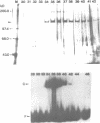
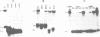Abstract
We have identified a protein, BAF1, which has two oppositely oriented, partially overlapping binding sites within a symmetrical sequence located midway between and upstream of the divergently transcribed YPT1 and TUB2 genes of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The 120 kd BAF1 protein was purified to near homogeneity and used to delineate the two binding sites and to identify apparent protein contact sites by the missing contact technique, methylation interference and by site-directed mutagenesis. The BAF1-recognition sequence contains a conserved TCN7ACG element recently identified at autonomously replicating sequences (ARS) and in the 5' and 3' flanking region of other yeast genes. The symmetrical sequence of the YPT1/TUB2 intergene region seems not to be involved in DNA replication but activates transcription in an orientation-independent fashion.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achstetter T., Emter O., Ehmann C., Wolf D. H. Proteolysis in eukaryotic cells. Identification of multiple proteolytic enzymes in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13334–13343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bram R. J., Kornberg R. D. Specific protein binding to far upstream activating sequences in polymerase II promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):43–47. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunelle A., Schleif R. F. Missing contact probing of DNA-protein interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6673–6676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman A. R., Kimmerly W. J., Rine J., Kornberg R. D. Two DNA-binding factors recognize specific sequences at silencers, upstream activating sequences, autonomously replicating sequences, and telomeres in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):210–225. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diffley J. F., Stillman B. Purification of a yeast protein that binds to origins of DNA replication and a transcriptional silencer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2120–2124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsman J. C., van Heeswijk W. C., Grivell L. A. Identification of two factors which bind to the upstream sequences of a number of nuclear genes coding for mitochondrial proteins and to genetic elements important for cell division in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7287–7301. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S., Civalier C., Tye B. K. Specific interaction between a Saccharomyces cerevisiae protein and a DNA element associated with certain autonomously replicating sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):743–746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallwitz D., Donath C., Sander C. A yeast gene encoding a protein homologous to the human c-has/bas proto-oncogene product. Nature. 1983 Dec 15;306(5944):704–707. doi: 10.1038/306704a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giniger E., Varnum S. M., Ptashne M. Specific DNA binding of GAL4, a positive regulatory protein of yeast. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):767–774. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90336-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goel A., Pearlman R. E. Transposable element-mediated enhancement of gene expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae involves sequence-specific binding of a trans-acting factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2572–2580. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Ptashne M. Fusion of Escherichia coli lacZ to the cytochrome c gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2199–2203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamil K. G., Nam H. G., Fried H. M. Constitutive transcription of yeast ribosomal protein gene TCM1 is promoted by uncommon cis- and trans-acting elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4328–4341. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope I. A., Struhl K. GCN4 protein, synthesized in vitro, binds HIS3 regulatory sequences: implications for general control of amino acid biosynthetic genes in yeast. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):177–188. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90022-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet J., Sentenac A. TUF, the yeast DNA-binding factor specific for UASrpg upstream activating sequences: identification of the protein and its DNA-binding domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3648–3652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M., Davis R. W. Sequences that regulate the divergent GAL1-GAL10 promoter in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1440–1448. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Tjian R. Affinity purification of sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5889–5893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmerly W., Buchman A., Kornberg R., Rine J. Roles of two DNA-binding factors in replication, segregation and transcriptional repression mediated by a yeast silencer. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2241–2253. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03064.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moye-Rowley W. S., Harshman K. D., Parker C. S. Yeast YAP1 encodes a novel form of the jun family of transcriptional activator proteins. Genes Dev. 1989 Mar;3(3):283–292. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.3.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neff N. F., Thomas J. H., Grisafi P., Botstein D. Isolation of the beta-tubulin gene from yeast and demonstration of its essential function in vivo. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90350-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata R., Gilbert W. Contacts between the lac repressor and the thymines in the lac operator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4973–4976. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz P. J., Solomon F., Botstein D. Genetically essential and nonessential alpha-tubulin genes specify functionally interchangeable proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3722–3733. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt H. D., Wagner P., Pfaff E., Gallwitz D. The ras-related YPT1 gene product in yeast: a GTP-binding protein that might be involved in microtubule organization. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):401–412. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90597-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore D., Nasmyth K. Purification and cloning of a DNA binding protein from yeast that binds to both silencer and activator elements. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90095-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore D., Stillman D. J., Brand A. H., Nasmyth K. A. Identification of silencer binding proteins from yeast: possible roles in SIR control and DNA replication. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):461–467. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04776.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Gilbert W. Contacts between Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and an early promoter of phage T7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):122–126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Pelham H. R. Purification and characterization of a heat-shock element binding protein from yeast. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3035–3041. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02609.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweder K. S., Rhode P. R., Campbell J. L. Purification and characterization of proteins that bind to yeast ARSs. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17270–17277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Identification and purification of a polypeptide that binds to the c-fos serum response element. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2711–2717. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02564.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West R. W., Jr, Yocum R. R., Ptashne M. Saccharomyces cerevisiae GAL1-GAL10 divergent promoter region: location and function of the upstream activating sequence UASG. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2467–2478. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Wilson S., Walker B., Dawid I., Paisley T., Zimarino V., Ueda H. Purification and properties of Drosophila heat shock activator protein. Science. 1987 Nov 27;238(4831):1247–1253. doi: 10.1126/science.3685975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]