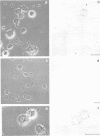
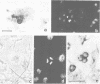
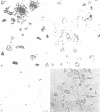
Abstract
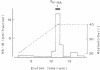
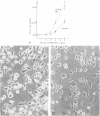
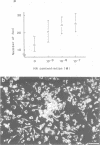
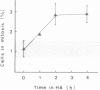
The neuropeptide head activator (HA) acts as an autocrine growth factor for the neural cell line NH15-CA2. Cell proliferation is increased in the presence of HA and inhibited by HA peptide-specific antisera. Stimulation of cellular proliferation is visible 2 h after HA application as an increase in cells in mitosis. HA has no direct effect on stimulating DNA synthesis. HA thus functions as a control signal in the G2/mitosis transition and not in the G1/S transition. Receptors for HA are present on small round cells in clusters of foci and not on cells with differentiated morphology, suggesting cell-cycle-dependent HA receptor expression.
Full text
PDF
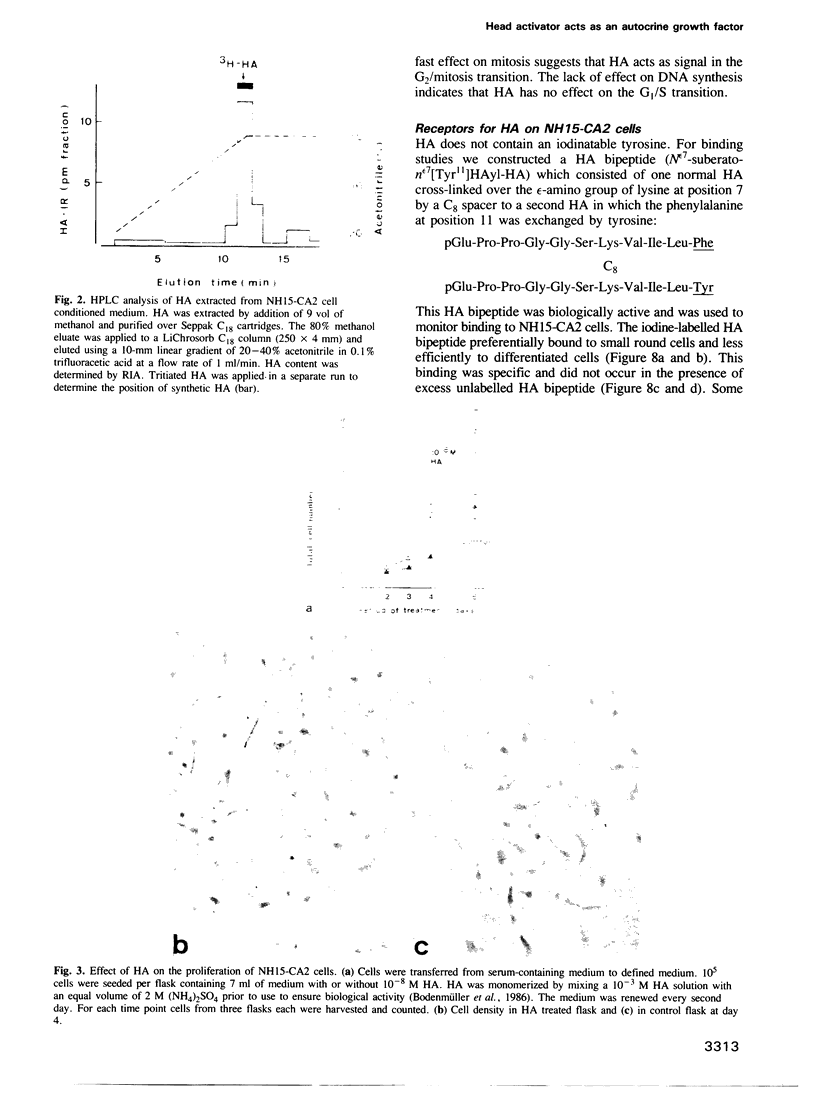
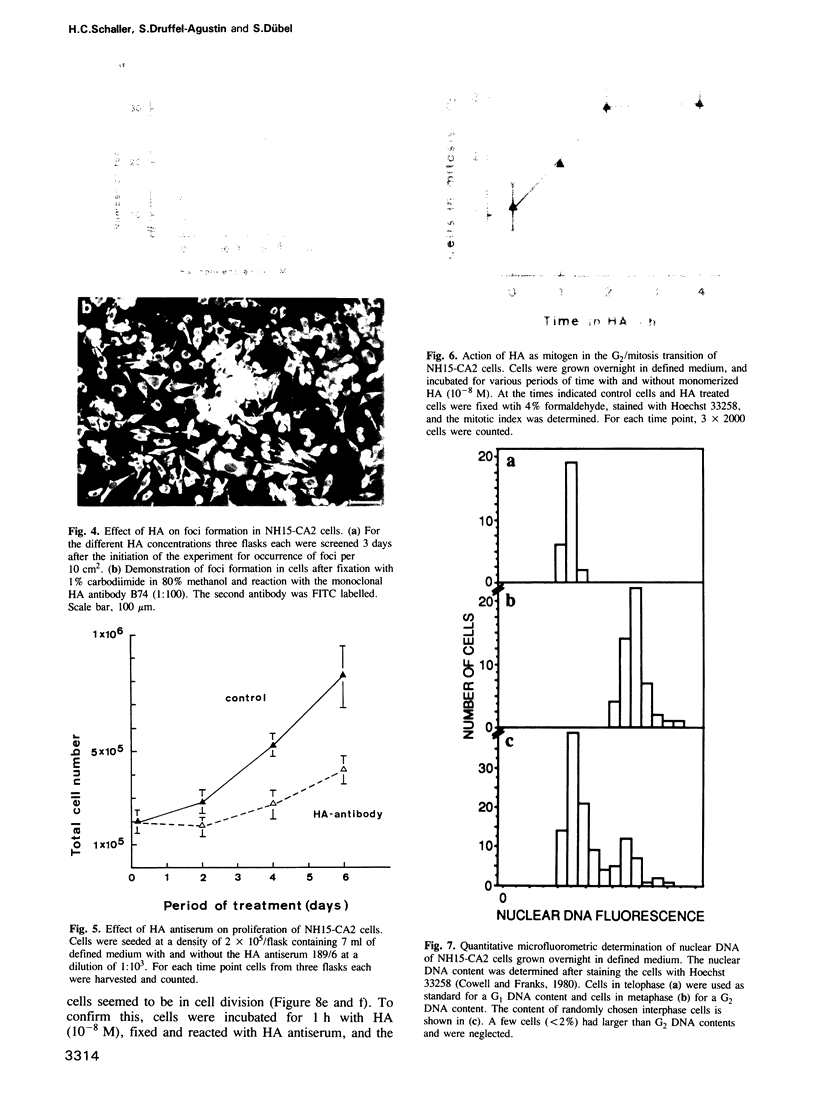

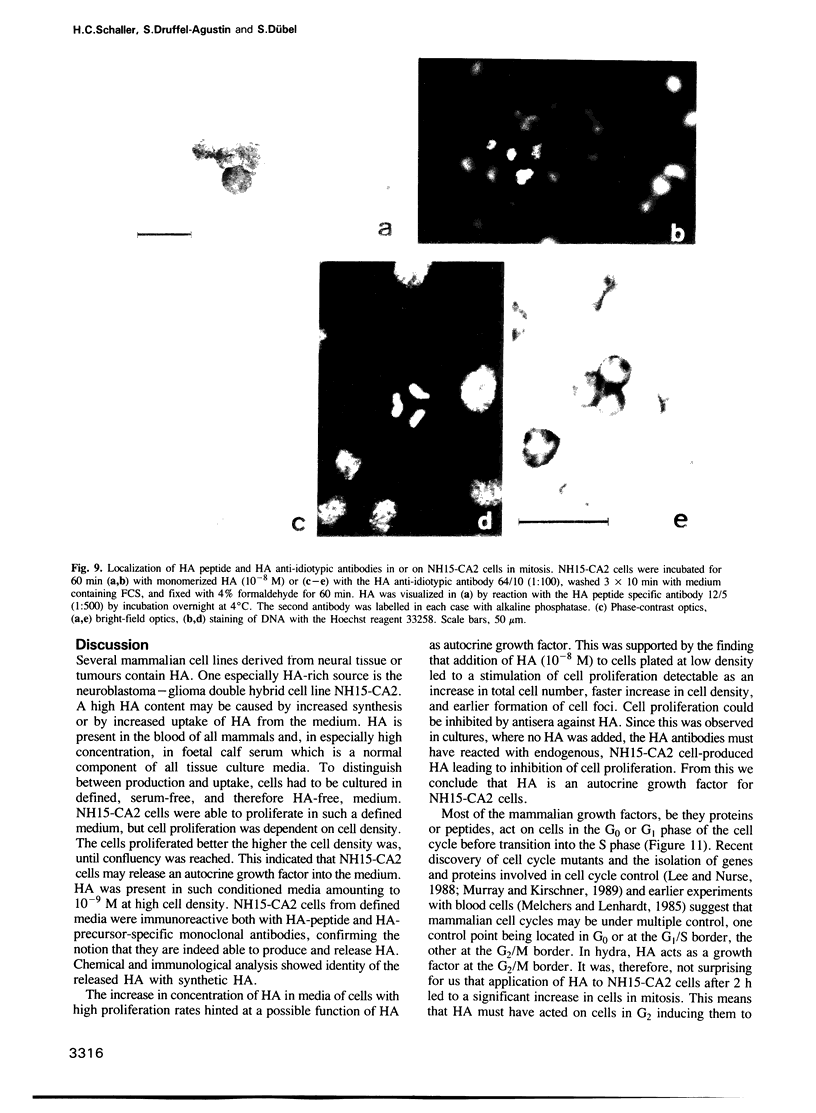


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bodenmüller H., Schaller H. C. Conserved amino acid sequence of a neuropeptide, the head activator, from coelenterates to humans. Nature. 1981 Oct 15;293(5833):579–580. doi: 10.1038/293579a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodenmüller H., Schilling E., Zachmann B., Schaller H. C. The neuropeptide head activator loses its biological acitivity by dimerization. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1825–1829. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04433.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottenstein J. E., Sato G. H. Growth of a rat neuroblastoma cell line in serum-free supplemented medium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):514–517. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowell J. K., Franks L. M. A rapid method for accurate DNA measurements in single cells in situ using a simple microfluorimeter and Hoechst 33258 as a quantitative fluorochrome. J Histochem Cytochem. 1980 Mar;28(3):206–210. doi: 10.1177/28.3.6153398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David C. N., Campbell R. D. Cell cycle kinetics and development of Hydra attenuata. I. Epithelial cells. J Cell Sci. 1972 Sep;11(2):557–568. doi: 10.1242/jcs.11.2.557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar B. A., O'Farrell P. H. Genetic control of cell division patterns in the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):177–187. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90183-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantes P. Intersecting cell cycles. Trends Genet. 1988 Oct;4(10):275–276. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90168-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heumann R., Ocalan M., Kachel V., Hamprecht B. Clonal hybrid cell lines expressing cholinergic and adrenergic properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4674–4677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmeister S. A. Action of foot activator on growth and differentiation of cells in hydra. Dev Biol. 1989 May;133(1):254–261. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90316-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M., Nurse P. Cell cycle control genes in fission yeast and mammalian cells. Trends Genet. 1988 Oct;4(10):287–290. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90171-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchers F., Lernhardt W. Three restriction points in the cell cycle of activated murine B lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7681–7685. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W. A mitotic inducer matures. Nature. 1988 Sep 15;335(6187):207–208. doi: 10.1038/335207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin synthesis drives the early embryonic cell cycle. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):275–280. doi: 10.1038/339275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaller H. C., Bodenmüller H. Ninth Adolf Butenandt lecture. Role of the neuropeptide head activator for nerve function and development. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1985 Nov;366(11):1003–1007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaller H. C., Bodenmüller H., Zachmann B., Schilling E. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the neuropeptide 'head activator'. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jan 16;138(2):365–371. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb07924.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaller H. C., Roberge M., Zachmann B., Hoffmeister S., Schilling E., Bodenmüller H. The head activator is released from regenerating Hydra bound to a carrier molecule. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1821–1824. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04432.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaller H. C., Schilling E., Theilmann L., Bodenmüller H., Sachsenheimer W. Elevated levels of head activator in human brain tumors and in serum of patients with brain and other neurally derived tumors. J Neurooncol. 1988 Nov;6(3):251–258. doi: 10.1007/BF00163709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
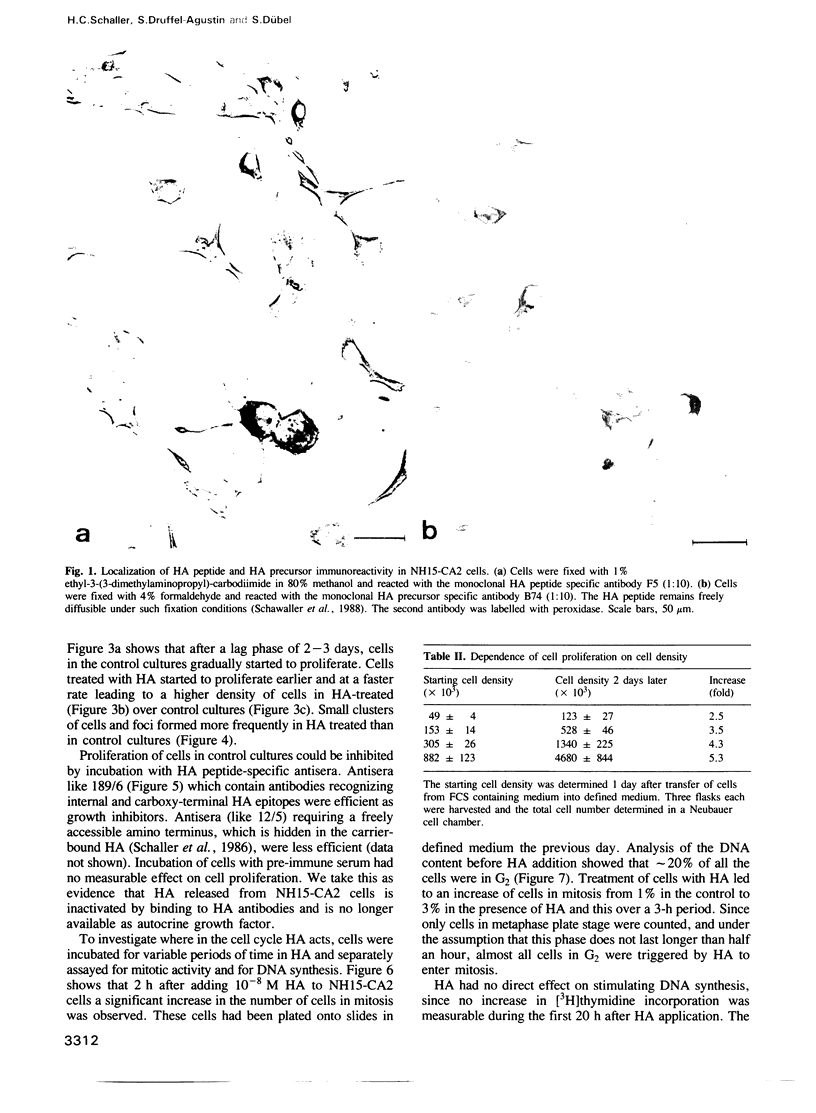
- Schawaller M., Schenck K., Hoffmeister S. A., Schaller H., Schaller H. C. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies recognizing head activator in precursor form and immunocytochemical localization of head activator precursor and head activator peptide in the neural cell line NH15-CA2 and in hydra. Differentiation. 1988 Sep;38(3):149–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1988.tb00209.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeats J. C., Allen J. M., Bloom S. R., Leigh P. J., MacDermot J. Neuropeptide Y in neuroblastoma X glioma hybrid cells. Response to dexamethasone and nerve growth factor. FEBS Lett. 1983 Oct 31;163(1):57–61. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)81162-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]