Abstract
The ocs-element is an enhancer element first identified in the promoter of the octopine synthase gene (OCS) where it occurs as a 16 bp palindromic sequence. The transcriptional enhancing activity of the ocs-element correlated with in vitro binding of a transcription factor. We have now identified ocs-elements in the promoter regions of six other T-DNA genes involved in opine synthesis and three plant viral promoters including the 35S promoter of cauliflower mosaic virus. These elements bind the ocs transcription factor in vitro and enhance transcription in plant cells. Comparison of the sequences of these 10 elements has defined a 20 bp consensus sequence, TGACG(T/C)AAG(C/G)(G/A)(A/C)T(G/T)ACG(T/C)(A/C)(A/C), which includes the 16 bp palindrome in its central region. We propose the name ocs-element for this class of promoter elements of similar sequence and function.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- An G., Watson B. D., Chiang C. C. Transformation of Tobacco, Tomato, Potato, and Arabidopsis thaliana Using a Binary Ti Vector System. Plant Physiol. 1986 May;81(1):301–305. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.1.301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavener D. R. Comparison of the consensus sequence flanking translational start sites in Drosophila and vertebrates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1353–1361. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Greve H., Dhaese P., Seurinck J., Lemmers M., Van Montagu M., Schell J. Nucleotide sequence and transcript map of the Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti plasmid-encoded octopine synthase gene. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(6):499–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vos G., De Beuckeleer M., Van Montagu M., Schell J. Restriction endonuclease mapping of the octopine tumor-inducing plasmid pTiAch5 of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plasmid. 1981 Sep;6(2):249–253. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(81)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depicker A., Stachel S., Dhaese P., Zambryski P., Goodman H. M. Nopaline synthase: transcript mapping and DNA sequence. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(6):561–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derbyshire K. M., Salvo J. J., Grindley N. D. A simple and efficient procedure for saturation mutagenesis using mixed oligodeoxynucleotides. Gene. 1986;46(2-3):145–152. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90398-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebert P. R., Ha S. B., An G. Identification of an essential upstream element in the nopaline synthase promoter by stable and transient assays. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5745–5749. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis J. G., Llewellyn D. J., Dennis E. S., Peacock W. J. Maize Adh-1 promoter sequences control anaerobic regulation: addition of upstream promoter elements from constitutive genes is necessary for expression in tobacco. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):11–16. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04711.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
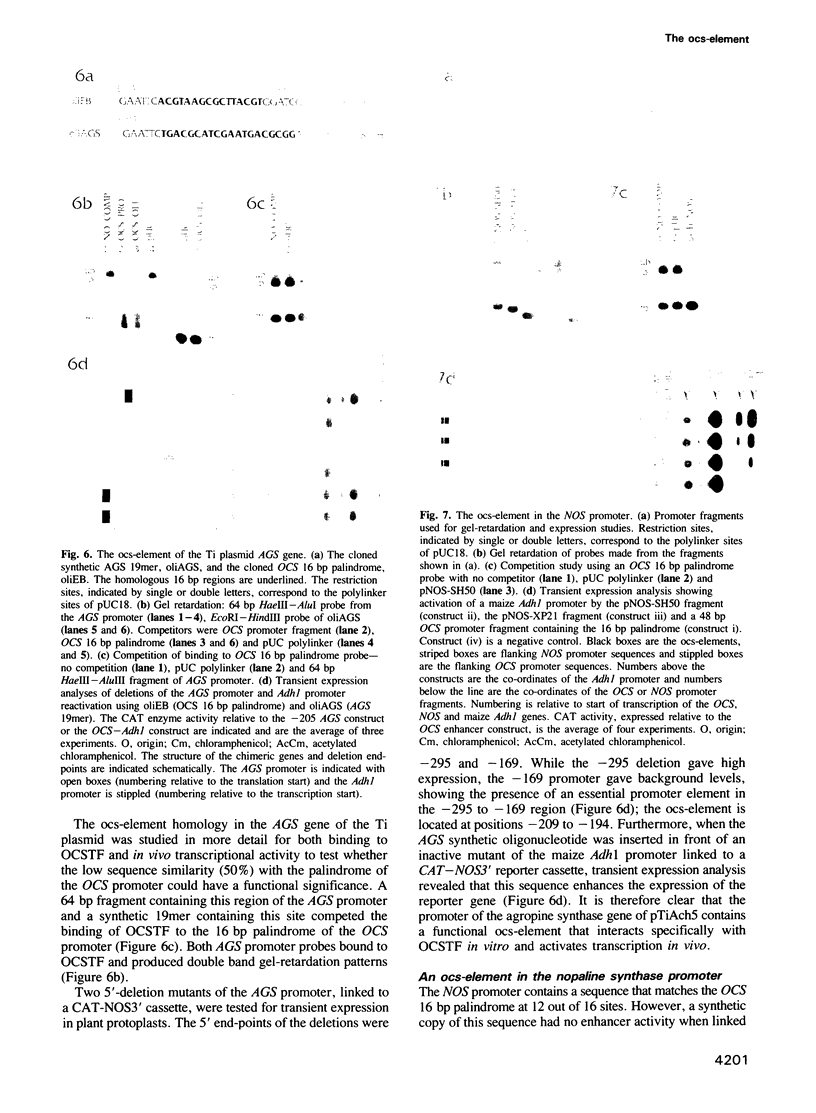
- Ellis J. G., Llewellyn D. J., Walker J. C., Dennis E. S., Peacock W. J. The ocs element: a 16 base pair palindrome essential for activity of the octopine synthase enhancer. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3203–3208. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02636.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang R. X., Nagy F., Sivasubramaniam S., Chua N. H. Multiple cis regulatory elements for maximal expression of the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter in transgenic plants. Plant Cell. 1989 Jan;1(1):141–150. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.1.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fesenko E. E., Kolesnikov S. S., Lyubarsky A. L. Induction by cyclic GMP of cationic conductance in plasma membrane of retinal rod outer segment. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):310–313. doi: 10.1038/313310a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franck A., Guilley H., Jonard G., Richards K., Hirth L. Nucleotide sequence of cauliflower mosaic virus DNA. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):285–294. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90136-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoni D., Brosio P., Bond-Nutter D., Bedbrook J., Dunsmuir P. Novel cis-acting elements in Petunia Cab gene promoters. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Jan;215(2):337–344. doi: 10.1007/BF00339739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. J., Kay S. A., Chua N. H. Sequence-specific interactions of a pea nuclear factor with light-responsive elements upstream of the rbcS-3A gene. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2543–2549. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02542.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. J., Yong M. H., Cuozzo M., Kano-Murakami Y., Silverstein P., Chua N. H. Binding site requirements for pea nuclear protein factor GT-1 correlate with sequences required for light-dependent transcriptional activation of the rbcS-3A gene. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4035–4044. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03297.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hull R., Sadler J., Longstaff M. The sequence of carnation etched ring virus DNA: comparison with cauliflower mosaic virus and retroviruses. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3083–3090. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04614.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson R. A., Kavanagh T. A., Bevan M. W. GUS fusions: beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):3901–3907. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02730.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llewellyn D. J., Finnegan E. J., Ellis J. G., Dennis E. S., Peacock W. J. Structure and expression of an alcohol dehydrogenase 1 gene from Pisum sativum (cv. "Greenfeast"). J Mol Biol. 1987 May 5;195(1):115–123. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90331-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitra A., An G. Three distinct regulatory elements comprise the upstream promoter region of the nopaline synthase gene. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Jan;215(2):294–299. doi: 10.1007/BF00339731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ow D. W., Jacobs J. D., Howell S. H. Functional regions of the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S RNA promoter determined by use of the firefly luciferase gene as a reporter of promoter activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4870–4874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prat S., Willmitzer L., Sánchez-Serrano J. J. Nuclear proteins binding to a cauliflower mosaic virus 35S truncated promoter. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Jun;217(2-3):209–214. doi: 10.1007/BF02464883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richins R. D., Scholthof H. B., Shepherd R. J. Sequence of figwort mosaic virus DNA (caulimovirus group). Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8451–8466. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roesler W. J., Vandenbark G. R., Hanson R. W. Cyclic AMP and the induction of eukaryotic gene transcription. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9063–9066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon F., Deblaere R., Leemans J., Hernalsteens J. P., Van Montagu M., Schell J. Genetic identification of functions of TR-DNA transcripts in octopine crown galls. EMBO J. 1984 Jan;3(1):141–146. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01774.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze-Lefert P., Dangl J. L., Becker-André M., Hahlbrock K., Schulz W. Inducible in vivo DNA footprints define sequences necessary for UV light activation of the parsley chalcone synthase gene. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):651–656. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03422.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh K., Tokuhisa J. G., Dennis E. S., Peacock W. J. Saturation mutagenesis of the octopine synthase enhancer: correlation of mutant phenotypes with binding of a nuclear protein factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3733–3737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slightom J. L., Durand-Tardif M., Jouanin L., Tepfer D. Nucleotide sequence analysis of TL-DNA of Agrobacterium rhizogenes agropine type plasmid. Identification of open reading frames. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):108–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teeri T. H., Lehväslaiho H., Franck M., Uotila J., Heino P., Palva E. T., Van Montagu M., Herrera-Estrella L. Gene fusions to lacZ reveal new expression patterns of chimeric genes in transgenic plants. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):343–350. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03383.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velten J., Velten L., Hain R., Schell J. Isolation of a dual plant promoter fragment from the Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2723–2730. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02202.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. C., Howard E. A., Dennis E. S., Peacock W. J. DNA sequences required for anaerobic expression of the maize alcohol dehydrogenase 1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6624–6628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werr W., Frommer W. B., Maas C., Starlinger P. Structure of the sucrose synthase gene on chromosome 9 of Zea mays L. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1373–1380. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03789.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]








