Abstract
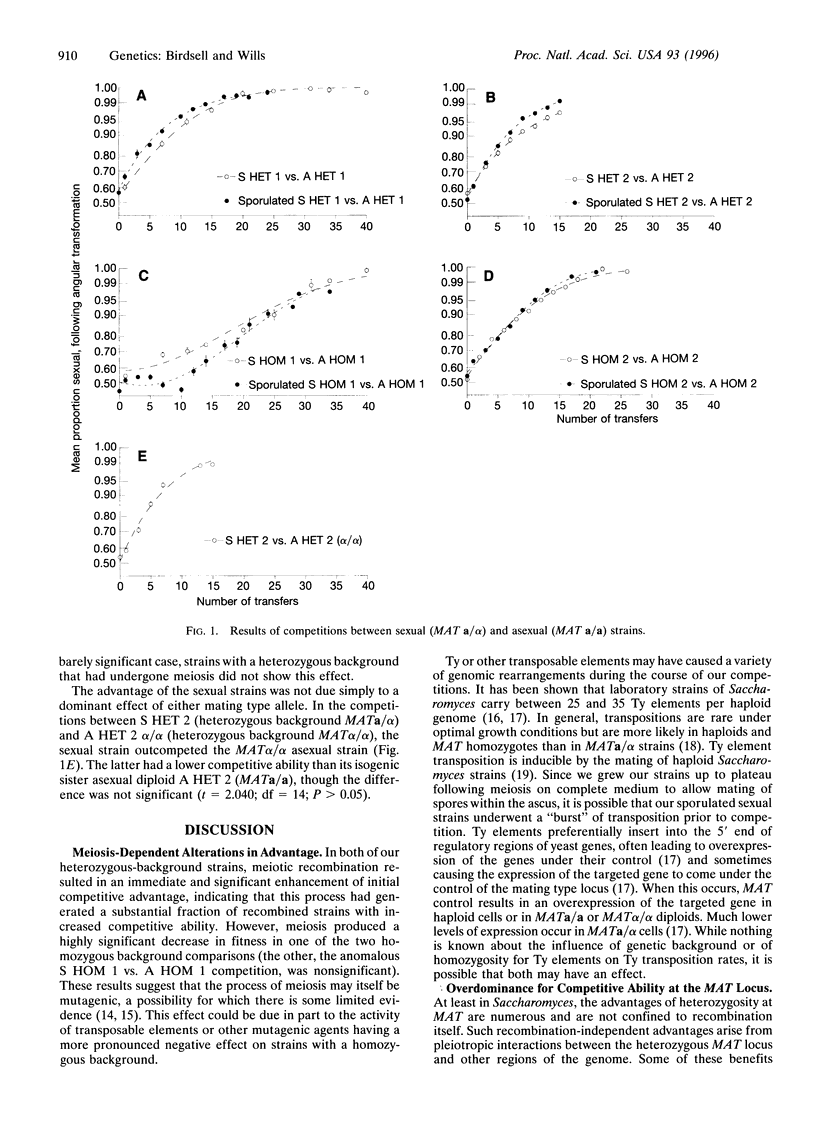
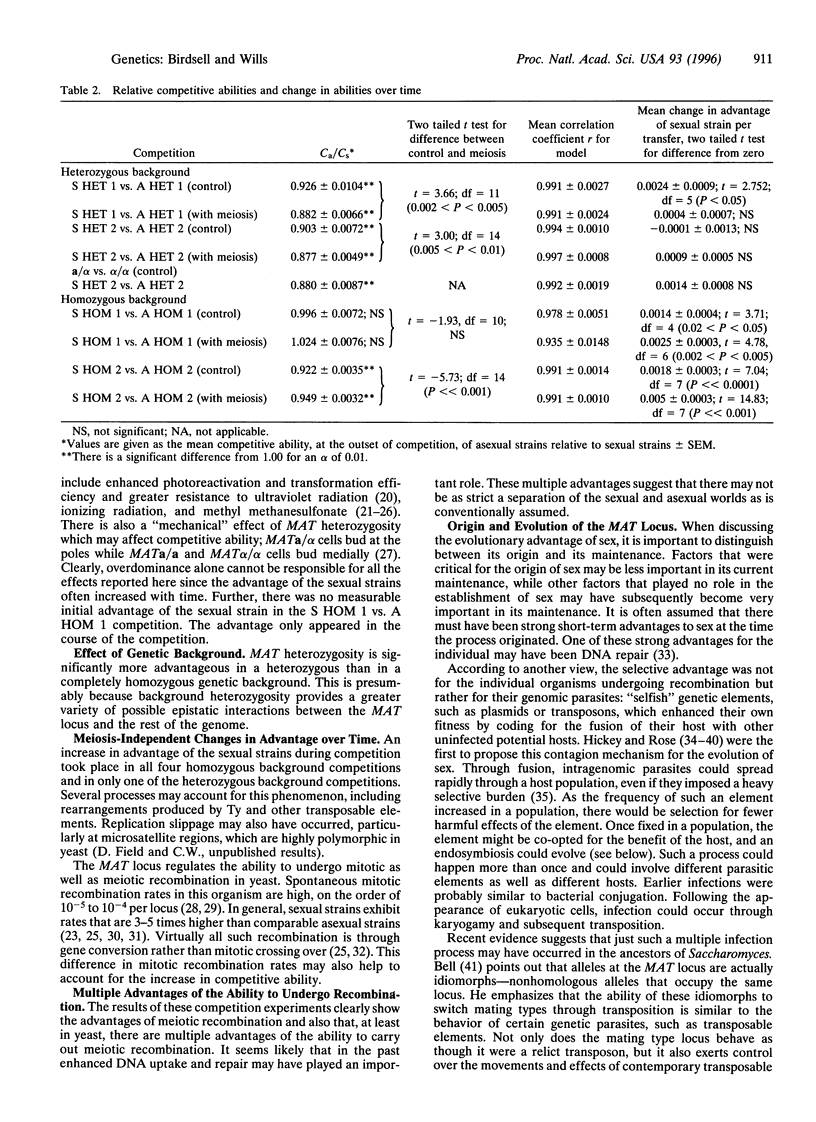
The presumed advantages of genetic recombinations are difficult to demonstrate directly. To investigate the effects of recombination and background heterozygosity on competitive ability, we have performed serial-transfer competition experiments between isogenic sexual and asexual strains of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The members of these diploid pairs of strains differed only in being heterozygous (sexual) or homozygous (asexual) at the mating type or MAT locus. Competing pairs had either a completely homozygous or a heterozygous genetic background, the latter being heterozygous at many different loci throughout the genome. A round of meiotic recombination (automixis) conferred a large and statistically significant enhancement of competitive ability on sexual strains with a heterozygous genetic background. By contrast, in homozygous background competitions, meiosis decreased the sexual strains' initial relative competitive ability. In all cases, however, the sexual strains outcompeted their isogenic asexual counterparts, whether meiotic recombination had occurred or not. In some genetic backgrounds, this was due in part to an overdominance effect on competitive advantage of heterozygosity at the MAT locus. The advantage of the sexual strains also increased significantly during the course of the homozygous background competitions, particularly when meiosis had occurred. This latter effect either did not occur or was very weak in heterozygous background competitions. Overall, sexual strains with heterozygous genetic backgrounds had a significantly higher initial relative competitive ability than those with homozygous backgrounds. The advantage of mating type heterozygosity in this organism extends far beyond the ability to recombine meiotically.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chan R. K., Otte C. A. Isolation and genetic analysis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutants supersensitive to G1 arrest by a factor and alpha factor pheromones. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;2(1):11–20. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan R. K., Otte C. A. Physiological characterization of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutants supersensitive to G1 arrest by a factor and alpha factor pheromones. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;2(1):21–29. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber J. E. Mating-type gene switching in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Trends Genet. 1992 Dec;8(12):446–452. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90329-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herskowitz I., Jensen R. E. Putting the HO gene to work: practical uses for mating-type switching. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:132–146. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94011-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondrashov A. S. Classification of hypotheses on the advantage of amphimixis. J Hered. 1993 Sep-Oct;84(5):372–387. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a111358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondrashov A. S. The asexual ploidy cycle and the origin of sex. Nature. 1994 Jul 21;370(6486):213–216. doi: 10.1038/370213a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis W. M., Jr The cost of sex. Experientia Suppl. 1987;55:33–57. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-6273-8_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



