Significance
The selective loss of dopaminergic neurons is characteristic of Parkinson disease (PD). Protein folding stress is a salient feature of PD. This study uncovers a previously undefined function of a major unfolded protein response (UPR) transcription factor (XBP1) in supporting the survival of nigral dopaminergic neurons at basal levels and under pathological conditions. Our results reveal an important role for a canonical UPR pathway in the maintenance of dopaminergic neuron proteostasis, which also could be relevant to understand the selective neuronal vulnerability observed in Parkinson disease.
Abstract
Parkinson disease (PD) is characterized by the selective loss of dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc). Although growing evidence indicates that endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress is a hallmark of PD, its exact contribution to the disease process is not well understood. Here we report that developmental ablation of X-Box binding protein 1 (XBP1) in the nervous system, a key regulator of the unfolded protein response (UPR), protects dopaminergic neurons against a PD-inducing neurotoxin. This survival effect was associated with a preconditioning condition that resulted from induction of an adaptive ER stress response in dopaminergic neurons of the SNpc, but not in other brain regions. In contrast, silencing XBP1 in adult animals triggered chronic ER stress and dopaminergic neuron degeneration. Supporting this finding, gene therapy to deliver an active form of XBP1 provided neuroprotection and reduced striatal denervation in animals injected with 6-hydroxydopamine. Our results reveal a physiological role of the UPR in the maintenance of protein homeostasis in dopaminergic neurons that may help explain the differential neuronal vulnerability observed in PD.
Parkinson disease (PD) is part of a group of diseases classified as protein-misfolding disorders (PMDs), which also includes Alzheimer’s disease, Huntington disease, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). PMDs share common pathological features, characterized by the accumulation of abnormal protein inclusions and oligomers of an underlying protein (1). PD is the second most common age-related neurodegenerative disease, affecting 1% of the population over 60 y of age and associated with the appearance of several motor symptoms, including rigidity, resting tremor, bradykinesia, and postural instability (2). The pathological hallmarks underlying the clinical phenotypes are triggered by the loss of dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc) and the presence of intracellular inclusions known as Lewy bodies that are formed by fibrillar and ubiquitinated aggregates of αSynuclein (3). Several perturbations in cellular homeostasis are observed in PD, including alterations in mitophagy, calcium regulation, energy metabolism, redox balance, and proteasome function, among other pathological events (4–6). Accumulating evidence also supports a disruption in the function of the secretory pathway in genetic and pharmacologic models of PD, leading to pathological levels of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress (7).
ER stress engages an adaptive signaling cascade known as the unfolded protein response (UPR) (8). Activation of the UPR decreases the load of misfolded proteins through different complementary mechanisms, including the transcriptional modulation of various genes involved in protein folding, quality control, and protein degradation (9). When these mechanisms of stress adaptation fail to restore protein homeostasis, the UPR triggers apoptosis (10, 11). The most conserved UPR signaling pathway is initiated by the activation of inositol-requiring enzyme 1α (IRE1α), a serine-threonine kinase and endoribonuclease located at the ER membrane. On activation, IRE1α excises a 26-nt intron of the mRNA encoding the transcription factor X-Box binding protein 1 (XBP1). This unconventional splicing event changes the coding reading frame of the mRNA, leading to the expression of a more stable and active transcription factor, termed XBP1s (12–14). Genetic manipulations of xbp1 in different organs have revealed an essential function of this transcription factor in the maintenance of secretory cell function, including plasma B cells, pancreatic beta cells, and salivary glands (15). In addition, XBP1 has important functions beyond ER stress in liver lipogenesis, inflammation, and energy metabolism (16, 17).
Although most common neurodegenerative diseases are associated with the occurrence of pathological ER stress levels (18, 19), the possible impact of the UPR in the physiology of the nervous system remains poorly explored. Signs of ER stress are observed in human postmortem tissue derived from PD patients (20–22), and recent reports indicate that ER stress is observed in early-symptomatic animals overexpressing αSynuclein which is associated with the presence of αSynuclein oligomers at the ER lumen (23, 24). Remarkably, neuronal cultures generated from PD-derived induced pluripotent stem cells indicated the occurrence of chronic ER stress in the model (25). In addition, ER stress represents the main transcriptional signature triggered in neurotoxin-based models of PD (26, 27), which has been confirmed in several animal models (28–31). Other studies in cell culture have linked ER stress with the expression of most PD-related genes, including αSynuclein/PARK1, Parkin/PARK2, DJ-1/PARK7, LRRK2/PARK8, ATP13A2/PARK9, and PaelR (7).
In this study, we explored the consequences of manipulating XBP1 expression in the survival of dopaminergic neurons under basal and pathological conditions. Unexpectedly, XBP1-deficient SNpc neurons selectively exhibited mild ER stress, suggesting a functional requirement for this signaling branch to the maintenance of protein homeostasis in nigral dopaminergic neurons. Basal stress induction in XBP1-deficient animals was correlated with significant protection against a PD-inducing neurotoxin. Consistent with these observations, knockdown of XBP1 in adult SNpc triggered spontaneous signs of neurodegeneration associated with a chronic ER stress response, whereas local expression of XBP1s protected against experimental PD. Our results uncover a critical role for XBP1 in maintaining protein homeostasis in dopaminergic neurons and suggest that targeting the UPR in PD has therapeutic potential.
Results
XBP1-Deficient Dopaminergic Neurons Are Resistant to 6-Hydroxydopamine.
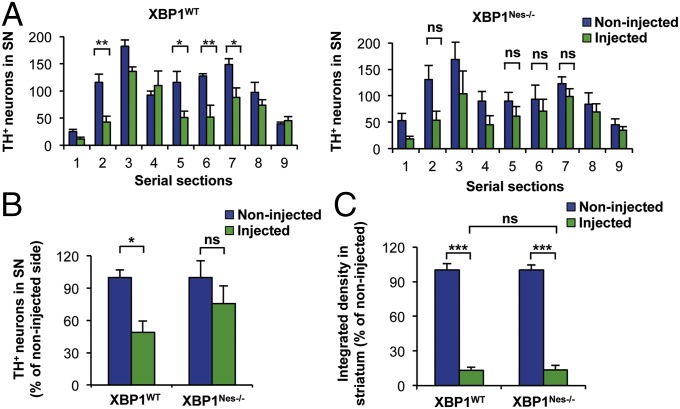
We previously generated a conditional KO mouse model for xbp1 in the nervous system using the Nestin-Cre system (XBP1Nes−/−) (32). To determine the contribution of XBP1 to dopaminergic neuron survival, we performed unilateral stereotaxic injections of 8 μg of 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) into the striatum and analyzed the neurodegenerative process at the SNpc under experimental conditions that induce dopaminergic neuron loss (Fig. S1 A and B). Decreased viability of a subpopulation of dopaminergic neurons of the SNpc was observed at 7 d after administration of 6-OHDA followed by tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) staining of the entire brain region (Fig. 1A and Fig. S1C). Despite the expectation that XBP1 deficiency would enhance the susceptibility to PD-inducing neurotoxins, as observed in ATF6-deficient mice (30), we found a subregion of the SNpc (serial sections 2 and 5–7) that was resistant to 6-OHDA in XBP1Nes−/− mice (Fig. 1B and Fig. S1D). In addition, we observed no alterations in the overall number of dopaminergic neurons in XBP1Nes−/− SNpc by stereologic analysis at basal levels compared with littermate control animals (Fig. S1E). As a control, we determined the efficiency of the neurotoxin-induced lesion by measuring the extent of striatal denervation triggered by 6-OHDA (Fig. 1C and Fig. S1C).
Fig. 1.
Dopaminergic neurons of XBP1-deficient mice are resistant to 6-OHDA–induced neurotoxicity. (A) XBP1WT and XBP1Nes−/− mice were injected with 8 μg of 6-OHDA in the right striatum, and after 7 d, dopaminergic neurons (TH+) were quantified by anti-TH immunohistochemistry. Histograms show the number of TH-positive neurons of injected and noninjected sides in 25-μm midbrain serial sections separated by 150 μm and covering the entire SN. The numbers of serial sections indicate the orientation from anterior to posterior (Fig. S1C). (B) Total content of TH-positive somas was quantified in midbrain sections 2, 5, 6, and 7 and presented as a percentage of the noninjected (control) side for the indicated genotypes. (C) 6-OHDA–induced striatal denervation in XBP1WT and XBP1Nes−/− mice. The integrated density of pixel intensity was calculated from images of anti-TH immunohistochemistry covering the entire striatum and is presented as a percentage of the noninjected (control) sides for both genotypes. For all quantifications, data are mean ± SEM (n = 4 per group). Statistical analyses were performed by two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni posttest. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. ns, not significant.
XBP1 Deficiency Triggers Spontaneous ER Stress in the SNpc.
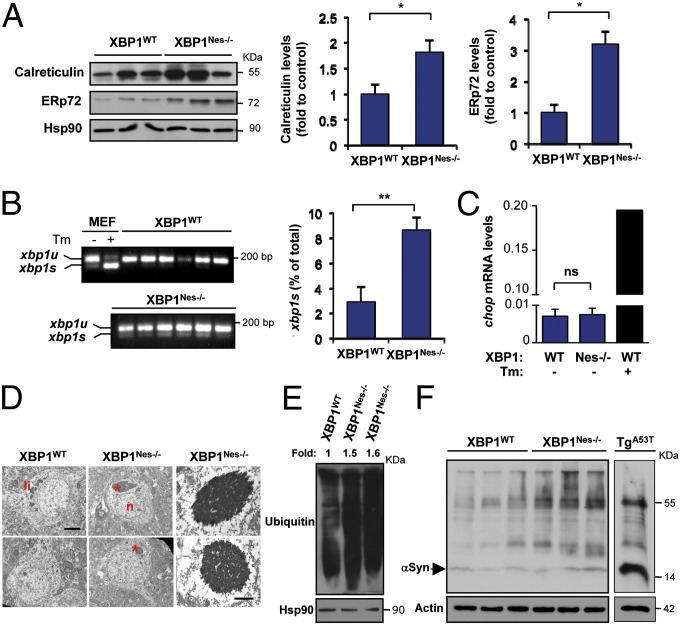
XBP1 is crucial to the function of professional secretory cells, and its deficiency triggers drastic phenotypes associated with a basal ER stress response or decreased cell survival (15), a phenomenon that has not been reported previously in the nervous system. To study the possible effect of XBP1 on dopaminergic neuron proteostasis, we monitored the levels of basal ER stress in ventral midbrains dissected from the brains of adult XBP1Nes−/− and littermate control animals. Unexpectedly, we observed a significant up-regulation of the UPR-responsive chaperones calreticulin and the disulfide isomerase ERp72 in XBP1Nes−/−-derived tissue, as determined by Western blot analysis (Fig. 2A). Histological analysis of midbrain tissue sections revealed restricted expression of ERp72 to SNpc dopaminergic neurons (Fig. S2A). Similar results were obtained when the levels of protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) and immunoglobulin heavy chain-binding protein (BiP) were monitored (Fig. S2B).
Fig. 2.
ER stress in XBP1-deficient SNpc. (A) (Left) Levels of the ER stress-responsive proteins calreticulin and ERp72 were determined by Western blot analysis in midbrain tissue dissected from XBP1WT and XBP1Nes−/− mice. Hsp90 was measured as loading control. (Right) Relative levels of calreticulin and ERp72 were estimated after normalization with Hsp90 (n = 5 for calreticulin; n = 3 for ERp72). (B) (Left) XBP1 mRNA splicing levels were determined by RT-PCR in mRNA extracted from dissected midbrain from XBP1WT and XBP1Nes−/− mice. Mouse embryonic fibroblast (MEF) cells treated for 24 h with 10 μg/mL of Tm served as a positive control. (Right) Quantification of the xbp1s splicing. Values represent the percentage of xbp1s relative to total xbp1 mRNA expression (xbp1s + xbp1u) (n = 6 per group). (C) Chop mRNA levels were determined in dissected SNpc of XBP1WT and XBP1Nes−/− mice using real-time PCR (n = 3 per group). As a positive control, chop mRNA levels were analyzed in animals injected with 10 μg of Tm directly into the SNpc. Statistical analyses were performed using the Student t test. Data are reported as mean and SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ns, not significant. (D) EM images of dopaminergic neurons in the SNpc of XBP1WT and XBP1Nes−/− mice. (Left) Representative lower-magnification images showing the nucleus (n), lipofuscin (li), and protein aggregates (*). (Scale bar: 5 μm.) (Right) Higher-magnification images of protein aggregates observed in XBP1Nes−/− mice. (Scale bar: 1.2 μm.) (E) Total ubiquitinated proteins were detected by Western blot analysis in dissected SNpc of XBP1WT and XBP1Nes−/− mice. Hsp90 was monitored as a loading control. Relative levels of total ubiquitinated proteins were estimated after normalization with Hsp90 and expressed as fold of change to the WT control, as indicated at the top of the gel. (F) αSynuclein (αSyn) protein levels were evaluated in midbrain dissections containing the SN from XBP1WT and XBP1Nes−/− mice by Western blot analysis. Actin was monitored as a loading control. Each lane represents an independent animal. αSyn monomers are indicated by an arrowhead. As a positive control for aggregation, brain extract from αSynA53T transgenic mice was run in the same gel.
To further explore the consequences of XBP1 ablation in dopaminergic neurons, we monitored the activation of UPR proximal signaling events by measuring the splicing of the truncated mRNA of the deleted xbp1 in XBP1Nes−/− mice. This method is a useful tool for directly measuring IRE1α activity in vivo (33, 34). A threefold increase in XBP1-spliced mRNA was detected in XBP1Nes−/− mice using a PCR-based assay, evaluated as the ratio of XBP1-spliced mRNA to total mRNA levels (Fig. 2B). Although signs of ER stress were detected in dopaminergic neurons of the SNpc of XBP1-deficient animals, the total number of neurons in this brain region was similar to that seen in littermate control animals (Fig. S1E), suggesting the occurrence of sublethal levels of ER stress at basal conditions. ER stress-mediated apoptosis is induced in part by the transcriptional up-regulation of CHOP/GADD153 and downstream proapoptotic BCL-2 family members (11). Real-time PCR analysis of chop mRNA indicated no difference in expression levels in ventral midbrain tissue from XBP1Nes−/− mice and control mice (Fig. 2C). As a positive control, mice were injected by stereotaxy with 10 μg of the ER stress agent tunicamycin (Tm) directly into the SNpc, which triggered a robust up-regulation of chop mRNA (Fig. 2C).
Remarkably, analysis of ER stress markers in the brain cortex revealed no changes in the expression levels of several ER chaperones and foldases (Fig. S2 C and D), suggesting that XBP1 deficiency selectively affects the homeostasis of SNpc neurons. Similarly, no signs of spontaneous ER stress were reported in previous studies of spinal cord, hippocampal, or striatal tissue from these animals (32, 35–37). ER stress triggers macroautophagy in several experimental systems and serves to degrade abnormally folded proteins and damaged organelles (38). Consistent with the occurrence of ER stress in dopaminergic neurons of XBP1Nes−/− mice, we observed an increased number of LC3-positive vacuoles in these animals (Fig. S3A). Similarly, the levels of active and lipidated form of LC3, known as LC3-II, and the autophagy regulator Beclin 1, were augmented in protein extracts from ventral midbrain of XBP1-deficient animals (Fig. S3 B and C).
To further assess the consequences of disrupted ER proteostasis in XBP1-deficient dopaminergic neurons, we examined the SNpc of 6-mo-old XBP1-deficient mice by electron microscopy (EM). Surprisingly, visualization of dopaminergic neurons revealed a striking phenotype in which most neurons contain large electrodense inclusions with a perinuclear distribution (Fig. 2D). We also analyzed by EM the overall integrity and content of the ER and mitochondria and observed no clear changes in the abundance of these organelles or their overall morphology (Fig. S3D). Of note, these large electrodense aggregates were not observed in neurons from striatum or spinal cord of XBP1-deficient mice (Fig. S3E). Assessment of the general pattern of protein ubiquitination by Western blot analysis also revealed enhanced accumulation of polyubiquitinated proteins in protein extracts from XBP1Nes−/− ventral midbrain tissue (Fig. 2E). In addition, increased ubiquitin staining was observed in XBP1-deficient SNpc compared with SNpc of littermate controls (Fig. S3F). Finally, we also explored the possible effects of XBP1 deficiency on αSynuclein levels and aggregation. We observed a slight increment in αSynuclein aggregation in the SNpc of XBP1Nes−/− mice on Western blot analysis (Fig. 2F and Fig. S3G). The electrophoretic pattern was similar to that seen in brain samples from αSynucleinA53T transgenic mice (39) (Fig. 2F). Taken together, these results indicate that xbp1 contributes to the maintenance of proteostasis in dopaminergic neurons, where its developmental ablation triggers ER dysfunction and accumulation of abnormal protein aggregates.
Down-Regulation of XBP1 Locally in the SNpc Triggers Spontaneous Neurodegeneration.
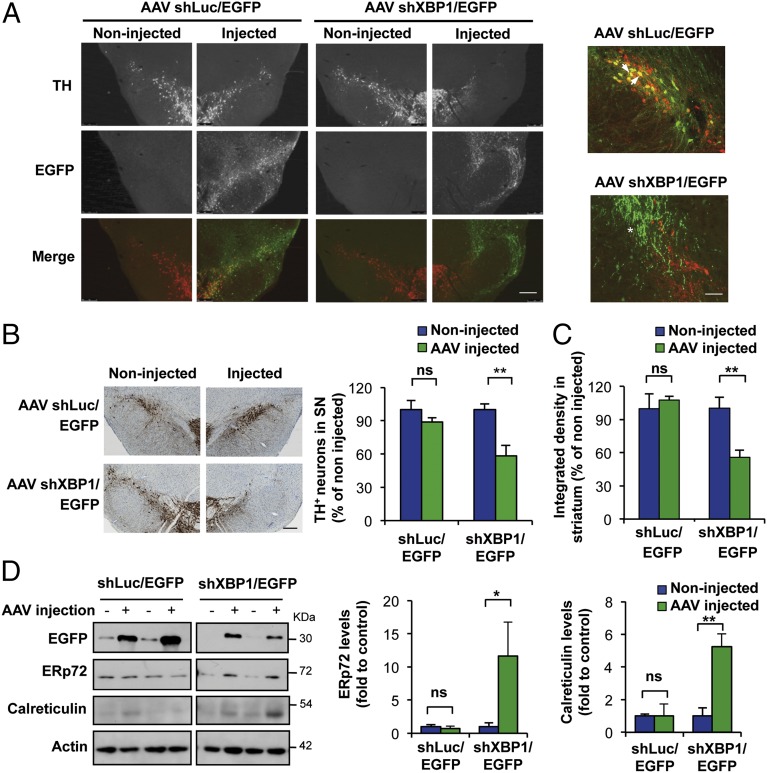
Our results suggest that deletion of XBP1 in mice triggers mild levels of stress in the SNpc, which may represent an adaptive reaction to sustain dopaminergic neuron function and viability. To test the relevance of XBP1 function in dopaminergic neurons of adult animals, we developed serotype 2 adeno-associated viral vectors (AAVs) to deliver a previously characterized shRNA against XBP1 mRNA (35, 37). This vector also expresses EGFP to aid in the identification of transduced cells. We performed stereotaxic injections of AAV shRNA/EGFP into the SNpc of adult WT mice to target XBP1 mRNA (shXBP1) or to deliver a control shRNA against the luciferase mRNA (shLuc). We corroborated the knockdown of xbp1 by performing laser-capture microdissection of EGFP-positive tissue, followed by mRNA extraction and real-time PCR analysis (Fig. S4). We then determined the effects of XBP1 knockdown on dopaminergic neuron survival by performing unilateral stereotaxic AAV injections. In contrast to the results seen in XBP1-deficient mice, knockdown of XBP1 in adult SNpc led to a dramatic decrease in neuronal viability, associated with a significant reduction of TH-positive neurons (Fig. 3A). Remarkably, the morphology of the remaining cells expressing shXBP1 was drastically altered, with evident signs of neurodegeneration and atrophy of dendrites and axons (Fig. 3A, Right). The neuronal loss induced by targeting XBP1 was also confirmed by neuronal nuclei (NeuN) staining (Fig. S5A). Quantification of TH-positive cells using immunohistochemistry revealed a significant decrease in neuronal viability after the injection of AAV shXBP1/EGFP, but not after injection of the control vector (Fig. 3B). Consistent with a significant impact on dopaminergic neuron survival, knockdown of XBP1 triggered nearly 45% striatal denervation compared with control animals as assessed by TH staining (Fig. 3C). Taken together, these results suggest that XBP1 expression has a significant role in maintaining dopaminergic neuron function in adult mice.
Fig. 3.
XBP1 down-regulation in dopaminergic neurons of adult SNpc induces spontaneous neurodegeneration and chronic ER stress. (A) In WT mice, the SNpc was injected with AAVs carrying a shRNA construct designed against either XBP1 (shXBP1/EGFP) or luciferase (shLuc/EGFP) mRNA by brain stereotaxis. (Left) At 1 mo after the injections, dopaminergic neurons were visualized by TH immunofluorescence (red) in midbrain tissue sections. (Scale bar: 200 μm.) (Right) Higher-magnification images indicating transduced (EGFP-positive) dopaminergic neurons (TH-positive) with AAV shLuc/EGFP-injected animals (arrowhead: example of a double-positive cell) or AAV shXBP1/EGFP (asterisk: degenerating neurites). (Scale bar: 50 μm.) (B) Immunohistochemical analysis was performed to quantify the extent of neuronal loss after expression of the shXBP1. (Left) Representative images of anti-TH immunohistochemistry followed by Nissl staining. (Scale bar: 200 μm.) (Right) TH-positive neurons were counted and normalized as the percentage of neurons detected on the injected side relative to the noninjected (control) side (n = 3, AAV shXBP1/EGFP; n = 4, AAV shLuc/EGFP). (C) In the same animals as in B, the integrated density of the pixel intensity of images of anti-TH immunohistochemistry covering the entire striatum was calculated to quantify denervation levels (n = 3, AAV shXBP1/EGFP; n = 4, AAV shLuc/EGFP). (D) WT mice were injected with AAVs carrying either shXBP1/EGFP or shLuc/EGFP into the SNpc by brain stereotaxis. (Left) After 2 wk, midbrains were dissected and analyzed by Western blot to monitor ERp72 and calreticulin levels. EGFP levels were also assessed to corroborate the transduction of the SNpc after AAV injections. (Right) Quantification of ERp72 and calreticulin levels relative to TH levels (n = 3 per group). Data are presented as mean and SEM. Statistical analyses were performed by two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni posttest: *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. ns, not significant.
Knockdown of XBP1 in Adult SNpc Triggers Chronic ER Stress.
To investigate the molecular mechanisms involved in the loss of dopaminergic neurons triggered by XBP1 knockdown, we analyzed dissected ventral midbrain tissue from AAV shRNA/EGFP-injected mice. EGFP expression on the injected side was monitored to corroborate the targeting of AAVs to the dissected area (Fig. 3D). Nevertheless, we also observed low EGFP expression on the control side in some mice, suggesting a slight diffusion of viral particles to the noninjected side. At 2 wk postinjection, a reduction in total TH expression was observed (Fig. S5B), associated with strong up-regulation of the stress markers ERp72 and calreticulin in mice transduced with AAV shXBP1, but not in those transduced with control shLuc vector (Fig. 3D). Consistent with these results, XBP1 knockdown in the SNpc caused a significant increase in the mRNA levels of chop (Figs. S4 and S5C), suggesting the occurrence of proapoptotic ER stress when XBP1 is targeted in adult animals. Taken together, these results indicate a fundamental role for XBP1 in the maintenance of dopaminergic neuron survival in the SNpc, where manipulation of its expression levels in adult mice has deleterious consequences for ER proteostasis.
Neuroprotective Effects of Local Delivery of XBP1s into the SNpc of Adult Mice.
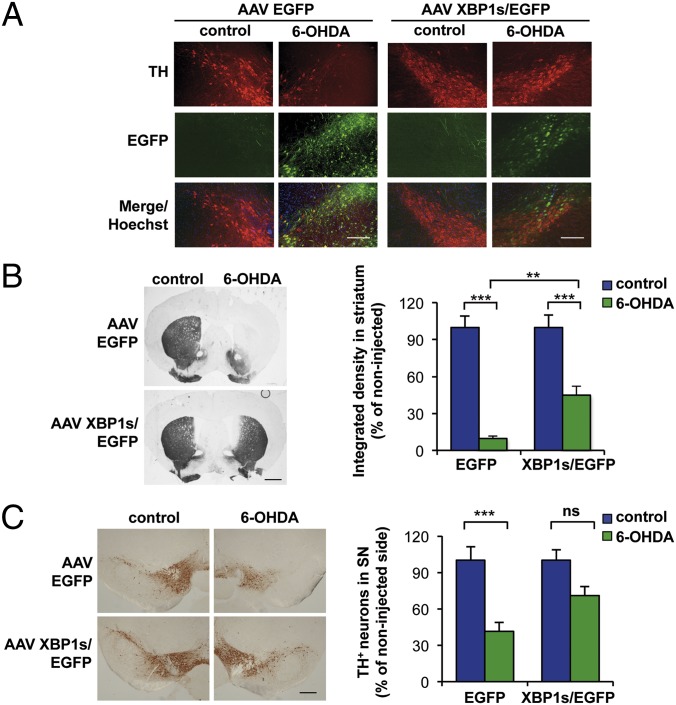
Based on the foregoing results, we next tested the possible beneficial consequences of artificially enforcing XBP1s expression in a neurotoxin-based model of PD. We used a recently described AAV construct to overexpress XBP1s under the control of the CMV promoter (AAV XBP1s/EGFP) (36, 40). Unilateral injections of AAV XBP1s/EGFP into the SNpc led to high expression of xbp1s mRNA in this brain region but not in the striatum, as monitored by real-time PCR (Fig. S6A). In addition, the ectopic expression of XBP1s triggered a UPR transcriptional response in vivo, as demonstrated by the induction of several UPR target genes (Fig. S6 B and C). To determine the possible prosurvival activity of XBP1s, we injected AAV XBP1s/EGFP or control AAV EGFP into the SNpc by brain stereotaxy. After 1 mo, we challenged the mice by injecting 6-OHDA into the striatum to follow the neurodegeneration process of dopaminergic neurons (Fig. 4A). Remarkably, XBP1s overexpression resulted in significantly reduced striatal denervation (Fig. 4B). Consistent with these results, enhanced survival of dopaminergic neurons was observed after exposure to 6-OHDA in XBP1s-overexpressing mice (Fig. 4C). An average increase in neuronal viability of ∼42% was observed upon expression of XBP1s (Fig. 4C, Right). Taken together, the foregoing results indicate that modulation of XBP1 levels has a neuroprotective effect in dopaminergic neurons.
Fig. 4.
Local delivery of XBP1s into the SNpc protects dopaminergic neurons against 6-OHDA–induced neurotoxicity. (A) WT animals were injected hemilaterally with AAV carrying either XBP1s/EGFP or EGFP alone into the right SNpc by brain stereotaxis. At 1 mo after AAV delivery, the mice were injected with 6-OHDA into the right striatum. After 7 d, dopaminergic neurons were visualized in midbrain tissue sections by anti-TH immunostaining (red). (Scale bar: 200 μm.) (B) Immunohistochemistry analysis was performed in striatal sections to quantify 6-OHDA–induced denervation in both injected and noninjected sides. (Scale bar: 1 mm.) (Right) The integrated density of pixel intensity was calculated from images of anti-TH immunohistochemistry covering the entire striatum and expressed as percentage of the noninjected (control) sides (n = 8 per group). (C) Anti-TH immunohistochemistry was performed in the SNpc. (Left) Representative images of anti-TH staining in midbrain tissue sections. (Scale bar: 200 μm.) (Right) TH-positive neurons were quantified as the percentage of neurons in the injected side relative to the noninjected (control) side (n = 8 per group). Data are presented as mean and SEM. Statistical analyses were performed with two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni posttest. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. ns, not significant.
Discussion
The UPR is an essential homeostatic network responding to an overload of unfolded proteins at the ER lumen under physiological and pathological conditions. XBP1 is a major UPR transcription factor that has a fundamental role in supporting professional secretory cell function. Even though IRE1α/XBP1 and ER stress have been implicated in the pathogenesis of many neurodegenerative diseases (18, 19), the possible function of this UPR signaling branch in the physiology of the central nervous system remains poorly explored. In this study, we investigated the activity of XBP1 in dopaminergic neurons. Analysis of several markers of ER stress revealed the occurrence of basal alterations in dopaminergic neurons lacking XBP1. Several ER chaperones, foldases, and autophagy components were found to be up-regulated in XBP1 KO SNpc, correlating with the spontaneous accumulation of protein aggregates and increased levels of polyubiquitinated proteins in the absence of cell death markers. Remarkably, the spontaneous ER stress was specific for dopaminergic neurons and not detected in other brain regions examined in XBP1Nes−/− mice.
Our results suggest that the changes observed at basal levels in XBP1-deficient dopaminergic neurons may represent an adaptive reaction during development to maintain protein homeostasis when the XBP1/UPR signaling branch is compromised. According to this hypothesis, the adaptive capacity of this tissue was tested when we challenged animals with 6-OHDA and observed resistance to this stress stimulus in XBP1-KO mice. Then when we down-regulated XBP1 expression in adult SNpc, a strong chronic ER stress response was triggered that led to massive dopaminergic neuron degeneration. We speculate that in adult mice, XBP1 is required to sustain proteostasis in these cells when no compensatory mechanism can counteract an acute loss of function. Supporting this idea, we observed a strong protective effect against 6-OHDA when we locally delivered active XBP1 into the SNpc of adult mice. This results is in contrast with previous findings indicating that targeting the stress sensor ATF6 enhances the susceptibility of dopaminergic neurons to PD-triggering neurotoxins, whereas CHOP deficiency provides protection (29, 30, 41). In those mouse models, no signs of ER stress were detected in the SNpc at basal levels, suggesting that XBP1 may have a specific activity in maintaining dopaminergic neuron function.Interestingly, ATF6 deficiency has been shown to down-regulate the levels of several ER chaperones and ER-associated protein degradation components at the SNpc (30). Based on this observation, we speculate that the stress response observed in XBP1-deficient neurons may be related to ATF6 overactivation, leading to the up-regulation of UPR target genes, a model that we are currently investigating.
The concept that low levels of stress may actually protect against a subsequent injury has been proposed in several disease models. Low levels of ER stress selectively engage a subset of UPR signaling events, highlighting the specific induction of XBP1 and not proapoptotic components of the pathway, such as CHOP (42, 43). ER stress preconditioning by exposure to nonlethal doses of pharmacologic stressors protects against brain ischemia (44), retinal endothelial inflammation (45), and heart ischemia/reperfusion (46). The concept of hormesis is seen in conditions that engage adaptive stress signaling events rendering cells resistant against a high dose of the same stimuli (47). We speculate that the protection observed when XBP1 is deleted in the nervous system during development may be associated with mild perturbations of ER function that trigger a hormetic mechanism of protection. In agreement with this idea, a recent report indicated that the exposure of fly and mouse models of PD to sublethal levels of the ER stress agent Tm provides protection against neurodegeneration (48).
Remarkably, numerous small molecules and gene therapy approaches are emerging to target the UPR in a pathological context, some with proven efficacy in many preclinical models of disease (49). Thus, strategies to alleviate ER stress in PD may be available to provide therapeutic benefits by reestablishing ER proteostasis and prolonging the survival of dopaminergic neurons (7). To extend our results to PD, it is necessary to assess the impact of targeting XBP1 in genetic models of the disease. Based on the finding that XBP1 deficiency triggers a mild aggregation of endogenous αSynuclein, we speculate that XBP1 may have important neuroprotective effects in the context of alpha-synucleinopathies.
In summary, our results describe and compare the functional consequences of targeting the UPR during development and in adulthood, revealing an important function of XBP1 in the physiology of the nervous system. Given that SNpc neurons were selectively prompt to undergo ER stress in XBP1-deficient animals, this study may contribute to our understanding of the basis of the differential neuronal vulnerability observed in PD.
Materials and Methods
Animals and Surgical Procedures.
All experiments under resting conditions were performed using 6-mo-old male XBP1WT and XBP1Nes−/− mice on a C57BL/6 background. The generation of XBP1Nes−/− mice has been described previously (32). For XBP1 overexpression or down-regulation in the SNpc using AAVs, 3-mo-old male C57BL/6 mice were used. All experiments were performed in accordance with the guidelines of the Animal Care and Use Committee of the Faculty of Medicine, University of Chile, under approved animal experimentation protocol CBA#0265 FMUCH. Each 6-OHDA injection was performed in a single point, injecting 8 μg in the right striatum at the following coordinates: anteroposterior (AP), +0.07 cm; mediolateral (ML), −0.17 cm; dorsoventral (DV), −0.31 cm (50). Mice were killed at 7 d after the surgical procedure for histological analysis. More details are provided in SI Materials and Methods.
AAVs.
All AAVs (serotype 2) were produced by triple transfection of 293 cells using a rep/cap plasmid and pHelper (Stratagene), and then purified by column-affinity chromatography as described previously (36, 51). Then 2 μL of virus was injected unilaterally into the right SNpc at a single point at concentrations of 1 × 109 viral genomes (VGs)/μL for AAV XBP1s/EGFP and AAV EGFP and 1 × 108 VG/μL for AAV shXBP1/EGFP and AAV shLuc/EGFP, using the following coordinates: AP, −0.29 cm; ML, −0.13 cm; DV, −0.42 cm (50). Mice were killed at 1, 2, or 4 wk after viral vector injections. Further information is provided in SI Materials and Methods.
Tissue Preparation and Analysis.
The ventral midbrain (containing entire SN), striatum, and cortex from both hemispheres were dissected. For Western blot analyses, samples were lysed, and extracts were loaded onto SDS/PAGE gels and blotted onto PVDF membranes. Membranes were incubated with primary antibodies, followed by secondary antibodies tagged with HRP. These protocols, as well as the antibodies and dilutions used, are described in detail in SI Materials and Methods.
For RNA extraction and real-time PCR, total RNA was isolated from ventral midbrain (containing the entire SN), striatum, and cortex. After cDNA production, real-time PCR was performed in a Stratagene Light-Cycler system using SYBR Green fluorescent reagent (Applied Biosystems). XBP1 mRNA splicing assays were performed as described previously (52). Mice were anesthetized and perfused through the ascending aorta with isotonic saline, followed by ice-cold 4% paraformaldehyde in 0.1 M PBS (pH 7.4). Brains were frozen, and 25- or 30-μm coronal sections containing the rostral striatum and midbrain were cut on a Leica cryostat. Free-floating midbrain and striatal tissue sections were stained following standard protocols. The protocols and antibodies used in these experiments are described in SI Materials and Methods.
Cell Counting.
Unbiased stereologic estimation of the number of TH-positive neurons stained by immunohistochemistry was performed to quantify the number of dopaminergic neurons in the SNpc of XBP1WT and XBP1Nes−/− mice. Results are expressed as the total number of TH-positive neurons per hemisphere. To determine the percentage of TH-positive cell loss in the SNpc of injected mice, the number of dopaminergic cells in the injected and noninjected side was determined by counting in a blinded manner the total number of TH-positive cells obtained by immunohistochemistry in midbrain serial sections. Results were expressed as the percentage of TH-positive neurons in the injected side compared with the noninjected side. The quantification protocol is described in detail in SI Materials and Methods.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank Silke Escobar for technical support with animal care and Peter Thielen for technical support. We also thank Centro de Microscopía Avanzada Bio-Bio (ECM-12) for assistance with the laser capture experiments. This work was funded primarily by the Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research, Fondo de Fomento al Desarrollo Científico y Tecnológico D11I1007, Millennium Institute P09-015-F, Fondo Nacional de Desarrollo Científico y Tecnológico (FONDECYT) 1140549 (to C.H.), FONDECYT 3120146 (to G.M.), Comisión Nacional de Investigación Científica y Tecnológica (CONICYT) Capital Humano en la Academia 7912010006 (to R.L.V.), and Ring Initiative ACT1109 (to C.H. and F.A.C.). Funding was also provided by Comité de Evaluación y Orientación de la Cooperación Científica con Chile del Gobierno de Francia-CONICYT C13S02, CONICYT Grant USA2013-0003, the Muscular Dystrophy Association, the ALS Therapy Alliance, and the Alzheimer Association (C.H.). P.V., C.M., and A.M. are doctoral fellows supported by a CONICYT fellowship and CONICYT Research Grant AT-24100179). F.A.C. is supported by FONDECYT 1110987 and Millennium Nucleus P07-011-F. B.L.S. is supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation (Grant 31003A_135696).
Footnotes
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
This article is a PNAS Direct Submission.
This article contains supporting information online at www.pnas.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.1073/pnas.1321845111/-/DCSupplemental.
References
- 1.Soto C. Transmissible proteins: Expanding the prion heresy. Cell. 2012;149(5):968–977. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.05.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.de Lau LM, Breteler MM. Epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2006;5(6):525–535. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(06)70471-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Dauer W, Przedborski S. Parkinson’s disease: Mechanisms and models. Neuron. 2003;39(6):889–909. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(03)00568-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Vives-Bauza C, Przedborski S. Mitophagy: The latest problem for Parkinson’s disease. Trends Mol Med. 2011;17(3):158–165. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2010.11.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Martin I, Dawson VL, Dawson TM. Recent advances in the genetics of Parkinson’s disease. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2011;12:301–325. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genom-082410-101440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Calì T, Ottolini D, Brini M. Mitochondria, calcium, and endoplasmic reticulum stress in Parkinson’s disease. Biofactors. 2011;37(3):228–240. doi: 10.1002/biof.159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Mercado G, Valdés P, Hetz C. An ERcentric view of Parkinson’s disease. Trends Mol Med. 2013;19(3):165–175. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2012.12.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hetz C. The unfolded protein response: Controlling cell fate decisions under ER stress and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012;13(2):89–102. doi: 10.1038/nrm3270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Walter P, Ron D. The unfolded protein response: From stress pathway to homeostatic regulation. Science. 2011;334(6059):1081–1086. doi: 10.1126/science.1209038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Tabas I, Ron D. Integrating the mechanisms of apoptosis induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress. Nat Cell Biol. 2011;13(3):184–190. doi: 10.1038/ncb0311-184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Urra H, Dufey E, Lisbona F, Rojas-Rivera D, Hetz C. When ER stress reaches a dead end. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1833(12):3507–3517. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.07.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Calfon M, et al. IRE1 couples endoplasmic reticulum load to secretory capacity by processing the XBP-1 mRNA. Nature. 2002;415(6867):92–96. doi: 10.1038/415092a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lee K, et al. IRE1-mediated unconventional mRNA splicing and S2P-mediated ATF6 cleavage merge to regulate XBP1 in signaling the unfolded protein response. Genes Dev. 2002;16(4):452–466. doi: 10.1101/gad.964702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Yoshida H, Matsui T, Yamamoto A, Okada T, Mori K. XBP1 mRNA is induced by ATF6 and spliced by IRE1 in response to ER stress to produce a highly active transcription factor. Cell. 2001;107(7):881–891. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00611-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hetz C, Martinon F, Rodriguez D, Glimcher LH. The unfolded protein response: Integrating stress signals through the stress sensor IRE1α. Physiol Rev. 2011;91(4):1219–1243. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00001.2011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Wang S, Kaufman RJ. The impact of the unfolded protein response on human disease. J Cell Biol. 2012;197(7):857–867. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201110131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Cornejo VH, Pihán P, Vidal RL, Hetz C. Role of the unfolded protein response in organ physiology: Lessons from mouse models. IUBMB Life. 2013;65(12):962–975. doi: 10.1002/iub.1224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hetz C, Mollereau B. Disturbance of endoplasmic reticulum proteostasis in neurodegenerative diseases. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2014;15(4):233–249. doi: 10.1038/nrn3689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Roussel BD, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum dysfunction in neurological disease. Lancet Neurol. 2013;12(1):105–118. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(12)70238-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Conn KJ, et al. Identification of the protein disulfide isomerase family member PDIp in experimental Parkinson’s disease and Lewy body pathology. Brain Res. 2004;1022(1-2):164–172. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2004.07.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Slodzinski H, et al. Homocysteine-induced endoplasmic reticulum protein (herp) is up-regulated in parkinsonian substantia nigra and present in the core of Lewy bodies. Clin Neuropathol. 2009;28(5):333–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hoozemans JJ, et al. Activation of the unfolded protein response in Parkinson’s disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;354(3):707–711. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.01.043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Colla E, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress is important for the manifestations of α-synucleinopathy in vivo. J Neurosci. 2012;32(10):3306–3320. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5367-11.2012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Colla E, et al. Accumulation of toxic α-synuclein oligomer within endoplasmic reticulum occurs in α-synucleinopathy in vivo. J Neurosci. 2012;32(10):3301–3305. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5368-11.2012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Chung CY, et al. Identification and rescue of α-synuclein toxicity in Parkinson patient-derived neurons. Science. 2013;342(6161):983–987. doi: 10.1126/science.1245296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Holtz WA, O’Malley KL. Parkinsonian mimetics induce aspects of unfolded protein response in death of dopaminergic neurons. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(21):19367–19377. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M211821200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ryu EJ, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the unfolded protein response in cellular models of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurosci. 2002;22(24):10690–10698. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-24-10690.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Sado M, et al. Protective effect against Parkinson’s disease-related insults through the activation of XBP1. Brain Res. 2009;1257:16–24. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.11.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Silva RM, et al. CHOP/GADD153 is a mediator of apoptotic death in substantia nigra dopamine neurons in an in vivo neurotoxin model of parkinsonism. J Neurochem. 2005;95(4):974–986. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03428.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Egawa N, et al. The endoplasmic reticulum stress sensor, ATF6α, protects against neurotoxin-induced dopaminergic neuronal death. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(10):7947–7957. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.156430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Selvaraj S, et al. Neurotoxin-induced ER stress in mouse dopaminergic neurons involves down-regulation of TRPC1 and inhibition of AKT/mTOR signaling. J Clin Invest. 2012;122(4):1354–1367. doi: 10.1172/JCI61332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Hetz C, et al. Unfolded protein response transcription factor XBP-1 does not influence prion replication or pathogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105(2):757–762. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0711094105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lee AH, Scapa EF, Cohen DE, Glimcher LH. Regulation of hepatic lipogenesis by the transcription factor XBP1. Science. 2008;320(5882):1492–1496. doi: 10.1126/science.1158042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kaser A, et al. XBP1 links ER stress to intestinal inflammation and confers genetic risk for human inflammatory bowel disease. Cell. 2008;134(5):743–756. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.07.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Vidal RL, et al. Targeting the UPR transcription factor XBP1 protects against Huntington’s disease through the regulation of FoxO1 and autophagy. Hum Mol Genet. 2012;21(10):2245–2262. doi: 10.1093/hmg/dds040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Valenzuela V, et al. Activation of the unfolded protein response enhances motor recovery after spinal cord injury. Cell Death Dis. 2012;3:e272. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2012.8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Hetz C, et al. XBP-1 deficiency in the nervous system protects against amyotrophic lateral sclerosis by increasing autophagy. Genes Dev. 2009;23(19):2294–2306. doi: 10.1101/gad.1830709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kroemer G, Mariño G, Levine B. Autophagy and the integrated stress response. Mol Cell. 2010;40(2):280–293. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.09.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Giasson BI, et al. Neuronal alpha-synucleinopathy with severe movement disorder in mice expressing A53T human alpha-synuclein. Neuron. 2002;34(4):521–533. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(02)00682-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Zuleta A, Vidal RL, Armentano D, Parsons G, Hetz C. AAV-mediated delivery of the transcription factor XBP1s into the striatum reduces mutant Huntingtin aggregation in a mouse model of Huntington’s disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;420(3):558–563. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.03.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Hashida K, et al. ATF6alpha promotes astroglial activation and neuronal survival in a chronic mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(10):e47950. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Rutkowski DT, et al. Adaptation to ER stress is mediated by differential stabilities of pro-survival and pro-apoptotic mRNAs and proteins. PLoS Biol. 2006;4(11):e374. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Mendes CS, et al. ER stress protects from retinal degeneration. EMBO J. 2009;28(9):1296–1307. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2009.76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Mao XR, Crowder CM. Protein misfolding induces hypoxic preconditioning via a subset of the unfolded protein response machinery. Mol Cell Biol. 2010;30(21):5033–5042. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00922-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Li J, Wang JJ, Zhang SX. Preconditioning with endoplasmic reticulum stress mitigates retinal endothelial inflammation via activation of X-box binding protein 1. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(6):4912–4921. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.199729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Petrovski G, et al. Cardioprotection by endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced autophagy. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011;14(11):2191–2200. doi: 10.1089/ars.2010.3486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Matus S, Castillo K, Hetz C. Hormesis: Protecting neurons against cellular stress in Parkinson disease. Autophagy. 2012;8(6):997–1001. doi: 10.4161/auto.20748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Fouillet A, et al. ER stress inhibits neuronal death by promoting autophagy. Autophagy. 2012;8(6):915–926. doi: 10.4161/auto.19716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Hetz C, Chevet E, Harding HP. Targeting the unfolded protein response in disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013;12(9):703–719. doi: 10.1038/nrd3976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Paxinos G, Franklin KBJ. The Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates. 2nd Ed. London: Academic; 2001. [Google Scholar]
- 51.O’Riordan CR, Lachapelle AL, Vincent KA, Wadsworth SC. Scaleable chromatographic purification process for recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) J Gene Med. 2000;2(6):444–454. doi: 10.1002/1521-2254(200011/12)2:6<444::AID-JGM132>3.0.CO;2-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Rodriguez DA, et al. BH3-only proteins are part of a regulatory network that control the sustained signalling of the unfolded protein response sensor IRE1α. EMBO J. 2012;31(10):2322–2335. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.