Abstract
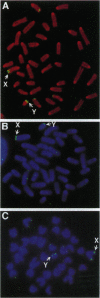
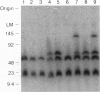
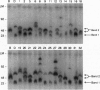
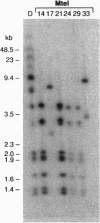
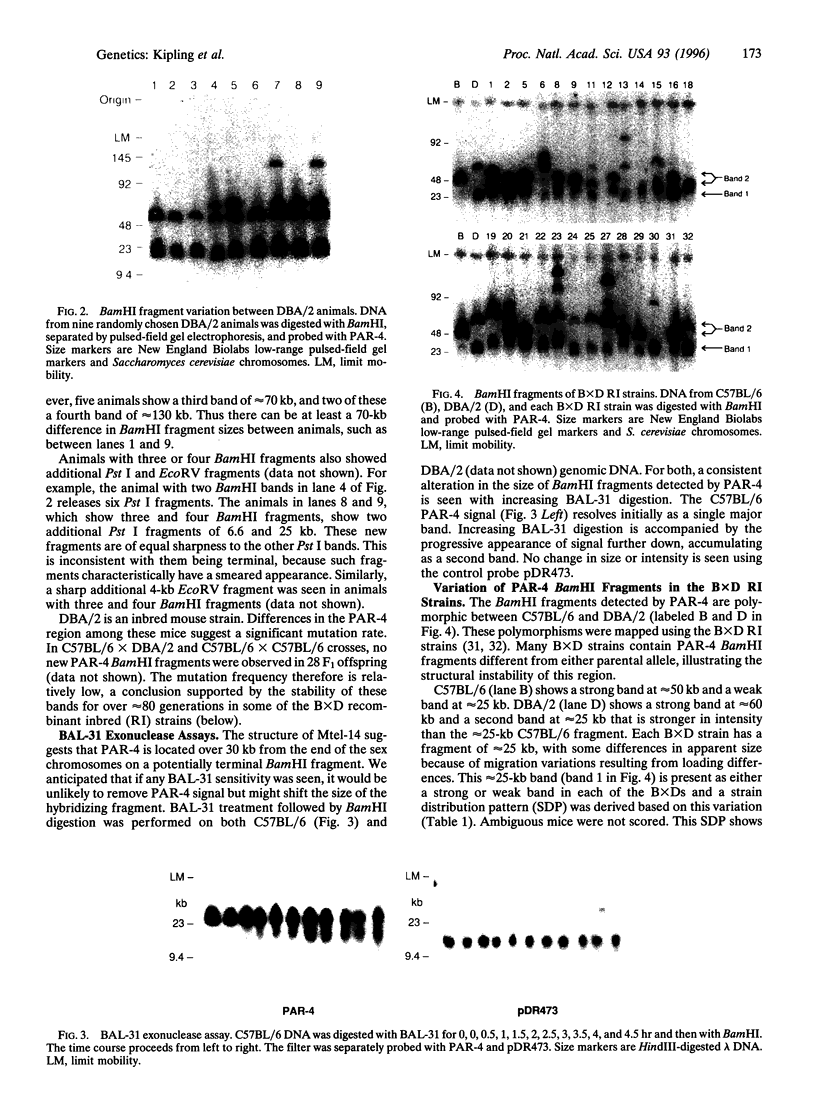
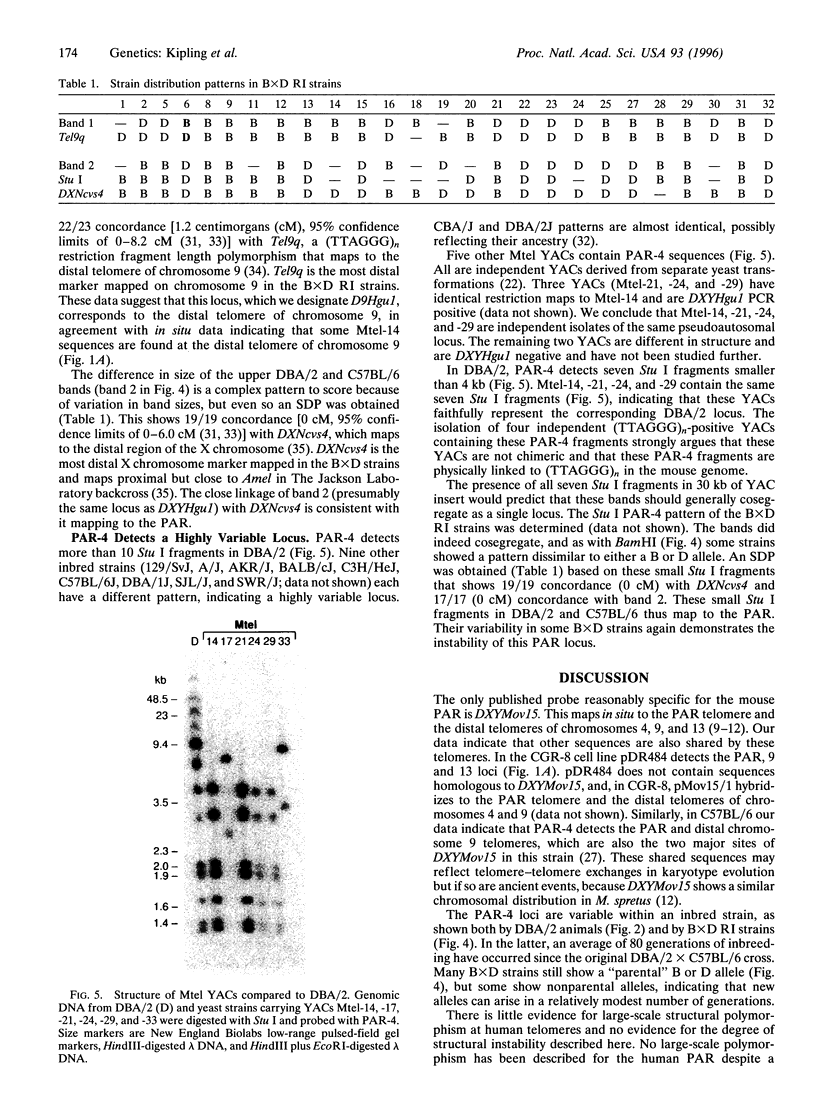
The pseudoautosomal region (PAR) is a segment of shared homology between the sex chromosomes. Here we report additional probes for this region of the mouse genome. Genetic and fluorescence in situ hybridization analyses indicate that one probe, PAR-4, hybridizes to the pseudoautosomal telomere and a minor locus at the telomere of chromosome 9 and that a PCR assay based on the PAR-4 sequence amplifies only the pseudoautosomal locus (DXYHgu1). The region detected by PAR-4 is structurally unstable; it shows polymorphism both between mouse strains and between animals of the same inbred strain, which implies an unusually high mutation rate. Variation occurs in the region adjacent to a (TTAGGG)n array. Two pseudoautosomal probes can also hybridize to the distal telomeres of chromosomes 9 and 13, and all three telomeres contain DXYMov15. The similarity between these telomeres may reflect ancestral telomere-telomere exchange.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashley T., Ried T., Ward D. C. Detection of nondisjunction and recombination in meiotic and postmeiotic cells from XYSxr [XY,Tp(Y)1Ct] mice using multicolor fluorescence in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 18;91(2):524–528. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.2.524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattanach B. M., Pollard C. E., Hawker S. G. Sex-reversed mice: XX and XO males. Cytogenetics. 1971;10(5):318–337. doi: 10.1159/000130151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Disteche C. M., Brannan C. I., Larsen A., Adler D. A., Schorderet D. F., Gearing D., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A., Park L. S. The human pseudoautosomal GM-CSF receptor alpha subunit gene is autosomal in mouse. Nat Genet. 1992 Aug;1(5):333–336. doi: 10.1038/ng0892-333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eicher E. M., Hale D. W., Hunt P. A., Lee B. K., Tucker P. K., King T. R., Eppig J. T., Washburn L. L. The mouse Y* chromosome involves a complex rearrangement, including interstitial positioning of the pseudoautosomal region. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1991;57(4):221–230. doi: 10.1159/000133152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eicher E. M., Lee B. K., Washburn L. L., Hale D. W., King T. R. Telomere-related markers for the pseudoautosomal region of the mouse genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2160–2164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eicher E. M., Shown E. P. Molecular markers that define the distal ends of mouse autosomes 4, 13, and 19 and the sex chromosomes. Mamm Genome. 1993;4(4):226–229. doi: 10.1007/BF00417568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott R. W., Yen C. H. DNA variants with telomere probe enable genetic mapping of ends of mouse chromosomes. Mamm Genome. 1991;1(2):118–122. doi: 10.1007/BF02443788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantes J. A., Bickmore W. A., Fletcher J. M., Ballesta F., Hanson I. M., van Heyningen V. Submicroscopic deletions at the WAGR locus, revealed by nonradioactive in situ hybridization. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Dec;51(6):1286–1294. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freije D., Helms C., Watson M. S., Donis-Keller H. Identification of a second pseudoautosomal region near the Xq and Yq telomeres. Science. 1992 Dec 11;258(5089):1784–1787. doi: 10.1126/science.1465614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gish W., States D. J. Identification of protein coding regions by database similarity search. Nat Genet. 1993 Mar;3(3):266–272. doi: 10.1038/ng0393-266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale D. W. Is X-Y recombination necessary for spermatocyte survival during mammalian spermatogenesis? Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1994;65(4):278–282. doi: 10.1159/000133648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale D. W., Washburn L. L., Eicher E. M. Meiotic abnormalities in hybrid mice of the C57BL/6J x Mus spretus cross suggest a cytogenetic basis for Haldane's rule of hybrid sterility. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1993;63(4):221–234. doi: 10.1159/000133539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbers K., Francke U., Soriano P., Jaenisch R., Müller U. Structure and chromosomal mapping of a highly polymorphic repetitive DNA sequence from the pseudoautosomal region of the mouse sex chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1990;53(2-3):129–133. doi: 10.1159/000132912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbers K., Soriano P., Müller U., Jaenisch R. High frequency of unequal recombination in pseudoautosomal region shown by proviral insertion in transgenic mouse. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):682–685. doi: 10.1038/324682a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashizaki Y., Hirotsune S., Okazaki Y., Shibata H., Akasako A., Muramatsu M., Kawai J., Hirasawa T., Watanabe S., Shiroishi T. A genetic linkage map of the mouse using restriction landmark genomic scanning (RLGS). Genetics. 1994 Dec;138(4):1207–1238. doi: 10.1093/genetics/138.4.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman G. E., Boyd Y., Chapman V., Chatterjee A., Brown S. D. Mouse X chromosome. Mamm Genome. 1994;5(Spec No):S276–S288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keitges E. A., Schorderet D. F., Gartler S. M. Linkage of the steroid sulfatase gene to the sex-reversed mutation in the mouse. Genetics. 1987 Jul;116(3):465–468. doi: 10.1093/genetics/116.3.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keitges E., Rivest M., Siniscalco M., Gartler S. M. X-linkage of steroid sulphatase in the mouse is evidence for a functional Y-linked allele. Nature. 1985 May 16;315(6016):226–227. doi: 10.1038/315226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kipling D., Cooke H. J. Hypervariable ultra-long telomeres in mice. Nature. 1990 Sep 27;347(6291):400–402. doi: 10.1038/347400a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kipling D., Wilson H. E., Thomson E. J., Cooke H. J. YAC cloning Mus musculus telomeric DNA: physical, genetic, in situ and STS markers for the distal telomere of chromosome 10. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Jun;4(6):1007–1014. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.6.1007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvaløy K., Galvagni F., Brown W. R. The sequence organization of the long arm pseudoautosomal region of the human sex chromosomes. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 May;3(5):771–778. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.5.771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda Y., Chapman V. M. Application of fluorescence in situ hybridization in genome analysis of the mouse. Electrophoresis. 1995 Feb;16(2):261–272. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150160142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda Y., Hirobe T., Chapman V. M. Genetic basis of X-Y chromosome dissociation and male sterility in interspecific hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4850–4854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyajima I., Levitt L., Hara T., Bedell M. A., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A., Miyajima A. The murine interleukin-3 receptor alpha subunit gene: chromosomal localization, genomic structure, and promoter function. Blood. 1995 Mar 1;85(5):1246–1253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagamine C. M., Michot J. L., Roberts C., Guénet J. L., Bishop C. E. Linkage of the murine steroid sulfatase locus, Sts, to sex reversed, Sxr: a genetic and molecular analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9227–9238. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappold G. A. The pseudoautosomal regions of the human sex chromosomes. Hum Genet. 1993 Oct;92(4):315–324. doi: 10.1007/BF01247327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roubertoux P. L., Carlier M., Degrelle H., Haas-Dupertuis M. C., Phillips J., Moutier R. Co-segregation of intermale aggression with the pseudoautosomal region of the Y chromosome in mice. Genetics. 1994 Jan;136(1):225–230. doi: 10.1093/genetics/136.1.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe L. B., Nadeau J. H., Turner R., Frankel W. N., Letts V. A., Eppig J. T., Ko M. S., Thurston S. J., Birkenmeier E. H. Maps from two interspecific backcross DNA panels available as a community genetic mapping resource. Mamm Genome. 1994 May;5(5):253–274. doi: 10.1007/BF00389540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton L., Arnaud D., Goodfellow P. N., Simmler M. C., Avner P. Characterization of the central region containing the X-inactivation center and terminal region of the mouse X chromosome using irradiation and fusion gene transfer hybrids. Mamm Genome. 1992;2(1):21–31. doi: 10.1007/BF00570437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver J. Confidence limits for estimates of gene linkage based on analysis of recombinant inbred strains. J Hered. 1985 Nov-Dec;76(6):436–440. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a110140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi Y., Mitani K., Kuwabara K., Hayashi T., Niwa M., Miyashita N., Moriwaki K., Kominami R. Methylation imprinting was observed of mouse mo-2 macrosatellite on the pseudoautosomal region but not on chromosome 9. Chromosoma. 1994 Dec;103(7):450–458. doi: 10.1007/BF00337383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie A. O., Higgs D. R., Rack K. A., Buckle V. J., Spurr N. K., Fischel-Ghodsian N., Ceccherini I., Brown W. R., Harris P. C. Stable length polymorphism of up to 260 kb at the tip of the short arm of human chromosome 16. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):595–606. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90243-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]