Abstract
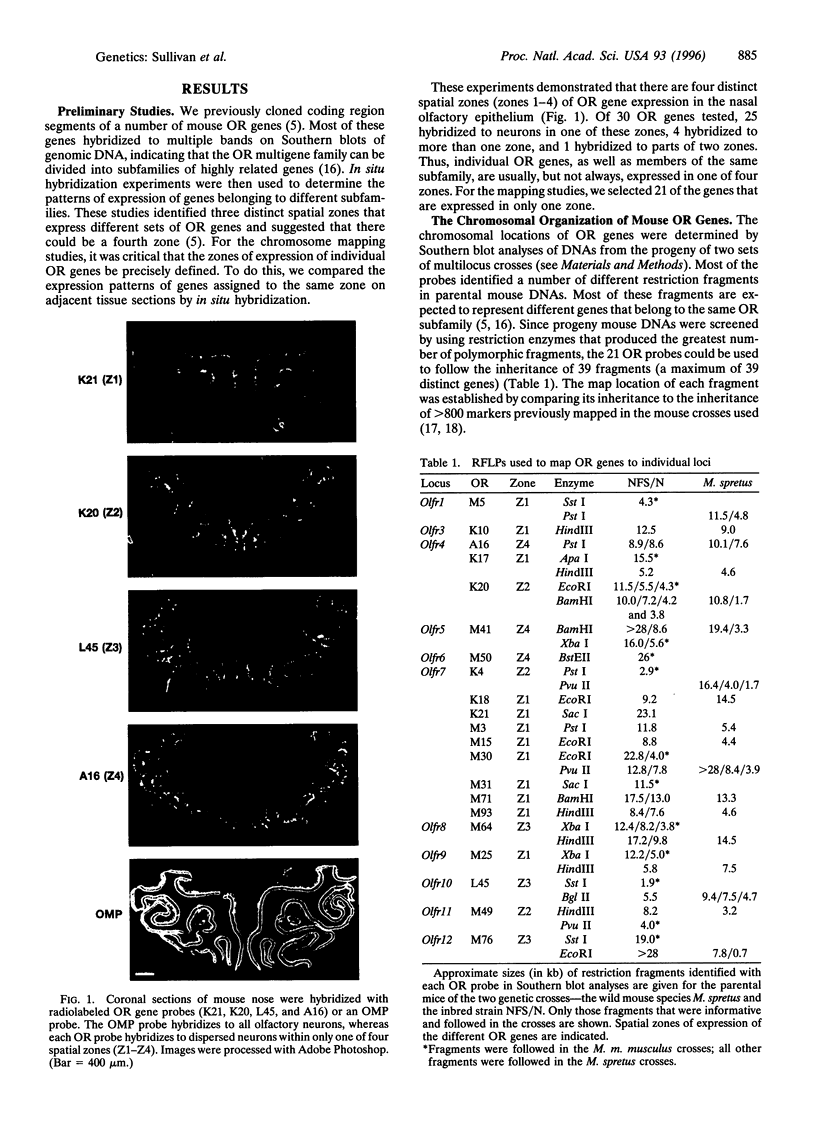
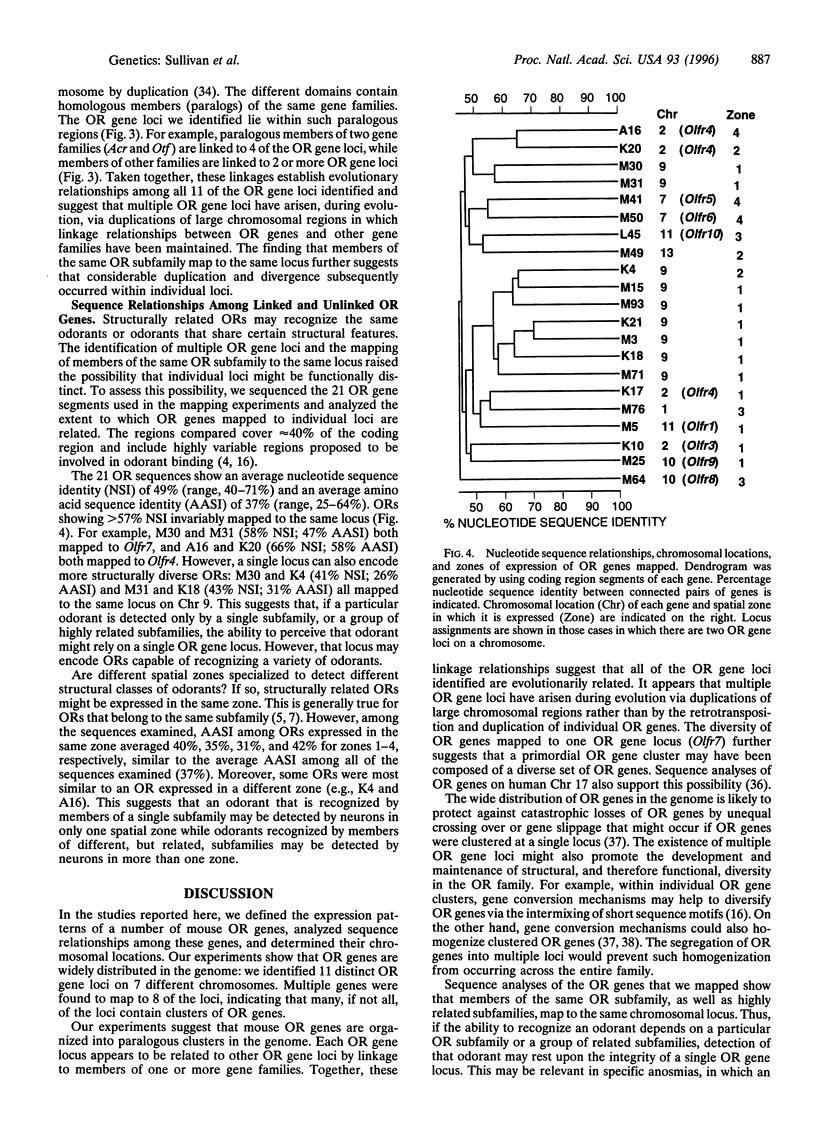
Odorant receptors (ORs) on nasal olfactory sensory neurons are encoded by a large multigene family. Each member of the family is expressed in a small percentage of neurons that are confined to one of several spatial zones in the nose but are randomly distributed throughout that zone. This pattern of expression suggests that when the sensory neuron selects which OR gene to express it may be confined to a particular zonal gene set of several hundred OR genes but select from among the members of that set via a stochastic mechanism. Both locus-dependent and locus-independent models of OR gene choice have been proposed. To investigate the feasibility of these models, we determined the chromosomal locations of 21 OR genes expressed in four different spatial zones. We found that OR genes are clustered within multiple loci that are broadly distributed in the genome. These loci lie within paralogous chromosomal regions that appear to have arisen by duplications of large chromosomal domains followed by extensive gene duplication and divergence. Our studies show that OR genes expressed in the same zone map to numerous loci; moreover, a single locus can contain genes expressed in different zones. These findings raise the possibility that OR gene choice may be locus-independent or involve consecutive stochastic choices.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamson M. C., Silver J., Kozak C. A. The mouse homolog of the Gibbon ape leukemia virus receptor: genetic mapping and a possible receptor function in rodents. Virology. 1991 Aug;183(2):778–781. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)91010-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alt F. W., Blackwell T. K., Yancopoulos G. D. Development of the primary antibody repertoire. Science. 1987 Nov 20;238(4830):1079–1087. doi: 10.1126/science.3317825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballantyne C. M., Kozak C. A., O'Brien W. E., Beaudet A. L. Assignment of the gene for intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (Icam-1) to proximal mouse chromosome 9. Genomics. 1991 Mar;9(3):547–550. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90423-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Arie N., Lancet D., Taylor C., Khen M., Walker N., Ledbetter D. H., Carrozzo R., Patel K., Sheer D., Lehrach H. Olfactory receptor gene cluster on human chromosome 17: possible duplication of an ancestral receptor repertoire. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Feb;3(2):229–235. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.2.229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck L. B. The olfactory multigene family. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1992 Jun;2(3):467–473. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80159-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck L., Axel R. A novel multigene family may encode odorant receptors: a molecular basis for odor recognition. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):175–187. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90418-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchell B., Nebert D. W., Nelson D. R., Bock K. W., Iyanagi T., Jansen P. L., Lancet D., Mulder G. J., Chowdhury J. R., Siest G. The UDP glucuronosyltransferase gene superfamily: suggested nomenclature based on evolutionary divergence. DNA Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;10(7):487–494. doi: 10.1089/dna.1991.10.487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborti A., Lippman D. L., Loh H. H., Kozak C. A., Lee N. M. Genetic mapping of opioid binding protein gene(s) to mouse chromosome 9. Mamm Genome. 1993;4(3):179–182. doi: 10.1007/BF00352235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chess A., Simon I., Cedar H., Axel R. Allelic inactivation regulates olfactory receptor gene expression. Cell. 1994 Sep 9;78(5):823–834. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(94)90562-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi O. R., Engel J. D. Developmental regulation of beta-globin gene switching. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):17–26. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A., Gilbert D. J., Eppig J. T., Maltais L. J., Miller J. C., Dietrich W. F., Weaver A., Lincoln S. E., Steen R. G. A genetic linkage map of the mouse: current applications and future prospects. Science. 1993 Oct 1;262(5130):57–66. doi: 10.1126/science.8211130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dover G. A. DNA turnover and the molecular clock. J Mol Evol. 1987;26(1-2):47–58. doi: 10.1007/BF02111281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dover G. A. Evolution of genetic redundancy for advanced players. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993 Dec;3(6):902–910. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(93)90012-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hake L. E., Kuemmerle N., Hecht N. B., Kozak C. A. The genes encoding the somatic and testis-specific isotypes of the mouse cytochrome c genes map to paralogous regions of chromosomes 6 and 2. Genomics. 1994 Apr;20(3):503–505. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt C. R., Gasser D. L., Chaplin D. D., Pierce J. C., Kozak C. A. Chromosomal localization of five murine HSP70 gene family members: Hsp70-1, Hsp70-2, Hsp70-3, Hsc70t, and Grp78. Genomics. 1993 Apr;16(1):193–198. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak C. A., Adamson M. C., Buckler C. E., Segovia L., Paralkar V., Wistow G. Genomic cloning of mouse MIF (macrophage inhibitory factor) and genetic mapping of the human and mouse expressed gene and nine mouse pseudogenes. Genomics. 1995 Jun 10;27(3):405–411. doi: 10.1006/geno.1995.1070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak C. A., Danciger M., Bowes C., Adamson M. C., Palczewski K., Polans A. S., Farber D. B. Localization of three genes expressed in retina on mouse chromosome 11. Mamm Genome. 1995 Feb;6(2):142–144. doi: 10.1007/BF00303262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak C. A., Peyser M., Krall M., Mariano T. M., Kumar C. S., Pestka S., Mock B. A. Molecular genetic markers spanning mouse chromosome 10. Genomics. 1990 Nov;8(3):519–524. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90039-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krissansen G. W., Gorman P. A., Kozak C. A., Spurr N. K., Sheer D., Goodfellow P. N., Crumpton M. J. Chromosomal locations of the gene coding for the CD3 (T3) gamma subunit of the human and mouse CD3/T-cell antigen receptor complexes. Immunogenetics. 1987;26(4-5):258–266. doi: 10.1007/BF00346520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon B. S., Chintamaneni C., Kozak C. A., Copeland N. G., Gilbert D. J., Jenkins N., Barton D., Francke U., Kobayashi Y., Kim K. K. A melanocyte-specific gene, Pmel 17, maps near the silver coat color locus on mouse chromosome 10 and is in a syntenic region on human chromosome 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9228–9232. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancet D., Ben-Arie N. Olfactory receptors. Curr Biol. 1993 Oct 1;3(10):668–674. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90064-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer D. I., Nathans D. Nucleotide sequence of a growth-related mRNA encoding a member of the prolactin-growth hormone family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4255–4259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundin L. G. Evolution of the vertebrate genome as reflected in paralogous chromosomal regions in man and the house mouse. Genomics. 1993 Apr;16(1):1–19. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mock B. A., Krall M., Kozak C. A., Nesbitt M. N., McBride O. W., Renauld J. C., Van Snick J. IL9 maps to mouse chromosome 13 and human chromosome 5. Immunogenetics. 1990;31(4):265–270. doi: 10.1007/BF00204898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nef P., Hermans-Borgmeyer I., Artières-Pin H., Beasley L., Dionne V. E., Heinemann S. F. Spatial pattern of receptor expression in the olfactory epithelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):8948–8952. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.8948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ngai J., Chess A., Dowling M. M., Necles N., Macagno E. R., Axel R. Coding of olfactory information: topography of odorant receptor expression in the catfish olfactory epithelium. Cell. 1993 Mar 12;72(5):667–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90396-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ressler K. J., Sullivan S. L., Buck L. B. A molecular dissection of spatial patterning in the olfactory system. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1994 Aug;4(4):588–596. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(94)90061-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ressler K. J., Sullivan S. L., Buck L. B. A zonal organization of odorant receptor gene expression in the olfactory epithelium. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):597–609. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90145-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleif R. DNA looping. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:199–223. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.001215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strotmann J., Wanner I., Helfrich T., Beck A., Breer H. Rostro-caudal patterning of receptor-expressing olfactory neurones in the rat nasal cavity. Cell Tissue Res. 1994 Oct;278(1):11–20. doi: 10.1007/BF00305773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strotmann J., Wanner I., Krieger J., Raming K., Breer H. Expression of odorant receptors in spatially restricted subsets of chemosensory neurones. Neuroreport. 1992 Dec;3(12):1053–1056. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199212000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S. Somatic generation of antibody diversity. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):575–581. doi: 10.1038/302575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassar R., Ngai J., Axel R. Spatial segregation of odorant receptor expression in the mammalian olfactory epithelium. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):309–318. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90422-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe H., Kimata K., Line S., Strong D., Gao L. Y., Kozak C. A., Yamada Y. Mouse cartilage matrix deficiency (cmd) caused by a 7 bp deletion in the aggrecan gene. Nat Genet. 1994 Jun;7(2):154–157. doi: 10.1038/ng0694-154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





