Abstract
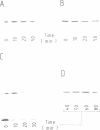
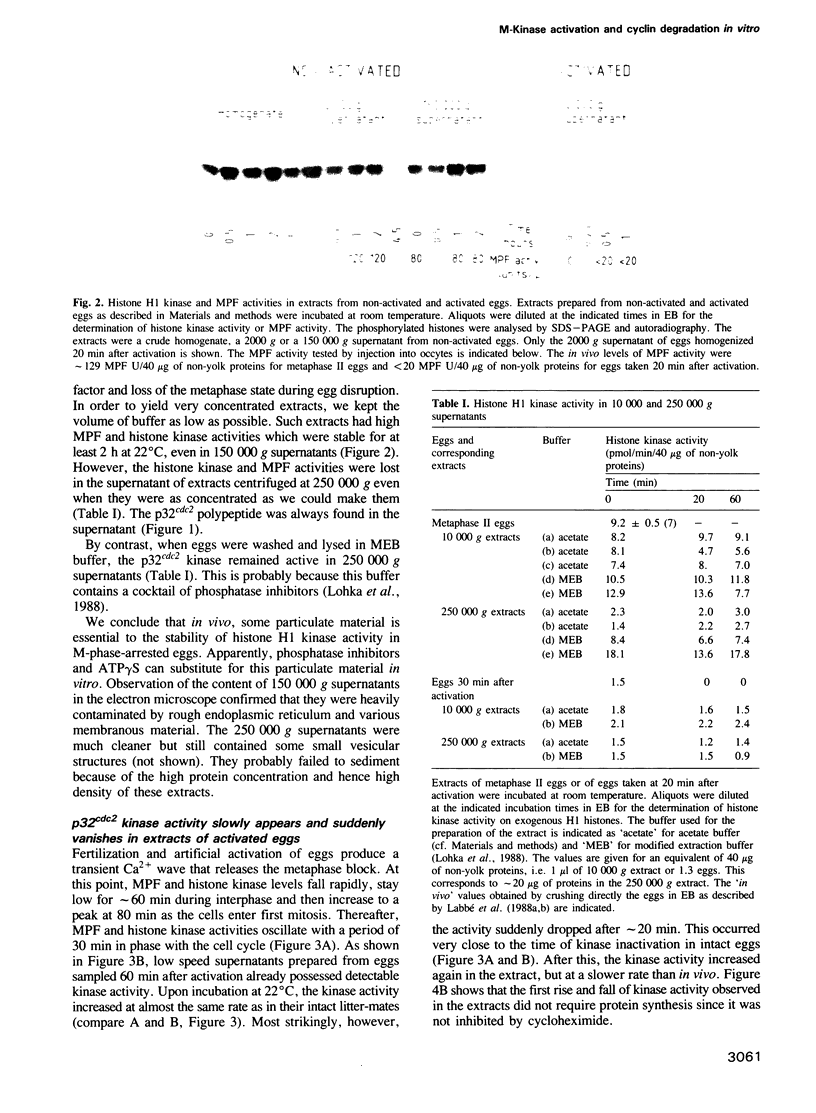
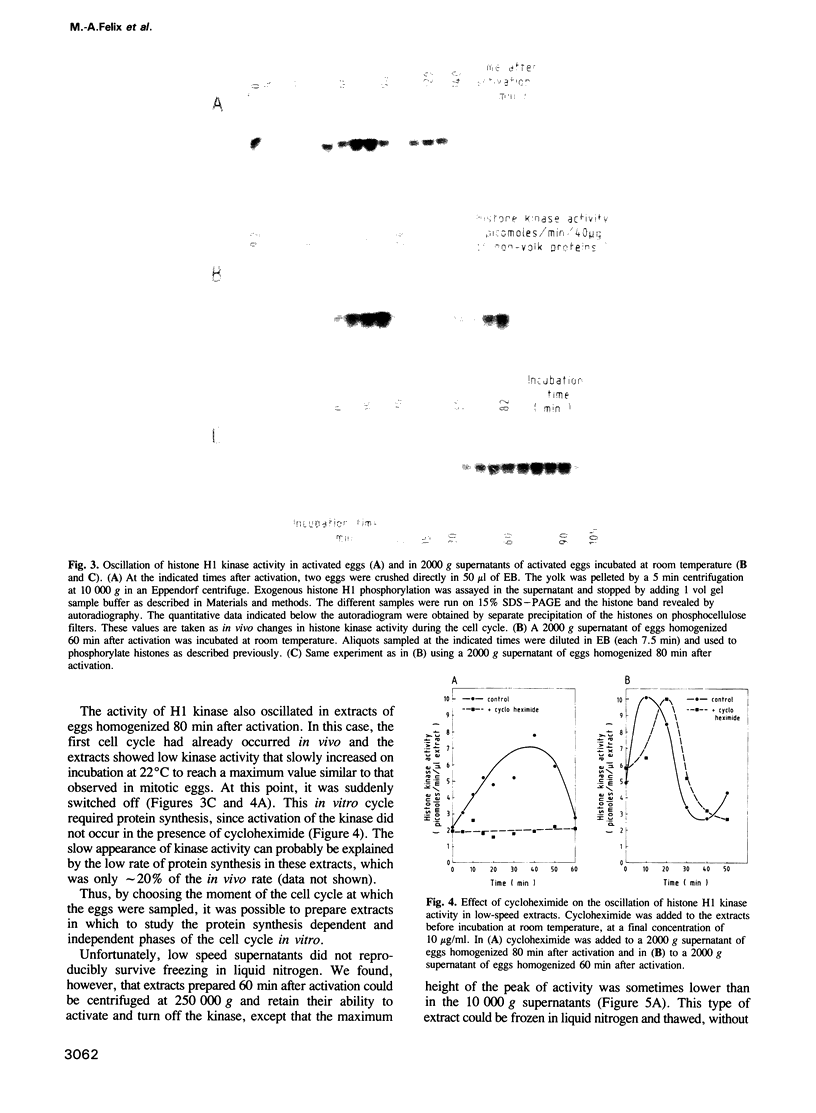
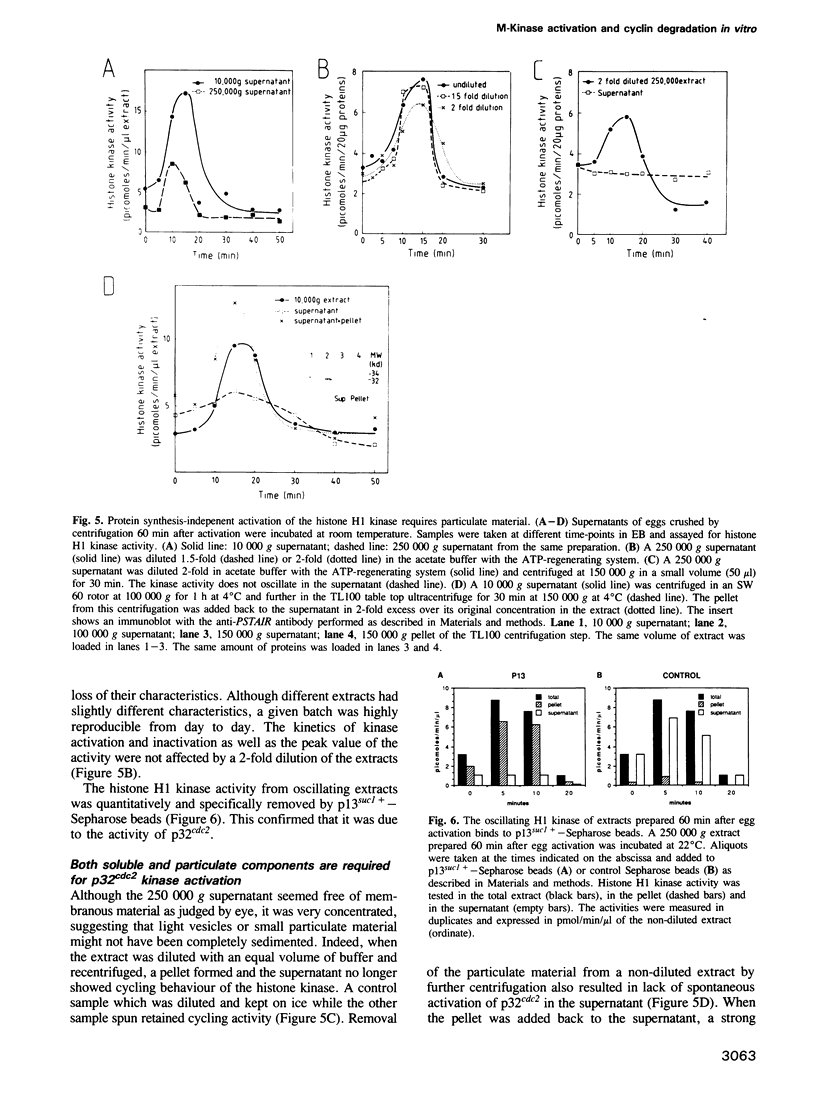
A cell-free extract prepared from activated Xenopus eggs by high-speed centrifugation displays one spontaneous cycle of activation and inactivation of histone H1 kinase and MPF activity that is largely attributable to Xenopus p32cdc2. The timing of the oscillation closely follows that observed in intact eggs, is associated with large changes in endogenous protein phosphorylation and depends entirely on post-translational events. The extract can be fractionated into soluble and particulate material, both of which components are required for the oscillatory behaviour. Kinase activation does not require Mg+ ATP, but its rapid inactivation, which coincides with the destruction of cyclin, is inhibited both by EDTA and the protein kinase inhibitor 6-dimethylaminopurine. This suggests that protein phosphorylation is required for cyclin destruction and kinase inactivation.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ajiro K., Borun T. W., Cohen L. H. Phosphorylation states of different histone 1 subtypes and their relationship to chromatin functions during the HeLa S-3 cell cycle. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 17;20(6):1445–1454. doi: 10.1021/bi00509a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arion D., Meijer L., Brizuela L., Beach D. cdc2 is a component of the M phase-specific histone H1 kinase: evidence for identity with MPF. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):371–378. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90060-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury E. M., Inglis R. J., Matthews H. R., Sarner N. Phosphorylation of very-lysine-rich histone in Physarum polycephalum. Correlation with chromosome condensation. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Feb 15;33(1):131–139. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02664.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brizuela L., Draetta G., Beach D. p13suc1 acts in the fission yeast cell division cycle as a component of the p34cdc2 protein kinase. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3507–3514. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02676.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capoly J. P., Picard A., Peaucellier G., Labbé J. C., Dorée M. Changes in the activity of the maturation-promoting factor during meiotic maturation and following activation of amphibian and starfish oocytes: their correlations with protein phosphorylation. Dev Biol. 1986 Sep;117(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90342-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabauvalle M. C., Doree M., Bravo R., Karsenti E. Role of nuclear material in the early cell cycle of Xenopus embryos. Cell. 1988 Feb 26;52(4):525–533. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90465-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorée M., Peaucellier G., Picard A. Activity of the maturation-promoting factor and the extent of protein phosphorylation oscillate simultaneously during meiotic maturation of starfish oocytes. Dev Biol. 1983 Oct;99(2):489–501. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90298-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Beach D. Activation of cdc2 protein kinase during mitosis in human cells: cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation and subunit rearrangement. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):17–26. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90175-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Brizuela L., Beach D., Newport J. The Xenopus cdc2 protein is a component of MPF, a cytoplasmic regulator of mitosis. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):423–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90205-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Rosenthal E. T., Youngblom J., Distel D., Hunt T. Cyclin: a protein specified by maternal mRNA in sea urchin eggs that is destroyed at each cleavage division. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):389–396. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90420-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbes D. J., Kornberg T. B., Kirschner M. W. Small nuclear RNA transcription and ribonucleoprotein assembly in early Xenopus development. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;97(1):62–72. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.1.62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford C. C. Maturation promoting factor and cell cycle regulation. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1985 Nov;89 (Suppl):271–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Norbury C., Lohka M., Nurse P., Maller J. Purified maturation-promoting factor contains the product of a Xenopus homolog of the fission yeast cell cycle control gene cdc2+. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):433–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90206-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhart J., Wu M., Kirschner M. Cell cycle dynamics of an M-phase-specific cytoplasmic factor in Xenopus laevis oocytes and eggs. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1247–1255. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrier P., Moreau M., Doree M. Hormonal control of meiosis in starfish: stimulation of protein phosphorylation induced by 1-methyladenine. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1977 Apr;7(2):137–150. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(77)90063-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara K., Tydeman P., Kirschner M. A cytoplasmic clock with the same period as the division cycle in Xenopus eggs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):462–466. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harland R. M., Laskey R. A. Regulated replication of DNA microinjected into eggs of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):761–771. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90439-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindley J., Phear G. A. Sequence of the cell division gene CDC2 from Schizosaccharomyces pombe; patterns of splicing and homology to protein kinases. Gene. 1984 Nov;31(1-3):129–134. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90203-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindley J., Phear G., Stein M., Beach D. Sucl+ encodes a predicted 13-kilodalton protein that is essential for cell viability and is directly involved in the division cycle of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):504–511. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karsenti E., Bravo R., Kirschner M. Phosphorylation changes associated with the early cell cycle in Xenopus eggs. Dev Biol. 1987 Feb;119(2):442–453. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90048-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karsenti E., Newport J., Hubble R., Kirschner M. Interconversion of metaphase and interphase microtubule arrays, as studied by the injection of centrosomes and nuclei into Xenopus eggs. J Cell Biol. 1984 May;98(5):1730–1745. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.5.1730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labbe J. C., Lee M. G., Nurse P., Picard A., Doree M. Activation at M-phase of a protein kinase encoded by a starfish homologue of the cell cycle control gene cdc2+. Nature. 1988 Sep 15;335(6187):251–254. doi: 10.1038/335251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labbe J. C., Picard A., Peaucellier G., Cavadore J. C., Nurse P., Doree M. Purification of MPF from starfish: identification as the H1 histone kinase p34cdc2 and a possible mechanism for its periodic activation. Cell. 1989 Apr 21;57(2):253–263. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90963-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labbé J. C., Picard A., Karsenti E., Dorée M. An M-phase-specific protein kinase of Xenopus oocytes: partial purification and possible mechanism of its periodic activation. Dev Biol. 1988 May;127(1):157–169. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90197-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. G., Nurse P. Complementation used to clone a human homologue of the fission yeast cell cycle control gene cdc2. Nature. 1987 May 7;327(6117):31–35. doi: 10.1038/327031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohka M. J., Hayes M. K., Maller J. L. Purification of maturation-promoting factor, an intracellular regulator of early mitotic events. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3009–3013. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohka M. J., Maller J. L. Induction of nuclear envelope breakdown, chromosome condensation, and spindle formation in cell-free extracts. J Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;101(2):518–523. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.2.518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohka M. J., Masui Y. Effects of Ca2+ ions on the formation of metaphase chromosomes and sperm pronuclei in cell-free preparations from unactivated Rana pipiens eggs. Dev Biol. 1984 Jun;103(2):434–442. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90331-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maller J., Wu M., Gerhart J. C. Changes in protein phosphorylation accompanying maturation of Xenopus laevis oocytes. Dev Biol. 1977 Jul 15;58(2):295–312. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90093-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer L., Paul M., Epel D. Stimulation of protein phosphorylation during fertilization-induced maturation of Urechis caupo oocytes. Dev Biol. 1982 Nov;94(1):62–70. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90068-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miake-Lye R., Kirschner M. W. Induction of early mitotic events in a cell-free system. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90071-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miake-Lye R., Newport J., Kirschner M. Maturation-promoting factor induces nuclear envelope breakdown in cycloheximide-arrested embryos of Xenopus laevis. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;97(1):81–91. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minshull J., Blow J. J., Hunt T. Translation of cyclin mRNA is necessary for extracts of activated xenopus eggs to enter mitosis. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):947–956. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90628-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin synthesis drives the early embryonic cell cycle. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):275–280. doi: 10.1038/339275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neant I., Guerrier P. 6-Dimethylaminopurine blocks starfish oocyte maturation by inhibiting a relevant protein kinase activity. Exp Cell Res. 1988 May;176(1):68–79. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90121-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newport J. W., Kirschner M. W. Regulation of the cell cycle during early Xenopus development. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):731–742. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90409-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newport J., Kirschner M. A major developmental transition in early Xenopus embryos: I. characterization and timing of cellular changes at the midblastula stage. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):675–686. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peaucellier G., Dorée M., Picard A. Rise and fall of protein phosphorylation during meiotic maturation in oocytes of Sabellaria alveolata (polychaete annelid). Dev Biol. 1984 Dec;106(2):267–274. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90224-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard A., Peaucellier G., le Bouffant F., Le Peuch C., Dorée M. Role of protein synthesis and proteases in production and inactivation of maturation-promoting activity during meiotic maturation of starfish oocytes. Dev Biol. 1985 Jun;109(2):311–320. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90458-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunt T. Molecular cloning and characterization of the mRNA for cyclin from sea urchin eggs. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):2987–2995. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02604.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebhun L. I., White D., Sander G., Ivy N. Cleavage inhibition in marine eggs by puromycin and 6-dimethylaminopurine. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Mar 15;77(1):312–318. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90582-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I., Hadwiger J. A., Lörincz A. T. Protein kinase activity associated with the product of the yeast cell division cycle gene CDC28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4055–4059. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Nurse P. The mitotic inducer nim1+ functions in a regulatory network of protein kinase homologs controlling the initiation of mitosis. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):569–576. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90459-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simanis V., Nurse P. The cell cycle control gene cdc2+ of fission yeast encodes a protein kinase potentially regulated by phosphorylation. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):261–268. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90390-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standart N., Minshull J., Pines J., Hunt T. Cyclin synthesis, modification and destruction during meiotic maturation of the starfish oocyte. Dev Biol. 1987 Nov;124(1):248–258. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90476-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson K. I., Farrell K. M., Ruderman J. V. The clam embryo protein cyclin A induces entry into M phase and the resumption of meiosis in Xenopus oocytes. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):861–870. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90801-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagenaar E. B. The timing of synthesis of proteins required for mitosis in the cell cycle of the sea urchin embryo. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Apr 1;144(2):393–403. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90419-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]