Abstract
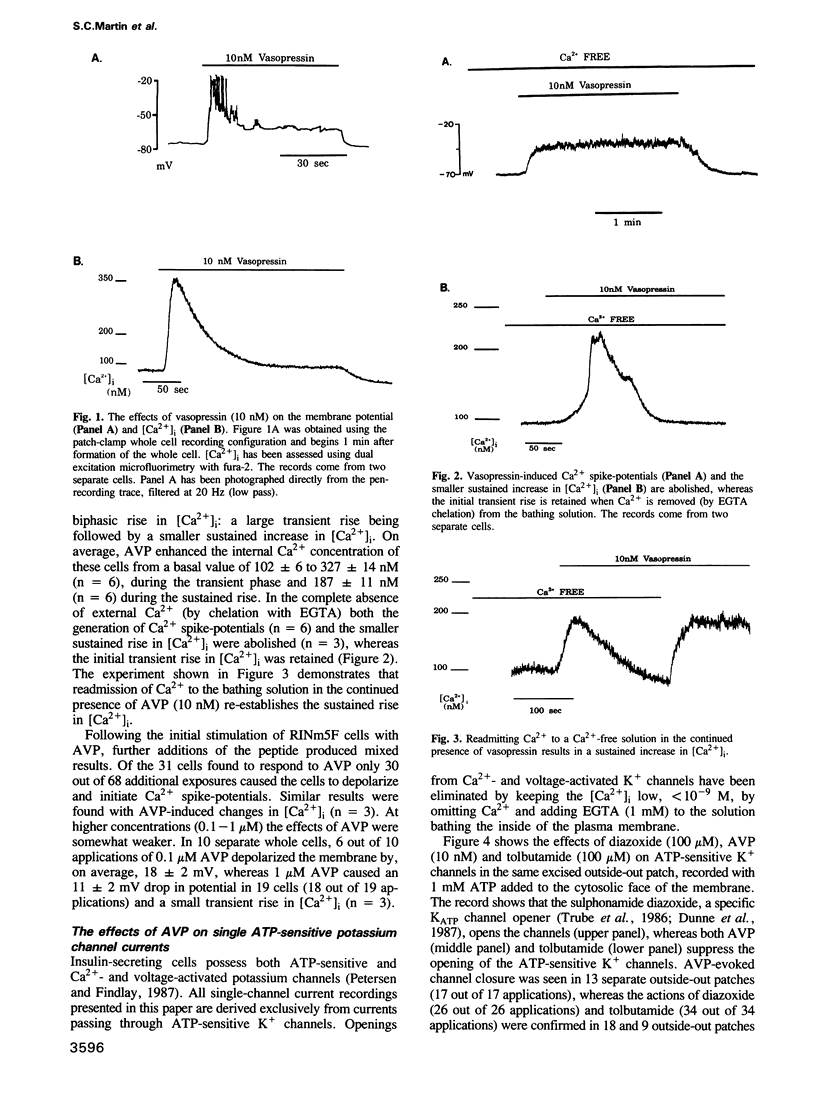
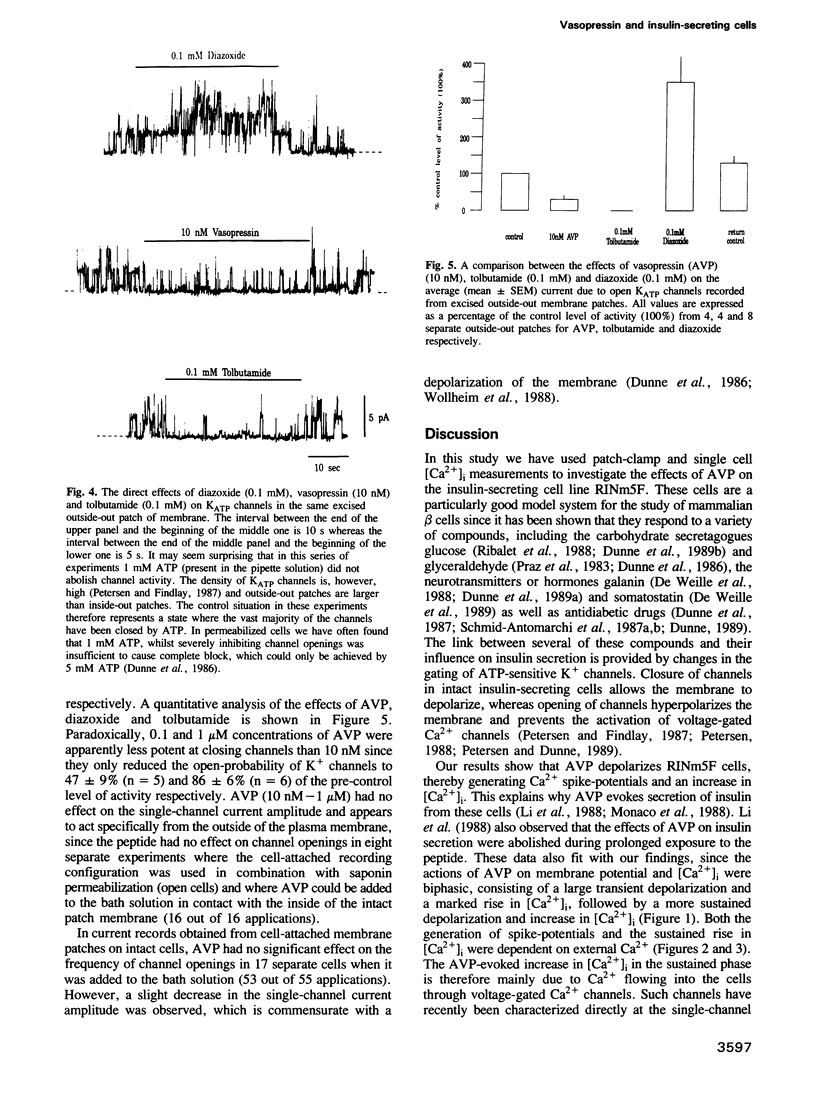
The effects of arginine-vasopressin (AVP) (0.01-1 microM) on membrane potential, [Ca2+]i and ATP-sensitive potassium channels have been studied in the insulin-secreting cell line RINm5F. In whole cells, with an average spontaneous cellular transmembrane potential of -64 +/- 3 mV (n = 33) and an average basal [Ca2+]i of 102 +/- 6 nM (n = 40), AVP evoked: (i) membrane depolarization, (ii) voltage-dependent Ca2+ spike-potentials and (iii) a sharp rise in [Ca2+]i. Single-channel current events recorded from excised outside-out membrane patches show that AVP closes potassium channels that are also closed by tolbutamide (100 microM) and opened by diazoxide (100 microM). AVP acts on KATP channels specifically from the outside of the membrane and a soluble cytosolic messenger appears not to be involved, since there is no channel activation in cell-attached membrane patches when the peptide is added to the bath solution.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashcroft F. M. Adenosine 5'-triphosphate-sensitive potassium channels. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1988;11:97–118. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.11.030188.000525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft F. M., Harrison D. E., Ashcroft S. J. Glucose induces closure of single potassium channels in isolated rat pancreatic beta-cells. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):446–448. doi: 10.1038/312446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook D. L., Hales C. N. Intracellular ATP directly blocks K+ channels in pancreatic B-cells. Nature. 1984 Sep 20;311(5983):271–273. doi: 10.1038/311271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunne M. J., Bullett M. J., Li G. D., Wollheim C. B., Petersen O. H. Galanin activates nucleotide-dependent K+ channels in insulin-secreting cells via a pertussis toxin-sensitive G-protein. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):413–420. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03392.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunne M. J., Findlay I., Petersen O. H. Effects of pyridine nucleotides on the gating of ATP-sensitive potassium channels in insulin-secreting cells. J Membr Biol. 1988 Jun;102(3):205–216. doi: 10.1007/BF01925714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunne M. J., Findlay I., Petersen O. H., Wollheim C. B. ATP-sensitive K+ channels in an insulin-secreting cell line are inhibited by D-glyceraldehyde and activated by membrane permeabilization. J Membr Biol. 1986;93(3):271–279. doi: 10.1007/BF01871181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunne M. J., Illot M. C., Peterson O. H. Interaction of diazoxide, tolbutamide and ATP4- on nucleotide-dependent K+ channels in an insulin-secreting cell line. J Membr Biol. 1987;99(3):215–224. doi: 10.1007/BF01995702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunne M. J. Protein phosphorylation is required for diazoxide to open ATP-sensitive potassium channels in insulin (RINm5F) secreting cells. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 3;250(2):262–266. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80734-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunne M. J., West-Jordan J. A., Abraham R. J., Edwards R. H., Petersen O. H. The gating of nucleotide-sensitive K+ channels in insulin-secreting cells can be modulated by changes in the ratio ATP4-/ADP3- and by nonhydrolyzable derivatives of both ATP and ADP. J Membr Biol. 1988 Sep;104(2):165–177. doi: 10.1007/BF01870928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunne M. J., Yule D. I., Gallacher D. V., Petersen O. H. Cromakalim (BRL 34915) and diazoxide activate ATP-regulated potassium channels in insulin-secreting cells. Pflugers Arch. 1989;414 (Suppl 1):S154–S155. doi: 10.1007/BF00582279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay I., Dunne M. J., Petersen O. H. ATP-sensitive inward rectifier and voltage- and calcium-activated K+ channels in cultured pancreatic islet cells. J Membr Biol. 1985;88(2):165–172. doi: 10.1007/BF01868430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews E. K., Sakamoto Y. Electrical characteristics of pancreatic islet cells. J Physiol. 1975 Mar;246(2):421–437. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misler S., Falke L. C., Gillis K., McDaniel M. L. A metabolite-regulated potassium channel in rat pancreatic B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):7119–7123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.7119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco M. E., Levy B. L., Richardson S. B. Synergism between vasopressin and phorbol esters in stimulation of insulin secretion and phosphatidylcholine metabolism in RIN insulinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Mar 15;151(2):717–724. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80339-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen O. H., Dunne M. J. Regulation of K+ channels plays a crucial role in the control of insulin secretion. Pflugers Arch. 1989;414 (Suppl 1):S115–S120. doi: 10.1007/BF00582259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen O. H., Findlay I. Electrophysiology of the pancreas. Physiol Rev. 1987 Jul;67(3):1054–1116. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1987.67.3.1054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Praz G. A., Halban P. A., Wollheim C. B., Blondel B., Strauss A. J., Renold A. E. Regulation of immunoreactive-insulin release from a rat cell line (RINm5F). Biochem J. 1983 Feb 15;210(2):345–352. doi: 10.1042/bj2100345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribalet B., Eddlestone G. T., Ciani S. Metabolic regulation of the K(ATP) and a maxi-K(V) channel in the insulin-secreting RINm5F cell. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Aug;92(2):219–237. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.2.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorsman P., Ashcroft F. M., Trube G. Single Ca channel currents in mouse pancreatic B-cells. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Oct;412(6):597–603. doi: 10.1007/BF00583760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorsman P., Trube G. Glucose dependent K+-channels in pancreatic beta-cells are regulated by intracellular ATP. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Dec;405(4):305–309. doi: 10.1007/BF00595682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel W., Winiger B. P., Mollard P., Vacher P., Wuarin F., Zahnd G. R., Wollheim C. B., Dufy B. Oscillations of cytosolic Ca2+ in pituitary cells due to action potentials. Nature. 1987 Oct 22;329(6141):719–721. doi: 10.1038/329719a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel W., Winiger B. P., Wuarin F., Zahnd G. R., Wollheim C. B. Monitoring receptor mediated regulation of cytosolic calcium in single pituitary cells by dual excitation microfluorimetry. J Recept Res. 1988;8(1-4):493–507. doi: 10.3109/10799898809049007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid-Antomarchi H., De Weille J., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. The receptor for antidiabetic sulfonylureas controls the activity of the ATP-modulated K+ channel in insulin-secreting cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):15840–15844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid-Antomarchi H., de Weille J., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. The antidiabetic sulfonylurea glibenclamide is a potent blocker of the ATP-modulated K+ channel in insulin secreting cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jul 15;146(1):21–25. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90684-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trube G., Rorsman P., Ohno-Shosaku T. Opposite effects of tolbutamide and diazoxide on the ATP-dependent K+ channel in mouse pancreatic beta-cells. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Nov;407(5):493–499. doi: 10.1007/BF00657506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velasco J. M., Petersen J. U., Petersen O. H. Single-channel Ba2+ currents in insulin-secreting cells are activated by glyceraldehyde stimulation. FEBS Lett. 1988 Apr 25;231(2):366–370. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80851-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velasco J. M., Petersen O. H. The effect of a cell-permeable diacylglycerol analogue on single Ca2+ (Ba2+) channel currents in the insulin-secreting cell line RINm5F. Q J Exp Physiol. 1989 May;74(3):367–370. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1989.sp003280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Biden T. J. Signal transduction in insulin secretion: comparison between fuel stimuli and receptor agonists. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;488:317–333. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb46568.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Dunne M. J., Peter-Riesch B., Bruzzone R., Pozzan T., Petersen O. H. Activators of protein kinase C depolarize insulin-secreting cells by closing K+ channels. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2443–2449. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03090.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Weille J. R., Schmid-Antomarchi H., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. Regulation of ATP-sensitive K+ channels in insulinoma cells: activation by somatostatin and protein kinase C and the role of cAMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2971–2975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Weille J., Schmid-Antomarchi H., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. ATP-sensitive K+ channels that are blocked by hypoglycemia-inducing sulfonylureas in insulin-secreting cells are activated by galanin, a hyperglycemia-inducing hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1312–1316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



