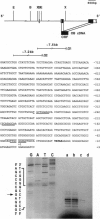
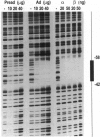
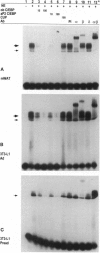
Abstract
Like other adipocyte genes that are transcriptionally activated by CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha (C/EBP alpha) during preadipocyte differentiation, expression of the mouse obese (ob) gene is immediately preceded by the expression of C/EBP alpha. While the 5' flanking region of the mouse ob gene contains several consensus C/EBP binding sites, only one of these sites appears to be functional. DNase I cleavage inhibition patterns (footprinting) of the ob gene promoter revealed that recombinant C/EBP alpha, as well as a nuclear factor present in fully differentiated 3T3-L1 adipocytes, but present at a much lower level in preadipocytes, protects the same region between nucleotides -58 and -42 relative to the transcriptional start site. Electrophoretic mobility-shift analysis using nuclear extracts from adipose tissue or 3T3-L1 adipocytes and an oligonucleotide probe corresponding to a consensus C/EBP binding site at nucleotides -55 to -47 generated a specific protein-oligonucleotide complex that was supershifted by antibody against C/EBP alpha. Probes corresponding to two upstream consensus C/EBP binding sites failed to generate protein-oligonucleotide complexes. Cotransfection of a C/EBP alpha expression vector into 3T3-L1 cells with a series of 5' truncated ob gene promoter constructs activated reporter gene expression with all constructs containing the proximal C/EBP binding site (nucleotides -55 to -47). Mutation of this site blocked transactivation by C/EBP alpha. Taken together, these findings implicate C/EBP alpha as a transcriptional activator of the ob gene promoter and identify the functional C/EBP binding site in the promoter.
Full text
PDF
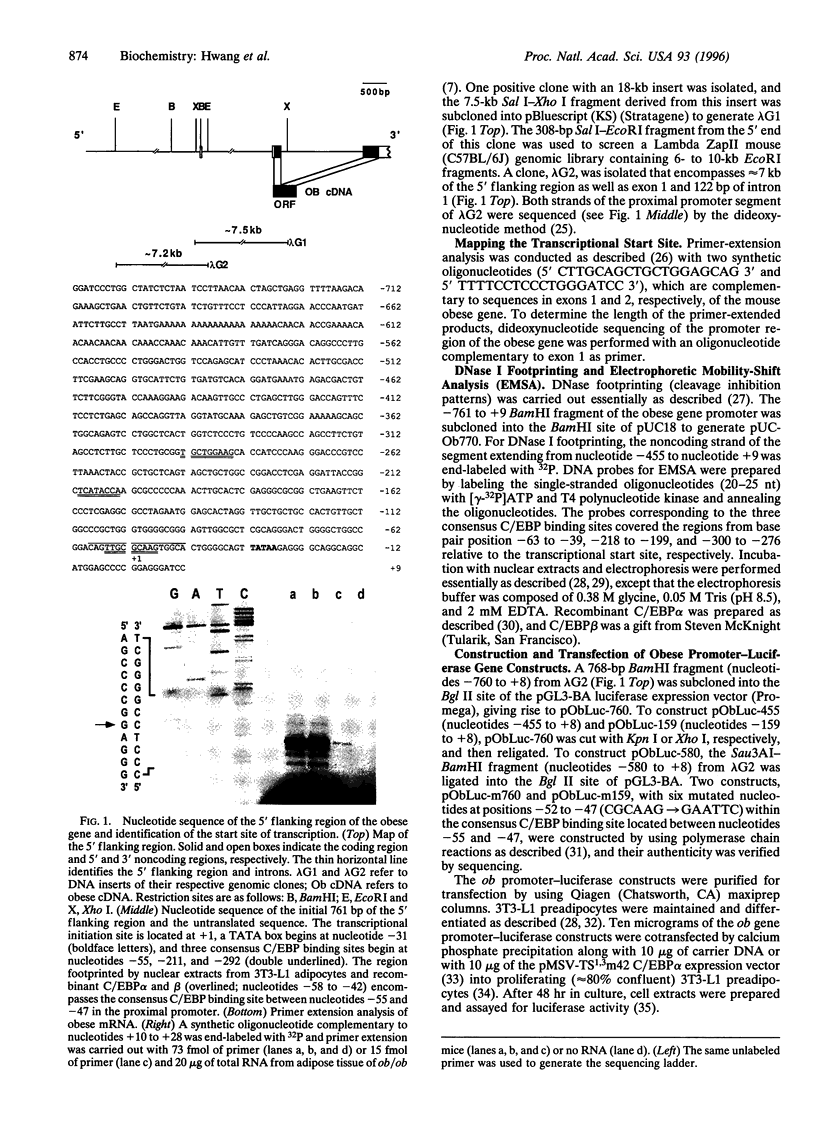
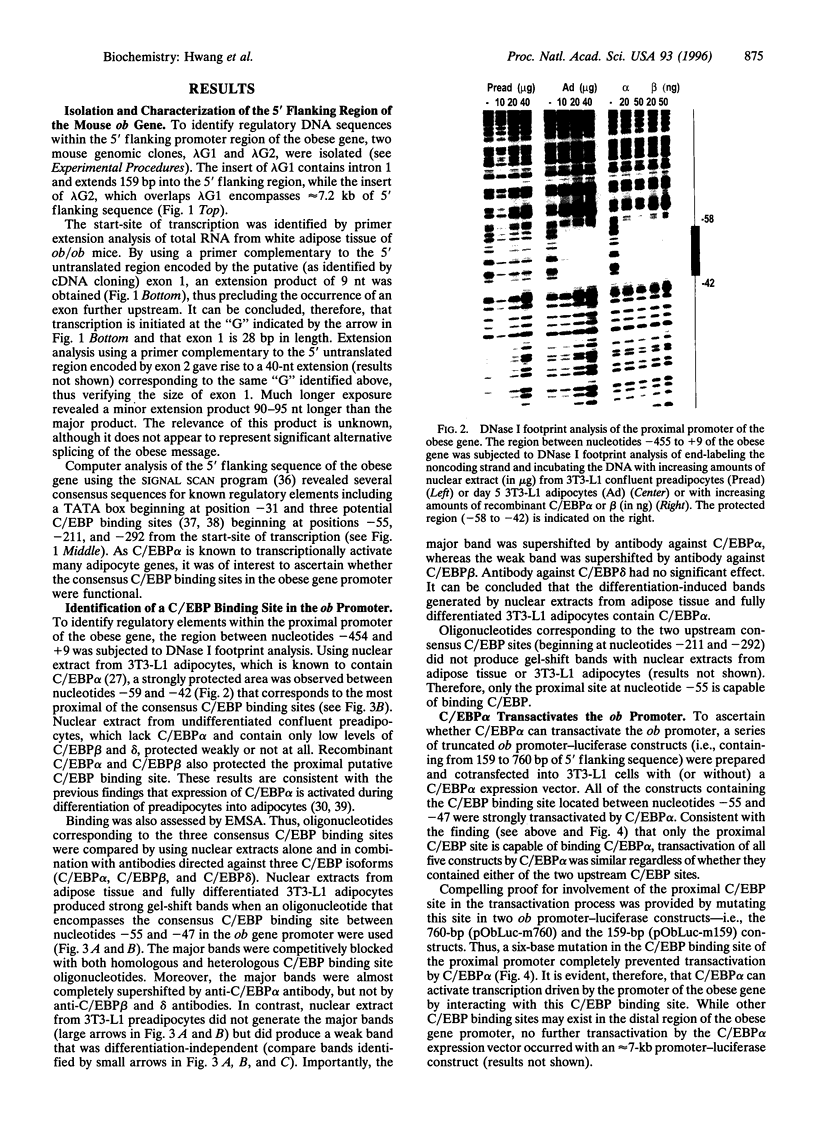
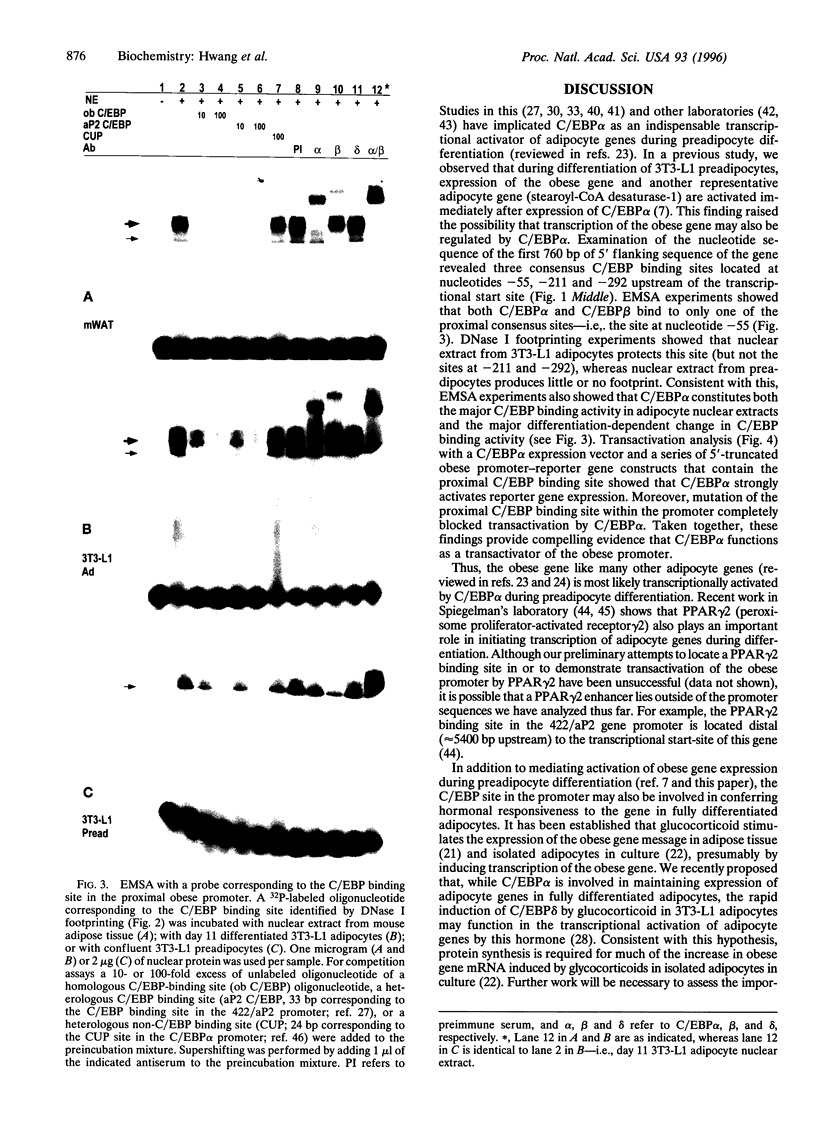

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker D. J., Ongemba L. N., Brichard V., Henquin J. C., Brichard S. M. Diet- and diabetes-induced changes of ob gene expression in rat adipose tissue. FEBS Lett. 1995 Sep 11;371(3):324–328. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)00943-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkenmeier E. H., Gwynn B., Howard S., Jerry J., Gordon J. I., Landschulz W. H., McKnight S. L. Tissue-specific expression, developmental regulation, and genetic mapping of the gene encoding CCAAT/enhancer binding protein. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1146–1156. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.8.1146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray G. A. 1989 McCollum Award lecture. Genetic and hypothalamic mechanisms for obesity--finding the needle in the haystack. Am J Clin Nutr. 1989 Nov;50(5):891–902. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/50.5.891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray G. A., York D. A. Hypothalamic and genetic obesity in experimental animals: an autonomic and endocrine hypothesis. Physiol Rev. 1979 Jul;59(3):719–809. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.3.719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campfield L. A., Smith F. J., Guisez Y., Devos R., Burn P. Recombinant mouse OB protein: evidence for a peripheral signal linking adiposity and central neural networks. Science. 1995 Jul 28;269(5223):546–549. doi: 10.1126/science.7624778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christy R. J., Kaestner K. H., Geiman D. E., Lane M. D. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein gene promoter: binding of nuclear factors during differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2593–2597. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christy R. J., Yang V. W., Ntambi J. M., Geiman D. E., Landschulz W. H., Friedman A. D., Nakabeppu Y., Kelly T. J., Lane M. D. Differentiation-induced gene expression in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes: CCAAT/enhancer binding protein interacts with and activates the promoters of two adipocyte-specific genes. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1323–1335. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman D. L. Effects of parabiosis of obese with diabetes and normal mice. Diabetologia. 1973 Aug;9(4):294–298. doi: 10.1007/BF01221857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman D. L. Obese and diabetes: two mutant genes causing diabetes-obesity syndromes in mice. Diabetologia. 1978 Mar;14(3):141–148. doi: 10.1007/BF00429772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa R. H., Grayson D. R., Xanthopoulos K. G., Darnell J. E., Jr A liver-specific DNA-binding protein recognizes multiple nucleotide sites in regulatory regions of transthyretin, alpha 1-antitrypsin, albumin, and simian virus 40 genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3840–3844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danesch U., Hoeck W., Ringold G. M. Cloning and transcriptional regulation of a novel adipocyte-specific gene, FSP27. CAAT-enhancer-binding protein (C/EBP) and C/EBP-like proteins interact with sequences required for differentiation-dependent expression. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):7185–7193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vos P., Saladin R., Auwerx J., Staels B. Induction of ob gene expression by corticosteroids is accompanied by body weight loss and reduced food intake. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jul 7;270(27):15958–15961. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.27.15958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faisst S., Meyer S. Compilation of vertebrate-encoded transcription factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 11;20(1):3–26. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.1.3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flier J. S. The adipocyte: storage depot or node on the energy information superhighway? Cell. 1995 Jan 13;80(1):15–18. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90445-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frederich R. C., Löllmann B., Hamann A., Napolitano-Rosen A., Kahn B. B., Lowell B. B., Flier J. S. Expression of ob mRNA and its encoded protein in rodents. Impact of nutrition and obesity. J Clin Invest. 1995 Sep;96(3):1658–1663. doi: 10.1172/JCI118206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman J. M., Leibel R. L. Tackling a weighty problem. Cell. 1992 Apr 17;69(2):217–220. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90402-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halaas J. L., Gajiwala K. S., Maffei M., Cohen S. L., Chait B. T., Rabinowitz D., Lallone R. L., Burley S. K., Friedman J. M. Weight-reducing effects of the plasma protein encoded by the obese gene. Science. 1995 Jul 28;269(5223):543–546. doi: 10.1126/science.7624777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGALLS A. M., DICKIE M. M., SNELL G. D. Obese, a new mutation in the house mouse. J Hered. 1950 Dec;41(12):317–318. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a106073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaestner K. H., Christy R. J., Lane M. D. Mouse insulin-responsive glucose transporter gene: characterization of the gene and trans-activation by the CCAAT/enhancer binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):251–255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. T., Lane M. D. Antisense CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein RNA suppresses coordinate gene expression and triglyceride accumulation during differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Genes Dev. 1992 Apr;6(4):533–544. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.4.533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. T., Lane M. D. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha is sufficient to initiate the 3T3-L1 adipocyte differentiation program. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Sep 13;91(19):8757–8761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.19.8757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDougald O. A., Cornelius P., Lin F. T., Chen S. S., Lane M. D. Glucocorticoids reciprocally regulate expression of the CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha and delta genes in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and white adipose tissue. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 22;269(29):19041–19047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDougald O. A., Cornelius P., Liu R., Lane M. D. Insulin regulates transcription of the CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP) alpha, beta, and delta genes in fully-differentiated 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jan 13;270(2):647–654. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.2.647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDougald O. A., Hwang C. S., Fan H., Lane M. D. Regulated expression of the obese gene product (leptin) in white adipose tissue and 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Sep 26;92(20):9034–9037. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.20.9034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDougald O. A., Lane M. D. Adipocyte differentiation. When precursors are also regulators. Curr Biol. 1995 Jun 1;5(6):618–621. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(95)00125-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDougald O. A., Lane M. D. Transcriptional regulation of gene expression during adipocyte differentiation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1995;64:345–373. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.64.070195.002021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maffei M., Fei H., Lee G. H., Dani C., Leroy P., Zhang Y., Proenca R., Negrel R., Ailhaud G., Friedman J. M. Increased expression in adipocytes of ob RNA in mice with lesions of the hypothalamus and with mutations at the db locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jul 18;92(15):6957–6960. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.15.6957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuzaki H., Ogawa Y., Isse N., Satoh N., Okazaki T., Shigemoto M., Mori K., Tamura N., Hosoda K., Yoshimasa Y. Human obese gene expression. Adipocyte-specific expression and regional differences in the adipose tissue. Diabetes. 1995 Jul;44(7):855–858. doi: 10.2337/diab.44.7.855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeon C., Pham T. Transactivation of the human insulin receptor gene by the CAAT/enhancer binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jan 31;174(2):721–728. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91477-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami T., Iida M., Shima K. Dexamethasone regulates obese expression in isolated rat adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995 Sep 25;214(3):1260–1267. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.2422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa Y., Masuzaki H., Isse N., Okazaki T., Mori K., Shigemoto M., Satoh N., Tamura N., Hosoda K., Yoshimasa Y. Molecular cloning of rat obese cDNA and augmented gene expression in genetically obese Zucker fatty (fa/fa) rats. J Clin Invest. 1995 Sep;96(3):1647–1652. doi: 10.1172/JCI118204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelleymounter M. A., Cullen M. J., Baker M. B., Hecht R., Winters D., Boone T., Collins F. Effects of the obese gene product on body weight regulation in ob/ob mice. Science. 1995 Jul 28;269(5223):540–543. doi: 10.1126/science.7624776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prestridge D. S. SIGNAL SCAN: a computer program that scans DNA sequences for eukaryotic transcriptional elements. Comput Appl Biosci. 1991 Apr;7(2):203–206. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/7.2.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rentsch J., Levens N., Chiesi M. Recombinant ob-gene product reduces food intake in fasted mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995 Sep 5;214(1):131–136. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.2266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saladin R., De Vos P., Guerre-Millo M., Leturque A., Girard J., Staels B., Auwerx J. Transient increase in obese gene expression after food intake or insulin administration. Nature. 1995 Oct 12;377(6549):527–529. doi: 10.1038/377527a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens T. W., Basinski M., Bristow P. K., Bue-Valleskey J. M., Burgett S. G., Craft L., Hale J., Hoffmann J., Hsiung H. M., Kriauciunas A. The role of neuropeptide Y in the antiobesity action of the obese gene product. Nature. 1995 Oct 12;377(6549):530–532. doi: 10.1038/377530a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Student A. K., Hsu R. Y., Lane M. D. Induction of fatty acid synthetase synthesis in differentiating 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4745–4750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tontonoz P., Hu E., Spiegelman B. M. Stimulation of adipogenesis in fibroblasts by PPAR gamma 2, a lipid-activated transcription factor. Cell. 1994 Dec 30;79(7):1147–1156. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasseur-Cognet M., Lane M. D. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha (C/EBP alpha) undifferentiated protein: a developmentally regulated nuclear protein that binds to the C/EBP alpha gene promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):7312–7316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.7312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Proenca R., Maffei M., Barone M., Leopold L., Friedman J. M. Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature. 1994 Dec 1;372(6505):425–432. doi: 10.1038/372425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]