Abstract
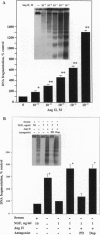
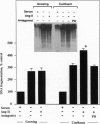
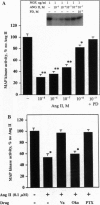
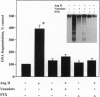
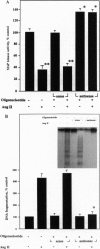
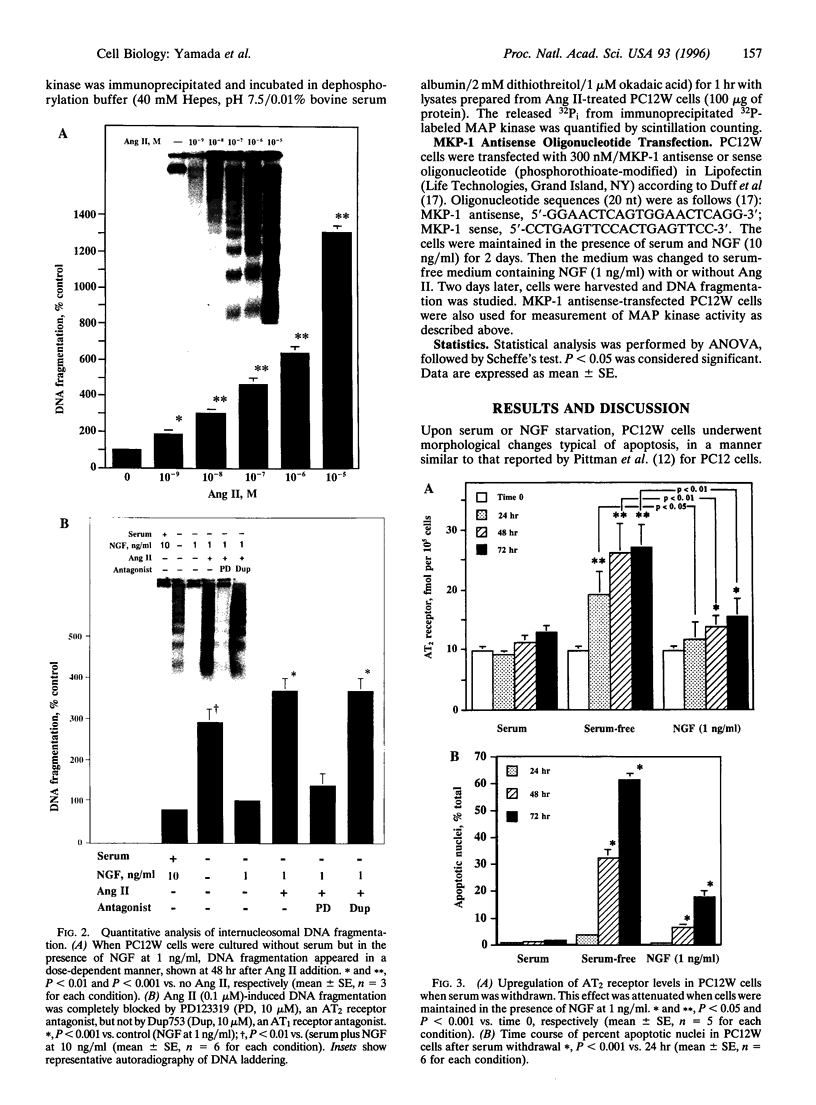
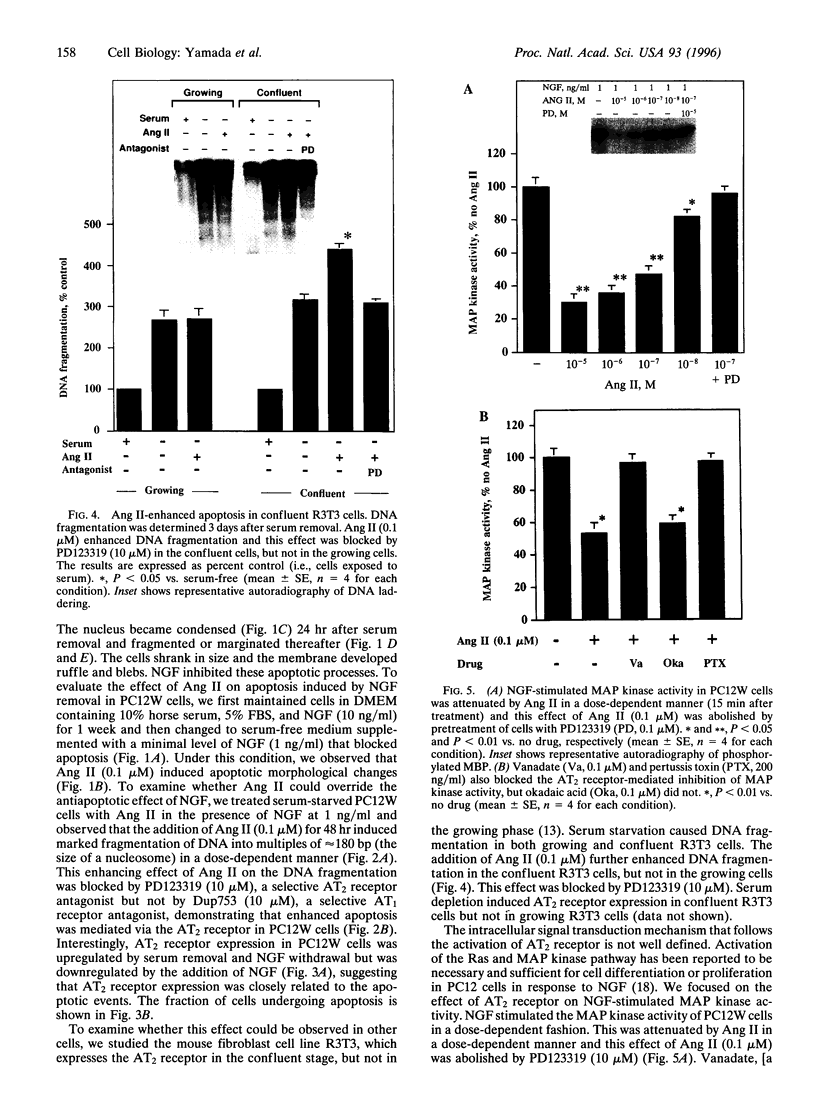
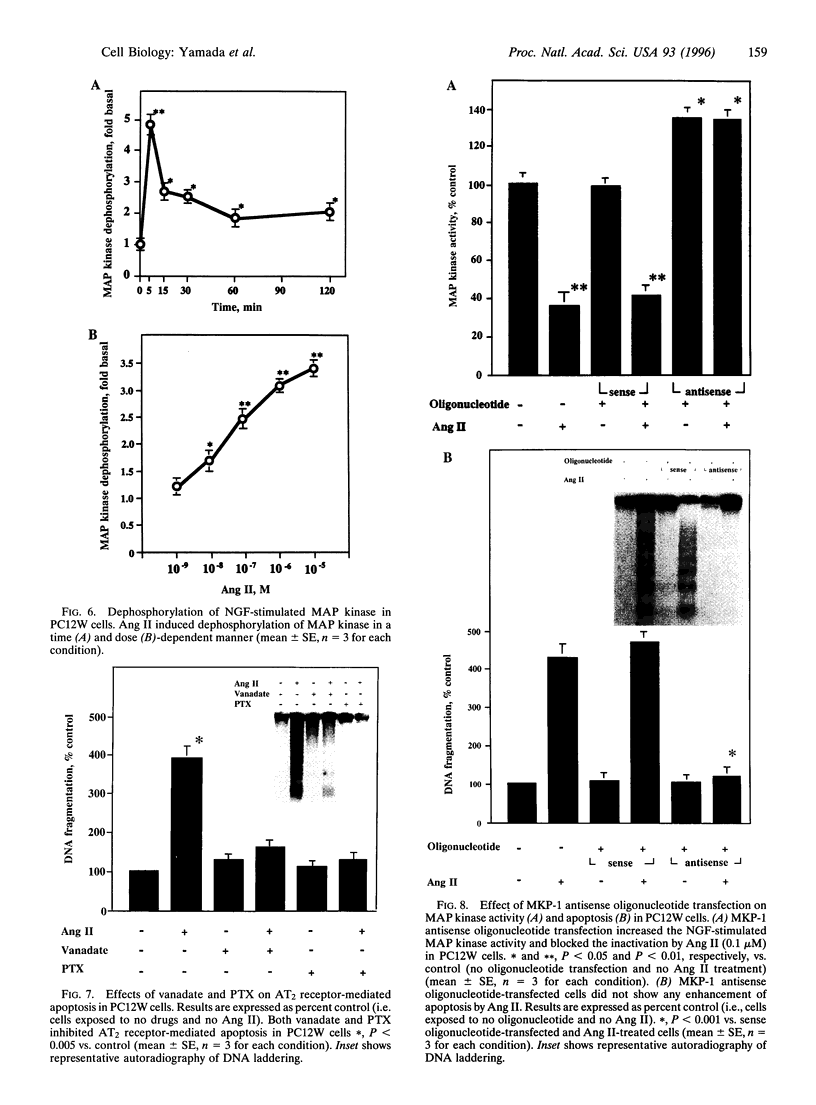
The function of the recently discovered angiotensin II type 2 (AT2) receptor remains elusive. This receptor is expressed abundantly in fetus, but scantily in adult tissues except brain, adrenal medulla, and atretic ovary. In this study, we demonstrated that this receptor mediates programmed cell death (apoptosis). We observed this effect in PC12W cells (rat pheochromocytoma cell line) and R3T3 cells (mouse fibroblast cell line), which express abundant AT2 receptor but not AT1 receptor. The cellular mechanism appears to involve the dephosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAP kinase). Vanadate, a protein-tyrosine-phosphatase inhibitor, attenuated the dephosphorylation of MAP kinases by the AT2 receptor and restored the apoptotic changes. Antisense oligonucleotide to MAP kinase phosphatase 1 inhibited the AT2 receptor-mediated MAP kinase dephosphorylation and blocked the AT2 receptor-mediated apoptosis. These results suggest that protein-tyrosine-phosphatase, including MAP kinase phosphatase 1 activated by the AT2 receptor, is involved in apoptosis. We hypothesize that this apoptotic function of the AT2 receptor may play an important role in developmental biology and pathophysiology.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Charles C. H., Sun H., Lau L. F., Tonks N. K. The growth factor-inducible immediate-early gene 3CH134 encodes a protein-tyrosine-phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5292–5296. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu A. T., Herblin W. F., McCall D. E., Ardecky R. J., Carini D. J., Duncia J. V., Pease L. J., Wong P. C., Wexler R. R., Johnson A. L. Identification of angiotensin II receptor subtypes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Nov 30;165(1):196–203. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91054-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowley S., Paterson H., Kemp P., Marshall C. J. Activation of MAP kinase kinase is necessary and sufficient for PC12 differentiation and for transformation of NIH 3T3 cells. Cell. 1994 Jun 17;77(6):841–852. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90133-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudley D. T., Summerfelt R. M. Regulated expression of angiotensin II (AT2) binding sites in R3T3 cells. Regul Pept. 1993 Mar 19;44(2):199–206. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(93)90243-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duff J. L., Monia B. P., Berk B. C. Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase is regulated by the MAP kinase phosphatase (MKP-1) in vascular smooth muscle cells. Effect of actinomycin D and antisense oligonucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 31;270(13):7161–7166. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.13.7161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grady E. F., Sechi L. A., Griffin C. A., Schambelan M., Kalinyak J. E. Expression of AT2 receptors in the developing rat fetus. J Clin Invest. 1991 Sep;88(3):921–933. doi: 10.1172/JCI115395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kambayashi Y., Bardhan S., Takahashi K., Tsuzuki S., Inui H., Hamakubo T., Inagami T. Molecular cloning of a novel angiotensin II receptor isoform involved in phosphotyrosine phosphatase inhibition. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 25;268(33):24543–24546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millan M. A., Jacobowitz D. M., Aguilera G., Catt K. J. Differential distribution of AT1 and AT2 angiotensin II receptor subtypes in the rat brain during development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11440–11444. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukoyama M., Nakajima M., Horiuchi M., Sasamura H., Pratt R. E., Dzau V. J. Expression cloning of type 2 angiotensin II receptor reveals a unique class of seven-transmembrane receptors. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 25;268(33):24539–24542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima M., Hutchinson H. G., Fujinaga M., Hayashida W., Morishita R., Zhang L., Horiuchi M., Pratt R. E., Dzau V. J. The angiotensin II type 2 (AT2) receptor antagonizes the growth effects of the AT1 receptor: gain-of-function study using gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Nov 7;92(23):10663–10667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.23.10663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman R. N., Wang S., DiBenedetto A. J., Mills J. C. A system for characterizing cellular and molecular events in programmed neuronal cell death. J Neurosci. 1993 Sep;13(9):3669–3680. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-09-03669.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pucell A. G., Hodges J. C., Sen I., Bumpus F. M., Husain A. Biochemical properties of the ovarian granulosa cell type 2-angiotensin II receptor. Endocrinology. 1991 Apr;128(4):1947–1959. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-4-1947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki K., Yamano Y., Bardhan S., Iwai N., Murray J. J., Hasegawa M., Matsuda Y., Inagami T. Cloning and expression of a complementary DNA encoding a bovine adrenal angiotensin II type-1 receptor. Nature. 1991 May 16;351(6323):230–233. doi: 10.1038/351230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya E. K., Polverino A. J., Chang E., Wigler M., Ruderman J. V. Oncogenic ras triggers the activation of 42-kDa mitogen-activated protein kinase in extracts of quiescent Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9831–9835. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speth R. C., Kim K. H. Discrimination of two angiotensin II receptor subtypes with a selective agonist analogue of angiotensin II, p-aminophenylalanine6 angiotensin II. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jun 29;169(3):997–1006. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91993-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll M., Steckelings U. M., Paul M., Bottari S. P., Metzger R., Unger T. The angiotensin AT2-receptor mediates inhibition of cell proliferation in coronary endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1995 Feb;95(2):651–657. doi: 10.1172/JCI117710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll M., Steckelings U. M., Paul M., Bottari S. P., Metzger R., Unger T. The angiotensin AT2-receptor mediates inhibition of cell proliferation in coronary endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1995 Feb;95(2):651–657. doi: 10.1172/JCI117710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilly J. L., Hsueh A. J. Microscale autoradiographic method for the qualitative and quantitative analysis of apoptotic DNA fragmentation. J Cell Physiol. 1993 Mar;154(3):519–526. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041540310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobe K., Kadowaki T., Tamemoto H., Ueki K., Hara K., Koshio O., Momomura K., Gotoh Y., Nishida E., Akanuma Y. Insulin and 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate activation of two immunologically distinct myelin basic protein/microtubule-associated protein 2 (MBP/MAP2) kinases via de novo phosphorylation of threonine and tyrosine residues. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24793–24803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viswanathan M., Saavedra J. M. Expression of angiotensin II AT2 receptors in the rat skin during experimental wound healing. Peptides. 1992 Jul-Aug;13(4):783–786. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(92)90187-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]