Abstract
Sorafenib is a multi-kinase inhibitor approved for hepatocellular carcinoma, but rarely causes tumor regression in patients with chronic liver diseases. To investigate whether growth factor-mediated signaling is involved in sorafenib resistance, HepG2 and PLC/PRF/5 hepatoma cells were exposed to epidermal growth factor (EGF), hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) or transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) prior to treatment with sorafenib. Furthermore, to identify an effective combination treatment with sorafenib, growth factor-sensitized cells were treated with sorafenib alone or in combination with celecoxib, lovastatin or valproic acid (VPA). Trypan blue staining and Annexin V assays showed that the cytotoxic effect of sorafenib was inhibited by 15-54% in cells sensitized to TGF-β (P<0.05). Western blotting analysis showed that TGF-β significantly activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)-mediated AKT signaling, and sorafenib failed to suppress both ERK and AKT in TGF-β-sensitized cells. The decreased anti-tumor effect of sorafenib was rescued by chemical inhibition of ERK and AKT. When TGF-β-sensitized cells were treated with sorafenib plus VPA, the levels of phosphorylated ERK and AKT were considerably suppressed and the numbers of dead cells were increased by 3.7-5.7-fold compared with those exposed to sorafenib alone (P<0.05). Moreover, low dose sorafenib-induced cell migration was effectively suppressed by combination treatment with sorafenib and VPA. Collectively, TGF-β/ERK/AKT signaling might play a critical role in sorafenib resistance in hepatoma cells, and combination treatment with VPA may be effective against this drug resistance.
Keywords: Sorafenib, TGF-β, hepatocellular carcinoma
Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most frequent malignancies worldwide. HCC is etiologically unique, in that most cases are associated with chronic liver injuries induced by hepatitis B and C virus infection and alcohol abuse [1-3]. Recently, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis has emerged as a new clinicopathological entity of this malignancy in civilized countries, and thus HCC is a long-standing concern of investigators in the field of oncology [3,4]. The prognosis of HCC is poor because it frequently recurs following surgery [5,6]. DNA damage-inducing agents such as cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil have been used as standard chemotherapy drugs for treating patients with unresectable recurrent HCC, but strong chemoresistance in hepatoma cells has been a major obstacle for clinicians dealing with this disease.
Sorafenib (sorafenib tosylate; CAS Number, 475207-59-1) is an oral multi-kinase inhibitor recently approved for the clinical treatment of advanced HCC [7,8]. Sorafenib was originally designed to target RAF-mediated signaling, and accumulating experimental evidence suggests that this agent inhibits broad-spectrum signaling pathways including C-RAF (RAF-1) and B-RAF, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptors 2 and 3, platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) receptor, c-KIT and fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3) [9]. Along with these pharmacological properties, sorafenib downregulates the RAS/RAF/MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) and AKT/STAT3 (signal transducer and activator of transcription 3) signaling pathways, both critical for the proliferation and survival of HCC cells [10,11]. Thus far, numerous in vitro and in vivo experimental studies have reported that sorafenib effectively induces apoptosis of hepatoma cells. In the clinical field, however, many reports have indicated that sorafenib rarely causes tumor regression [7,8,10]. In large population-based randomized trials, a partial tumor response (PR; at least 30% decrease in the sum of the longest diameter of target lesions; Response Evaluation Criteria In Solid Tumors (RECIST)) was only seen in 2-3.3% of patients enrolled in the study [12,13]. However, the reason for the discrepancy between experimental and clinical data has remained unclear.
It is widely accepted that most HCC patients have chronic hepatitis or liver cirrhosis in which various types of cytokines and growth factors are overexpressed. The relationship between extracellular stimuli by such soluble factors and sorafenib efficacy has been unclear to date. We therefore set out to address whether growth factor-mediated signaling might contribute to sorafenib resistance in hepatoma cells, and investigated whether combination therapy with clinically available agents can overcome the drug resistance in growth factor-sensitized hepatoma cells.
Materials and methods
Reagents
Sorafenib (Toronto Research Chemicals, Downsview, ON, Canada) was dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and used at concentrations as indicated in the text. LY294002 (an inhibitor of PI3K/AKT) (Cell Signaling Technology, Beverly, MA), U0126 (an inhibitor of MEK1/2 (mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1/2)) (Calbiochem, San Diego, CA), SB203580 (an inhibitor of p38MAPK) (Enzo Life Sciences, Farmingdale, NY), and SP600125 (an inhibitor of JNK (c-jun N-terminal kinase)) (Enzo Life Sciences, Farmingdale, NY) were dissolved in DMSO and used at 25, 10, 20, and 50 μM, respectively. For combination treatment with sorafenib, anti-antiepileptic drug valproic acid (IC50 = 1.3-2.5 mM [14]; Toronto Research Chemicals), a selective Cox-2 inhibitor celecoxib (IC50 = 61-70 μM [15]; Toronto Research Chemicals) and HMG-CoA reductase lovastatin (IC50 = 0.8-4.2 μM [16]; Enzo Life Sciences) were used at 1 mM, 60 μM, and 4 μM, respectively. When the drug solutions were diluted in culture medium, the final concentration of DMSO was set at 0.1% as a solvent control in all experiments.
For western blotting analysis, polyclonal antibodies recognizing cleaved PARP (Asp214), phospho-AKT (p-AKT) (Thr308), phospho-p44/42 MAPK (p-ERK1/2) (Thr202/Tyr204), phospho-B-RAF (Ser445) and phospho-C-RAF (Ser338) were obtained from Cell Signaling Technology. A mouse monoclonal antibody against β-actin was obtained from Sigma Chemical Co. (St. Louis, MO, USA).
Cell culture
Human hepatoma cell lines HepG2 and PLC/PRF/5 cells (American Type Culture Collection, Manassas, VA, USA) were cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS). The cells were incubated with recombinant human epithelial growth factor (EGF; 20 ng/mL) (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA), hepatocyte growth factor (HGF; 10 ng/mL) (R&D Systems) or transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β; 5 ng/mL) (R&D Systems) for 48 h. After the culture media was refreshed, cells were again treated with the same concentration of growth factor and exposed to sorafenib at various concentrations for 48 h. The concentration of sorafenib used in apoptosis assays and western blotting was set at 5-10 μM, which is comparable to the plasma concentration of individuals medicated with sorafenib [17]. Pre-treatment with the chemical agents was performed 1 h before the addition of sorafenib.
Cell cytotoxic assay
Cells (0.2 × 105 cells/mL) were plated in 96-well plates in complete media, and maintained in the presence or absence of EGF, HGF or TGF-β for 48 h. Culture medium was then replaced, and cells were exposed to the same growth factor plus sorafenib for 48-72 h. Cell proliferation was determined using a water-soluble tetrazolium (WST)-based cell proliferation assay using a Cell Counting Kit WST-8 (Dojindo Laboratories, Kumamoto, Japan) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The amount of formazan product was measured at 450 nm using a Multiscan FC microtiter-plate reader (Thermo Scientific, Vantaa, Finland). To evaluate apoptosis, cells were stained using an Annexin V FITC Kit (Invitrogen, Karlsruhe, Germany), and images were obtained with a fluorescence microscope (BZ-9000; Keyence, Osaka, Japan). To assess the ratios of apoptotic cells, 300 cells in a given microscopic field were counted, and Annexin V-positive cells were considered to be apoptotic. The percentage of dead cells was determined by the trypan blue exclusion assay using a TC10 automated cell counter (Bio-Rad, Richmond, CA, USA). The results were obtained from three independent experiments performed in triplicate and data represent the mean ± standard error of the means of three independent experiments each performed in triplicate.
Western blotting
After treatment with sorafenib for 2 or 24 h, cultured cells were lysed in a modified radioimmunoprecipitation assay buffer (25 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.6, 150 mM NaCl, 1% NP-40, 1% sodium deoxycholate, 0.1% SDS) supplemented with complete protease inhibitor. After the samples were heat-denatured, aliquots (20 μg of protein) were electrophoresed on 5-20% SDS-polyacrylamide gels and transferred onto Immobilon-P polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. The membranes were probed with appropriate primary antibodies and with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibodies. Protein blots were visualized using an enhanced ECL western blotting detection system (GE Healthcare). Protein band intensity normalized against the β-actin band was quantified using image analysis software (Image-J, ver. 1.44; NIH, Bethesda, MD).
Cell migration assay
Transwell migration assays were performed using transwell chambers with 8-μm pores (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA). Cells were treated with 0.5 μM sorafenib for 24 h with or without pre-treatment with TGF-β and chemical inhibitors for 2 h. The cells were suspended in DMEM containing 1% FBS, and seeded in the upper chambers of the transwell at a density of 1 × 104 cells/ml. The lower chambers were filled with the same culture media containing 10% FBS. After incubation for 10 h, cells that had migrated through the pores were counted in five random microscopic fields. For wound healing assays, a linear wound using a sterile 2-mm blade cells was created in a monolayer of cells grown to confluence in DMEM containing 10% FBS. Cells were treated with hydroxyurea (2.5 mM) to reduce proliferation, and treated with 0.5 μM sorafenib with or without pre-treatment with TGF-β and chemical inhibitors for 24 h. The length of the wound closure was evaluated at five points along the wound edge under a microscope. Each experiment was independently performed in triplicate.
Statistical analysis
All experiments were performed in triplicate. Statistical analyses were performed with mean ± standard deviation (SD) values using Student’s t-test and two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with the Bonferroni’s correction. P values less than 0.05 were considered significant.
Results
TGF-β interferes with the anti-tumor effect of sorafenib
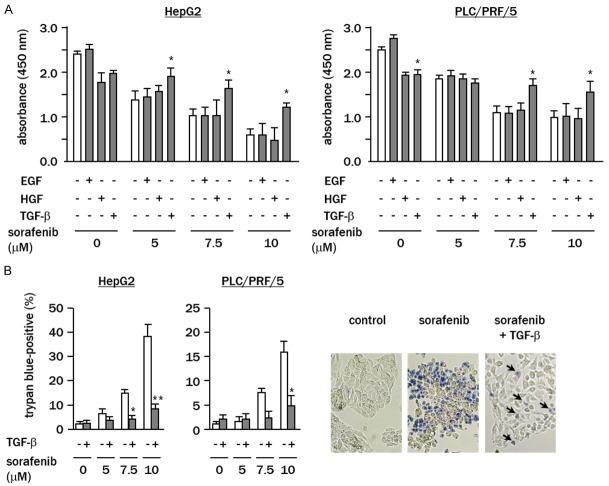
WST assays showed that sorafenib dose-dependently inhibited the proliferation of both HepG2 and PLC/PRF/5 cells (Figure 1A). The effect of sorafenib on the proliferation of cell pre-treated with EGF or HGF was not significantly changed. However, in HepG2 and PLC/PRF/5 cells pre-treated with TGF-β the anti-tumor effect of sorafenib was significantly inhibited (both P<0.05). Trypan blue assays revealed that pre-treatment with TGF-β significantly repressed the proportion of dead cells following treatment of HepG2 and PLC/PRF/5 with sorafenib (P<0.01 and P<0.05, respectively) (Figure 1B).
Figure 1.
TGF-β suppresses the cytotoxic effect of sorafenib in hepatoma cells. A. Cell were treated with sorafenib (0-10 μM) for 48 h with or without pre-treatment with growth factors for 48 h. Cell proliferation was examined by WST assay. B. Cells were treated with sorafenib (0-10 μM) for 72 h with or without TGF-β pre-treatment, and the percentage of dead cells was analyzed by trypan blue assays. Representative images show cells treated with sorafenib (10 μM) with or without TGF-β pretreatment of (arrows, dye-positive dead cells). White column, cells under growth factor-free conditions. Experiments were performed in triplicate, and data represent the means ± SD of triplicate experiments (*P<0.05 vs. cells under growth factor-free conditions).
Western blotting analyses showed that the levels of cleaved PARP, a cell apoptosis marker, were increased from 2.8 to 4 fold in sorafenib-treated cells compared with that of the controls, without reference to the pre-treatment with EGF or HGF (Figure 2A). In contrast, in the cells pre-treated with TGF-β, the levels of cleaved PARP were significantly reduced and remained almost at control levels (HepG2; 1.3 fold of control, PLC/PRF/5; 0.9 fold of control). The results of Annexin V labeling revealed that the fraction of sorafenib-induced apoptotic cells was repressed in TGF-β-sensitized HepG2 and PLC/PRF/5 cells (P<0.01 and P<0.05) (Figure 2B), indicating that TGF-β antagonizes the process of sorafenib-mediated cell apoptosis.
Figure 2.
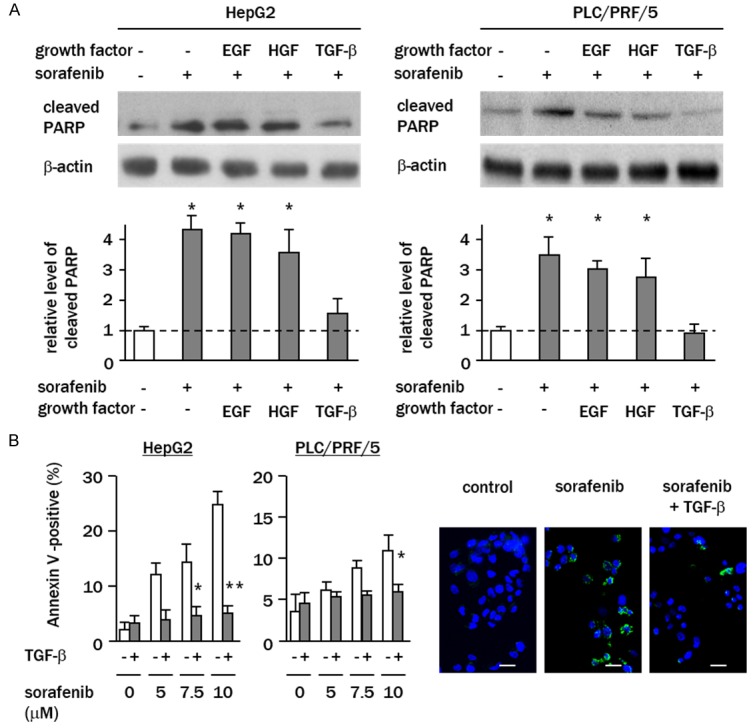
TGF-β abrogates sorafenib-induced apoptosis. A. Cells were treated with sorafenib (10 μM) for 24 h with or without pre-treatment with growth factors. Levels of cleaved PARP were determined by western blotting. Columns represent relative band intensities normalized against β-actin bands expressed as fold changes relative to non-treated control cells (white column). B. Cells were treated with sorafenib (0-10 μM) for 48 h, and the percentages of apoptotic cells were analyzed using Annexin V assays. Representative images of Annexin V assays are shown. Green, Annexin V-positive cells; blue, nuclear DAPI staining (bar, 20 μm). White column, TGF-β-free cells. Data represent the means ± SD of triplicate experiments (*P<0.05, *P<0.01, vs. growth factor-free cells).
Sorafenib fails to inhibit ERK and AKT signaling pathways in TGF-β-sensitized cells
To address whether non-canonical TGF-β-mediated signaling (MAPK and AKT) is involved in sorafenib resistance, western blotting analyses of phosphorylated ERK and AKT were performed. The results showed that sorafenib treatment alone effectively decreased the levels of phosphorylated ERK and AKT from 0.2–0.6-fold that of the controls (P<0.05) (Figure 3). Decreased levels of phospho-ERK and -AKT were also detected in cells sensitized to EGF or HGF prior to treatment with sorafenib. Intriguingly, when cells were pre-treated with TGF-β, sora-fenib failed to decrease the phosphorylation of ERK (HepG2; control vs. sorafenib plus TGF-β, 1.0 vs. 1.2 fold, PLC/PRF/5; 1 vs. 2.9 fold of the relative intensity) (Figure 3). The levels of phosphorylated AKT in TGF-β-sensitized cells were 1.3-fold and 2.5-fold that of the controls following sorafenib treatment in HepG2 and PLC/PRF/5, respectively, indicating that sorafenib cannot suppress TGF-β-induced AKT activation at clinical doses.
Figure 3.
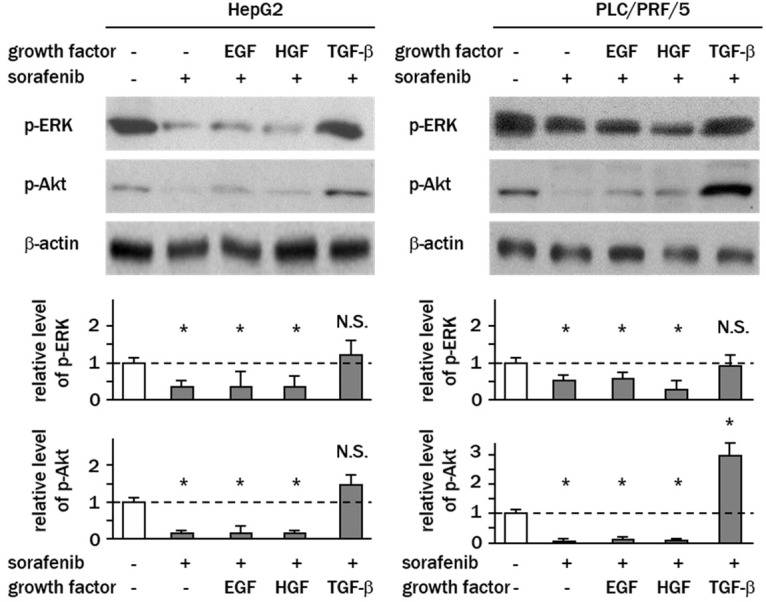
Sorafenib fails to suppress ERK and AKT signaling in the presence of TGF-β. Cells were treated with sorafenib (10 μM) for 2 h with or without pre-treatment with growth factors. Levels of phospho-ERK1/2 (Thr202/Tyr204) and phospho-AKT (Thr308) were determined by western blotting. Experiments were performed in triplicate, and columns represent the means ± SD of the band intensities normalized against β-actin bands expressed as fold changes relative to non-treated control cells (white column) (*P<0.05, vs. control cells; N.S., not significant). In PLC/PRF/5 cells, AKT was significantly phosphorylated by TGF-β.
TGF-β stimulates the B-RAF/ERK/AKT signaling pathway
To determine whether there is crosstalk between ERK and AKT signaling in a state of sorafenib resistance, HepG2 cells were treated with specific inhibitors of MAPKs or AKT before exposure to sorafenib and TGF-β. Of all the chemical MAPK and AKT inhibitors examined, only U0126 (a specific inhibitor of MEK1/2) blocked the phosphorylation of ERK in TGF-β-sensitized cells, indicating that ERK is not regulated by other MAPKs or AKT. In contrast, AKT phosphorylation levels were significantly decreased by U0126 and LY294002, suggesting that AKT acts downstream of ERK signaling in sorafenib-resistant cells (Figure 4A). To identify the mechanism for increased activity of ERK in TGF-β-treated cells, the phosphorylation levels of B-RAF and c-RAF were examined by western blotting. TGF-β treatment stimulated the phosphorylation of both B-RAF and c-RAF to 5.5-7-fold that of the controls (Figure 4B). Sorafenib treatment effectively suppressed the levels of phospho-C-RAF relative to the controls (1.2-fold), while the phosphorylation levels of B-RAF were not affected by sorafenib at the clinical dose (10 μM) (Figure 4B).
Figure 4.
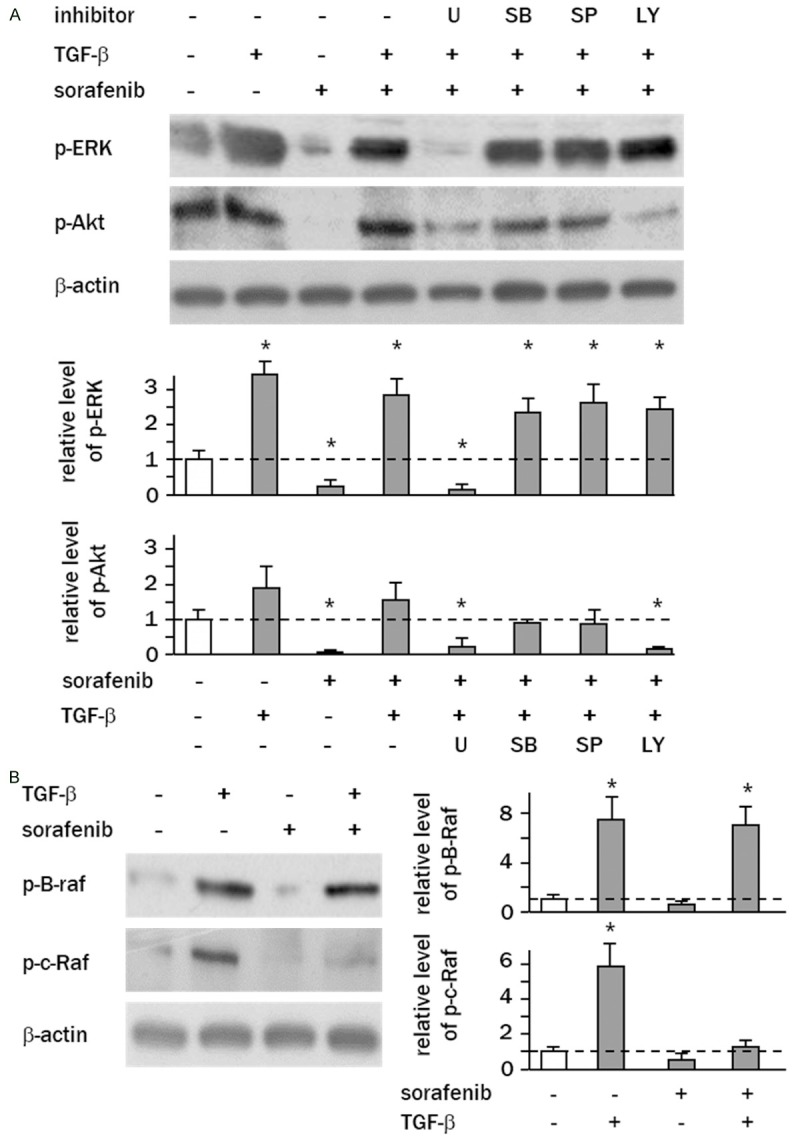
TGF-β stimulates B-RAF/ERK/AKT signaling in hepatoma cells. A. Cells were pretreated with TGF-β and then administered sorafenib (10 μM) in the presence of chemical inhibitors of MAPK or AKT for 2 h. Levels of phospho-ERK1/2 (Thr202/Tyr204) and phospho-AKT (Thr308) were determined by western blotting. B. Levels of phospho-B-RAF (Ser445) and phospho-C-RAF (Ser338) in HepG2 cells were analyzed by western blotting. Experiments were performed in triplicate, and columns represent the means ± SD of the band intensities normalized against β-actin bands expressed as fold-change relative to non-treated control cells (white column) (*P<0.05, vs. control cells).
TGF-β antagonizes the cytotoxic effect of sorafenib through the ERK/AKT signaling pathway
To address whether non-canonical TGF-β signaling contributes to the decreased efficacy of sorafenib, cells were treated with chemical inhibitors of MAPK or AKT prior to treatment with sorafenib and trypan blue assays were performed to analyze dead cells. The data revealed that the percentages of sorafenib-induced dead cells were increased by U0126 or LY294002 in TGF-β-sensitized HepG2 cells (10 μM of sorafenib alone vs. sorafenib plus U0126 vs. sorafenib plus LY294002: 9 ± 2% vs. 43 ± 4% vs. 38 ± 3%, P<0.05, P<0.05 vs. sorafenib alone). and PLC/PRF/5 cells (10 μM of sorafenib vs. sorafenib plus U0126 vs. sorafenib plus LY294002: 5 ± 2% vs. 26 ± 4% vs. 20 ± 3%, P<0.05, P<0.05 vs. sorafenib alone) (Figure 5A). Annexin V assay showed that combination treatment with sorafenib and U0126 or LY294002 significantly increased apoptosis of TGF-β-sensitized HepG2 cells (sorafenib vs. sorafenib plus U0126 vs. LY294002: 4 ± 2% vs. 28 ± 4% vs. 20 ± 3%, p, 0.05, p<0.05 vs. sorafenib) and PLC/PRF/5 cells (sorafenib vs. sorafenib plus U0126 vs. LY294002: 4 ± 2% vs. 13 ± 2% vs. 15 ± 3%, p, 0.05, p<0.05 vs. sorafenib) (Figure 5B).
Figure 5.
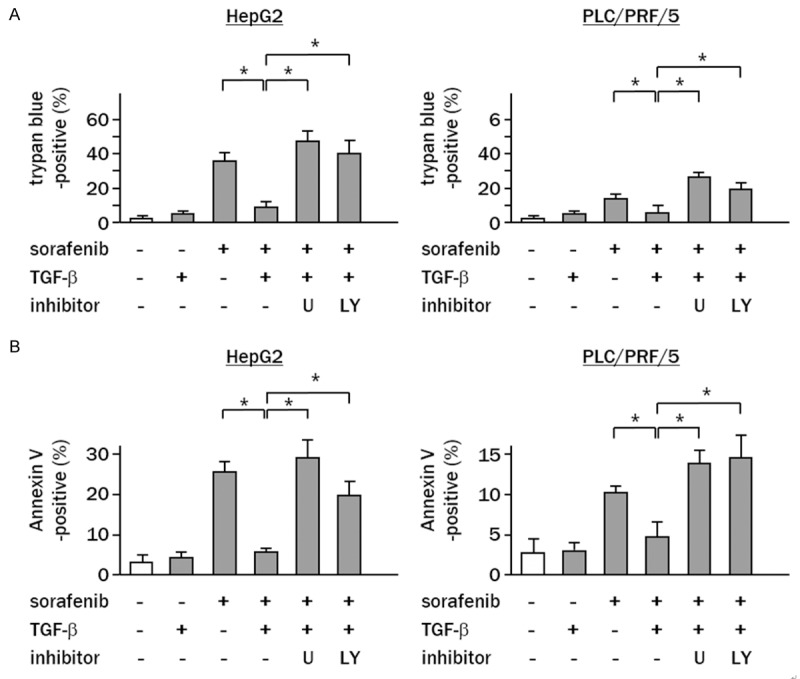
ERK/AKT signaling pathway is a critical mediator of TGF-β-induced sorafenib resistance. (A) Cells were pretreated with TGF-β, and then exposed to sorafenib (10 μM) in the presence or absence of chemical inhibitors for (A) 72 h or (B) 48 h. (A) Columns represent the percentage of dead cells as assessed by trypan blue assay. (B) Apoptotic cell numbers were assessed by Annexin V assay. White column, non-treated control cells. Experiments were performed in triplicate, and the data represent the means ± SD of triplicate experiments (*P<0.05 vs. cells treated with sorafenib and TGF-β).
Valproic acid suppresses TGF-β-induced ERK/AKT signaling
We next examined whether combination treatment with clinically available agents ameliorated sorafenib resistance. When cells were independently treated with valproic acid (VPA), celecoxib or lovastatin, VPA was found to most potently suppress the phosphorylation of ERK (HepG2: 0.3-fold; PLC/PRF/5: 0.4-fold of controls) (Figure 6A). Intriguingly, this inhibitory effect of VPA was relatively strong as compared with the effect of sorafenib at a clinical dose (10 μM). Lovastatin also suppressed the phosphorylation of ERK in PLC/PRF/5 cells, but its effect was marginal in HepG2 cells (Figure 6A). When these agents were added to TGF-β-sensitized cells in combination with sorafenib, decreased ERK phosphorylation was only detected in cells treated with sorafenib plus VPA (HepG2: 0.2-fold; PLC/PRF/5: 0.1-fold of controls) (Figure 6B). TGF-β-induced phosphorylation of AKT was also decreased by combination treatment with sorafenib and VPA (HepG2: 0.3-fold; PLC/PRF/5: 0.1-fold of controls) (Figure 6C).
Figure 6.
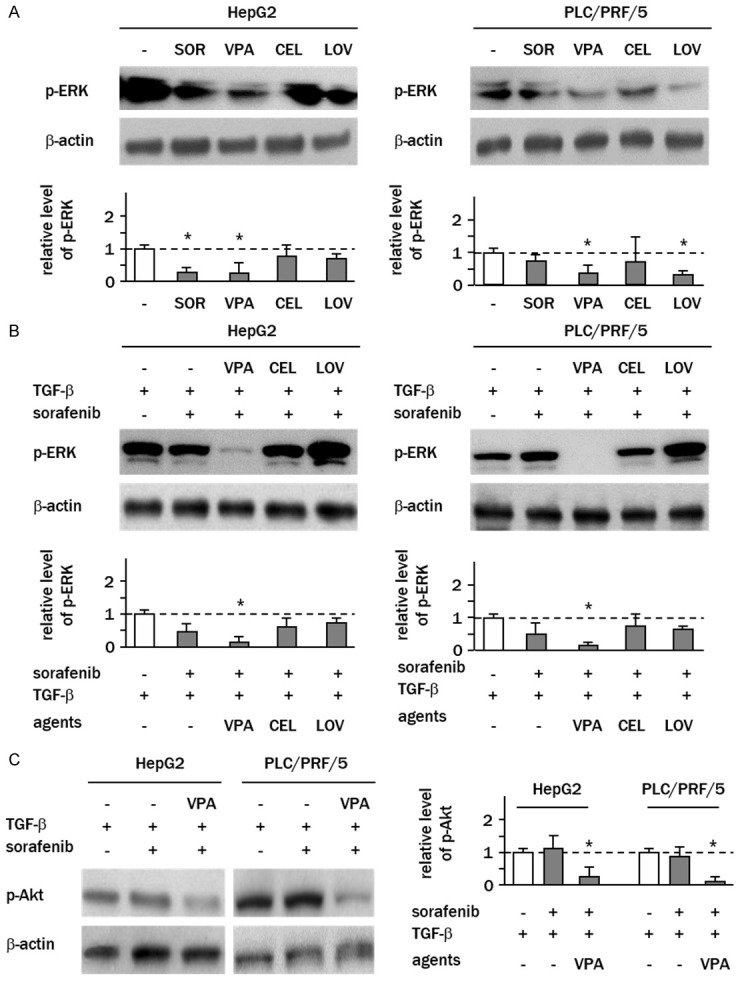
VPA attenuates TGF-β-induced activation of ERK/AKT signaling. A. Cells were cultured in serum-free media overnight, and treated with sorafenib (SOR), valproic acid (VPA), celecoxib (CEL) or lovastatin (LOV) for 2 h. B and C. Cells pretreated with TGF-β were treated with sorafenib and clinical agents for 24 h. Levels of phospho-ERK1/2 (Thr202/Tyr204) and phospho-AKT (Thr308) were examined by western blotting. Columns represent the means ± SD of the band intensities normalized against β-actin bands expressed as fold-change relative to sorafenib-free control cells (white column) (*P<0.05, vs. control cells).
Valproic acid confers TGF-β-mediated sorafenib resistance
In the absence of TGF-β treatment, trypan blue staining revealed that treatment with VPA, celecoxib or lovastatin caused no significant increases in the ratio of dead cells at their set doses (Figure 7A). However, when combined with sorafenib all showed synergistic cytotoxic effects (Figure 7B). In HepG2 cells treated with sorafenib in combination with VPA, celecoxib and lovastatin, the ratios of dead cells were 72 ± 4% (P<0.05), 74 ± 5% (P<0.05) and 58 ± 5% (P<0.05), respectively, which were considerably higher than sorafenib treatment alone (32 ± 4%). Synergic effects by these agents were also observed in PLC/PRF/5 (sorafenib plus VPA, sorafenib plus celecoxib and sorafenib plus lovastatin; 32 ± 5% (P<0.05), 28 ± 4% (P<0.05) and 33 ± 4% (P<0.05) vs. 14 ± 3% of sorafenib alone).
Figure 7.
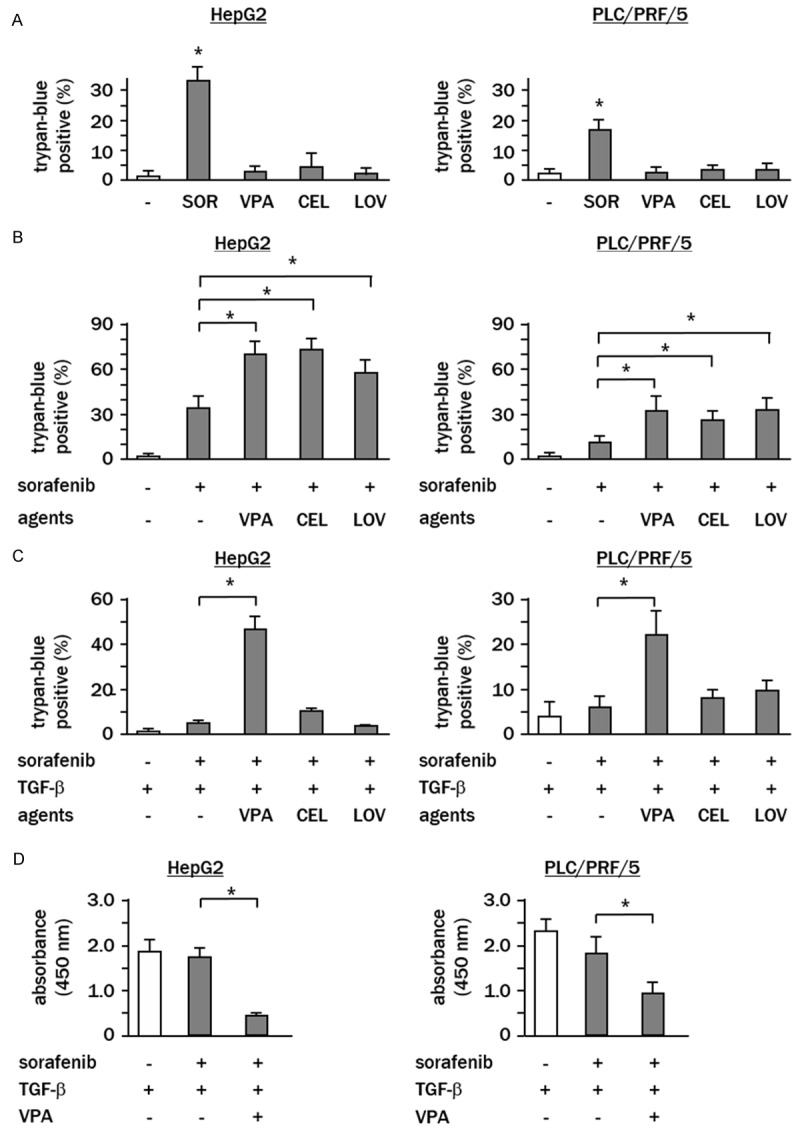
VPA confers TGF-β-induced sorafenib resistance. (A) Cells were independently treated for 7 h with agents, or (B) treated with a combination of sorafenib and agents, or (C) treated with combination treatment with or without TGF-β pretreatment, and the ratios of dead cells were analyzed using trypan blue. (D) Cells were pretreated with TGF-β, and thereafter treated with sorafenib plus VPA. Cell proliferation was assessed by WST assay. White column, sorafenib-free control cells. Experiments were performed in triplicate, and data represent the means ± SD of triplicate experiments (*P<0.05).
In contrast, when cells were pre-treated with TGF-β, a synergistic cytotoxic effect was only observed in cells treated with sorafenib plus VPA (HepG2: sorafenib vs. sorafenib plus VPA, 8 ± 3% vs. 46 ± 5%, P<0.05; PLC/PRF/5; (sorafenib vs. sorafenib plus VPA, 6 ± 2% vs. 22 ± 4%, P<0.05) (Figure 7C). WST assay showed that combination treatment with sorafenib and VPA effectively suppressed proliferation of TGF-β-treated HepG2 (sorafenib alone vs. sorafenib plus VPA; absorbance value 1.6 ± 0.3 vs. 0.5 ± 0.1, P<0.05) and PLC/PRF/5 cells (sorafenib alone vs. sorafenib plus VPA; 1.8 ± 0.4 vs. 0.9 ± 0.3, P<0.05) (Figure 7D).
Valproic acid suppresses sorafenib-induced cell migration
Recently, it has been revealed that low-dose of sorafenib (<1 μM; non-cytotoxic concentration) stimulates cell migration through AKT signaling [18,19]. To examine whether VPA can ameliorate sorafenib-induced cell migration, cells were treated with low dose sorafenib (0.5 μM) with or without VPA or LY294002. The results of transwell cell migration assays showed that, in the absence of TGF-β, sorafenib induced cell migration of HepG2 and PLC/PRF/5 cells by 1.4- (P<0.05) and 1.6-fold (P<0.05) that of the controls, respectively. Combination treatment with sorafenib and VPA effectively decreased the numbers of migrated cells (HepG2: 0.8-fold; and PLC/PRF/5: 1.1-fold of control; P<0.05, P<0.05 vs. TGF-β treated controls) (Figure 8A). When cells were pre-treated with TGF-β, the numbers of migrated cells were increased by sorafenib treatment in HepG2 cells (TGF-β-treated control vs. sorafenib, 20 ± 3 vs. 32 ± 6 cells/HPF, P<0.05) and in PLC/PRF/5 cells (11 ± 3 vs. 21 ± 3 cells/HPF, P<0.05). In both cell lines, VPA effectively suppressed the number of migrated cells, which was comparable to those treated with LY294002 (HepG2; 4 ± 2 and PLC/PRF/5; 3 ± 1 cells/HPF, P<0.05, P<0.05 vs. sorafenib treated alone) (Figure 8A). Wound healing assays showed that combined treatment with sorafenib plus VPA significantly repressed sorafenib-induced cell migration in HepG2 cells in both the presence and absence of TGF-β (Figure 8B), and the inhibitory effect of VPA on sorafenib-induced cell migration was comparable to LY294002 (relative rate of the wound closure; TGF-β alone vs. TGF-β plus sorafenib vs. TGF-β plus sorafenib plus VPA vs. TGF-β plus sorafenib plus LY294002; 38 ± 5% vs. 63 ± 7% vs. -3 ± 4% vs. 2 ± 3%, all P<0.05 vs. TGF-β treatment alone).
Figure 8.
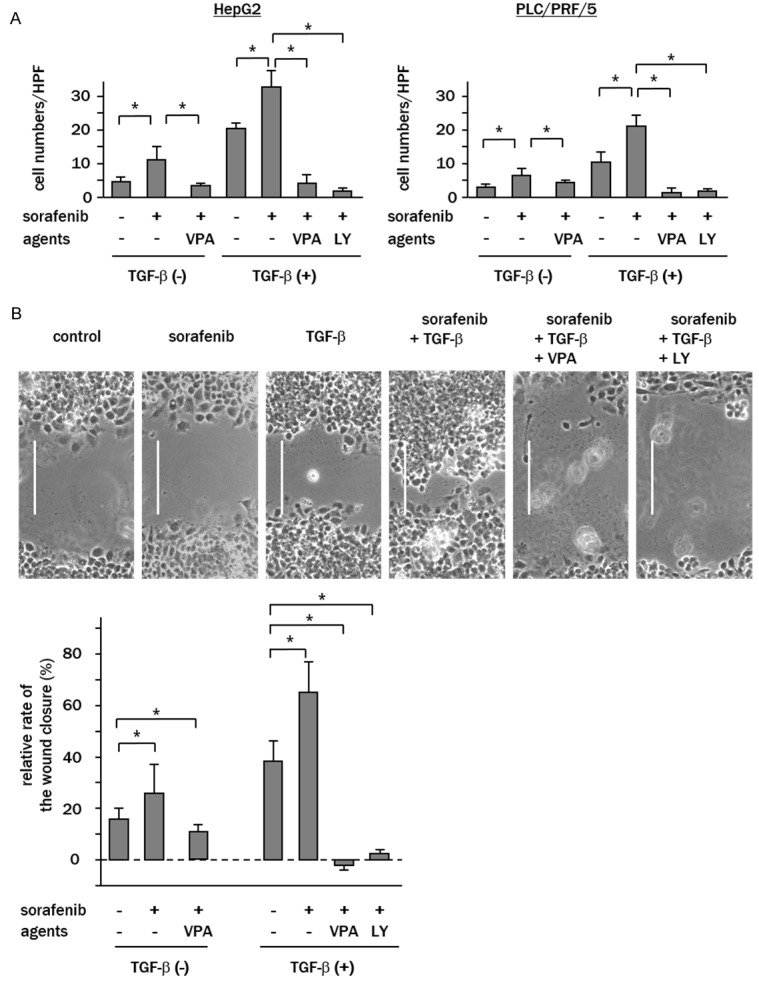
VPA suppresses sorafenib-induced cell migration of TGF-β-sensitized cells. Cells were pretreated with TGF-β for 24 h and then treated with 0.5 μM sorafenib with or without VPA or LY294002 (LY). A. Transwell migration assays revealed that the rate of cell migration was increased by low dose sorafenib, which was enhanced by TGF-β. Combination treatment with sorafenib and VPA or LY294002 (LY) significantly inhibited migration. B. Wound healing assays of HepG2 cells showed that treatment with low dose sorafenib accelerated wound closure, which was enhanced by TGF-β. Combination treatment with VPA or LY294002 (LY) significantly reduced migration. Representative images of wounded cell monolayers are shown (bar; 100 μm). Data represent the means ± SD of triplicate experiments (**P<0.05).
Discussion
In this study, we found that the anti-tumor effect of sorafenib was greatly impaired in hepatoma cells sensitized with TGF-β. B-RAF/ERK/AKT signaling was found to be significantly activated in TGF-β-treated cells, and sorafenib could not antagonize the phosphorylation of ERK and AKT at the putative clinical dose. We observed that ERK-mediated activation of AKT is an important mechanism for overcoming sorafenib resistance, and found that VPA might be a favorable candidate for combination therapy. To date, many studies have reported that TGF-β is a critical soluble factor implicated in the process of chronic liver injury [20]. Because many HCC patients suffer from chronic hepatitis or liver cirrhosis with various etiologies, our results indicate that consideration of the growth factors/cytokines in the regulation of tumor microenvironment might help to improve the therapeutic efficacy of sorafenib. The possible relationship between liver damage and sorafenib efficacy has been already provided by clinical studies. Pinter et al. reported a clinical trial of sorafenib in HCC patients with different degrees of liver injury, and suggested that cancer patients with Child-Pugh class C (severe degree of liver dysfunction) had a limited life expectancy after treatment with sorafenib [21]. Schütte et al. reported that the median survival of HCC patients with Child-Pugh class B (medium degree of liver dysfunction) was poorer than those with better liver function [22]. Although the role of liver injury in sorafenib efficacy is unclear, we surmise some soluble factors released from damaged liver, such as TGF-β, might determine sorafenib efficacy in HCC patients.
There have only been a few studies investigating the functional relationship between TGF-β and sorafenib, and the reported results have indicated that the role of TGF-β is distinctly different in varying cellular conditions. Chen et al. reported that sorafenib inhibits TGF-β-induced STAT3 phosphorylation and apoptosis in mouse hepatocytes [23]. In this regard, Fernando et al. reported that sorafenib induces apoptosis in hepatoma cells but not in untransformed hepatocytes, suggesting that the apoptotic effect of sorafenib might be characteristic of liver tumor cells. Intriguingly, they also reported that when hepatoma cells were sensitized with sorafenib just prior to treatment with TGF-β, mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis is induced through increasing levels of PUMA (a key mediator of p53-inducible apoptosis) and BIM (a pro-apoptotic member of the BCL-2 protein family) [24]. Very recently, Xia et al. reported that microRNA-216a/217 activates the TGF-β-mediated PI3K/AKT-signaling pathway in hepatoma cells, leading to the acquisition of drug resistance to sorafenib [25]. Our study might support the reports of Xia et al., by providing evidence that sorafenib cannot suppress TGF-β-mediated B-RAF/ERK/AKT signaling at the putative clinical dose. Together with our data, these evidences suggest that the cell type and timing of drug administration might determine the relationship between sorafenib and TGF-β. It seems that sorafenib generally antagonizes the apoptotic effect of TGF-β in normal hepatocytes, while in hepatoma cells its apoptotic effects are enhanced in case TGF-β signaling is preceded by the sorafenib-mediated apoptotic process. However, when hepatoma cells are constitutively sensitized by TGF-β, a condition expected to exist in chronic liver diseases [20], the anti-tumor effect of sorafenib might be greatly impaired through the significant activation of ERK/AKT signaling.
It is well recognized that the RAS oncogene product plays a critical role in cancer aggressiveness. RAS activates the RAF serine/threonine kinase family, leading to the activation of ERK signaling [26]. The RAF kinase family is composed of A-RAF, B-RAF and C-RAF, which interact with each other and confer varying kinase activities according to their different counterparts in the RAF complexes. For example, B-RAF and C-RAF heterodimers stimulate ERK signaling to a greater extent than B-RAF and C-RAF homodimers. Moreover, when B-RAF is mutated via a valine to glutamic acid substitution at amino acid position 600 (B-RAF V600E), its kinase activity is significantly increased [27]. Sorafenib is a unique RAF inhibitor in that it effectively inhibits C-RAF at lower doses, while high doses are necessary for B-RAF inhibition [9,28]. Therefore, it is plausible that the status of RAF signaling strongly contributes to sorafenib resistance. Our results showed that TGF-β-sensitized hepatoma cells exhibit high levels of B-RAF and C-RAF phosphorylation, and sorafenib failed to inhibit the B-RAF phosphorylation. We also found that TGF-β-treated cells exhibited high levels of AKT phosphorylation, which could not be inhibited by sorafenib. Phospho-AKT was repressed by ERK inhibition by U0126, indicating that TGF-β activates AKT through the ERK signaling pathway. Cell viability was significantly decreased when cells were treated with sorafenib plus ERK or AKT inhibitor. Taken together, we hypothesize that the TGF-β-mediated B-RAF/ERK/AKT signaling pathway is an important target for improving the therapeutic efficacy of sorafenib.
To date, various clinical trials of sorafenib-based combination therapy have been undertaken. For example, the chemotherapy drug doxorubicin was found to be useful for enhancing the anti-tumor effect of sorafenib [29]. More recently, combination treatment of sorafenib with an inhibitor of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) has been applied [30]. To develop more safe and efficient treatment protocols, understanding of the mechanism of sorafenib resistance would be of value. In this study, we focused on ERK-mediated AKT signaling and addressed whether any drugs might attenuate this signaling when combined with sorafenib. We examined the effect of several clinically available agents, VPA, celecoxib, and lovastatin, which are well known to be effective for enhancing the effect of chemotherapy [31-33]. Intriguingly, our results revealed that only VPA significantly inhibited ERK and AKT phosphorylation in TGF-β-sensitized cells when administered with sorafenib. Combination treatment with sorafenib plus VPA also resulted in a profound cytotoxic effect on hepatoma cells. Moreover, VPA suppressed the cell migration induced by low dose sorafenib; thus this drug might be useful for avoiding unexpected tumor metastasis in patients administered low dose sorafenib. The pharmaceutical mechanism of VPA should be investigated more in detail. It is noted that VPA regulates ERK1/2 phosphorylation independently of its own activity on histone deacetylase, and the effect of VPA on ERK1/2 is cell-type specific [34].
Although the mechanism underlying the relationship among TGF-β, sorafenib and VPA should be investigated in further detail, our study suggests that manipulation of extracellular stimuli by soluble factors such as TGF-β may be vital in improving sorafenib efficacy in HCC patients. To support our findings, further studies using in vivo models would be invaluable.
Acknowledgements
This work was partly supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (no. 24590962) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan.
Disclosure of conflict of interest
None.
References
- 1.Llovet JM, Burroughs A, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2003;362:1907–1917. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)14964-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Forner A, Llovet JM, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2012;379:1245–1255. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61347-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Gao J, Xie L, Yang WS, Zhang W, Gao S, Wang J, Xiang YB. Risk factors of hepatocellular carcinoma--current status and perspectives. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012;13:743–752. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2012.13.3.743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ascha MS, Hanouneh IA, Lopez R, Tamimi TA, Feldstein AF, Zein NN. The incidence and risk factors of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 2010;51:1972–1978. doi: 10.1002/hep.23527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Wakai T, Shirai Y, Sakata J, Korita PV, Ajioka Y, Hatakeyama K. Surgical outcomes for hepatocellular carcinoma in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Gastrointest Surg. 2011;15:1450–1458. doi: 10.1007/s11605-011-1540-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Matsuda Y, Ichida T, Fukumoto M. Hepatocellular carcinoma and liver transplantation: clinical perspective on molecular targeted strategies. Med Mol Morphol. 2011;44:117–124. doi: 10.1007/s00795-011-0547-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Llovet JM, Bruix J. Molecular targeted therapies in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2008;48:1312–1327. doi: 10.1002/hep.22506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Villanueva A, Llovet JM. Targeted therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2011;140:1410–1426. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.03.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Wilhelm SM, Carter C, Tang L, Wilkie D, McNabola A, Rong H, Chen C, Zhang X, Vincent P, McHugh M, Cao Y, Shujath J, Gawlak S, Eveleigh D, Rowley B, Liu L, Adnane L, Lynch M, Auclair D, Taylor I, Gedrich R, Voznesensky A, Riedl B, Post LE, Bollag G, Trail PA. BAY 43-9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral antitumor activity and targets the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and receptor tyrosine kinases involved in tumor progression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2004;64:7099–7109. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-1443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Matsuda Y, Fukumoto M. Sorafenib: complexities of Raf-dependent and Raf-independent signaling are now unveiled. Med Mol Morphol. 2011;44:183–189. doi: 10.1007/s00795-011-0558-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.El-Nassan HB. Recent progress in the identification of BRAF inhibitors as anti-cancer agents. Eur J Med Chem. 2014;72:170–205. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2013.11.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc JF, de Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul JL, Forner A, Schwartz M, Porta C, Zeuzem S, Bolondi L, Greten TF, Galle PR, Seitz JF, Borbath I, Haussinger D, Giannaris T, Shan M, Moscovici M, Voliotis D, Bruix J. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:378–390. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0708857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Cheng AL, Kang YK, Chen Z, Tsao CJ, Qin S, Kim JS, Luo R, Feng J, Ye S, Yang TS, Xu J, Sun Y, Liang H, Liu J, Wang J, Tak WY, Pan H, Burock K, Zou J, Voliotis D, Guan Z. Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:25–34. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(08)70285-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Duenas-Gonzalez A, Candelaria M, Perez-Plascencia C, Perez-Cardenas E, de la Cruz-Hernandez E, Herrera LA. Valproic acid as epigenetic cancer drug: preclinical, clinical and transcriptional effects on solid tumors. Cancer Treat Rev. 2008;34:206–222. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2007.11.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Cui W, Yu CH, Hu KQ. In vitro and in vivo effects and mechanisms of celecoxib-induced growth inhibition of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:8213–8221. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-1044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lawler OA, Miggin SM, Kinsella BT. The effects of the statins lovastatin and cerivastatin on signalling by the prostanoid IP-receptor. Br J Pharmacol. 2001;132:1639–1649. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Strumberg D, Richly H, Hilger RA, Schleucher N, Korfee S, Tewes M, Faghih M, Brendel E, Voliotis D, Haase CG, Schwartz B, Awada A, Voigtmann R, Scheulen ME, Seeber S. Phase I clinical and pharmacokinetic study of the Novel Raf kinase and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor inhibitor BAY 43-9006 in patients with advanced refractory solid tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005;23:965–972. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.06.124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Rose A, Grandoch M, vom Dorp F, Rubben H, Rosenkranz A, Fischer JW, Weber AA. Stimulatory effects of the multi-kinase inhibitor sorafenib on human bladder cancer cells. Br J Pharmacol. 2010;160:1690–1698. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00838.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Fujimaki S, Matsuda Y, Wakai T, Sanpei A, Kubota M, Takamura M, Yamagiwa S, Yano M, Ohkoshi S, Aoyagi Y. Blockade of ataxia telangiectasia mutated sensitizes hepatoma cell lines to sorafenib by interfering with Akt signaling. Cancer Lett. 2012;319:98–108. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2011.12.043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Border WA, Noble NA. Transforming growth factor beta in tissue fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 1994;331:1286–1292. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199411103311907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Pinter M, Sieghart W, Graziadei I, Vogel W, Maieron A, Konigsberg R, Weissmann A, Kornek G, Plank C, Peck-Radosavljevic M. Sorafenib in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma from mild to advanced stage liver cirrhosis. Oncologist. 2009;14:70–76. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2008-0191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Schutte K, Zimmermann L, Bornschein J, Csepregi A, Ruhl R, Ricke J, Malfertheiner P. Sorafenib therapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma in advanced liver cirrhosis. Digestion. 2011;83:275–282. doi: 10.1159/000320377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Chen YL, Lv J, Ye XL, Sun MY, Xu Q, Liu CH, Min LH, Li HP, Liu P, Ding X. Sorafenib inhibits transforming growth factor beta1-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition and apoptosis in mouse hepatocytes. Hepatology. 2011;53:1708–1718. doi: 10.1002/hep.24254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Fernando J, Sancho P, Fernandez-Rodriguez CM, Lledo JL, Caja L, Campbell JS, Fausto N, Fabregat I. Sorafenib sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells to physiological apoptotic stimuli. J Cell Physiol. 2012;227:1319–1325. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Xia H, Ooi LL, Hui KM. MicroRNA-216a/217-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition targets PTEN and SMAD7 to promote drug resistance and recurrence of liver cancer. Hepatology. 2013;58:629–641. doi: 10.1002/hep.26369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Avruch J, Zhang XF, Kyriakis JM. Raf meets Ras: completing the framework of a signal transduction pathway. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994;19:279–283. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Garnett MJ, Rana S, Paterson H, Barford D, Marais R. Wild-type and mutant B-RAF activate C-RAF through distinct mechanisms involving heterodimerization. Mol Cell. 2005;20:963–969. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2005.10.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wilhelm SM, Adnane L, Newell P, Villanueva A, Llovet JM, Lynch M. Preclinical overview of sorafenib, a multikinase inhibitor that targets both Raf and VEGF and PDGF receptor tyrosine kinase signaling. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008;7:3129–3140. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-08-0013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Abou-Alfa GK, Johnson P, Knox JJ, Capanu M, Davidenko I, Lacava J, Leung T, Gansukh B, Saltz LB. Doxorubicin plus sorafenib vs doxorubicin alone in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomized trial. Jama. 2010;304:2154–2160. doi: 10.1001/jama.2010.1672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Finn RS, Poon RT, Yau T, Klumpen HJ, Chen LT, Kang YK, Kim TY, Gomez-Martin C, Rodriguez-Lope C, Kunz T, Paquet T, Brandt U, Sellami D, Bruix J. Phase I study investigating everolimus combined with sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2013;59:1271–1277. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.07.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kuendgen A, Gattermann N. Valproic acid for the treatment of myeloid malignancies. Cancer. 2007;110:943–954. doi: 10.1002/cncr.22891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Bar EE, Stearns D. New developments in medulloblastoma treatment: the potential of a cyclopamine-lovastatin combination. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2008;17:185–195. doi: 10.1517/13543784.17.2.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Chow LW, Tung SY, Ng TY, Im SA, Lee MH, Yip AY, Toi M, Gluck S. Concurrent celecoxib with 5-fluorouracil/epirubicin/cyclophosphamide followed by docetaxel for stages II - III invasive breast cancer: the OOTR-N001 study. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2013;22:299–307. doi: 10.1517/13543784.2013.766715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Gotfryd K, Skladchikova G, Lepekhin EA, Berezin V, Bock E, Walmod PS. Cell type-specific anti-cancer properties of valproic acid: independent effects on HDAC activity and Erk1/2 phosphorylation. BMC Cancer. 2010;10:383. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]