Abstract
Due to the innate ability of bacteria to develop resistance to available antibiotics, there is a critical need to develop new agents to treat more resilient strains. As a continuation of our research in this area, we have synthesized a series of racemic 2,4-diaminopyrimidine-based drug candidates, and evaluated them against Bacillus anthracis. The structures are comprised of a 2,4-diaminopyrimidine ring, a 3,4-dimethoxybenzyl ring, and an N-acryloyl-substituted 1,2-dihydrophthalazine ring. Various changes were made at the C1 stereocenter of the dihydrophthalazine moiety in the structure, and the biological activity was assessed by measurement of the MIC and Ki values to identify the most potent drug candidate.
Keywords: Gram-positive bacteria; Bacillus anthracis; 2,4-diaminopyrimidine; Heck reaction; antibiotic resistance; dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR); antifolates
1. Introduction
The growing problem of antibiotic resistance is prominent in medical reports and the scientific literature, which highlight the emergence of multidrug resistant bacteria [1,2]. For example, Bacillus anthracis continues to be one of the most fatal pathogens to humans and has become a major concern due to its potential use as a bioterrorism weapon [3]. The threat of bioterrorism arises from dormant spores of B. anthracis, which can readily germinate into an infectious form upon inhalation [4]. Like other Gram-positive bacteria, resistance of B. anthracis to traditional antimicrobials can complicate treatment regimens. New drugs are essential to address these resistant strains, particularly in situations requiring urgent treatment without knowledge of the resistance profile as in a bioterror event [5,6].
Inhibition of the critical metabolic enzyme dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) is an actively pursued area in antibacterial research, and its value as a target has been validated by the success of the antibiotic trimethoprim (TMP) [7]. New compounds with pharmacokinetics differing from those of TMP are sought to address different sites of infection and then, indirectly, the problem of bacterial resistance. In addition, some bacteria, including B. anthracis, encode a chromosomal DHFR that is resistant to TMP but can be targeted by other antifolates, as we have demonstrated previously [8,9,10]. We now have an expanded library of dihydrophthalazine appended 2,4-diaminopyrimidines with demonstrated potency against the DHFR [6] found in B. anthracis and other Gram-positive bacteria [11,12,13,14,15,16]. In particular, alteration of the substituent at the C1 stereocenter of the dihydrophthalazine has been demonstrated to modulate interactions at the interface of the protein surface and the surrounding solvent. In our effort to develop a more active drug for B. anthracis, our current library presents a refinement of the group at this position to optimize potency against this organism.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
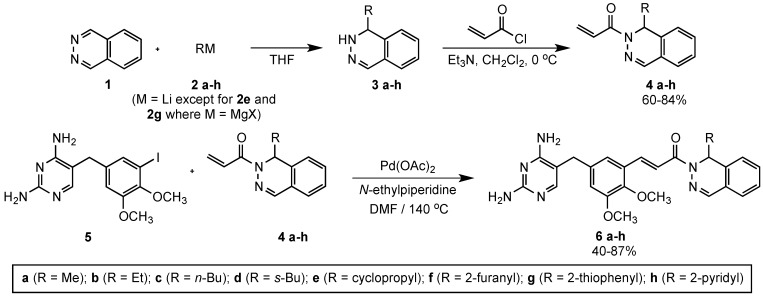
In an effort to develop more active compounds against B. anthracis and other Gram-positive bacteria, an earlier synthetic strategy to prepare related structures was modified [14,15]. In this project, we synthesized a series of racemic targets as shown in Scheme 1 and Scheme 2. Starting with commercially available phthalazine (1), treatment with an organolithium or organomagnesium reagent (compounds 2a–h) in THF under anhydrous conditions furnished racemic adducts 3a–h. These substrates were further subjected to N-acylation using acryloyl chloride and triethylamine to obtain the 1-(phthalazin-2(1H)-yl)prop-2-en-1-one derivatives 4a–h. Acrylamides 4a–h were then linked to the known 2,4-diaminopyrimidine intermediate 5 [15] via a Heck coupling in the presence of Pd(OAc)2 and N-ethylpiperidine to afford targets 6a–h in yields of 40%–87% (Scheme 1) [16,17].
Scheme 1.
Synthesis of drug candidates 6a–h.
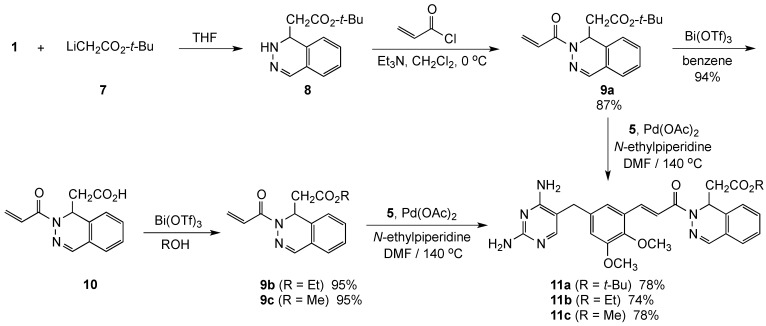
Scheme 2.
Synthesis of drug candidates 11a–c.
In addition, we have also developed a synthetic route for the preparation of several ester-containing drug candidates (Scheme 2). These targets were assembled by addition of t-butyl lithioacetate to 1 to give ester 8, followed by N-acylation with acryloyl chloride to give racemic t-butyl 2-(phthalazin-2(1H)-yl)acetate (9a) in 87% yield. Mild hydrolysis of 9a using catalytic Bi(OTf)3 led to acid 10, which was re-esterified using this same catalyst in the presence of ethanol or methanol [18] to give 9b and 9c, respectively, in 95% yields. Finally, Heck coupling of 9a–c furnished the desired ester-substituted derivatives 11a–c in 74%–78% yields.
2.2. Biological Potency
The potency of our synthesized compounds was evaluated in a whole cell model using bacterial cultures, and for activity against the purified DHFR protein target. The ability to halt the growth of standardized cultures gives insight into the utility of the compound as a potential therapeutic, but it does not inform on the cellular target. In the case of whole cells, the lowest concentration of compound needed to inhibit all visible bacterial growth was assessed as in previous studies [9,10,12,15,16] and followed the Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute guidelines [19]. These values are reported in Table 1 as the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) in μg/mL. The activity of each compound was evaluated by its ability to halt the enzymatic reaction carried out by the purified DHFR protein in a standardized assay. The results are reported as the compound concentration, in nM, required to inhibit the enzyme activity to one-half the uninhibited rate. This concentration was then used in combination with the substrate affinity of the DHFR enzyme, in this case the KM for dihydrofolate, to derive the inhibition constant Ki as reported in Table 1. The combination of the MIC and the Ki allowed unbiased assessment of compound potency between bacterial species.
Table 1.
MIC and Ki values of the substrates 6a–h and 11a–c against B. anthracis.
| Compound | MIC (μg/mL) | Ki (nM) ± SEM |
|---|---|---|
| B. anthracis | B anthracis DHFR | |
| TMP | >128 * | ~8,770 * |
| RAB1 | 2–4 * | 9.4 ± 0.2 * |
| 6a | 2.0 | 8.8 ± 0.2 |
| 6b | 1.0 | 6.8 ± 0.2 |
| 6c | 2–4 | 7.9 ± 0.2 |
| 6d | 4 | 10.4 ± 0.2 |
| 6e | 0.5 | 4.9 ± 0.2 |
| 6f | 4 | 5.9 ± 0.2 |
| 6g | 4 | 8.4 ± 0.2 |
| 6h | 4 | 9.0 ± 0.2 |
| 11a | 8 | 59.0 ± 0.9 |
| 11b | 8 | 24.9 ± 0.3 |
| 11c | 8 | 20.0 ± 0.3 |
* Indicates previously published data: TMP [8]; RAB1 [9,10,12,15,16]; Ki = 50% inhibition normalized for the intrinsic affinity for the substrate, as outlined in the Cheng-Prusoff formalism [20]. SEM = standard error of the mean. MIC values report the range of values from two independent experiments performed in duplicate. Ki values report the mean from at least three independent measurements.
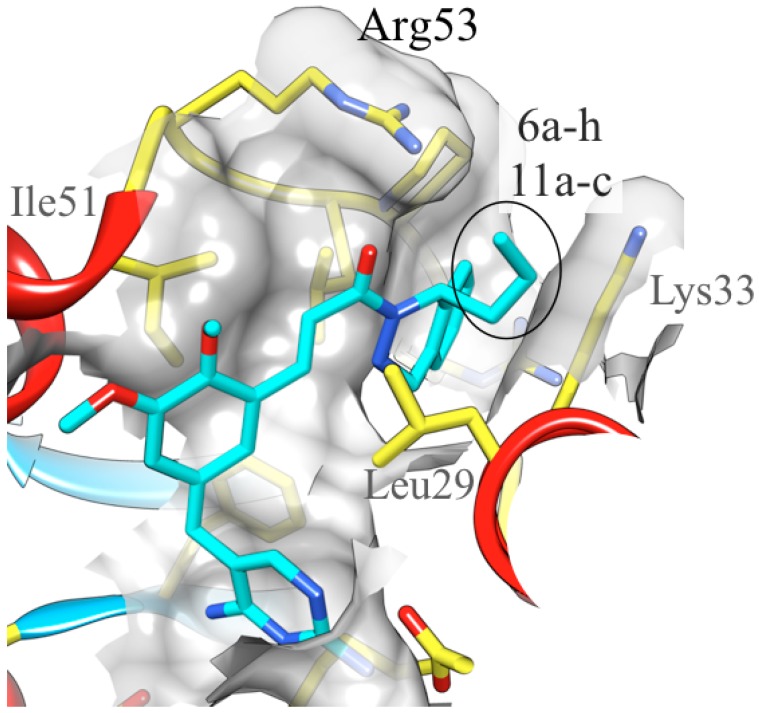
These studies build upon previous results [9,10,12,15,16] and highlight a clear preference for small or planar groups at the C1 dihydrophthalazine stereocenter. Compounds 6a–d are derivatives bearing alkyl substituents at this site, similar to RAB1 (R = n–Pr), but with variable lengths. Of these modified derivatives, 6b (R = Et) showed the greatest activity, while 6a (R = Me) was intermediate. Derivatives 6c (R = n–Bu) and 6d (R = s–Bu) proved the least efficacious within this series. Placement of heteroaromatic groups and acetic ester moieties at C1 of the dihydrophthalazine, as in 6f–h and 11a–c, respectively, yielded moderately active structures, but these possessed the lowest activities in the current screening. While compounds 11a–c did not demonstrate exceptional potency, the intent was to utilize the ester-bearing modifications as pro-drugs. Within the body, numerous esterase enzymes would carry out cleavage of these esters to generate the acid [21]. It was anticipated that this form would be more soluble in aqueous medium and would be more potent than the parent compound. This, however, was apparently not the case. Furthermore, while we have prepared the acid, we have been unable to purify it to an acceptable level for screening. Finally, the installation of a cyclopropyl group at C1 gave structure 6e, which is the most potent compound generated to date. Based on available crystallographic studies of RAB1, the cyclopropyl moiety likely forms favorable stacking interactions with an arginine residue at position 53 within the B. anthracis DHFR binding site (Figure 1) [9,10].
Figure 1.
Interactions between the DHFR protein and the RAB1 (R = n–Pr) inhibitor. This structure illustrates the position of substituents R at the C1 stereocenter of the dihydrophthalazine with a black oval; selected residues are labeled. It is hypothesized that the superior potency of compound 6e (R = cyclopropyl) results from stacking interactions with the guanidinium group of Arg 53.
3. Experimental
3.1. General Information
Commercial anhydrous N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) were stored under dry N2 and transferred by syringe into reactions when required. Tetrahydrofuran (THF) was dried over KOH pellets and distilled from LiAlH4 prior to use. K2CO3 was dried at 120 °C under high vacuum for a period of 16 h before use. All other commercial reagents were used as received. Unless otherwise specified, all reactions were run under dry N2 in oven-dried glassware. The saturated NaCl and NH4Cl used in workup procedures were aqueous solutions. Reactions were monitored by thin layer chromatography (TLC) on silica gel GF plates (Analtech, 21521). Preparative separations were performed by chromatography on silica gel (Davisil®, grade 62, 60–200 mesh) mixed with UV-active phosphor (Sorbent Technologies, UV-05). Band elution for all chromatographic separations was monitored using a hand-held UV lamp. Melting points were uncorrected. FT-IR spectra were run as thin films on NaCl disks. 1H- and 13C-NMR spectra were measured at 300 MHz or 400 MHz (1H) and 75 or 100 MHz (13C) in the indicated solvent. Chemical shifts (δ) are referenced to internal (CH3)4Si and coupling constants (J) are given in Hz. Elemental analyses were ±0.4% from Atlantic Microlab, Inc. (Norcross, GA, USA).
3.2. Synthesis of 1-(Phthalazin-2(1H)-yl)prop-2-en-1-ones 4a‒h
(±)-1-(1-Methylphthalazin-2(1H)-yl)prop-2-en-1-one (4a). A stirred solution of phthalazine (1) (2.00 g, 15.4 mmol) in dry THF (50 mL) was treated dropwise with a solution of methyllithium (2a, 1.5 M in ether, 11.3 mL, 16.9 mmol) over a period of 15 min at –20 °C. The reaction was stirred at this temperature for 45 min and was then poured into saturated NH4Cl (50 mL) and extracted with ethyl acetate (3 × 50 mL). The combined organic extracts were washed with saturated NaCl (100 mL), dried (MgSO4), filtered, and concentrated under vacuum to afford 3a as a dark brown liquid. The crude product 3a was dissolved in dichloromethane (DCM, 50 mL), and triethylamine (1.86 g, 2.56 mL, 18.4 mmol) was added, followed by dropwise addition of acryloyl chloride (1.39 g, 1.25 mL, 15.4 mmol) at 0 °C. The reaction mixture was stirred at 0 °C for 2 h. The reaction was then quenched with saturated NaCl (100 mL), the organic layer was separated, and the aqueous layer was extracted with DCM (2 × 50 mL). The combined organic extracts were washed with saturated NaCl (50 mL), dried (MgSO4), filtered, and concentrated to afford the crude product. The crude product was purified on a silica gel column eluted with hexanes:EtOAc (4:1) to afford 4a as a pale yellow liquid (2.60 g, 84%). IR: 1663, 1621 cm−1; 1H-NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.60 (s, 1H), 7.43 (td, J = 7.1, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.37–7.23 (complex m, 3H), 7.16 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 6.49 (dd, J = 17.5, 2.2 Hz, 1H), 5.90 (q, J = 6.6 Hz, 1H), 5.78 (dd, J = 10.4, 2.2 Hz, 1H), 1.31 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, 3H); 13C-NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ 165.8, 141.4, 135.2, 131.5, 128.0, 127.7, 126.9, 125.42, 125.40, 122.9, 47.1, 20.9.
(±)-1-(1-Ethylphthalazin-2(1H)-yl)prop-2-en-1-one (4b). This compound was prepared as above using 1 (2.00 g, 15.4 mmol) and ethyllithium (2b, 1.5 M in dibutyl ether, 11.2 mL, 16.9 mmol), followed by triethylamine (1.86 g, 2.56 mL, 18.4 mmol) and acryloyl chloride (1.39 g, 1.25 mL, 15.4 mmol) to afford 4b (2.63 g, 80%) as a viscous, colorless oil. IR: 1666, 1621 cm−1; 1H-NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.60 (s, 1H), 7.43 (td, J = 7.7, 1.1 Hz, 1H), 7.39–7.28 (complex m, 2H), 7.27 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 7.14 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 6.48 (dd, J = 17.0, 2.2 Hz, 1H), 5.77 (overlapping dd, J = 10.4, 2.2 Hz, 1H and t, J = 6.6 Hz, 1H), 1.64 (m, 2H), 0.81 (t, J = 7.7 Hz, 3H); 13C-NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ 166.1, 142.1, 133.4, 131.2, 128.1, 127.9, 127.0, 126.4, 125.5, 123.7, 52.3, 28.0, 9.3.
(±)-1-(1-n-Butylphthalazin-2(1H)-yl)prop-2-en-1-one (4c). This compound was prepared as above using 1 (2.00 g, 15.4 mmol) and n-butyllithium (2c, 2.2 M in hexanes, 7.68 mL, 16.9 mmol), followed by triethylamine (1.86 g, 2.56 mL, 18.4 mmol) and acryloyl chloride (1.39 g, 1.25 mL, 15.4 mmol) to afford 4c (3.09 g, 83%) as viscous, colorless oil. IR: 1665, 1621 cm‒1; 1H-NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.62 (s, 1H), 7.44 (td, J = 7.7, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.35 (td, J = 7.1, 1.1 Hz, 1H), 7.32 (dd, J = 17.0, 10.4 Hz, 1H), 7.28 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 7.16 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 6.48 (dd, J = 17.0, 2.2 Hz, 1H), 5.84 (t, J = 6.6 Hz, 1H), 5.78 (dd, J = 10.4, 2,2 Hz, 1H), 1.64 (q, J = 6.6 Hz, 2H), 1.23 (m, 4H), 0.82 (t, J = 6.8 Hz, 3H); 13C-NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ 166.1, 142.4, 134.0, 131.3, 128.2, 127.9, 127.1, 126.4, 125.6, 123.8, 51.2, 34.8, 26.9, 22.4, 13.8.
(±)-1-(1-s-Butylphthalazin-2(1H)-yl)prop-2-en-1-one (4d). This compound was prepared as above using 1 (2.00 g, 15.4 mmol) and s-butyllithium (2d, 1.4 M in cyclohexane, 12.1 mL, 16.9 mmol), followed by triethylamine (1.86 g, 2.56 mL, 18.4 mmol) and acryloyl chloride (1.39 g, 1.25 mL, 15.4 mmol) to afford 4d (3.00 g, 81%) as a viscous, colorless oil. IR: 1663, 1620 cm−1; 1H-NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3, mixture of diastereomers): δ 7.64 and 7.61 (2s, 1H), 7.44 (t, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 7.40–7.25 (complex m, 3H), 7.17 (apparent t, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 6.46 (d, J = 17.0 Hz, 1H), 5.76 (m, 2H), 1.73 (m, 1H), 1.46 (m, 1H), 1.10 (m, 1H), 0.92 and 0.82 (2t, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 0.88 and 0.70 (2d, J = 6.6 Hz, 3H); 13C-NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3, mixture of diastereomers): δ 166.5, 143.4, 143.1, 132.5, 131.6, 131.1, 131.0, 128.2, 127.95, 127.90, 127.5, 127.4, 127.2, 125.4, 124.7, 124.4, 55.74, 55.26, 40.6, 39.9, 25.4, 24.3, 15.0, 14.2, 11.6, 11.4.
(±)-1-(1-Cyclopropylphthalazin-2(1H)-yl)prop-2-en-1-one (4e). To a stirred solution of 1 (2.00 g, 15.4 mmol) in dry THF (50 mL) was added dropwise cyclopropylmagnesium chloride (0.5 M in THF, 33.8 mL, 16.9 mmol) over a period of 10 min at 0 °C. The reaction was stirred at 0 °C for 2 h and was then quenched with saturated NH4Cl (50 mL) and extracted with ethyl acetate (2 × 50 mL). The combined extracts were washed with saturated NaCl, dried (MgSO4), filtered, and concentrated to give 3e as a light brown oil. The crude product 3e was acylated as described for compound 4a using triethylamine (1.86 g, 2.56 mL, 18.4 mmol) and acryloyl chloride (1.39 g, 1.25 mL, 15.4 mmol) in DCM (50 mL) to obtain 4e (2.71 g, 78%) as a pale yellow oil. IR: 1662, 1621 cm−1; 1H-NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 7.66 (s, 1H), 7.45 (td, J = 7.1, 1.1 Hz, 1H), 7.37 (td, J = 7.7, 1.1 Hz, 1H), 7.36 (dd, J = 17.0, 10.4 Hz, 1H), 7.30 (m, 2H), 7.16 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 6.48 (dd, J = 17.0, 2.2 Hz, 1H), 5.79 (dd, J = 10.4, 2.2 Hz, 1H), 5.47 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 1.17 (m, 1H), 0.66 (quintet, J = 4.9 Hz, 1H), 0.44 (m, 1H), 0.36 (m, 1H); 13C-NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 166.6, 142.5, 132.9, 131.5, 128.3, 128.1, 127.2, 126.5, 125.5, 124.0, 54.0, 16.7, 3.8, 2.3.
(±)-1-(1-(Furan-2-yl)phthalazin-2(1H)-yl)prop-2-en-1-one (4f). To a stirred solution of furan (1.20 g, 17.6 mmol) in dry THF (20 mL) was added dropwise n-butyllithium (2.5 M in hexanes, 7.30 mL, 18.3 mmol) over a period of 30 min at –78 °C. The solution was warmed to –25 °C, and stirring was continued at this temperature for 30 min. The reaction mixture was cooled back to –78 °C, and a solution of 1 (2.00 g, 15.3 mmol) in dry THF (20 mL) was added dropwise over 30 min. The reaction mixture was stirred at this temperature for 2 h. The mixture was poured into saturated NH4Cl (100 mL) and extracted with ethyl acetate (3 × 50 mL). The combined organic extracts were then washed with saturated NaCl (50 mL), dried (MgSO4), filtered, and concentrated under vacuum to afford 3f as a light brown oil. The crude product 3f was dissolved in DCM (30 mL), and triethylamine (2.37 g, 3.26 mL, 23.4 mmol) was added, followed by dropwise addition of acryloyl chloride (1.59 g, 1.43 mL, 17.6 mmol) at 0 °C. The reaction mixture was stirred at 0 °C for 2 h. The reaction was then quenched with saturated NaCl (25 mL), and the organic layer was separated. The aqueous layer was extracted with DCM (2 × 30 mL), and the combined organic extracts were washed with saturated NaCl (50 mL), dried (MgSO4), filtered, and concentrated to afford the crude product. The product was purified on a silica gel column eluted with hexanes–EtOAc (7:3) to afford 4f (2.66 g, 60%) as a yellow liquid. IR: 1666, 1616 cm−1; 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.68 (s, 1H), 7.47 (dd, J = 7.4, 1.4 Hz, 1H), 7.41 (td, J = 7.4, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 7.37–7.26 (complex m, 3H), 7.25 (d, J = 1.8 Hz, 1H), 7.04 (s, 1H), 6.52 (dd, J = 17.1, 2.0 Hz, 1H), 6.19 (dd, J = 3.2, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 5.94 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 5.80 (dd, J = 10.5, 2.0 Hz, 1H); 13C-NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 166.2, 149.5, 143.5, 142.0, 131.5, 131.2, 128.7, 128.0, 126.6, 126.1, 126.0, 123.7, 111.7, 111.3, 41.8.
(±)-1-(1-(Thiophen-2-yl)phthalazin-2(1H)-yl)prop-2-en-1-one (4g). This compound was prepared by addition of 2-thiophenylmagnesium bromide, prepared from 2-bromothiophene (1.77 g, 1.69 mL, 21.0 mmol) and magnesium (0.69 g, 28.4 mmol) in dry THF (25 mL), to a solution of 1 (2.50 g, 19.2 mmol) in dry THF (30 mL). Product 3g was acylated using triethylamine (2.80 g, 3.86 mL, 27.7 mmol) and acryloyl chloride (1.90 g, 1.71 mL, 21.0 mmol) in DCM to afford 4g (3.09 g, 60%) as a light yellow liquid. IR: 1662, 1617 cm−1; 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.68 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 7.48 (td, J = 7.6, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 7.46-7.32 (complex m, 4H), 7.29 (d, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 7.13 (dd, J = 5.1, 3.7 Hz, 1H), 6.51 (dd, J = 17.1, 2.0 Hz, 1H), 5.83 (dd, J = 10.3, 2.0 Hz, 1H), 5.02 (s, 2H); 13C-NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 166.2, 143.7, 141.8, 132.1, 131.9, 129.1, 128.7, 127.0, 126.8, 126.3, 126.2, 125.84, 125.80, 123.7, 49.1.
(±)-1-(1-(Pyridin-2-yl)phthalazin-2(1H)-yl)prop-2-en-1-one (4h). This compound was prepared by the procedure described for 4f using 2-bromopyridine (1.30 g, 8.22 mmol), n-butyllithium (2.5 M in hexanes, 3.38 mL, 8.45 mmol), and 1 (1.00 g, 7.69 mmol) in dry THF (25 mL). Product 3h was acylated using triethylamine (0.93 g, 1.28 mL, 9.2 mmol) and acryloyl chloride (0.70 g, 0.63 mL, 7.73 mmol) in DCM (30 mL) to afford 4h (1.53 g, 76%) as a light yellow liquid. IR: 1662, 1617 cm−1; 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.48 (dq, J = 4.9, 0.8 Hz, 1H), 7.63 (s, 1H), 7.57 (td, J = 7.6, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 7.47–7.37 (complex m, 3H), 7.34 (td, J = 7.6, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 7.28 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H), 7.08 (ddd, J = 7.6, 4.9, 1.0 Hz, 1H), 6.94 (s, 1H), 6.47 (dd, J = 17.4, 2.0 Hz, 1H), 5.80 (dd, J = 10.3, 2.0 Hz, 1H); 13C-NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 166.6, 159.6, 149.7, 141.2, 136.8, 132.2, 131.8, 129.0, 128.5, 127.5, 127.1, 126.1, 122.5, 122.2, 120.3, 56.7.
3.3. Synthesis of 2,4-Diaminopyrimidine 5
2,4-Diamino-5(5-iodo-3,4-dimethoxybenzyl)pyrimidine (5). This compound was prepared in 60% yield from morpholine and acrylonitrile on a 0.47-mol scale according to the literature procedure [15], mp 217–218 °C (lit. [15] mp 217–218 °C). IR: 3467, 3315, 3140, 1638 cm-1; 1H-NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 7.57 (s, 1H), 7.14 (d, J = 1.8 Hz, 1H), 6.98 (d, J = 1.8 Hz, 1H), 6.16 (br s, 2H), 5.77 (br s, 2H), 3.77 (s, 3H), 3.66 (s, 3H), 3.54 (s, 2H); 13C-NMR (75 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 162.4, 162.1, 156.0, 152.0, 146.3, 138.9, 129.1, 113.8, 105.2, 92.4, 59.8, 55.8, 31.7.
3.4. Synthesis of Drug Candidates 6
(±)-(E)-3-(5-((2,4-Diaminopyrimidin-5-yl)methyl)-2,3-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-(1-methylphthalazin-2(1H)-yl)prop-2-en-1-one (6a). To a stirred solution of 5 (1.00 g, 2.59 mmol) in dry DMF (6 mL) was added a solution of 4a (0.57 g, 2.85 mmol) in DMF (2 mL), followed by N-ethylpiperidine (0.32 g, 0.40 mL, 2.84 mmol) and Pd(OAc)2 (20 mg, 0.089 mmol). The reaction was heated at 140 °C for 20 h and then cooled using an ice bath. The product was purified by directly pouring the crude reaction mixture onto a 50 cm × 2.5 cm silica gel chromatography column slurry packed with CH2Cl2. Impurities were eluted using CH2Cl2, and the final product was collected using CH2Cl2/MeOH/Et3N (97:3:1). Evaporation of the solvent gave an oily, yellow-brown foam, which was dried under high vacuum for a period of 2 h. Methanol (3 mL) was added, followed by ether (10 mL), to crystallize the product, and the mixture was allowed to cool for 4 h. The product was filtered and dried under vacuum to afford 6a (0.97 g, 82%) as an off-white solid, mp 153–155 °C. IR: 3612, 3308, 3192, 1634, 1600 cm−1; 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 7.93 (s, 1H), 7.88 (d, J = 16.5 Hz, 1H), 7.64 (d, J = 16.5 Hz, 1H), 7.62–7.35 (complex m, 5H), 7.29 (s, 1H), 7.15 (br s, 2H), 7.04 (s, 1H), 6.64 (br s, 2H), 5.89 (m, 1H), 3.81 (s, 3H), 3.76 (s, 3H), 3.65 (s, 2H), 1.23 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 3H); 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 165.5, 163.0, 158.6, 152.6, 148.6, 146.2, 142.1, 136.6, 135.3, 135.1, 132.0, 128.2, 127.9, 126.1, 126.0, 123.0, 118.7, 118.0, 114.9, 107.2, 60.8, 55.8, 46.8, 32.0, 21.1. Anal. Calcd for C25H26N6O3·3.9 H2O: C, 56.79; H, 6.44; N, 15.89. Found: C, 56.75; H, 6.32; N, 15.63.
(±)-(E)-3-(5-((2,4-Diaminopyrimidin-5-yl)methyl)-2,3-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-(1-ethylphthalazin-2(1H)-yl)prop-2-en-1-one (6b). This compound was prepared as above using 5 (1.00 g, 2.59 mmol), 4b (0.61 g, 2.85 mmol), N-ethylpiperidine (0.32 g, 0.40 mL, 2.85 mmol), and Pd(OAc)2 (20 mg, 0.089 mmol) in dry DMF (8 mL) to give 6b (0.98 g, 80%) as an off-white solid, mp 232–234 °C. IR: 3472, 3325, 3179, 1635, 1598 cm−1; 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 7.92 (s, 1H), 7.88 (d, J = 15.9 Hz, 1H), 7.65 (d, J = 15.9 Hz, 1H), 7.62 (s, 1H), 7.58-7.43 (complex m, 3H), 7.40 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 7.26 (s, 1H), 7.00 (s, 1H), 6.21 (br s, 2H), 5.80 (t, J = 6.6 Hz, 1H), 5.77 (br s, 2H), 3.80 (s, 3H), 3.74 (s, 3H), 3.61 (s, 2H), 1.61 (m, 2H), 0.74 (t, J = 7.7 Hz, 3H); 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 165.7, 162.4, 162.2, 155.9, 152.5, 146.0, 142.6, 136.7, 133.2, 131.7, 128.3, 127.8, 126.7, 126.1, 123.7, 118.4, 117.9, 114.7, 105.8, 60.8, 55.8, 51.7, 32.5, 27.8, 9.3 (1 aromatic C unresolved). Anal. Calcd for C26H28N6O3: C, 65.83; H, 5.99; N, 17.72. Found: C, 65.84; H, 5.96; N, 17.63.
(±)-(E)-1-(1-n-Butylphthalazin-2(1H)-yl)-3-(5-((2,4-diaminopyrimidin-5-yl)methyl)-2,3-dimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one (6c). This compound was prepared as above using 5 (1.00 g, 2.59 mmol), 4c (0.69 g, 2.85 mmol), N-ethylpiperidine (0.32 g, 0.40 mL, 2.85 mmol), and Pd(OAc)2 (20 mg, 0.089 mmol) in dry DMF (8 mL) to give 6c (0.97 g, 75%) as an off-white solid, mp 112–114 °C. IR: 3474, 3329, 3177, 1637, 1603 cm−1; 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 7.94 (s, 1H), 7.87 (d, J = 15.9 Hz, 1H), 7.63 (d, J = 15.9 Hz, 1H), 7.61 (s, 1H), 7.52 (m, 2H), 7.45 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 7.39 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 7.25 (s, 1H), 7.00 (s, 1H), 6.22 (br s, 2H), 5.84 (t, J = 6.6 Hz, 1H), 5.78 (br s, 2H), 3.80 (s, 3H), 3.74 (s, 3H), 3.60 (s, 2H), 1.58 (m, 2H), 1.17 (m, 4H), 0.79 (t, J = 6.6 Hz, 3H); 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 165.6, 162.22, 162.18, 155.6, 152.5, 146.0, 142.8, 136.6 (2C), 133.6, 131.7, 128.2, 127.8, 126.5, 126.0, 123.6, 118.3, 117.8, 114.7, 105.8, 60.8, 55.7, 50.5, 34.3, 32.4, 26.6, 21.9, 13.8. Anal. Calcd for C28H32N6O3·0.8 H2O: C, 65.30; H, 6.58; N, 16.32. Found: C, 65.24; H, 6.39; N, 16.22.
(±)-(E)-1-(1-s-Butylphthalazin-2(1H)-yl)-3-(5-((2,4-diaminopyrimidin-5-yl)methyl)-2,3-dimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one (6d). This compound was prepared as above using 5 (1.00 g, 2.59 mmol), 4d (0.69 g, 2.85 mmol), N-ethylpiperidine (0.32 g, 0.40 mL, 2.85 mmol), and Pd(OAc)2 (20 mg, 0.089 mmol) in dry DMF (8 mL) to give 6d (0.93 g, 72%) as an off-white solid, mp 122–124 °C. IR: 3469, 3371, 3214, 1634, 1603 cm−1; 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6, mixture of diastereomers): δ 7.97 and 7.95 (2s, 1H), 7.86 (d, J = 15.9 Hz, 1H), 7.66 (2d, J = 15.9 Hz, 1H), 7.60 (s, 1H), 7.59-7.42 (complex m, 3H), 7.37 (apparent t, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 7.27 (s, 1H), 7.00 (s, 1H), 6.32 (br s, 2H), 5.86 (br s, 2H), 5.74 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, 1H), 3.79 (s, 3H), 3.74 (s, 3H), 3.60 (s, 2H), 1.64 (m, 1H), 1.39 (m, 1H), 0.94 (m, 1H), 0.87 and 0.78 (2t, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 0.81 and 0.65 (2d, J = 7. 1 Hz, 3H); 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6, mixture of diastereomers) δ 165.9, 165.6, 162.3, 161.8, 154.8, 152.5, 146.0, 143.8, 143.5, 136.6, 136.4, 132.0, 131.4, 131.1, 128.3, 127.8, 127.5, 127.4, 125.9, 124.4, 124.2, 118.4, 117.9, 114.7, 105.9, 60.8, 55.7, 54.5, 32.4, 24.9, 24.0, 15.0, 14.2, 11.4, 11.3. Anal. Calcd for C28H32N6O3·1.0 H2O: C, 64.85; H, 6.61; N, 16.20. Found: C, 64.83; H, 6.43; N, 16.28.
(±)-(E)-1-(1-Cyclopropylphthalazin-2(1H)-yl)-3-(5-((2,4-diaminopyrimidin-5-yl)methyl)-2,3-dimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one (6e). This compound was prepared as above using 5 (1.00 g, 2.59 mmol), 4e (0.64 g, 2.85 mmol), N-ethylpiperidine (0.32 g, 0.40 mL, 2.85 mmol), and Pd(OAc)2 (20 mg, 0.089 mmol) in dry DMF (8 mL) to give 6e (0.90 g, 72%) as an off-white solid, mp 155–157 °C. IR: 3464, 3359, 3202, 1636, 1602 cm−1; 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 7.99 (s, 1H), 7.87 (d, J = 15.9 Hz, 1H), 7.66 (d, J = 15.9 Hz, 1H), 7.59 (s, 1H), 7.53 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 2H), 7.46 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 2H), 7.28 (s, 1H), 7.02 (s, 1H), 6.64 (br s, 2H), 6.16 (br s, 2H), 5.42 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 3.80 (s, 3H), 3.75 (s, 3H), 3.62 (s, 2H), 1.13 (m, 1H), 0.55 (m, 1H), 0.44 (m, 2H), 0.33 (m, 1H); 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 165.9, 162.6, 160.4, 152.5, 152.1, 146.1, 142.9, 136.7, 135.9, 132.8, 131.8, 128.3, 127.8, 126.6, 125.9, 123.7, 118.6, 118.1, 114.8, 106.5, 60.8, 55.8, 53.4, 32.2, 16.7, 4.0, 2.0. Anal. Calcd for C27H28N6O3·2.2 H2O: C, 61.87; H, 6.23; N, 16.03. Found: C, 61.88; H, 6.32; N, 16.00.
(±)-(E)-3-(5-((2,4-Diaminopyrimidin-5-yl)methyl)-2,3-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-(1-(furan-2-yl)phthalazin-2(1H)-yl)prop-2-en-1-one (6f). This compound was prepared as above using 5 (1.50 g, 3.88 mmol), 4f (1.05 g, 4.15 mmol), N-ethylpiperidine (0.48 g, 0.58 mL, 4.27 mmol), and Pd(OAc)2 (30 mg, 0.134 mmol) in dry DMF (10 mL) to give 6f (0.82 g, 42%), as a brown solid, mp 242–244 °C. IR: 3439, 3336, 3181, 1639, 1601 cm−1; 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 8.01 (s, 1H), 7.91 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 7.66 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 7.61-7.49 (complex m, 6H), 7.32 (s, 1H), 7.17 (br s, 2H), 7.09 (s, 1H), 7.05 (s, 1H), 6.67 (br s, 2H), 6.33 (m, 1H), 5.99 (dd, J = 3.1, 0.6 Hz, 1H), 3.81 (s, 3H), 3.76 (s, 3H), 3.65 (s, 2H); 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 165.6, 163.1, 158.1, 152.59, 152.56, 147.8, 146.3, 143.0, 142.4, 137.2, 135.1, 132.1, 130.2, 129.0, 127.8, 127.2, 126.3, 123.7, 118.8, 117.7, 115.1, 110.4, 107.6, 107.4, 60.8, 55.8, 47.4, 32.0. Anal. Calcd for C28H26N6O4·4.6 H2O·0.1 Et2O: C, 56.77; H, 6.07; N, 13.99. Found: C, 56.44; H, 5.85; N, 13.72.
(±)-(E)-3-(5-((2,4-Diaminopyrimidin-5-yl)methyl)-2,3-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-(1-(thiophen-2-yl)-phthalazin-2(1H)-yl)prop-2-en-1-one (6g). This compound was prepared as above using 5 (1.00 g, 2.59 mmol), 4g (0.77 g, 2.85 mmol), N-ethylpiperidine (0.32 g, 0.40 mL, 2.85 mmol), and Pd(OAc)2 (20 mg, 0.089 mmol) in dry DMF (8 mL) to give 6g (0.93 g, 68%) as a brown solid, mp 235–237 °C. IR: 3452, 3345, 3179, 1637, 1602 cm−1; 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 8.06 (s, 1H), 7.94 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 7.70–7.50 (complex m, 6H), 7.40 (d, J = 4.1 Hz, 1H), 7.31 (s, 1H), 7.27 (s, 1H), 7.04 (s, 1H), 6.96 (br s, 2H), 6.89 (s, 1H), 6.66 (s, 1H), 6.47 (br s, 2H), 3.81 (s, 3H), 3.77 (s, 3H), 3.64 (s, 2H); 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 165.7, 162.9, 159.0, 152.6, 149.4, 146.3, 143.8, 142.4, 137.4, 135.4, 132.2, 132.1, 129.0, 127.7, 127.1, 126.5, 126.32, 126.27, 126.0, 123.4, 118.8, 117.7, 115.1, 107.9, 60.8, 55.8, 48.8, 32.1. Anal. Calcd for C28H26N6O3S·4.3 H2O: C, 55.67; H, 5.77; N, 13.91. Found: C, 55.99; H, 5.75; N, 13.82.
(±)-(E)-3-(5-((2,4-Diaminopyrimidin-5-yl)methyl)-2,3-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-(1-(pyridin-2-yl)phthalazin-2(1H)-yl)prop-2-en-1-one (6h). This compound was prepared as above using 5 (1.50 g, 3.88 mmol), 4h (1.10 g, 4.18 mmol), N-ethylpiperidine (0.48 g, 0.58 mL, 4.27 mmol), and Pd(OAc)2 (30 mg, 0.134 mmol) in dry DMF (10 mL) to give 6h (0.80 g, 40%) as a brown solid, mp 177–179 °C. IR: 3459, 3347, 3216, 1648, 1611 cm−1; 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 8.43 (d, J = 4.1 Hz, 1H), 7.89 (s, 1H), 7.85 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 7.76 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 7.74 (td, J = 7.4, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.61 (m, 2H), 7.50 (m, 2H), 7.42 (m, 2H), 7.30 (s, 1H), 7.23 (dd, J = 6.7, 5.0 Hz, 1H), 7.01 (d, J = 1.4 Hz, 1H), 6.95 (s, 1H), 6.48 (br s, 2H), 6.01 (br s, 2H), 3.79 (s, 3H), 3.73 (s, 3H), 3.63 (s, 2H); 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 166.0, 162.4, 161.1, 159.6, 153.5, 152.5, 149.3, 146.1, 140.9, 137.1, 136.9, 136.2, 132.0, 131.8, 128.6, 127.7, 127.5, 126.3, 122.9, 122.8, 120.2, 118.4, 117.8, 114.9, 106.2, 60.8, 56.0, 55.8, 32.3. Anal. Calcd for C29H27N7O3·2.4 H2O: C, 61.67; H, 5.68; N, 17.36. Found: C, 61.58; H, 5.47; N, 17.43.
3.5. Synthesis of Esters 9a–c
(±)-t-Butyl 2-(2-Acryloylphthalazin-2(1H)-yl)acetate (9a). To a stirred solution of tert-butyl acetate (2.67 g, 3.08 mL, 23.0 mmol) in dry THF (40 mL) at –78 °C was added dropwise n-butyllithium (2.5 M in hexanes, 7.68 mL, 19.2 mmol) over a period of 30 min. The solution was warmed to –25 °C and stirred at this temperature for a period of 30 min. To this reaction mixture was added a solution of 1 (2.00 g, 15.4 mmol) in dry THF (25 mL), and stirring was continued for an additional 30 min at 0 °C. The reaction mixture was poured into saturated NH4Cl (100 mL) and extracted with EtOAc (3 × 50 mL). The organic extracts were washed with saturated NaCl (50 mL), dried (MgSO4) and concentrated to afford 8 as a light brown oil. The crude product 8 was then dissolved in DCM (50 mL), and triethylamine (1.86 g, 2.56 mL, 18.4 mmol) was added, followed by dropwise addition of acryloyl chloride (1.39 g, 1.25 mL, 15.4 mmol) at 0 °C. The reaction mixture was stirred at 0 °C for a period of 2 h. The reaction was quenched with saturated NaCl (50 mL), and the organic layer was separated. The aqueous layer was extracted with DCM (2 × 50 mL) and the combined organic layers were washed with saturated NaCl (50 mL), dried (MgSO4), filtered, and concentrated to afford the crude product. The crude product was purified on a silica gel column eluted with hexanes–EtOAc (4:1) to afford 9a (4.00 g, 87%) as a colorless liquid. IR: 1727, 1668, 1621 cm−1; 1H-NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.64 (s, 1H), 7.44 (td, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 7.38 (td, J = 7.7, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.36-7.26 (complex m, 3H), 6.49 (dd, J = 17.0, 2.2 Hz, 1H), 6.25 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 5.79 (dd, J = 10.4, 2.2 Hz, 1H), 2.58 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 2H), 1.37 (s, 9H); 13C-NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ 168.7, 166.0, 142.0, 132.5, 131.6, 128.7, 128.4, 126.9, 126.7, 125.7, 123.6, 80.9, 48.0, 40.7, 27.8.
(±)-2-(2-Acryloylphthalazin-2(1H)-yl)acetic Acid (10). To a stirred solution of 9a (1.50 g, 5.00 mmol) in benzene (25 mL) was added Bi(OTf)3 (0.164 g, 0.25 mmol, 5 mol%), and the solution was refluxed for a period of 2 h. To this solution was added EtOAc (50 mL), followed by H2O (50 mL). The organic layer was washed with saturated NaCl (50 mL), dried (MgSO4), filtered, and concentrated to afford 10 (1.15 g, 94%) as a pale yellow solid, mp 142–145 °C. IR: 3400, 1734, 1670 cm−1; 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 12.4 (s, 1H), 7.93 (s, 1H), 7.56–7.43 (complex m, 3H), 7.39 (d, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 7.24 (dd, J = 17.2, 10.5 Hz, 1H), 6.34 (dd, J = 17.2, 2.1 Hz, 1H), 6.13 (t, J = 6.8 Hz, 1H), 5.86 (dd, J = 10.5, 2.1 Hz, 1H), 2.51 (m, 2H); 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 170.7, 165.1, 142.8, 132.3, 131.9, 128.9, 128.7, 127.0, 126.4, 126.3, 123.4, 47.5, 39.5. Attempts to further purify this compound failed to yield material with sufficient purity for biological testing.
(±)-Ethyl 2-(2-Acryloylphthalazin-2(1H)-yl)acetate (9b). To a stirred solution of 10 (1.00 g, 4.10 mmol) in ethanol (25 mL) was added Bi(OTf)3 (0.134 g, 0.20 mmol, 5 mol%), and the mixture was refluxed for a period of 2 h. The solution was concentrated and purified using a silica gel column eluted with hexanes–EtOAc (4:1) to afford 9b (1.06 g, 95%) as a colorless, viscous liquid. IR: 1733, 1667, 1621 cm−1; 1H-NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.66 (s, 1H), 7.45 (td, J = 7.1, 1.1 Hz, 1H), 7.38 (td, J = 7.7, 1.1 Hz, 1H), 7.35–7.23 (complex m, 3H), 6.49 (dd, J = 17.0, 2.2 Hz, 1H), 6.29 (t, J = 6.6 Hz, 1H), 5.81 (dd, J = 10.4, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 4.06 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 2H), 2.65 (m, 2H), 1.19 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H); 13C-NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ 169.5, 166.1, 142.1, 132.3, 131.7, 128.9, 128.6, 126.8, 126.6, 125.8, 123.6, 60.7, 47.9, 39.5, 14.0.
(±)-Methyl 2-(2-Acryloylphthalazin-2(1H)-yl)acetate (9c). To a stirred solution of 10 (1.00 g, 4.10 mmol) in methanol (25 mL) was added Bi(OTf)3 (0.134 g, 0.20 mmol, 5 mol%), and the reaction was refluxed for 2 h. The solution was concentrated and purified using a silica gel column eluted with hexanes:EtOAc (4:1) to afford 9c (1.00 g, 95%) as colorless, viscous liquid. IR: 1732, 1663, 1618 cm−1; 1H-NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.67 (s, 1H), 7.45 (td, J = 7.7, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.38 (td, J = 7.7, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.34–7.27 (complex m, 3H), 6.49 (dd, J = 17.0, 2.2 Hz, 1H), 6.28 (t, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 5.81 (dd, J = 10.4, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 3.61 (s, 3H), 2.66 (m, 2H); 13C-NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ 169.9, 166.1, 142.1, 132.2, 131.8, 128.9, 128.6, 126.7, 126.4, 125.8, 123.4, 51.7, 47.9, 39.2.
3.6. Synthesis of Drug Candidates 11a–c
t-Butyl (±)-(E)-2-(2-(3-(5-((2,4-Diaminopyrimidin-5-yl)methyl)-2,3-dimethoxyphenyl)acryloyl)-phthal-azin-2(1H)-yl)acetate (11a). This compound was prepared as described for 6a using 5 (1.00 g, 2.59 mmol), 9a (0.86 g, 2.85 mmol), N-ethylpiperidine (0.32 g, 0.40 mL, 2.85 mmol), and Pd(OAc)2 (20 mg, 0.089 mmol) in dry DMF (8 mL) to give 11a (1.12 g, 78%) as an off-white solid, mp 185–187 °C. IR: 3361, 3187, 3068, 1698, 1672, 1638 cm−1; 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 7.96 (s, 1H), 7.89 (d, J = 15.9 Hz, 1H), 7.64 (d, J = 15.9 Hz, 1H), 7.62–7.46 (complex m, 6H), 7.41 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 7.32 (s, 1H), 7.06 (s, 1H), 7.02 (br s, 2H), 6.18 (t, J = 6.6 Hz, 1H), 3.82 (s, 3H), 3.75 (s, 3H), 3.66 (s, 2H), 2.50 (m, 2H), 1.30 (s, 9H); 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 168.4, 163.54, 163.46, 156.4, 152.6, 146.3, 144.5, 142.5, 136.8, 134.6, 132.1, 131.9, 128.7, 127.9, 126.5, 126.2, 123.5, 118.8, 117.9, 115.1, 108.0, 80.4, 60.8, 55.9, 47.9, 40.7, 31.8, 27.5. Anal. Calcd for C30H34N6O5·6.2 H2O: C, 53.75; H, 5.90; N, 12.54. Found: C, 53.71; H, 5.53; N, 12.56.
Ethyl (±)-(E)-2-(2-(3-(5-((2,4-Diaminopyrimidin-5-yl)methyl)-(2,3-dimethoxyphenyl)acryloyl)-phthal-azin-2(1H)-yl)acetate (11b). This compound was prepared as above using 5 (1.00 g, 2.59 mmol), 9b (0.78 g, 2.85 mmol), N-ethylpiperidine (0.32 g, 0.40 mL, 2.85 mmol), and Pd(OAc)2 (20 mg, 0.089 mmol) in dry DMF (8 mL) to give 11b (1.01 g, 74%) as a pale yellow solid, mp 113–115 °C. IR: 3473, 3352, 3185, 1728, 1651, 1614 cm−1; 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 7.98 (s, 1H), 7.88 (d, J = 15.9 Hz, 1H), 7.61 (d, J = 15.9 Hz, 1H), 7.60 (s, 1H), 7.52 (complex m, 3H), 7.40 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 7.27 (s, 1H), 7.02 (s, 1H), 6.47 (br s, 2H), 6.20 (t, J = 6.6 Hz, 1H), 6.00 (br s, 2H), 3.96 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 2H), 3.80 (s, 3H), 3.74 (s, 3H), 3.61 (s, 2H), 2.59 (m, 2H), 1.09 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H); 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 169.2, 165.7, 162.4, 161.1, 153.6, 152.5, 146.1, 142.5, 136.9, 136.2, 132.0 (2C), 128.8, 127.7, 126.4, 126.2, 123.5, 118.4, 117.7, 114.9, 106.2, 60.8, 60.3, 55.8, 47.8, 39.4, 32.3, 13.8. Anal. Calcd for C28H30N6O5·2.1 H2O: C, 59.17; H, 6.06; N, 14.79. Found: C, 59.16; H, 5.74; N, 14.60.
Methyl (±)-(E)-2-(2-(3-(5-((2,4-Diaminopyrimidin-5-yl)methyl)-2,3-dimethoxyphenyl)acryloyl)-phthal-azin-2(1H)-yl)acetate (11c). This compound was prepared as above using 5 (1.00 g, 2.59 mmol), 9c (0.74 g, 2.85 mmol), N-ethylpiperidine (0.32 g, 0.40 mL, 2.85 mmol), and Pd(OAc)2 (20 mg, 0.089 mmol) in dry DMF (8 mL) to give 11c (1.04 g, 78%) as a pale yellow solid, mp 158–160 °C. IR: 3477, 3370, 3192, 1720, 1653, 1614 cm−1; 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 7.98 (s, 1H), 7.87 (d, J = 15.9 Hz, 1H), 7.60 (d, J = 15.9 Hz, 1H), 7.59-7.46 (complex m, 4H), 7.39 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 7.28 (s, 1H), 7.03 (s, 1H), 6.86 (br s, 2H), 6.37 (br s, 2H), 6.20 (t, J = 6.6 Hz, 1H), 3.80 (s, 3H), 3.75 (s, 3H), 3.62 (s, 2H), 3.51 (s, 3H), 2.60 (m, 2H); 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 169.6, 165.7, 162.8, 159.4, 152.5, 150.1, 146.2, 142.5, 136.9, 135.6, 132.01, 131.97, 128.8, 127.8, 126.3 (2C), 123.4, 118.6, 117.7, 115.0, 106.9, 60.8, 55.8, 51.6, 47.8, 32.1. Anal. Calcd for C27H28N6O5∙3.7 H2O: C, 55.61; H, 6.12; N, 14.41. Found: C, 55.63; H, 6.32; N, 14.43.
3.7. Biological Potency Measurements
Measurements of the MIC and the Ki utilized a racemic mixture of each compound and have been described previously [9,10,12,15,16]. In brief, MIC values were based on standardized cultures of B. anthracis Sterne strain as prescribed by the CLSI [19]. Evaluation of growth utilized spectrophotometric values of turbidity at 600 nm and on visual inspection for assessment of bacterial growth. The lowest concentration that yielded no growth was assigned as the MIC. Evaluation of the enzymatic activity and inhibition utilized purified DHFR protein cloned from B. anthracis Sterne strain and expressed recombinantly in E. coli BL21 (DE3) cells. The protein preparation utilized an N-terminal His-tag, which was determined to not interfere with the enzymatic activity assay and was left intact for the current studies. The reaction was reconstituted, including the NADPH co-factor, and was initiated by the addition of the dihydrofolate substrate. The reaction was carried out at 30 °C, and the linear rate was monitored for 2.8 min. These rates were plotted as a function of inhibitor concentration, and the 50% activity point was calculated using a 4-parameter curve fit. These IC50 values were converted to Ki values using the Cheng-Prusoff equation [20].
4. Conclusion
In summary, we have synthesized and evaluated a series of 11 new racemic dihydrophthalazine-bound 2,4-diaminopyrimidine-based compounds differing in substitution at C1 of the dihydrophthalazine moiety. From these new derivatives, compound 6e bearing a cyclopropyl group at this position proved to be the most active compound generated to date, showing maximum potency against B. anthracis with respect to MIC and in Ki values compared to the other compounds prepared in this family. The strong correlation of these biological potency values suggests successful in vivo targeting of the DHFR enzyme. Derivatives possessing small alkyl groups, e.g. 6a (R = Me) and 6b (R = Et) also showed impressive potency. Finally, structures substituted with heteroaromatic rings (compounds 6f–h) or acetic ester moieties (compounds 11a–c) exhibited lower, though still significant, activity. The use of catalytic Bi(OTf)3 for both saponification and esterification reactions was successfully applied to the synthesis of the acetic esters explored in this study. Further investigations are underway to evaluate the biological activities of these drug scaffolds for other bacterial infections.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge support of this work by the National Institutes of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (R01-AI090685) of the NIH/NIAID and the Sitlington Chair in Infectious Diseases, both to WWB. Funding for the 300 MHz and 400 MHz NMR spectrometers of the Oklahoma Statewide Shared NMR Facility was provided by the NSF (BIR-9512269), the Oklahoma State Regents for Higher Education, the W. M. Keck Foundation, and Conoco, Inc. The authors also wish to thank the OSU College of Arts and Sciences for funds to upgrade our departmental FT-IR instruments.
Author Contributions
Baskar Nammalwar, N. Prasad Muddala, Richard A. Bunce and K. Darrell Berlin performed the compound synthesis work. Christina R. Bourne, Mary Henry, Philip C. Bourne, Esther W. Barrow and William W. Barrow performed the biological screening. Richard A. Bunce and Christina R. Bourne wrote the paper, but all authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript before submission.
Conflictts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Footnotes
Sample Availability: Not available.
References
- 1.Boucher H.W., Talbot G.H., Bradley J.S., Edwards J.E., Gilbert D., Rice L.B., Scheld M., Spellberg B., Bartlett J. Bad Bugs, No Drugs: No ESKAPE! An update from the infectious diseases society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009;48:1–12. doi: 10.1086/595011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Fischbach M.A., Walsh C.T. Antibiotics for Emerging Pathogens. Science. 2009;325:1089–1093. doi: 10.1126/science.1176667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Riedel S. Anthrax: A continuing concern in the era of bioterrorism. Proc. (Bayl. Univ. Med. Cent.) 2005;18:234–243. doi: 10.1080/08998280.2005.11928074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Twenhafel N.A. Pathology of inhalational anthrax animal models. Vet. Pathol. 2010;47:819–830. doi: 10.1177/0300985810378112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Odendaal M.W., Pieterson P.M., Devos V. The antibiotic-sensitivity patterns of Bacillus anthracis isolated from the Kruger National Park. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 1991;58:17–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Proliferation of Weapons of Mass Destruction: Assessing the Risks. [(accessed on 13 March 2014)]. Available online: http://www.au.af.mil/au/awc/awcgate/ota/9341.pdf.
- 7.Wright D.L., Anderson A.C. Antifolate agents: A patent review (2006–2010) Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2011;21:1293–1308. doi: 10.1517/13543776.2011.587804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Barrow E.W., Bourne P.C., Barrow W.W. Functional cloning of Bacillus anthracis dihydrofolate reductase and confirmation of natural resistance to trimethoprim. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004;48:4643–4649. doi: 10.1128/AAC.48.12.4643-4649.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Bourne C.R., Bunce R.A., Bourne P.C., Berlin K.D., Barrow E.W., Barrow W.W. Crystal structure of Bacillus anthracis dihydrofolate reductase with the dihydrophthalazine-based trimethoprim derivative RAB1 provides a structural explanation of potency and selectivity. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009;53:3065–3073. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01666-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Bourne C.R., Wakeham N., Nammalwar B., Tseitin V., Bourne P.C., Barrow E.W., Mylvaganam S., Ramnarayan K., Bunce R.A., Berlin K.D., et al. Structure-activity relationship for enantiomers of potent inhibitors of B. anthracis dihydrofolate reductase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Proteins and Proteom. 2013;1834:46–52. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2012.09.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Barrow E.W., Dreier J., Reinelt S., Bourne P.C., Barrow W.W. In vitro efficacy of new antifolates against trimethoprim-resistant Bacillus anthracis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007;51:4447–4452. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00628-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bourne C.R., Barrow E.W., Bunce R.A., Bourne P.C., Berlin K.D., Barrow W.W. Inhibition of antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by the broad-spectrum dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor RAB1. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010;54:3825–3833. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00361-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Nammalwar B., Bourne C.R., Bunce R.A., Wakeham N., Bourne P.C., Ramnarayan K., Mylvaganam S., Berlin K.D., Barrow E.W., Barrow W.W. Inhibition of bacterial dihydrofolate reductase by 6-alkyl-2,4-diaminopyrimidines. ChemMedChem. 2012;7:1974–1982. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201200291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Guerry P., Hubschwerlen C., Jolidon S., Specklin J.-L., Wyss P.-C. Preparation of N-[(2,4-diaminopyrimidinylmethyl)cinnamoyl]phthalazines as Bactericides. Chem. Abstr. 1998;129:230736. WO9839328A1, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Nammalwar B., Bunce R.A., Berlin K.D., Bourne C.R., Bourne P.C., Barrow E.W., Barrow W.W. Synthesis and biological activity of substituted 2,4-diaminopyrimidines that inhibit Bacillus anthracis. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012;54:387–396. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2012.05.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Nammalwar B., Bunce R.A., Berlin K.D., Bourne C.R., Bourne P.C., Barrow E.W., Barrow W.W. Microwave-assisted Heck synthesis of substituted 2,4-diaminopyrimidine-based antibiotics. Org. Prep. Proced. Int. 2012;44:281–287. doi: 10.1080/00304948.2012.676823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Nammalwar B., Bunce R.A., Berlin K.D., Bourne C.R., Bourne P.C., Barrow E.W., Barrow W.W. Comparative study of the Frech catalyst with two conventional catalysts in the Heck synthesis of 2,4-diaminopyrimidine-based antibiotics. Org. Prep. Proced. Int. 2013;45:66–71. doi: 10.1080/00304948.2013.743755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kwie F.H.A., Baudoin-Dehoux C., Blonski C., Lherbet C. Bismuth(III) triflate, a safe and easily handled precursor for triflic acid. Application to the esterification reaction. Synth. Commun. 2010;40:1082–1087. doi: 10.1080/00397910903046846. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Test for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically. Approved Standard—Eighth Edition. CLSI; Wayne, PA, USA: 2009. CLSI document M07-A8. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Cheng Y., Prusoff W.H. Relationship between inhibition constant (K1) and concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent Inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1973;22:3099–3108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Rautio J., Kumpulainen H., Heimbach T., Oliyai R., Oh D., Jarvinen T., Savolainen J. Prodrugs: Design and clinical applications. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008;7:255–270. doi: 10.1038/nrd2468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]