Abstract
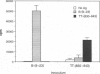
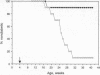
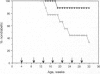
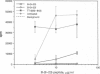
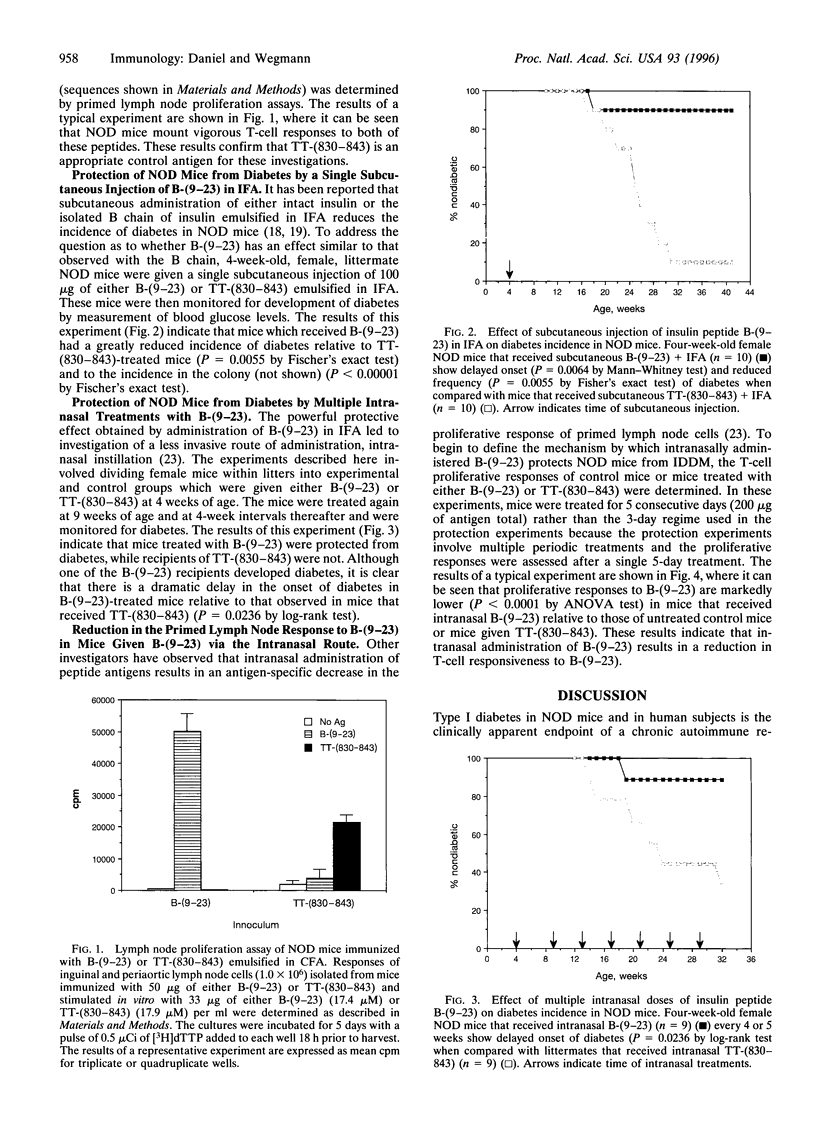
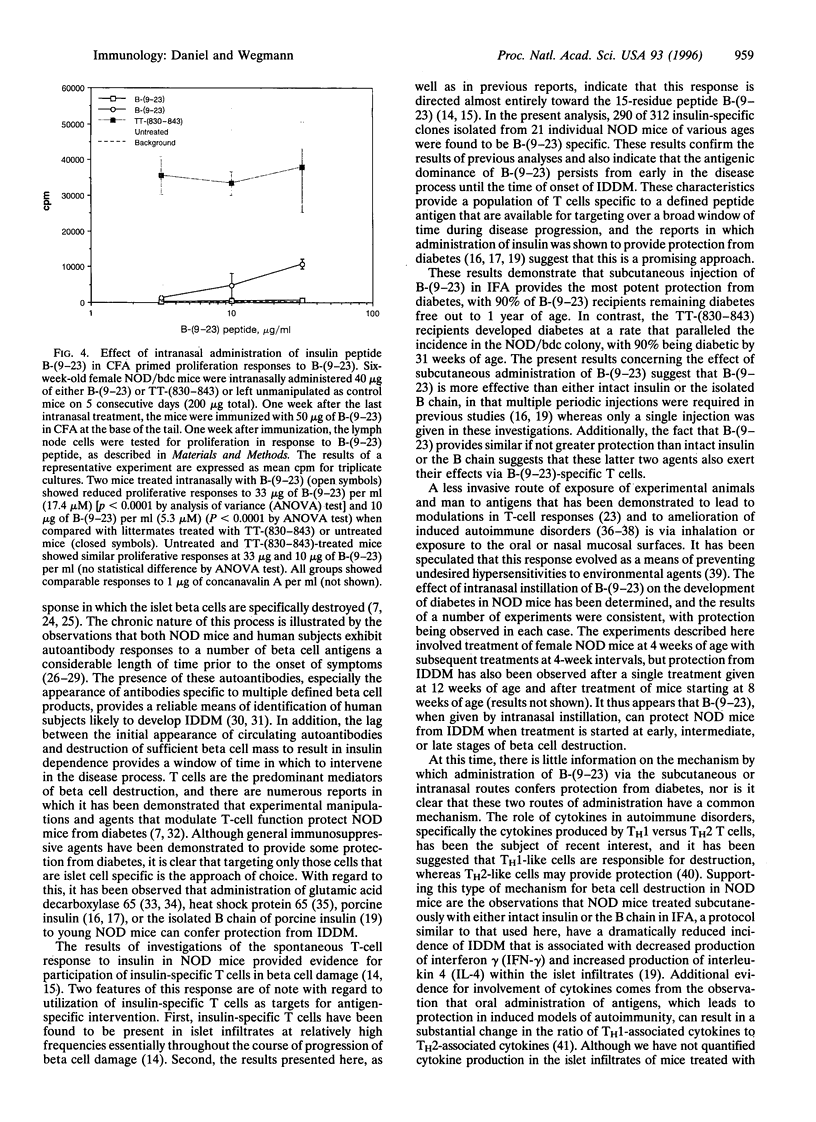
The observation that overt type I diabetes is often preceded by the appearance of insulin autoantibodies and the reports that prophylactic administration of insulin to biobreeding diabetes-prone (BB-DP) rats, nonobese diabetic (NOD) mice, and human subjects results in protection from diabetes suggest that an immune response to insulin is involved in the process of beta cell destruction. We have recently reported that islet-infiltrating cells isolated from NOD mice are enriched for insulin-specific T cells, that insulin-specific T cell clones are capable of adoptive transfer of diabetes, and that epitopes present on residues 9-23 of the B chain appear to be dominant in this spontaneous response. In the experiments described in this report, the epitope specificity of 312 independently isolated insulin-specific T cell clones was determined and B-(9-23) was found to be dominant, with 93% of the clones exhibiting specificity toward this peptide and the remainder to an epitope on residues 7-21 of the A chain. On the basis of these observations, the effect of either subcutaneous or intranasal administration of B-(9-23) on the incidence of diabetes in NOD mice was determined. The results presented here indicate that both subcutaneous and intranasal administration of B-(9-23) resulted in a marked delay in the onset and a decrease in the incidence of diabetes relative to mice given the control peptide, tetanus toxin-(830-843). This protective effect is associated with reduced T-cell proliferative response to B-(9-23) in B-(9-23)-treated mice.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson M. A., Maclaren N. K., Luchetta R. Insulitis and diabetes in NOD mice reduced by prophylactic insulin therapy. Diabetes. 1990 Aug;39(8):933–937. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.8.933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson M. A., Maclaren N. K. The pathogenesis of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1994 Nov 24;331(21):1428–1436. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199411243312107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach J. F. Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus as an autoimmune disease. Endocr Rev. 1994 Aug;15(4):516–542. doi: 10.1210/edrv-15-4-516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendelac A., Carnaud C., Boitard C., Bach J. F. Syngeneic transfer of autoimmune diabetes from diabetic NOD mice to healthy neonates. Requirement for both L3T4+ and Lyt-2+ T cells. J Exp Med. 1987 Oct 1;166(4):823–832. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.4.823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottazzo G. F., Florin-Christensen A., Doniach D. Islet-cell antibodies in diabetes mellitus with autoimmune polyendocrine deficiencies. Lancet. 1974 Nov 30;2(7892):1279–1283. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90140-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman M. A., Leiter E. H., Atkinson M. A. Prevention of diabetes in the NOD mouse: implications for therapeutic intervention in human disease. Immunol Today. 1994 Mar;15(3):115–120. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(94)90154-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castaño L., Ziegler A. G., Ziegler R., Shoelson S., Eisenbarth G. S. Characterization of insulin autoantibodies in relatives of patients with type I diabetes. Diabetes. 1993 Aug;42(8):1202–1209. doi: 10.2337/diab.42.8.1202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corradin G., Etlinger H. M., Chiller J. M. Lymphocyte specificity to protein antigens. I. Characterization of the antigen-induced in vitro T cell-dependent proliferative response with lymph node cells from primed mice. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):1048–1053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel D., Gill R. G., Schloot N., Wegmann D. Epitope specificity, cytokine production profile and diabetogenic activity of insulin-specific T cell clones isolated from NOD mice. Eur J Immunol. 1995 Apr;25(4):1056–1062. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830250430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dick A. D., Cheng Y. F., Liversidge J., Forrester J. V. Intranasal administration of retinal antigens suppresses retinal antigen-induced experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis. Immunology. 1994 Aug;82(4):625–631. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenbarth G. S., Gianani R., Pugliese A., Verge C. F., Pietropaolo M. Prediction and prevention of type I diabetes. Transplant Proc. 1994 Apr;26(2):361–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias D., Reshef T., Birk O. S., van der Zee R., Walker M. D., Cohen I. R. Vaccination against autoimmune mouse diabetes with a T-cell epitope of the human 65-kDa heat shock protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3088–3091. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haskins K., McDuffie M. Acceleration of diabetes in young NOD mice with a CD4+ islet-specific T cell clone. Science. 1990 Sep 21;249(4975):1433–1436. doi: 10.1126/science.2205920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt P. G., McMenamin C. Defence against allergic sensitization in the healthy lung: the role of inhalation tolerance. Clin Exp Allergy. 1989 May;19(3):255–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1989.tb02380.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyne G. F., O'Hehir R. E., Wraith D. C., Thomas W. R., Lamb J. R. Inhibition of T cell and antibody responses to house dust mite allergen by inhalation of the dominant T cell epitope in naive and sensitized mice. J Exp Med. 1993 Nov 1;178(5):1783–1788. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.5.1783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman D. L., Clare-Salzler M., Tian J., Forsthuber T., Ting G. S., Robinson P., Atkinson M. A., Sercarz E. E., Tobin A. J., Lehmann P. V. Spontaneous loss of T-cell tolerance to glutamic acid decarboxylase in murine insulin-dependent diabetes. Nature. 1993 Nov 4;366(6450):69–72. doi: 10.1038/366069a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller R. J., Eisenbarth G. S., Jackson R. A. Insulin prophylaxis in individuals at high risk of type I diabetes. Lancet. 1993 Apr 10;341(8850):927–928. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91215-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma C. G., Zhang G. X., Xiao B. G., Link J., Olsson T., Link H. Suppression of experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis by nasal administration of acetylcholine receptor. J Neuroimmunol. 1995 Apr;58(1):51–60. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(94)00187-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacCuish A. C., Jordan J., Campbell C. J., Duncan L. J., Irvine W. J. Cell-mediated immunity in diabetes mellitus; lymphocyte transformation by insulin and insulin fragments in insulin-treated and newly-diagnosed diabetes. Diabetes. 1975 Jan;24(1):36–43. doi: 10.2337/diab.24.1.36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino S., Kunimoto K., Muraoka Y., Mizushima Y., Katagiri K., Tochino Y. Breeding of a non-obese, diabetic strain of mice. Jikken Dobutsu. 1980 Jan;29(1):1–13. doi: 10.1538/expanim1978.29.1_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMenamin C., Pimm C., McKersey M., Holt P. G. Regulation of IgE responses to inhaled antigen in mice by antigen-specific gamma delta T cells. Science. 1994 Sep 23;265(5180):1869–1871. doi: 10.1126/science.7916481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzler B., Wraith D. C. Inhibition of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by inhalation but not oral administration of the encephalitogenic peptide: influence of MHC binding affinity. Int Immunol. 1993 Sep;5(9):1159–1165. doi: 10.1093/intimm/5.9.1159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer J. P., Asplin C. M., Clemons P., Lyen K., Tatpati O., Raghu P. K., Paquette T. L. Insulin antibodies in insulin-dependent diabetics before insulin treatment. Science. 1983 Dec 23;222(4630):1337–1339. doi: 10.1126/science.6362005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer J. P., McCulloch D. K. Prediction and prevention of IDDM--1991. Diabetes. 1991 Aug;40(8):943–947. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.8.943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panina-Bordignon P., Tan A., Termijtelen A., Demotz S., Corradin G., Lanzavecchia A. Universally immunogenic T cell epitopes: promiscuous binding to human MHC class II and promiscuous recognition by T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Dec;19(12):2237–2242. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830191209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch A. Immunoregulatory and cytokine imbalances in the pathogenesis of IDDM. Therapeutic intervention by immunostimulation? Diabetes. 1994 May;43(5):613–621. doi: 10.2337/diab.43.5.613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serreze D. V., Leiter E. H., Kuff E. L., Jardieu P., Ishizaka K. Molecular mimicry between insulin and retroviral antigen p73. Development of cross-reactive autoantibodies in sera of NOD and C57BL/KsJ db/db mice. Diabetes. 1988 Mar;37(3):351–358. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.3.351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tisch R., Yang X. D., Singer S. M., Liblau R. S., Fugger L., McDevitt H. O. Immune response to glutamic acid decarboxylase correlates with insulitis in non-obese diabetic mice. Nature. 1993 Nov 4;366(6450):72–75. doi: 10.1038/366072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegmann D. R., Gill R. G., Norbury-Glaser M., Schloot N., Daniel D. Analysis of the spontaneous T cell response to insulin in NOD mice. J Autoimmun. 1994 Dec;7(6):833–843. doi: 10.1006/jaut.1994.1066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegmann D. R., Norbury-Glaser M., Daniel D. Insulin-specific T cells are a predominant component of islet infiltrates in pre-diabetic NOD mice. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Aug;24(8):1853–1857. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner H. L. Oral tolerance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Nov 8;91(23):10762–10765. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.23.10762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Z. J., Davidson L., Eisenbarth G., Weiner H. L. Suppression of diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice by oral administration of porcine insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10252–10256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler A. G., Vardi P., Ricker A. T., Hattori M., Soeldner J. S., Eisenbarth G. S. Radioassay determination of insulin autoantibodies in NOD mice. Correlation with increased risk of progression to overt diabetes. Diabetes. 1989 Mar;38(3):358–363. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.3.358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]