Gillette J. R. Sex differences in the effects of abnormal physiological states on the metabolism of drugs by rat liver microsomes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1965 Nov;150(2):285–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann W. K., Ririe D. G., Kaufman D. G. Phenobarbital-dependent proliferation of putative initiated rat hepatocytes. Carcinogenesis. 1988 May;9(5):779–782. doi: 10.1093/carcin/9.5.779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khani S. C., Zaphiropoulos P. G., Fujita V. S., Porter T. D., Koop D. R., Coon M. J. cDNA and derived amino acid sequence of ethanol-inducible rabbit liver cytochrome P-450 isozyme 3a (P-450ALC). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):638–642. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch J. A., Waxman D. J. Posttranslational modification of hepatic cytochrome P-450. Phosphorylation of phenobarbital-inducible P-450 forms PB-4 (IIB1) and PB-5 (IIB2) in isolated rat hepatocytes and in vivo. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 18;28(8):3145–3152. doi: 10.1021/bi00434a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs E. G., Beavo J. A. Phosphorylation-dephosphorylation of enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:923–959. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kübler D., Gagelmann M., Pyerin W., Kinzel V. Isolation of the catalytic subunits of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinases from different mammalian tissues on the basis of charge differences of their subunits. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1979 Oct;360(10):1421–1431. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1979.360.2.1421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kübler D., Pyerin W., Kinzel V. Protein kinase activity and substrates at the surface of intact HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 10;257(1):322–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubet R. A., Nims R. W., Mayer R. T., Cameron J. W., Schechtman L. M. Measurement of cytochrome P-450 dependent dealkylation of alkoxyphenoxazones in hepatic S9s and hepatocyte homogenates: effects of dicumarol. Mutat Res. 1985 Mar;142(3):127–131. doi: 10.1016/0165-7992(85)90052-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morohashi K., Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Okada Y., Sogawa K., Hirose T., Inayama S., Omura T. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of cDNA for mRNA of mitochondrial cytochrome P-450(SCC) of bovine adrenal cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4647–4651. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Schmidt W. E., Stier A. The site of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase catalyzed phosphorylation of cytochrome P-450 LM2. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jul 22;187(1):21–24. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81205-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata K., Matsunaga T., Gillette J., Gelboin H. V., Gonzalez F. J. Rat testosterone 7 alpha-hydroxylase. Isolation, sequence, and expression of cDNA and its developmental regulation and induction by 3-methylcholanthrene. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 25;262(6):2787–2793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Gonzalez F. J. P450 genes: structure, evolution, and regulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:945–993. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Nelson D. R., Adesnik M., Coon M. J., Estabrook R. W., Gonzalez F. J., Guengerich F. P., Gunsalus I. C., Johnson E. F., Kemper B. The P450 superfamily: updated listing of all genes and recommended nomenclature for the chromosomal loci. DNA. 1989 Jan-Feb;8(1):1–13. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1989.8.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman S. B., Wunsch C. D. A general method applicable to the search for similarities in the amino acid sequence of two proteins. J Mol Biol. 1970 Mar;48(3):443–453. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negishi M., Jensen N. M., Garcia G. S., Nebert D. W. Structural gene products of the murine Ah complex. Differences in ontogenesis and glucosamine incorporation between liver microsomal cytochromes P1-450 and P-448 induced by polycyclic aromatic compounds. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Apr;115(3):585–594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OMURA T., SATO R. THE CARBON MONOXIDE-BINDING PIGMENT OF LIVER MICROSOMES. I. EVIDENCE FOR ITS HEMOPROTEIN NATURE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jul;239:2370–2378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozols J., Heinemann F. S., Johnson E. F. The complete amino acid sequence of a constitutive form of liver microsomal cytochrome P-450. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5427–5434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyerin W., Gagelmann M., Kübler D., Kinzel V. Catalytic subunit of adenosine cyclic 2',5'monophosphate-dependent protein kinase from rat muscle: basic properties and factors influencing the activity. Z Naturforsch C. 1979 Dec;34(12):1186–1194. doi: 10.1515/znc-1979-1217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyerin W., Marx M., Taniguchi H. Phosphorylation of microsome-bound cytochrome P-450 LM2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jan 29;134(2):461–468. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80443-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyerin W., Taniguchi H., Horn F., Oesch F., Amelizad Z., Friedberg T., Wolf C. R. Isoenzyme-specific phosphorylation of cytochromes P-450 and other drug metabolizing enzymes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Feb 13;142(3):885–892. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91496-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyerin W., Taniguchi H., Stier A., Oesch F., Wolf C. R. Phosphorylation of rabbit liver cytochrome P-450 LM2 and its effect on monooxygenase activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 31;122(2):620–626. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80078-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyerin W., Wolf C. R., Kinzel V., Kübler D., Oesch F. Phosphorylation of cytochrome-P-450-dependent monooxygenase components. Carcinogenesis. 1983;4(5):573–576. doi: 10.1093/carcin/4.5.573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W. E., Simrell C., Oppelt W. W. Sex-dependent effects of cyclic AMP on the hepatic mixed function oxidase system. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1973 Mar;5(2):319–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumruen K., Pool B. L. Metabolic activation capabilities of S9 and hepatocytes from uninduced rats to convert carcinogenic N-nitrosamines to mutagens. Mutat Res. 1984 Jun-Jul;140(2-3):147–153. doi: 10.1016/0165-7992(84)90060-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadano H., Omura T. Turnover of two drug-inducible forms of microsomal cytochrome P-450 in rat liver. J Biochem. 1983 May;93(5):1375–1383. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson E. R., Evans C. T., Corbin C. J., Powell F. E., Ledesma D. B., Mendelson C. R. Sequencing of cDNA inserts encoding aromatase cytochrome P-450 (P-450AROM). Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1987 Aug;52(3):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(87)90054-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogawa K., Gotoh O., Kawajiri K., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Distinct organization of methylcholanthrene- and phenobarbital-inducible cytochrome P-450 genes in the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5066–5070. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song B. J., Gelboin H. V., Park S. S., Yang C. S., Gonzalez F. J. Complementary DNA and protein sequences of ethanol-inducible rat and human cytochrome P-450s. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of the rat enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 15;261(35):16689–16697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi H., Imai Y., Sato R. Role of the electron transfer system in microsomal drug monooxygenase reaction catalyzed by cytochrome P-450. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Aug 1;232(2):585–596. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90577-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi H., Pyerin W. Separation and purification of component proteins of the cytochrome P-450-dependent microsomal monooxygenase system by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1989 Aug 4;476:299–308. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)93877-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi H., Pyerin W., Stier A. Conversion of hepatic microsomal cytochrome P-450 to P-420 upon phosphorylation by cyclic AMP dependent protein kinase. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985 May 15;34(10):1835–1837. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90657-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umbenhauer D. R., Martin M. V., Lloyd R. S., Guengerich F. P. Cloning and sequence determination of a complementary DNA related to human liver microsomal cytochrome P-450 S-mephenytoin 4-hydroxylase. Biochemistry. 1987 Feb 24;26(4):1094–1099. doi: 10.1021/bi00378a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh D. A., Ashby C. D., Gonzalez C., Calkins D., Fischer E. H. Krebs EG: Purification and characterization of a protein inhibitor of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 10;246(7):1977–1985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner M., Buterbaugh G. G., Blake D. A. Inhibition of hepatic drug metabolism by cyclic 3',5'-adenosine monophosphate. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1972 Mar;3(2):249–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner M., Buterbaugh G. G., Blake D. A. Studies on the mechanism of inhibition of drug biotransformation by cyclic adenine nucleotides. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1972 Jul;4(1):37–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuber M. X., John M. E., Okamura T., Simpson E. R., Waterman M. R. Bovine adrenocortical cytochrome P-450(17 alpha). Regulation of gene expression by ACTH and elucidation of primary sequence. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 15;261(5):2475–2482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]