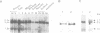Abstract
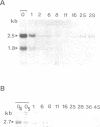
Two distinct Xenopus c-myc cDNA clones have been characterized from an oocyte cDNA library. This allowed a comparison of the c-myc protein sequence across the vertebrate phylum to be made and prominent conservations to be identified. The majority of the sequence differences between the two Xenopus c-myc cDNAs are in the 5' and 3' untranslated regions. Sequence-specific oligonucleotide probes from the 5' untranslated region were used to demonstrate the differential expression of the two c-myc mRNAs during development. One of the mRNAs corresponds to the Xenopus c-myc gene previously reported expressed as a stable maternal mRNA uncoupled from cell division during oogenesis (c-myc I). It is the major mRNA species expressed during oogenesis and is expressed again from the zygotic genome in post-gastrula embryos. In contrast, the second c-myc mRNA (c-myc II) is expressed only from the maternal genome during oogenesis. Primer extension experiments show that in the oocyte the transcriptional initiation sites for c-myc I and c-myc II are at different distances from the translational start site. The 'oocyte-specific' and 'somatic-type' developmental regulation of c-myc is reminiscent of polymerase III 5S RNA gene expression in Xenopus, and may provide new insights into the developmental regulation of genes transcribed by RNA polymerase II.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alitalo K., Ramsay G., Bishop J. M., Pfeifer S. O., Colby W. W., Levinson A. D. Identification of nuclear proteins encoded by viral and cellular myc oncogenes. Nature. 1983 Nov 17;306(5940):274–277. doi: 10.1038/306274a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battey J., Moulding C., Taub R., Murphy W., Stewart T., Potter H., Lenoir G., Leder P. The human c-myc oncogene: structural consequences of translocation into the IgH locus in Burkitt lymphoma. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):779–787. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90534-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender T. P., Kuehl W. M. Murine myb protooncogene mRNA: cDNA sequence and evidence for 5' heterogeneity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3204–3208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley D. L., Groudine M. A block to elongation is largely responsible for decreased transcription of c-myc in differentiated HL60 cells. Nature. 1986 Jun 12;321(6071):702–706. doi: 10.1038/321702a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley D. L., Groudine M. Novel promoter upstream of the human c-myc gene and regulation of c-myc expression in B-cell lymphomas. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3481–3489. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M. Potential metal-binding domains in nucleic acid binding proteins. Science. 1986 Apr 25;232(4749):485–487. doi: 10.1126/science.2421409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard O., Cory S., Gerondakis S., Webb E., Adams J. M. Sequence of the murine and human cellular myc oncogenes and two modes of myc transcription resulting from chromosome translocation in B lymphoid tumours. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2375–2383. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01749.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisbee C. A., Baker M. A., Wilson A. C., Haji-Azimi I., Fischberg M. Albumin phylogeny for clawed frogs (Xenopus). Science. 1977 Feb 25;195(4280):785–787. doi: 10.1126/science.65013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard J. M., Piechaczyk M., Dani C., Chambard J. C., Franchi A., Pouyssegur J., Jeanteur P. c-myc gene is transcribed at high rate in G0-arrested fibroblasts and is post-transcriptionally regulated in response to growth factors. Nature. 1985 Oct 3;317(6036):443–445. doi: 10.1038/317443a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caput D., Beutler B., Hartog K., Thayer R., Brown-Shimer S., Cerami A. Identification of a common nucleotide sequence in the 3'-untranslated region of mRNA molecules specifying inflammatory mediators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1670–1674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole M. D. The myc oncogene: its role in transformation and differentiation. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:361–384. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.002045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dang C. V., Lee W. M. Identification of the human c-myc protein nuclear translocation signal. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4048–4054. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dang C. V., McGuire M., Buckmire M., Lee W. M. Involvement of the 'leucine zipper' region in the oligomerization and transforming activity of human c-myc protein. Nature. 1989 Feb 16;337(6208):664–666. doi: 10.1038/337664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dani C., Mechti N., Piechaczyk M., Lebleu B., Jeanteur P., Blanchard J. M. Increased rate of degradation of c-myc mRNA in interferon-treated Daudi cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4896–4899. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnbrough C., Ford P. J. Turnover and processing of poly(A) in full-grown oocytes and during progesterone-induced oocyte maturation in Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1979 Aug;71(2):323–340. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90173-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darveau A., Pelletier J., Sonenberg N. Differential efficiencies of in vitro translation of mouse c-myc transcripts differing in the 5' untranslated region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2315–2319. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Weintraub H., Lassar A. B. Expression of a single transfected cDNA converts fibroblasts to myoblasts. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):987–1000. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90585-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont J. N. Oogenesis in Xenopus laevis (Daudin). I. Stages of oocyte development in laboratory maintained animals. J Morphol. 1972 Feb;136(2):153–179. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051360203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworkin M. B., Dworkin-Rastl E. Changes in RNA titers and polyadenylation during oogenesis and oocyte maturation in Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1985 Dec;112(2):451–457. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90417-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenman R. N., Tachibana C. Y., Abrams H. D., Hann S. R. V-myc- and c-myc-encoded proteins are associated with the nuclear matrix. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):114–126. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann S. R., Abrams H. D., Rohrschneider L. R., Eisenman R. N. Proteins encoded by v-myc and c-myc oncogenes: identification and localization in acute leukemia virus transformants and bursal lymphoma cell lines. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):789–798. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90535-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann S. R., King M. W., Bentley D. L., Anderson C. W., Eisenman R. N. A non-AUG translational initiation in c-myc exon 1 generates an N-terminally distinct protein whose synthesis is disrupted in Burkitt's lymphomas. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90507-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi K., Makino R., Kawamura H., Arisawa A., Yoneda K. Characterization of rat c-myc and adjacent regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 25;15(16):6419–6436. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.16.6419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heikkila R., Schwab G., Wickstrom E., Loke S. L., Pluznik D. H., Watt R., Neckers L. M. A c-myc antisense oligodeoxynucleotide inhibits entry into S phase but not progress from G0 to G1. 1987 Jul 30-Aug 5Nature. 328(6129):445–449. doi: 10.1038/328445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hourdry J., Brulfert A., Gusse M., Schoevaert D., Taylor M. V., Mechali M. Localization of c-myc expression during oogenesis and embryonic development in Xenopus laevis. Development. 1988 Dec;104(4):631–641. doi: 10.1242/dev.104.4.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. R., Cole M. D. Rapid cytoplasmic turnover of c-myc mRNA: requirement of the 3' untranslated sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4513–4521. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaczmarek L., Calabretta B., Baserga R. Expression of cell-cycle-dependent genes in phytohemagglutinin-stimulated human lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5375–5379. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King M. W., Roberts J. M., Eisenman R. N. Expression of the c-myc proto-oncogene during development of Xenopus laevis. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4499–4508. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl N. E., Legouy E., DePinho R. A., Nisen P. D., Smith R. K., Gee C. E., Alt F. W. Human N-myc is closely related in organization and nucleotide sequence to c-myc. Nature. 1986 Jan 2;319(6048):73–77. doi: 10.1038/319073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsten T., June C. H., Thompson C. B. Multiple mechanisms regulate c-myc gene expression during normal T cell activation. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2787–2794. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03133.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikura K. Expression of c-myc proto-oncogene during the early development of Xenopus laevis. Oncogene Res. 1987 Jul;1(2):179–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkin N., Darveau A., Nicholson R., Sonenberg N. cis-acting translational effects of the 5' noncoding region of c-myc mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2875–2883. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pei R., Calame K. Differential stability of c-myc mRNAS in a cell-free system. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2860–2868. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prochownik E. V., Kukowska J., Rodgers C. c-myc antisense transcripts accelerate differentiation and inhibit G1 progression in murine erythroleukemia cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3683–3695. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebagliati M. R., Weeks D. L., Harvey R. P., Melton D. A. Identification and cloning of localized maternal RNAs from Xenopus eggs. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):769–777. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90273-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarid J., Halazonetis T. D., Murphy W., Leder P. Evolutionarily conserved regions of the human c-myc protein can be uncoupled from transforming activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):170–173. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart M. A., Forrest D., McFarlane R., Onions D., Wilkie N., Neil J. C. Conservation of the c-myc coding sequence in transduced feline v-myc genes. Virology. 1986 Oct 15;154(1):121–134. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90435-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone J., de Lange T., Ramsay G., Jakobovits E., Bishop J. M., Varmus H., Lee W. Definition of regions in human c-myc that are involved in transformation and nuclear localization. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1697–1709. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor M. V., Gusse M., Evan G. I., Dathan N., Mechali M. Xenopus myc proto-oncogene during development: expression as a stable maternal mRNA uncoupled from cell division. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3563–3570. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04683.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Beneden R. J., Watson D. K., Chen T. T., Lautenberger J. A., Papas T. S. Cellular myc (c-myc) in fish (rainbow trout): its relationship to other vertebrate myc genes and to the transforming genes of the MC29 family of viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3698–3702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villares R., Cabrera C. V. The achaete-scute gene complex of D. melanogaster: conserved domains in a subset of genes required for neurogenesis and their homology to myc. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):415–424. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90495-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vriz S., Méchali M. Analysis of 3'-untranslated regions of seven c-myc genes reveals conserved elements prevalent in post-transcriptionally regulated genes. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 17;251(1-2):201–206. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81455-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. K., Reddy E. P., Duesberg P. H., Papas T. S. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the chicken c-myc gene reveals homologous and unique coding regions by comparison with the transforming gene of avian myelocytomatosis virus MC29, delta gag-myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2146–2150. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P., Brown D. D. Developmental regulation of two 5S ribosomal RNA genes. Science. 1988 Sep 23;241(4873):1626–1632. doi: 10.1126/science.241.4873.1626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]