Abstract
Aim
The aim of this study was to report the anatomical location and histologic type of colorectal polyps in a large series of Iranian patients that attended for colonoscopy.
Background
Polyps that develop through the adenoma-carcinoma pathway are considered neoplastic and may eventually progress to invasive carcinomas. In addition polyps can develop with no neoplastic potential. These neoplastic and non-neoplastic polyps can be identified and removed at colonoscopy.
Patients and methods
In this retrospective study, the medical records of patients who had attended for colonoscopy were reviewed. Patient demographics and colonoscopy findings were reviewed. The anatomical location, macroscopic appearance and histological assessment of any polyps were recorded.
Results
716 patients’ records were reviewed. 437 patients (61 %) were male and 279(39%) were females. The mean patient age was 55.3 yr (18-89 yr). A total of 936 polyps were identified. 779 (83.3%) were neoplastic and 157(16.7%) polyps were non-neoplastic.727 of the polyps were adenomatous. Of the 727 adenomatous polyps: 198(27.2%) were in sigmoid, 156(21.24%) were in caecum and ascending colon, 153(21%) were in descending colon, 131(18%) were in transverse colon and 89(12.3%) were in rectum. 39.5% of adenomas were proximal to the splenic flexure. Carcinoma was observed in 52 cases. 18 carcinomas (34.5%) were left sided and 34 (65.5% of carcinomas) were right sided. Of the 716 patients, 179 patients (25%) had synchronous lesion(s).
Conclusion
A significant number of adenomas and carcinomas lie proximal to the splenic flexure and occur in the absence of distal lesions. These lesions would be missed if the distal colon was examined and the entire colon examined only if a distal lesion was identified.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer, Screening, Colonoscopy
Introduction
The term polyp of the colon refers to a protuberance into the lumen from the normally flat colonic mucosa. Polyps are usually asymptomatic but may ulcerate and bleed, cause abdominal pain, and, when very large, produce intestinal obstruction. Colonic polyps are usually classified as hyperplastic, inflammatory and (neoplastic) adenomatous.
Hyperplastic polyps are the most common non-neoplastic polyp in the colon. They are small nodules or polypoid lesions composed of normal cellular components that may be indistinguishable macroscopically from adenomatous polyps. They do not exhibit dysplasia and have a characteristic satellite histologic appearance on cross section. Hyperplastic polyps are typically located in the left colon and are less than 5 mm in size (1, 2). They only rarely, if ever, develop into colorectal cancers. Multiple studies have evaluated the risk of proximal neoplasms in patients found to have distal hyperplastic polyps (3–7). A systematic review that included 18 studies estimated that 21 to 25 percent of patients found to have a distal hyperplastic polyp had a proximal neoplasm.
Inflammatory pseudopolyps are irregularly shaped islands of residual intact colonic mucosa that are the result of the mucosal ulceration and regeneration that occurs in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). These polyps are typically multiple and scattered throughout the colitic region of the colon (8–11).
Two-thirds of all colonic polyps are adenomatous. Adenomatous polyps are common in the general population. Advancing age is a major risk factor for the development of colonic adenomas. They are by definition dysplastic and thus have malignant potential. Nearly all colorectal cancers arise from adenomas, but only a small minority of adenomas progress to cancer. In the United States approximately 30 to 40 percent of the population over the age of 50 has one or more adenomas whereas the cumulative colorectal cancer risk is about 5 percent. Colonoscopic screening studies in asymptomatic people suggest that the prevalence of adenomas is about 25 to 30 percent at age 50 (12–14) and autopsy studies have found rates as high as 50 percent by age 70 (15). Adenomatous polyps are more common in men (14). An adenoma that is diagnosed at the same time as an index colorectal neoplasm is called a synchronous lesion. One that is diagnosed at least six months later is considered metachronous. Thirty to 50 percent of colons with one adenoma will contain at least one other synchronous adenoma (16). As for left sided neoplasms, advancing age is a risk factor for right-sided polyps and cancers. African ethnicity may also predispose to right sided neoplasms (17, 18). The prevalence of adenomatous polyps in an asymptomatic Iranian population has not been investigated, but would be of great significance if a colorectal screening programme was initiated.
The histological features and size of colonic adenomas are the major determinants of their malignant potential. The glandular architecture of adenomas is characterized as tubular, villous, or a mixture of the two (4): Tubular adenomas account for more than 80 percent of colonic adenomas. They are characterized by a network of branching adenomatous epithelium. To be classified as tubular, the adenoma should have a tubular component of at least 75 percent. Villous adenomas account for 5 to 15 percent of adenomas. They are characterized by glands that are long and extend straight down from the surface to the center of the polyp. To be classified as villous, the adenoma should have a villous component of at least 75 percent. Tubulovillous adenomas, having 26 to 75 percent villous component, account for 5 to 15 percent of adenomas. Polyps are further categorized as sessile if the base is attached to the colon wall, or pedunculated if a mucosal stalk is interposed between the polyp and the wall. Small polyps (<5 mm, also known as diminutive are rarely pedunculated. It is important to appreciate that while adenomas are most commonly found within raised lesions, up to 27 to 36 percent are flat (19–22).
The detection and removal of adenomatous polyps significantly decrease the morbidity and mortality associated with colorectal cancer. The location of adenomatous polyps has important implications for screening programs. A screening programme that only examine the left side of the colon may miss proximal, right sided neoplasms, if distal, left sided neoplasms are not present.
Materials and Methods
In this study, retrospectively evaluated colonoscopies were done in Taleghani Hospital of Tehran between 2004 and 2008.
Patients were referred to hospital because vary of reasons such as abdominal pain, gastrointestinal bleeding, weight loss, anemia or for colorectal cancer screening. Gastroenterologists’ of this center performed polypectomies after full colonoscopic examination by OLYMPUS CV-240 and samples were examined microscopically by two expert pathologists at same center. The polyps were described on the basis of anatomical distribution, size and histology. 437 males and 279 females had colonoscopic polypectomies. The mean age was 55.3 yr (18-89 yr).
Results
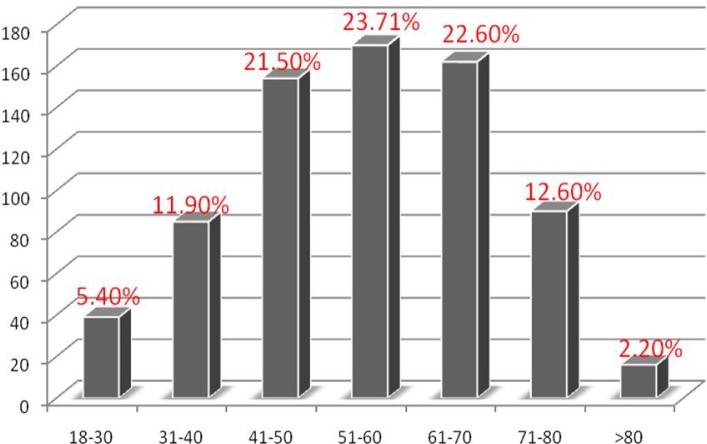
716 patients with polyps at colonoscopy were identified and considered eligible for this study. 437 (61%) were male and 279 (39%) female. The mean of age of the patients was 55.3 years (range 18-89). The majority of the patients were in the 51-60 year age group, a small minority of them were in the over 80 year age group (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Age distribution of colorectal polyps
On review of patient records, 238 (32.7%) of the cases had a positive family history for colorectal cancer. 28.3% had first degree relatives and 4.4% had second degree relatives that had been affected by colorectal cancer.
Of the 936 polyps detected in these 716 patients, 157 (16.7%) were non-neoplastic and 779 (83.3%) were neoplastic of these 727 (77.6%) of polyps were adenoma 52(5.5% of them) were carcinoma. Over half of all polyps 512(54.7%) were pedunculated. 179(25%) of the patients had synchronous lesions.
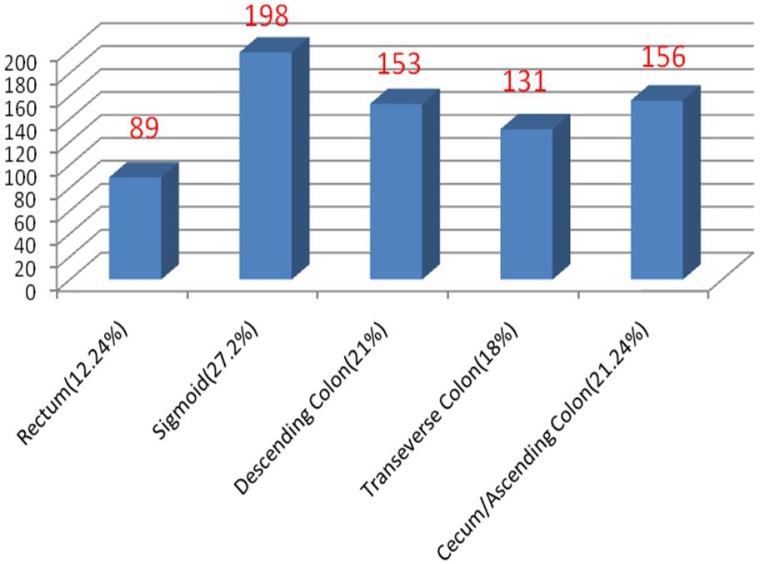
Of all 727 adenomas 440 (60.5%) were left sided and 287 (39.5%) were right sided. 89 polyps (12.2%) were in rectum, 198 (27.2%) were in sigmoid, 153 (21%) were in descending colon, 131 (18%) were in transverse colon and 156 (21.4%) were in caecum and ascending colon (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
Anatomical distribution of adenomatous polyp
Of all adenomatous polyps only 141 (19.3%) were greater than 20mm in diameters and 104 (14.3%) were 10-20 mm size and 482 (66.4%) were less than 10 mm in size.
Carcinoma was observed in 52 lesions, of these 18 (34.5%) were left sided and 34 (65.5%) were right sided.
Table 1 shows the relative frequency of Adenoma –Relation of histological type to size of colorectal polyps.
Table 1.
Relative frequency of Adenoma –Relation of histologic type to size
| Histological type | <10mm | 10-20mm | >20mm | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tubular | 415(86.1)* | 67 (64.4) | 64(45.3) | 546(75.3) |
| Tubulovillous | 63 (13.1) | 22(21.1) | 42 (29.7) | 127(17.3) |
| Villous | 4 (0.8) | 15 (14.4) | 35 (24.8) | 54(7.4) |
| total | 482(100) | 104(100) | 141(100) | 727(100) |
Figures in the parentheses represent percent.
Dysplasia in various type of adenoma was showed in Table 2. Villous type is associated higher rate of dysplasia (p=0.001).
Table 2.
Dysplasia in various type of adenoma
| Type of adenoma | Without dysplasia | Low Grade dysplasia | High Grade dysplasia |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tubular | 99(18.1)* | 425(77.8) | 22(4) |
| Tublovillous | 15(11.8) | 92(72.4) | 20(15.7) |
| Villous | 4(9) | 40(68.3) | 10(22.7) |
| Total | 118(16.2) | 557(76.6) | 52(7.2) |
Figures in the parentheses represent percent.
The mean polyp size in neoplastic polyps (15.5±0.8 mm) was significantly greater than the mean size of non-neoplastic polyps 0.8±0.4 mm, (P=0.01).
The absolute numbers and percentage of neoplastic polyps as a percentage of total polyps (non-neoplastic and neoplastic), according to anatomical location, is presented in Table 3. There were no relationship between polyp site and the likelihood that the polyp was neoplastic (p>0.05).
Table 3.
The frequency of pathological finding and site of polyp
| Neoplastic | Non-neoplastic | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cecum and ascending colon | 176(83.4)* | 35(16.6) | 211(100) |
| Transverse colon | 145(89) | 18(11) | 163 (100) |
| Descending colon | 158(81) | 37(19) | 195 (100) |
| Sigmoid | 204(83.2) | 41(16.8) | 245(100) |
| Rectum | 96(78.6) | 26(21.4) | 122 (100) |
| Total | 779 | 157 | 936 |
Figures in the parentheses represent percent.
Discussion
The aim of this study was to determine the age-matched anatomic location and histological features of colorectal polyps observed at colonoscopy over a 10-year period at our endoscopy unit. Endoscopy reports on 2,578 patients were reviewed; polyp/lesion histology and location (left, right, or both) were determined.
Of all 727 adenomas 440 (60.5%) were left sided and 287 (39.5%) were right sided. 89 polyps (12.2%) were in rectum, 198 (27.2%) were in sigmoid, 153 (21%) were in descending colon, 131 (18%) were in transverse colon and 156 (21.4%) were in caecum and ascending colon (Figure 2).
This was not a screening study, but it has shown that in our study population that a significant number of adenomas and carcinomas lie proximal to the splenic flexure. Thus, in the absence of left-sided lesions, it is expected that examination of the colon limited to the splenic flexure would miss 24 % of the polyps and the majority of carcinomas present.
The results reported in this study are comparable to other published series. An American Veteran’s Affairs study reported the prevalence and location of advanced colonic neoplasms in asymptomatic patients attending for a screening colonoscopy. 37 percent of the study patients were diagnosed with an adenoma, a villous adenoma or an invasive carcinoma. Furthermore 52 percent of patients with proximal neoplasms had no distal lesion. In addition a second American study reported that if the distal colon assessed and colonoscopy performed for individuals with distal neoplasms that a significant proportion of proximal lesions, approximately 50%, would be missed (23, 24). Our results suggest that in our study population, clinically significant proximal lesions are frequently present in the absence of distal lesions that would be detected by a screening sigmoidoscopy.
This study has shown that colonoscopy enables the diagnosis and treatment of a significant number of adenomas and carcinomas. A significant proportion of neoplasms lie proximal to the splenic flexure. In the absence of left-sided lesions, it is expected that examination of the colon limited to the splenic flexure would miss such lesions. The increasing right-sided prevalence of these lesions with age suggests that evaluation of the proximal bowel is particularly important in older patients. These results have implications if a screening programme is to be considered in our population.
(Please cite as: Eshghi MJ, Fatemi R, Hashemy A, Aldulaimi D, Khodadoostan M. A retrospective study of patients with colorectal polyps. Gastroenterology and Hepatology From Bed to Bench 2011; 4(1): 17-22).
References
- 1.Weston AP, Campbell DR. Diminutive colonic polyps: Histopathology, spatial distribution, concomitant significant lesions, and treatment complications. Am J Gastroenterol. 1995;90:24–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Provenzale D, Garrett JW, Condon SE, Sandler RS. Risk for colon adenomas in patients with rectosigmoid hyperplastic polyps. Ann Intern Med. 1990;113:760–63. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-113-10-760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Rex DK, Smith JJ, Ulbright TM, Lehman GA. Distal colonic hyperplastic polyps do not predict proximal adenomas in asymptomatic average-risk subjects. Gastroenterology. 1992;102:317–19. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)91817-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.O'Brien MJ, Winawer SJ, Zauber AG, Gottlieb LS, Sternberg SS, Diaz B, et al. The National Polyp Study: Patient and polyp characteristics associated with high-grade dysplasia in colorectal adenomas. Gastroenterology. 1990;98:371–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bensen SP, Cole BF, Mott LA, Baron JA, Sandler RS, Haile R. Colorectal hyperplastic polyps and risk of recurrence of adenomas and hyperplastic polyps. Lancet. 1999;354:1873–74. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(99)04469-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Dave S, Hui S, Kroenke K, Imperiale TF. Is the distal hyperplastic polyp a marker for proximal neoplasia? J Gen Intern Med. 2003;18:128–37. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1497.2003.20524.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Lin OS, Schembre DB, McCormick SE, Gluck M, Patterson DJ, Jiranek GC, et al. Risk of proximal colorectal neoplasia among asymptomatic patients with distal hyperplastic polyps. Am J Med. 2005;118:1113–19. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2005.03.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chow E, Lipton L, Lynch E, D'Souza R, Aragona C, Hodgkin L, et al. Hyperplastic polyposis syndrome: phenotypic presentations and the role of MBD4 and MYH. Gastroenterology. 2006;131:30–39. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2006.03.046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Renaut AJ, Douglas PR, Newstead GL. Hyperplastic polyposis of the colon and rectum. Colorectal Dis. 2002;4:213–15. doi: 10.1046/j.1463-1318.2002.00354.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ferrandez A, Samowitz W, DiSario JA, Burt RW. Phenotypic characteristics and risk of cancer development in hyperplastic polyposis: case series and literature review. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004;99:2012–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2004.30021.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Howe JR, Roth S, Ringold JC, Summers RW, Järvinen HJ, Sistonen P, et al. Mutations in the SMAD4/DPC4 gene in juvenile polyposis. Science. 1998;280:1086–88. doi: 10.1126/science.280.5366.1086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Rex DK, Lehman GA, Hawes RH, Ulbright TM, Smith JJ. Screening colonoscopy in asymptomatic average-risk persons with negative fecal occult blood tests. Gastroenterology. 1991;100:64–67. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90583-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Rex DK, Lehman GA, Ulbright TM, Smith JJ, Pound DC, Hawes RH, et al. Colonic neoplasia in asymptomatic persons with negative fecal occult blood tests: influence of age, gender, and family history. Am J Gastroenterol. 1993;88:825–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Rex DK. Colonoscopy: a review of its yield for cancers and adenomas by indication. Am J Gastroenterol. 1995;90:353–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Williams AR, Balasooriya BA, Day DW. Polyps and cancer of the large bowel: A necropsy study in Liverpool. Gut. 1982;123:835–42. doi: 10.1136/gut.23.10.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Carlsson G, Petrelli NJ, Nava H, Herrera L, Mittelman A. The value of colonoscopic surveillance after curative resection for colorectal cancer or synchronous adenomatous polyps. Arch Surg. 1987;122:1261–63. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1987.01400230047008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ozick LA, Jacob L, Donelson SS, Agarwal SK, Freeman HP. Distribution of adenomatous polyps in African-Americans. Am J Gastroenterol. 1995;90:758–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Patel K, Hoffman NE. The anatomical distribution of colorectal polyps at colonoscopy. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2001;33:222–25. doi: 10.1097/00004836-200109000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Rembacken BJ, Fujii T, Cairns A, Dixon MF, Yoshida S, Chalmers DM, et al. Flat and depressed colonic neoplasms: A prospective study of 1000 colonoscopies in the UK. Lancet. 2000;355:1211–14. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(00)02086-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Saitoh Y, Waxman I, West AB, Popnikolov NK, Gatalica Z, Watari J, et al. Prevalence and distinctive biologic features of flat colorectal adenomas in a North American population. Gastroenterology. 2001;120:1657–65. doi: 10.1053/gast.2001.24886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.O'Brien MJ, Winawer SJ, Zauber AG, Bushey MT, Sternberg SS, Gottlieb LS, et al. Flat adenomas in the National Polyp Study: is there increased risk for high-grade dysplasia initially or during surveillance? Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004;2:905–11. doi: 10.1016/s1542-3565(04)00392-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Soetikno R, Friedland S, Kaltenbach T, Chayama K, Tanaka S. Nonpolypoid (flat and depressed) colorectal neoplasms. Gastroenterology. 2006;130:566–76. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2005.12.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lieberman D, Weiss D, Bond J, Ahnen DJ, Garewal H, Chejfec G. Use of colonoscopy to screen asymptomatic adults for colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:162–68. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200007203430301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Imperiale T, Wagner D, Ching L, Larkin GN, Rogge JD, Ransohoff DF. Risk of advanced proximal neoplasm in asymptomatic adults according to the distal colorectal findings. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:169–74. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200007203430302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]