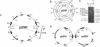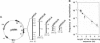Abstract
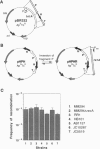
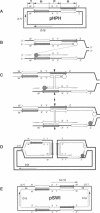
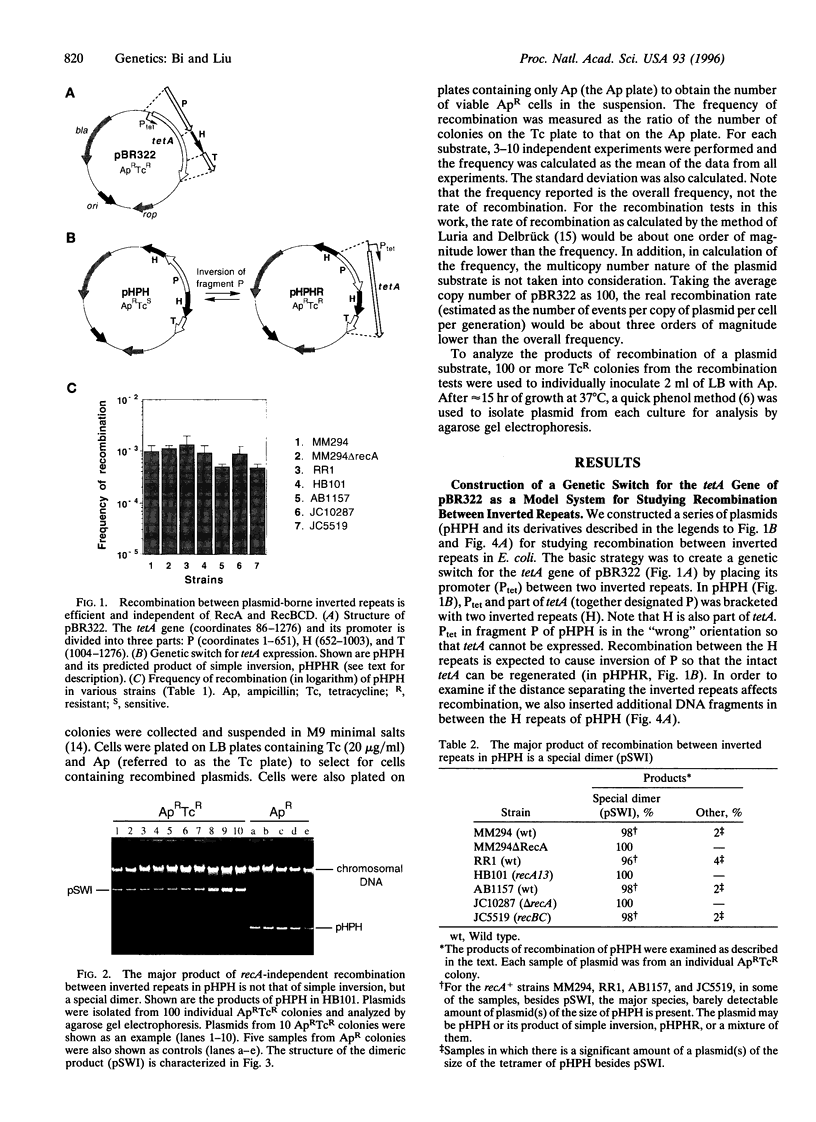
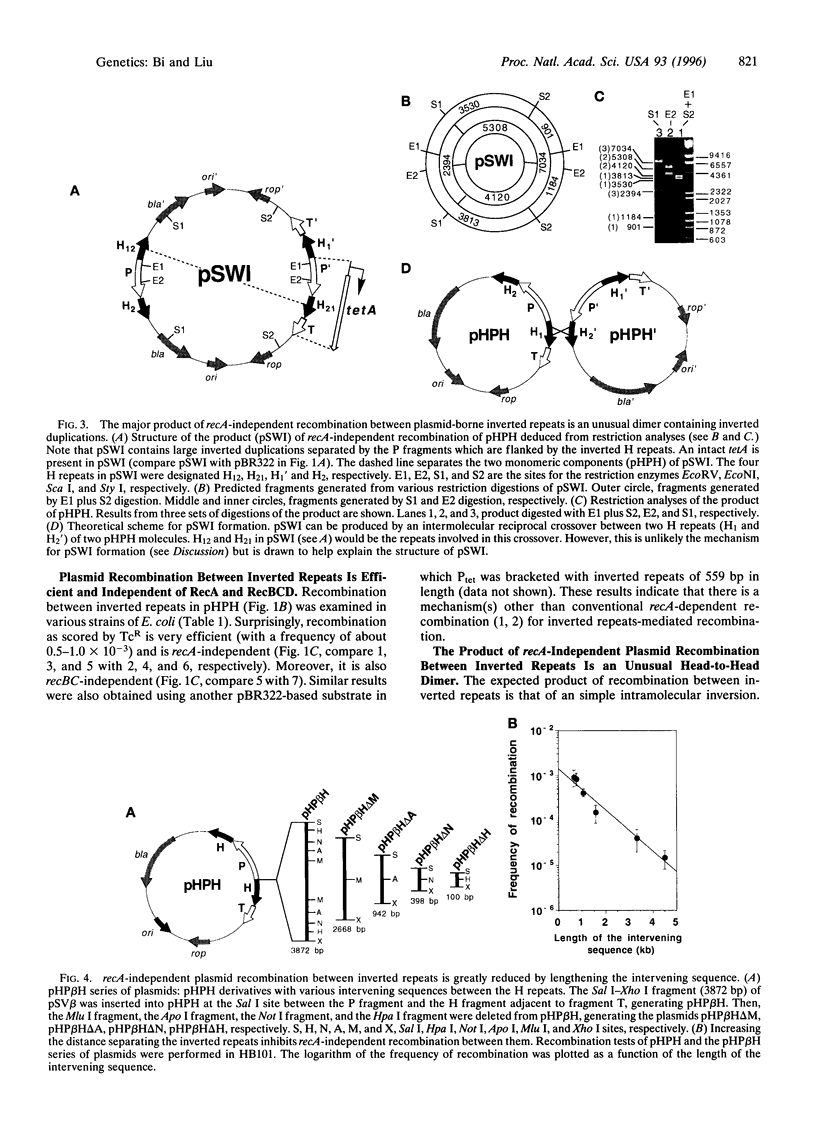
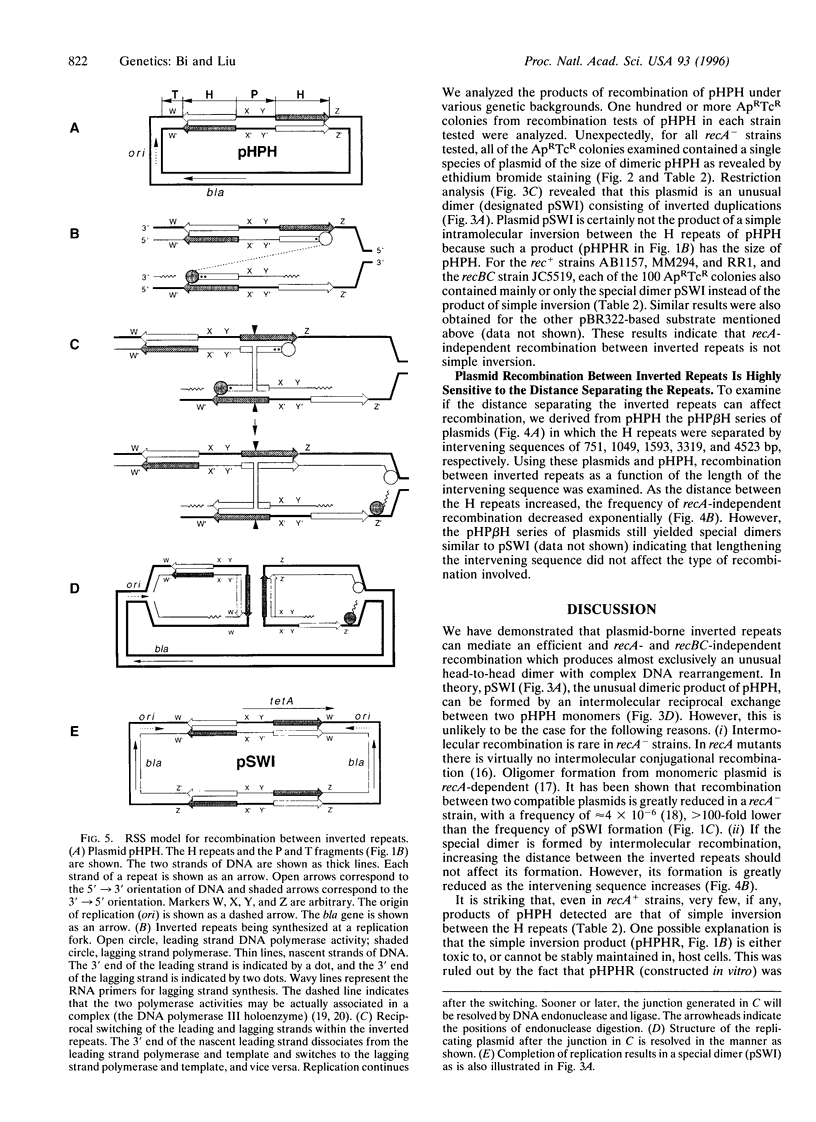
Inverted repeats of DNA are widespread in the genomes of eukaryotes and prokaryotes and can mediate genome rearrangement. We studied rearrangement mediated by plasmid-borne inverted repeats in Escherichia coli. We show that inverted repeats can mediate an efficient and recA-independent recombination event. Surprisingly, the product of this recombination is not that of simple inversion between the inverted repeats, but almost exclusively an unusual head-to-head dimer with complex DNA rearrangement. Moreover, this recombination is dramatically reduced by increasing the distance separating the repeats. These results can be readily explained by a model involving reciprocal switching of the leading and lagging strands of DNA replication within the inverted repeats, which leads to the formation of a Holliday junction. Reciprocal strand switching during DNA replication might be a common mechanism for genome rearrangement associated with inverted duplication.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bi X., Liu L. F. recA-independent and recA-dependent intramolecular plasmid recombination. Differential homology requirement and distance effect. J Mol Biol. 1994 Jan 14;235(2):414–423. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bi X., Lyu Y. L., Liu L. F. Specific stimulation of recA-independent plasmid recombination by a DNA sequence at a distance. J Mol Biol. 1995 Apr 14;247(5):890–902. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Davidson N. Electron microscope study of the structures of lambdadv DNAs. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jun 15;86(1):69–89. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(74)80008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennis D. G., Amundsen S. K., Smith G. R. Genetic functions promoting homologous recombination in Escherichia coli: a study of inversions in phage lambda. Genetics. 1987 Jan;115(1):11–24. doi: 10.1093/genetics/115.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Feo S., Heard E. The role of inverted duplication in the generation of gene amplification in mammalian cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Oct 8;1090(2):143–155. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90095-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyrien O., Debatisse M., Buttin G., de Saint Vincent B. R. The multicopy appearance of a large inverted duplication and the sequence at the inversion joint suggest a new model for gene amplification. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):407–417. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02828.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James A. A., Morrison P. T., Kolodner R. Genetic recombination of bacterial plasmid DNA. Analysis of the effect of recombination-deficient mutations on plasmid recombination. J Mol Biol. 1982 Sep 25;160(3):411–430. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90305-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N., Ross D. G. recA-dependent genetic switch generated by transposon Tn10. J Mol Biol. 1980 Dec 5;144(2):215–221. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90033-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laban A., Cohen A. Interplasmidic and intraplasmidic recombination in Escherichia coli K-12. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(2):200–207. doi: 10.1007/BF00272905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett S. T., Drapkin P. T., Sutera V. A., Jr, Gluckman-Peskind T. J. A sister-strand exchange mechanism for recA-independent deletion of repeated DNA sequences in Escherichia coli. Genetics. 1993 Nov;135(3):631–642. doi: 10.1093/genetics/135.3.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett S. T., Gluckman T. J., Simon P. J., Sutera V. A., Jr, Drapkin P. T. Recombination between repeats in Escherichia coli by a recA-independent, proximity-sensitive mechanism. Mol Gen Genet. 1994 Nov 1;245(3):294–300. doi: 10.1007/BF00290109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low B. Formation of merodiploids in matings with a class of Rec- recipient strains of Escherichia coli K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 May;60(1):160–167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.1.160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luria S. E., Delbrück M. Mutations of Bacteria from Virus Sensitivity to Virus Resistance. Genetics. 1943 Nov;28(6):491–511. doi: 10.1093/genetics/28.6.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marians K. J. Prokaryotic DNA replication. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:673–719. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.003325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nag D. K., Berg D. E. Specificity of bacteriophage Mu excision. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 May;207(2-3):395–401. doi: 10.1007/BF00331606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalbantoglu J., Meuth M. DNA amplification--deletion in a spontaneous mutation of the hamster aprt locus: structure and sequence of the novel joint. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 11;14(21):8361–8371. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.21.8361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonet G. H., Carroll S. M., DeRose M. L., Wahl G. M. Molecular dissection of an extrachromosomal amplicon reveals a circular structure consisting of an imperfect inverted duplication. Genomics. 1993 Mar;15(3):543–558. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouellette M., Hettema E., Wüst D., Fase-Fowler F., Borst P. Direct and inverted DNA repeats associated with P-glycoprotein gene amplification in drug resistant Leishmania. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):1009–1016. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08035.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schofield M. A., Agbunag R., Miller J. H. DNA inversions between short inverted repeats in Escherichia coli. Genetics. 1992 Oct;132(2):295–302. doi: 10.1093/genetics/132.2.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall A. M., Roth J. R. Approaches to half-tetrad analysis in bacteria: recombination between repeated, inverse-order chromosomal sequences. Genetics. 1994 Jan;136(1):27–39. doi: 10.1093/genetics/136.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White T. C., Fase-Fowler F., van Luenen H., Calafat J., Borst P. The H circles of Leishmania tarentolae are a unique amplifiable system of oligomeric DNAs associated with drug resistance. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16977–16983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wik Sjöstedt A., Alatalo M., Wahlström J., von Döbeln U., Olegård R. Replication error, a new hypothesis to explain the origin of a supernumerary marker chromosome in a mentally retarded boy. Hereditas. 1989;111(2):115–123. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1989.tb00385.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]