Abstract
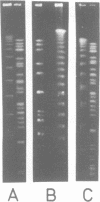
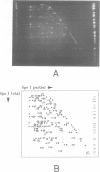
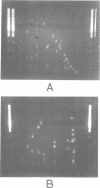
A complete macrorestriction map of the 5.9 Mb genome of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO (DSM 1707) was constructed by the combination of various one- and two-dimensional pulsed field gel electrophoresis techniques. A total of 51 restriction sites (36 SpeI sites, 15 DpnI sites) were placed on the physical map yielding an average resolution of 110 kb. Several genes encoding virulence factors and enzymes of metabolic pathways were located on the anonymous map by Southern hybridization. Distances between the gene loci were similar on the genetic and physical maps, suggesting an even distribution of genome mobility throughout the bacterial chromosome. The four rRNA operons were organized in pairs of inverted repeats. The two-dimensional macro-restriction techniques described herein are generally applicable for the genome mapping of any prokaryote and lower eukaryote which yields resolvable fragment patterns on two-dimensional pulsed field gels.
Full text
PDF


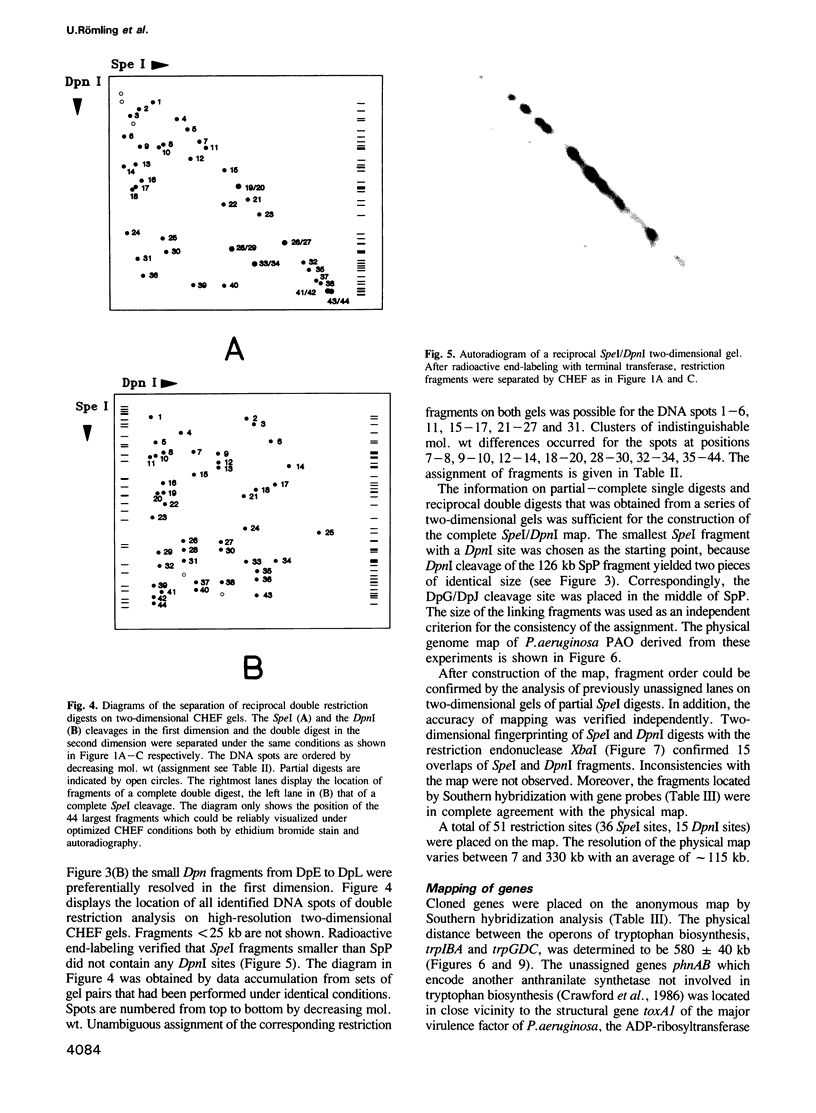
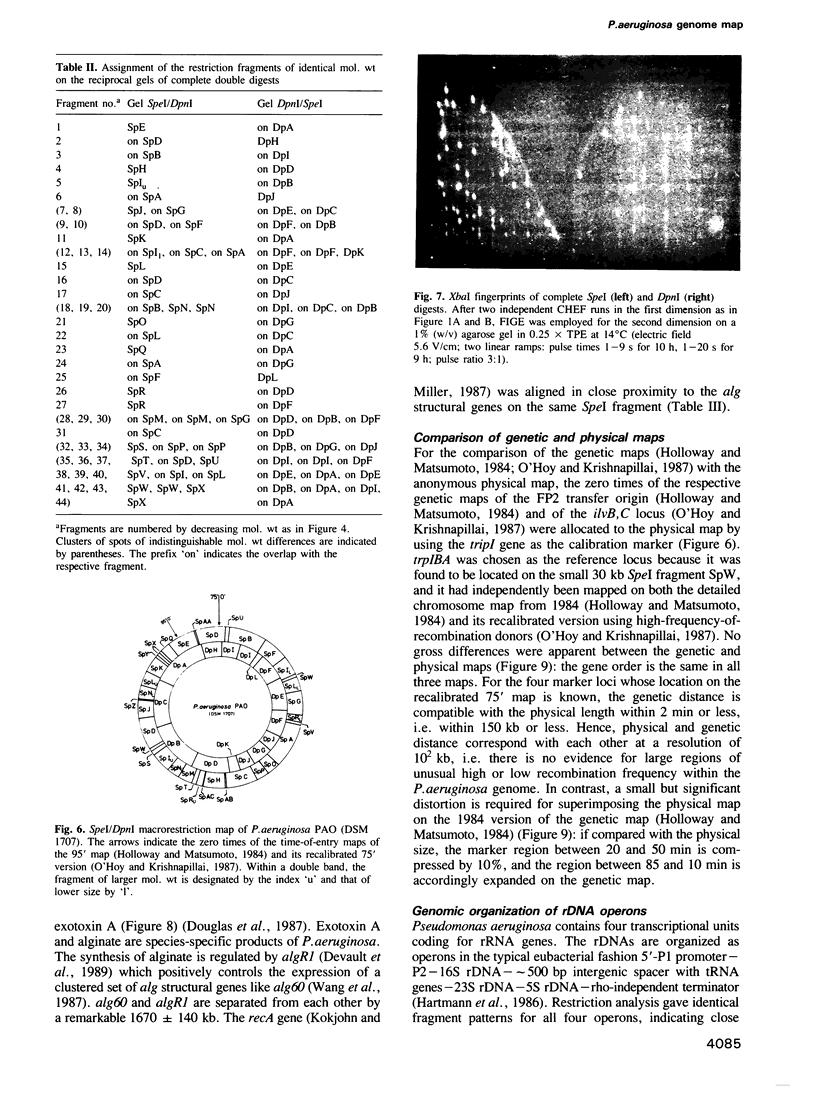
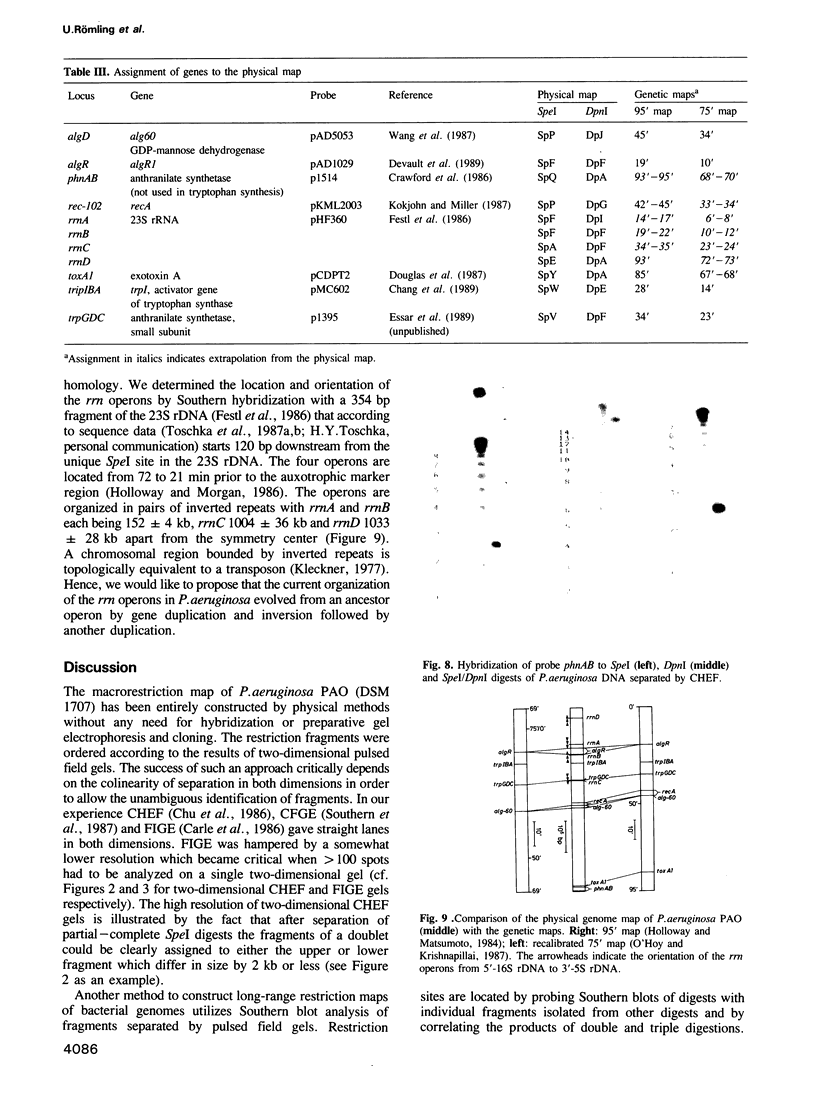



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bautsch W. Rapid physical mapping of the Mycoplasma mobile genome by two-dimensional field inversion gel electrophoresis techniques. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 23;16(24):11461–11467. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.24.11461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boehm T. L., Drahovsky D. Two-dimensional restriction mapping by digestion with restriction endonucleases of DNA in agarose and polyacrylamide gels. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1984 May;9(2):153–161. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(84)90006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer B. J. When polymerases collide: replication and the transcriptional organization of the E. coli chromosome. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):679–686. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90086-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D. T., Carle G. F., Olson M. V. Cloning of large segments of exogenous DNA into yeast by means of artificial chromosome vectors. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):806–812. doi: 10.1126/science.3033825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carle G. F., Frank M., Olson M. V. Electrophoretic separations of large DNA molecules by periodic inversion of the electric field. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):65–68. doi: 10.1126/science.3952500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang M., Hadero A., Crawford I. P. Sequence of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa trpI activator gene and relatedness of trpI to other procaryotic regulatory genes. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):172–183. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.172-183.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Vollrath D., Davis R. W. Separation of large DNA molecules by contour-clamped homogeneous electric fields. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1582–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.3538420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford I. P., Wilde A., Yelverton E. M., Figurski D., Hedges R. W. Structure and regulation of the anthranilate synthase genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: II. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli. Mol Biol Evol. 1986 Sep;3(5):449–458. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas C. M., Guidi-Rontani C., Collier R. J. Exotoxin A of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: active, cloned toxin is secreted into the periplasmic space of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):4962–4966. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.4962-4966.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellwood M., Nomura M. Chromosomal locations of the genes for rRNA in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):458–468. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.458-468.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ely B., Gerardot C. J. Use of pulsed-field-gradient gel electrophoresis to construct a physical map of the Caulobacter crescentus genome. Gene. 1988 Sep 7;68(2):323–333. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90035-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan J. B., Chikashige Y., Smith C. L., Niwa O., Yanagida M., Cantor C. R. Construction of a Not I restriction map of the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 11;17(7):2801–2818. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.7.2801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold J., Bellofatto V., Shapiro L., Amemiya K. Organization and nucleotide sequence analysis of an rRNA and tRNA gene cluster from Caulobacter crescentus. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):155–166. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.155-166.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Festl H., Ludwig W., Schleifer K. H. DNA hybridization probe for the Pseudomonas fluorescens group. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Nov;52(5):1190–1194. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.5.1190-1194.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidi-Rontani C., Collier R. J. Exotoxin A of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: evidence that domain I functions in receptor binding. Mol Microbiol. 1987 Jul;1(1):67–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1987.tb00528.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLOWAY B. W., JENNINGS P. A. An infectious fertility factor for Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nature. 1958 Mar 22;181(4612):855–856. doi: 10.1038/181855b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas D., Watson J., Krieg R., Leisinger T. Isolation of an Hfr donor of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO by insertion of the plasmid RP1 into the tryptophan synthase gene. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(2):240–244. doi: 10.1007/BF00269664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann R. K., Toschka H. Y., Ulbrich N., Erdmann V. A. Genomic organization of rDNA in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jan 20;195(1-2):187–193. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80158-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrand M., Jurgenson J. E., Ramage R. T., Bourque D. P. Derivation of a physical map of chloroplast DNA from Nicotiana tabacum by two-dimensional gel and computer-aided restriction analysis. Plasmid. 1985 Jul;14(1):64–79. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90033-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway B. W., Morgan A. F. Genome organization in Pseudomonas. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:79–105. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.000455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis E. D., Widom R. L., LaFauci G., Setoguchi Y., Richter I. R., Rudner R. Chromosomal organization of rRNA operons in Bacillus subtilis. Genetics. 1988 Nov;120(3):625–635. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.3.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N. Translocatable elements in procaryotes. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):11–23. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90313-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohara Y., Akiyama K., Isono K. The physical map of the whole E. coli chromosome: application of a new strategy for rapid analysis and sorting of a large genomic library. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):495–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90503-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokjohn T. A., Miller R. V. Characterization of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa recA analog and its protein product: rec-102 is a mutant allele of the P. aeruginosa PAO recA gene. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1499–1508. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1499-1508.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. J., Smith H. O., Redfield R. J. Organization of the Haemophilus influenzae Rd genome. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3016–3024. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3016-3024.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner A. F., Harvey S., Hill C. W. Mapping and spacer identification of rRNA operons of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1984 Nov;160(2):682–686. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.2.682-686.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClelland M., Jones R., Patel Y., Nelson M. Restriction endonucleases for pulsed field mapping of bacterial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 11;15(15):5985–6005. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.15.5985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan E. A., Ikemura T., Lindahl L., Fallon A. M., Nomura M. Some rRNA operons in E. coli have tRNA genes at their distal ends. Cell. 1978 Feb;13(2):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90202-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Morgan E. A. Genetics of bacterial ribosomes. Annu Rev Genet. 1977;11:297–347. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.11.120177.001501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hoy K., Krishnapillai V. Recalibration of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PAO chromosome map in time units using high-frequency-of-recombination donors. Genetics. 1987 Apr;115(4):611–618. doi: 10.1093/genetics/115.4.611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phibbs P. V., Jr, Feary T. W., Blevins W. T. Pyruvate carboxylase deficiency in pleiotropic carbohydrate-negative mutant strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jun;118(3):999–1009. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.3.999-1009.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyle L. E., Finch L. R. A physical map of the genome of Mycoplasma mycoides subspecies mycoides Y with some functional loci. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):6027–6039. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.6027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E., Roth J. R. Linkage map of Salmonella typhimurium, Edition VI. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Sep;47(3):410–453. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.3.410-453.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E., Roth J. R. Linkage map of Salmonella typhimurium, Edition VI. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Sep;47(3):410–453. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.3.410-453.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., Econome J. G., Schutt A., Klco S., Cantor C. R. A physical map of the Escherichia coli K12 genome. Science. 1987 Jun 12;236(4807):1448–1453. doi: 10.1126/science.3296194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M., Anand R., Brown W. R., Fletcher D. S. A model for the separation of large DNA molecules by crossed field gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 11;15(15):5925–5943. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.15.5925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thuring R. W., Sanders J. P., Borst P. A freeze-squeeze method for recovering long DNA from agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1975 May 26;66(1):213–220. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90739-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toschka H. Y., Höpfl P., Ludwig W., Schleifer K. H., Ulbrich N., Erdmann V. A. Complete nucleotide sequence of a 23S ribosomal RNA gene from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):7182–7182. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.7182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villems R., Duggleby C. J., Broda P. Restriction endonuclease mapping of DNA using in situ digestion in two-dimensional gels. FEBS Lett. 1978 May 15;89(2):267–270. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80233-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. K., Sa'-Correia I., Darzins A., Chakrabarty A. M. Characterization of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa alginate (alg) gene region II. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Aug;133(8):2303–2314. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-8-2303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenzel R., Herrmann R. Physical mapping of the Mycoplasma pneumoniae genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 12;16(17):8323–8336. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.17.8323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolf T., Lai E., Kronenberg M., Hood L. Mapping genomic organization by field inversion and two-dimensional gel electrophoresis: application to the murine T-cell receptor gamma gene family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 11;16(9):3863–3875. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.9.3863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee T., Inouye M. Two-dimensional DNA electrophoresis applied to the study of DNA methylation and the analysis of genome size in Myxococcus xanthus. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jan 15;154(2):181–196. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90059-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]