Figure 2.
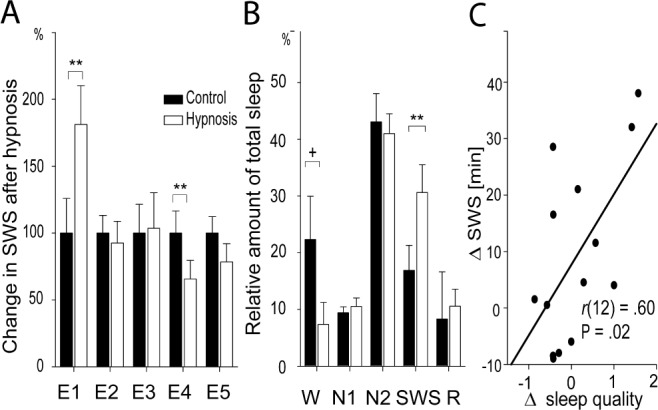
Effects of the hypnotic suggestions on sleep. (A) Highly suggestible subjects in experiment 1 almost doubled their amount of slow wave sleep (SWS) after the hypnotic suggestion “to sleep deeper” (white bar), with the SWS amount after the control tape set to 100% (black bar). Using the suggestion “to sleep shallower” the beneficial effect of hypnotic suggestions on SWS in a group of highly suggestible subjects was completely abolished (experiment 2). Similarly in experiment 3, no increase of SWS was observed after listening to verbal information, even though participants were informed previously that listening to verbal information should increase subsequent SWS (demand characteristics). In low suggestible subjects, the suggestion “to sleep deeper” even decreased the amount of SWS (experiment 4), and the direction of the effect was similar when subjects were asked to simulate the effect of hypnotic suggestion on subsequent sleep (experiment 5). (B) The hypnotic suggestion “to sleep deeper” specifically increased the amount of SWS in experiment 1, whereas time awake after sleep onset (W) was marginally reduced, leaving the other sleep stages unaffected (N1/N2: nonrapid eye movement sleep stage 1 and 2, R,: rapid eye movement sleep). Means ± standard error of the mean are indicated. +: P ≤ 0.08; *: P ≤ 0.05; **: P ≤ 0.01. (C) The hypnosis-induced increases in SWS significantly correlated with subjective increases in sleep quality in experiment 1.
