Abstract
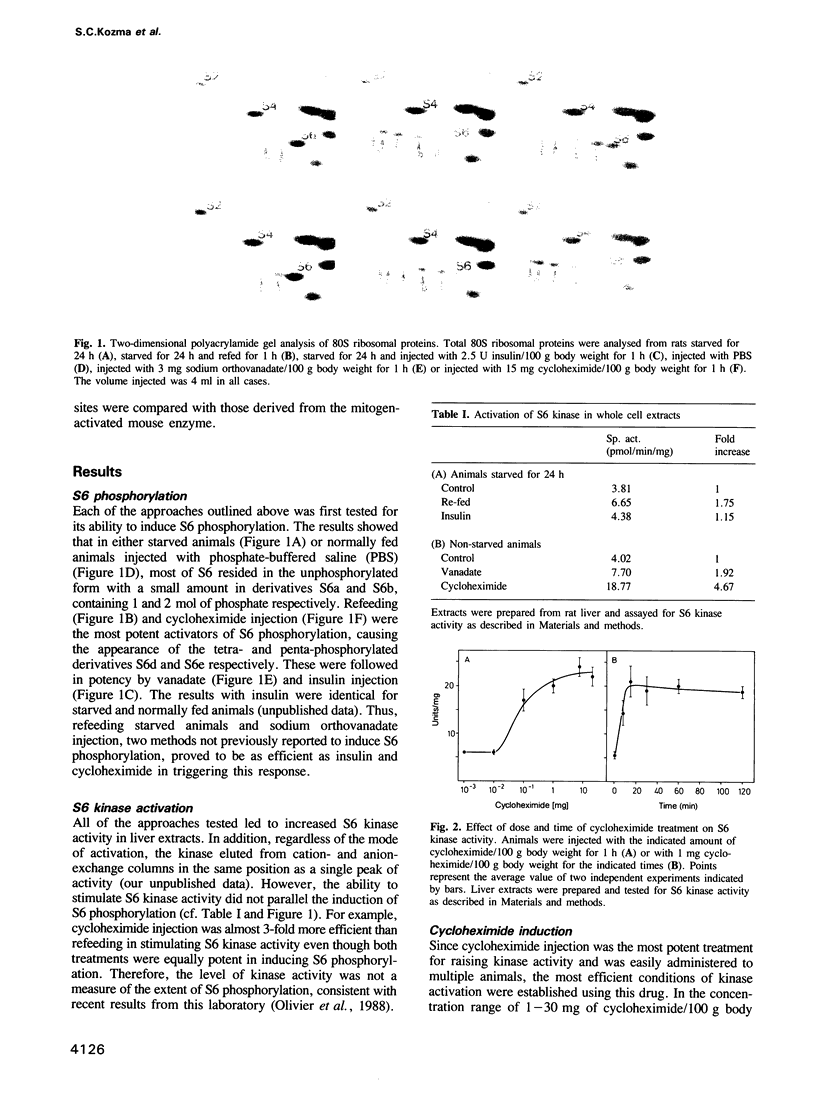
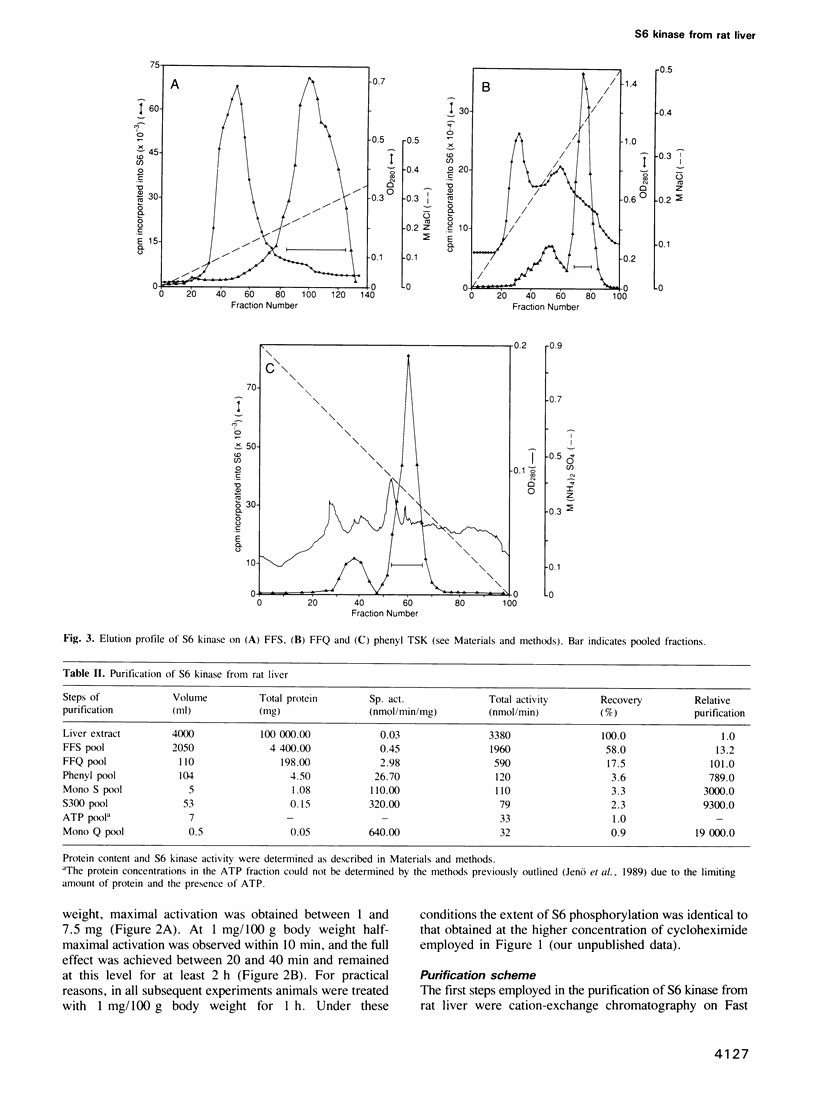
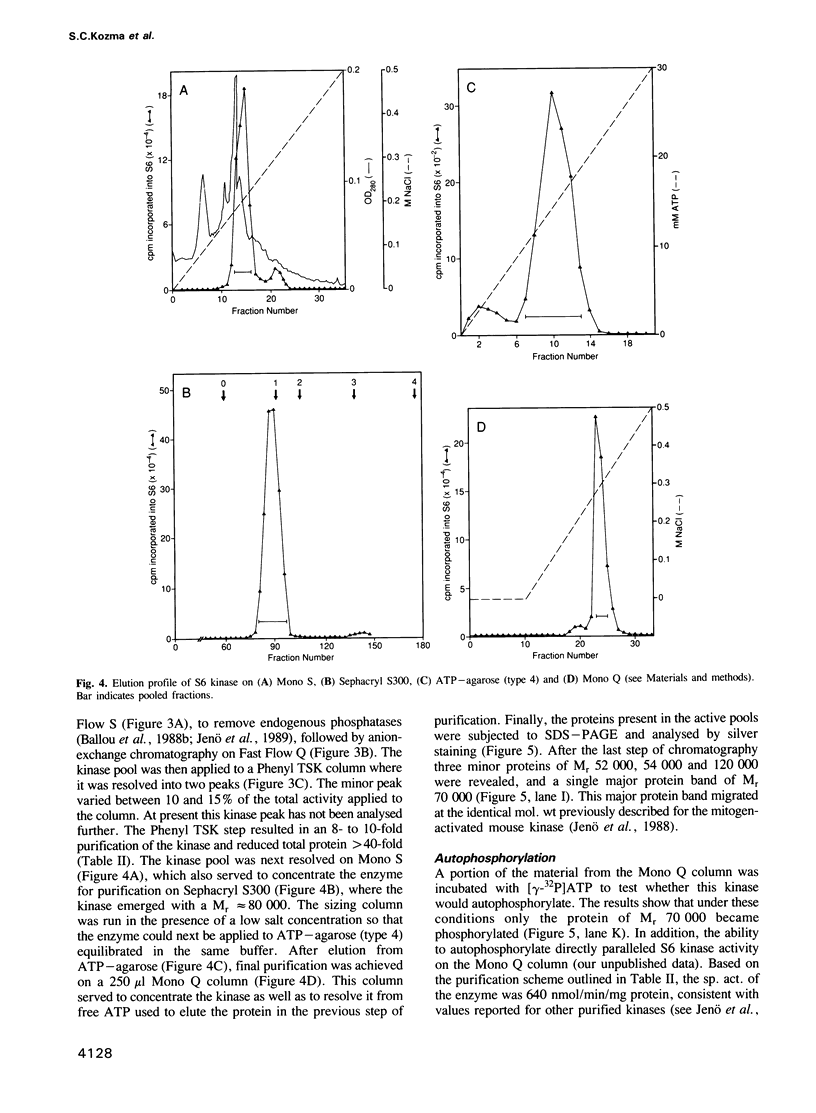
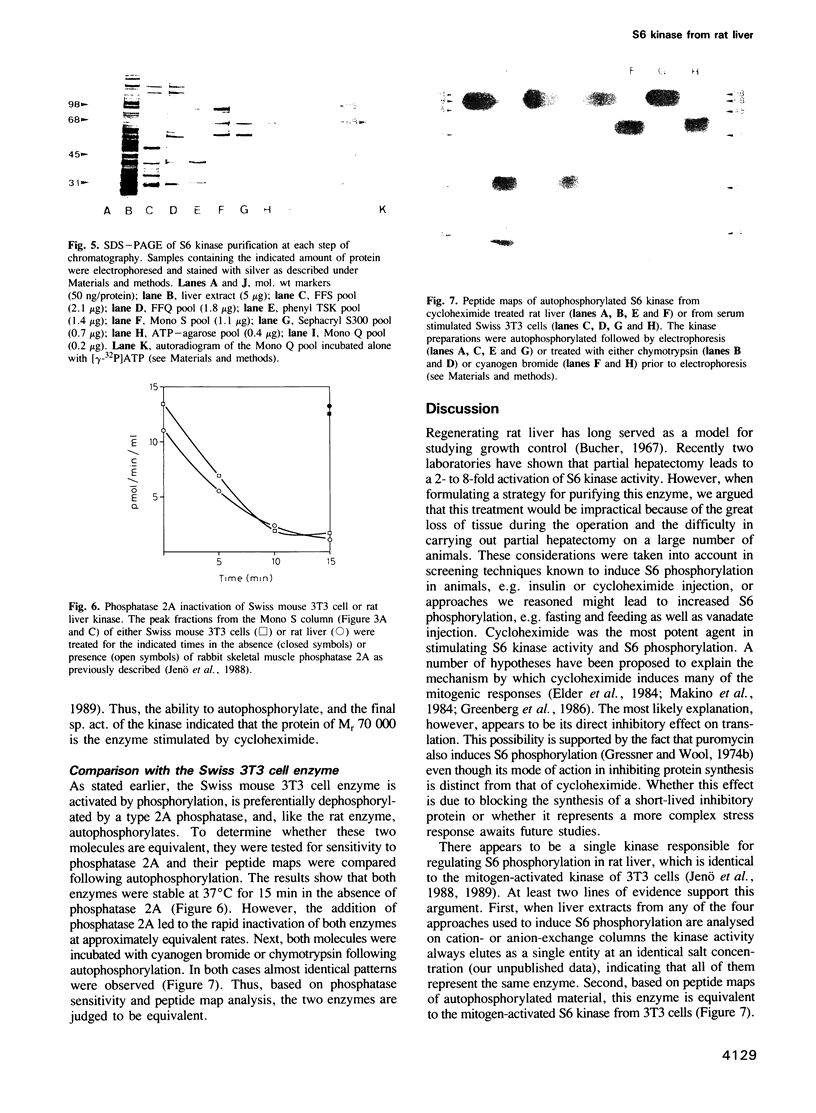
A number of approaches were tested for their ability to induce S6 phosphorylation and S6 kinase activation in rat liver, including i.p. injection of insulin, sodium orthovanadate or cycloheximide, as well as refeeding starved animals. All treatments led to increased S6 phosphorylation and activation of the apparent same enzyme. The most potent activator of the S6 kinase in liver extracts was cycloheximide. Maximum activation was achieved in 20 min at 1 mg cycloheximide/100 g body weight, with half-maximal activation in 10 min. Based on these findings a large-scale kinase purification procedure was established involving seven steps of chromatography. Following the final step a major protein band of Mr 70,000 was revealed. The protein was purified 20,000-fold, had a sp. act. of 640 nmol/min/mg of protein towards S6, autophosphorylated and was inactivated by phosphatase 2A. Peptide maps of autophosphorylated material were identical to those derived from the mitogen-activated kinase of 3T3 cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballou L. M., Jenö P., Thomas G. Protein phosphatase 2A inactivates the mitogen-stimulated S6 kinase from Swiss mouse 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1188–1194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballou L. M., Siegmann M., Thomas G. S6 kinase in quiescent Swiss mouse 3T3 cells is activated by phosphorylation in response to serum treatment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7154–7158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucher N. L. Experimental aspects of hepatic regeneration. N Engl J Med. 1967 Sep 28;277(13):686–contd. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196709282771306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donahue M. J., Masaracchia R. A. Phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 at multiple sites by a cyclic AMP-independent protein kinase from lymphoid cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):435–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder P. K., Schmidt L. J., Ono T., Getz M. J. Specific stimulation of actin gene transcription by epidermal growth factor and cycloheximide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7476–7480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Maller J. L. A protein kinase from Xenopus eggs specific for ribosomal protein S6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):742–746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Hermanowski A. L., Ziff E. B. Effect of protein synthesis inhibitors on growth factor activation of c-fos, c-myc, and actin gene transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1050–1057. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gressner A. M., Wool I. G. The phosphorylation of liver ribosomal proteins in vivo. Evidence that only a single small subunit protein (S6) is phosphorylated. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 10;249(21):6917–6925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gressner A. M., Wool I. G. The stimulation of the phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 by cycloheximide and puromycin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Oct 23;60(4):1482–1490. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90365-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenö P., Ballou L. M., Novak-Hofer I., Thomas G. Identification and characterization of a mitogen-activated S6 kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):406–410. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenö P., Jäggi N., Luther H., Siegmann M., Thomas G. Purification and characterization of a 40 S ribosomal protein S6 kinase from vanadate-stimulated Swiss 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):1293–1297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozma S. C., Ferrari S., Thomas G. Unmasking a growth factor/oncogene-activated S6 phosphorylation cascade. Cell Signal. 1989;1(3):219–225. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(89)90039-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg J., Hofsteenge J., Thomas G. Identification of the 40 S ribosomal protein S6 phosphorylation sites induced by cycloheximide. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11473–11477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg J., Olivier A. R., Thomas G. Analysis of 40S ribosomal protein S6 phosphorylation during the mitogenic response. Methods Enzymol. 1988;164:575–581. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(88)64070-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Peuch C. J., Ballester R., Rosen O. M. Purified rat brain calcium- and phospholipid-dependent protein kinase phosphorylates ribosomal protein S6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6858–6862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubben T. H., Traugh J. A. Cyclic nucleotide-independent protein kinases from rabbit reticulocytes. Purification and characterization of protease-activated kinase II. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13992–13997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino R., Hayashi K., Sugimura T. C-myc transcript is induced in rat liver at a very early stage of regeneration or by cycloheximide treatment. Nature. 1984 Aug 23;310(5979):697–698. doi: 10.1038/310697a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Pérez J., Thomas G. Ordered phosphorylation of 40S ribosomal protein S6 after serum stimulation of quiescent 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):926–930. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuta K., Hashimoto E., Sakanoue Y., Nakamura S., Kondo H., Yamamura H. An activated S6 kinase in regenerating rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jul 15;146(1):239–246. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90716-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan E. H., Peters T., Jr The biosynthesis of rat serum albumin. V. Effect of protein depletion and refeeding on albumin and transferrin synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jun 10;246(11):3500–3507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemenoff R. A., Price D. J., Mendelsohn M. J., Carter E. A., Avruch J. An S6 kinase activated during liver regeneration is related to the insulin-stimulated S6 kinase in H4 hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19455–19460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen P. J., Manchester K. L., Towbin H., Gordon J., Thomas G. The phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 in rat tissues following cycloheximide injection, in diabetes, and after denervation of diaphragm. A simple immunological determination of the extent of S6 phosphorylation on protein blots. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12316–12321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novak-Hofer I., Thomas G. An activated S6 kinase in extracts from serum- and epidermal growth factor-stimulated Swiss 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5995–6000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novak-Hofer I., Thomas G. Epidermal growth factor-mediated activation of an S6 kinase in Swiss mouse 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10314–10319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B. R., Kirsch D. R., Morris N. R. A simplified ultrasensitive silver stain for detecting proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):361–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivier A. R., Ballou L. M., Thomas G. Differential regulation of S6 phosphorylation by insulin and epidermal growth factor in Swiss mouse 3T3 cells: insulin activation of type 1 phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4720–4724. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pain V. M., Clemens M. J., Garlick P. J. The effect of dietary protein deficiency on albumin synthesis and on the concentration of active albumin messenger ribonucleic acid in rat liver. Biochem J. 1978 Apr 15;172(1):129–135. doi: 10.1042/bj1720129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker P. J., Katan M., Waterfield M. D., Leader D. P. The phosphorylation of eukaryotic ribosomal protein S6 by protein kinase C. Eur J Biochem. 1985 May 2;148(3):579–586. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08879.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray L. B., Sturgill T. W. Rapid stimulation by insulin of a serine/threonine kinase in 3T3-L1 adipocytes that phosphorylates microtubule-associated protein 2 in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1502–1506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shechter Y., Ron A. Effect of depletion of phosphate and bicarbonate ions on insulin action in rat adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):14945–14950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgill T. W., Ray L. B., Erikson E., Maller J. L. Insulin-stimulated MAP-2 kinase phosphorylates and activates ribosomal protein S6 kinase II. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):715–718. doi: 10.1038/334715a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Susa M., Olivier A. R., Fabbro D., Thomas G. EGF induces biphasic S6 kinase activation: late phase is protein kinase C-dependent and contributes to mitogenicity. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):817–824. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90796-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabarini D., Garcia de Herreros A., Heinrich J., Rosen O. M. Purification of a bovine liver S6 kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Apr 29;144(2):891–899. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80048-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Grande R. W., Traugh J. A. Phosphorylation of 40-S ribosomal subunits by cAMP-dependent, cGMP-dependent and protease-activated protein kinases. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Apr 1;123(2):421–428. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb19785.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






