Abstract
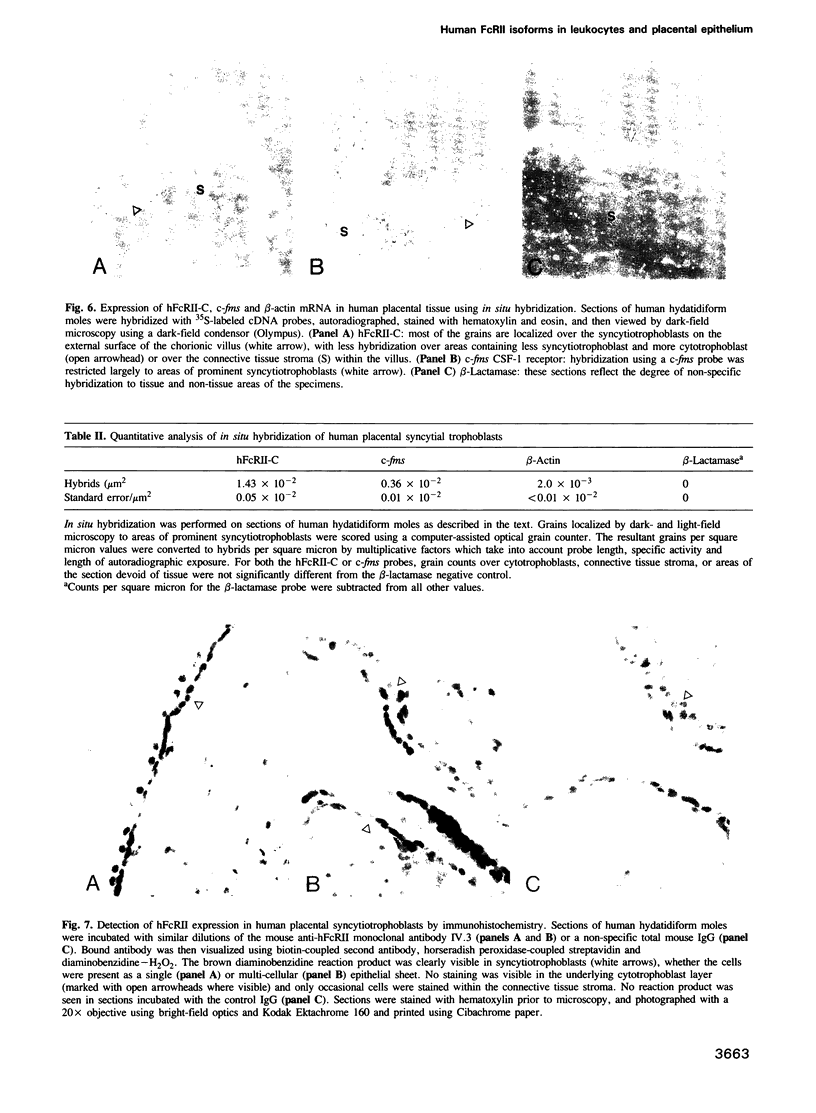
We previously isolated cDNA clones from a human monocyte library that encoded one member of a family of low-affinity surface receptors for the Fc domain of IgG (hFcRII-A). To investigate possible structural and functional heterogeneity among these receptors, we have now isolated two additional cDNAs (hFcRII-B and hFcRII-C) from a human placental library, placenta being a good source of FcR-bearing macrophages and epithelial cells. Three cDNAs encoded related but distinct transmembrane glycoproteins containing two immunoglobulin-like domains; however, transfected cells produced receptors that were indistinguishable on the basis of ligand binding or reactivity with anti-hFcRII monoclonal antibodies. The sequences of hFcRII-A and -B were most closely related and were identical except for several amino acid substitutions and one small internal deletion. While the ectodomain of hFcRII-C was identical to hFcRII-B, its cytoplasmic tail was unrelated but highly homologous to the corresponding domain of the receptor isoform (mFcRII-B2) found in murine macrophages. Thus, human FcRII may be derived from at least two alternatively spliced genes. Northern blots revealed little difference in the pattern of expression of hFcRII isoforms among various myeloid and lymphoid cells or cell lines. However, the blots--as well as in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry--demonstrated that hFcRII-C (along with a second monocyte marker, the c-fms encoded CSF-1 receptor) was expressed in placental syncytiotrophoblasts. Since syncytiotrophoblasts comprise the IgG-transporting epithelium of the placental villus, these findings suggest that FcR found in the immune system and in certain epithelia may be structurally or functionally related.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Lopata M. A., MacDonald R. J., Cowan N. J., Rutter W. J., Kirschner M. W. Number and evolutionary conservation of alpha- and beta-tubulin and cytoplasmic beta- and gamma-actin genes using specific cloned cDNA probes. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90238-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleit H. B., Wright S. D., Unkeless J. C. Human neutrophil Fc gamma receptor distribution and structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3275–3279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S. A., Plutner H., Mellman I. Biosynthesis and intracellular transport of the mouse macrophage Fc receptor. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 15;260(17):9867–9874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs M. L., Bonadonna L., Scott B. M., McKenzie I. F., Hogarth P. M. Molecular cloning of a human immunoglobulin G Fc receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2240–2244. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogarth P. M., Hibbs M. L., Bonadonna L., Scott B. M., Witort E., Pietersz G. A., McKenzie I. F. The mouse Fc receptor for IgG (Ly-17): molecular cloning and specificity. Immunogenetics. 1987;26(3):161–168. doi: 10.1007/BF00365906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwich A. L., Fenton W. A., Firgaira F. A., Fox J. E., Kolansky D., Mellman I. S., Rosenberg L. E. Expression of amplified DNA sequences for ornithine transcarbamylase in HeLa cells: arginine residues may be required for mitochondrial import of enzyme precursor. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1515–1521. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshina M., Nishio A., Bo M., Boime I., Mochizuki M. [The expression of oncogene fms in human chorionic tissue]. Nihon Sanka Fujinka Gakkai Zasshi. 1985 Dec;37(12):2791–2798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kacinski B. M., Carter D., Mittal K., Kohorn E. I., Bloodgood R. S., Donahue J., Donofrio L., Edwards R., Schwartz P. E., Chambers J. T. High level expression of fms proto-oncogene mRNA is observed in clinically aggressive human endometrial adenocarcinomas. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1988 Oct;15(4):823–829. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(88)90113-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinet J. P. Antibody-cell interactions: Fc receptors. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):351–354. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90910-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliman H. J., Nestler J. E., Sermasi E., Sanger J. M., Strauss J. F., 3rd Purification, characterization, and in vitro differentiation of cytotrophoblasts from human term placentae. Endocrinology. 1986 Apr;118(4):1567–1582. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-4-1567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence J. B., Singer R. H. Quantitative analysis of in situ hybridization methods for the detection of actin gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1777–1799. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis V. A., Koch T., Plutner H., Mellman I. A complementary DNA clone for a macrophage-lymphocyte Fc receptor. 1986 Nov 27-Dec 3Nature. 324(6095):372–375. doi: 10.1038/324372a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Looney R. J., Abraham G. N., Anderson C. L. Human monocytes and U937 cells bear two distinct Fc receptors for IgG. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 1;136(5):1641–1647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matre R., Kleppe G., Tönder O. Isolation and characterization of Fc gamma receptors from human placenta. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1981 Jun;89(3):209–213. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1981.tb02688.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellman I., Koch T., Healey G., Hunziker W., Lewis V., Plutner H., Miettinen H., Vaux D., Moore K., Stuart S. Structure and function of Fc receptors on macrophages and lymphocytes. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1988;9:45–65. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1988.supplement_9.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellman I. Relationships between structure and function in the Fc receptor family. Curr Opin Immunol. 1988 Sep-Oct;1(1):16–25. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(88)90046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen H. M., Rose J. K., Mellman I. Fc receptor isoforms exhibit distinct abilities for coated pit localization as a result of cytoplasmic domain heterogeneity. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):317–327. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90846-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard J. W., Bartocci A., Arceci R., Orlofsky A., Ladner M. B., Stanley E. R. Apparent role of the macrophage growth factor, CSF-1, in placental development. Nature. 1987 Dec 3;330(6147):484–486. doi: 10.1038/330484a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravetch J. V., Luster A. D., Weinshank R., Kochan J., Pavlovec A., Portnoy D. A., Hulmes J., Pan Y. C., Unkeless J. C. Structural heterogeneity and functional domains of murine immunoglobulin G Fc receptors. Science. 1986 Nov 7;234(4777):718–725. doi: 10.1126/science.2946078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rettenmier C. W., Sacca R., Furman W. L., Roussel M. F., Holt J. T., Nienhuis A. W., Stanley E. R., Sherr C. J. Expression of the human c-fms proto-oncogene product (colony-stimulating factor-1 receptor) on peripheral blood mononuclear cells and choriocarcinoma cell lines. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jun;77(6):1740–1746. doi: 10.1172/JCI112496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussel M. F., Dull T. J., Rettenmier C. W., Ralph P., Ullrich A., Sherr C. J. Transforming potential of the c-fms proto-oncogene (CSF-1 receptor). Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):549–552. doi: 10.1038/325549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scallon B. J., Scigliano E., Freedman V. H., Miedel M. C., Pan Y. C., Unkeless J. C., Kochan J. P. A human immunoglobulin G receptor exists in both polypeptide-anchored and phosphatidylinositol-glycan-anchored forms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5079–5083. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraj P., Rosse W. F., Silber R., Springer T. A. The major Fc receptor in blood has a phosphatidylinositol anchor and is deficient in paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria. Nature. 1988 Jun 9;333(6173):565–567. doi: 10.1038/333565a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simister N. E., Mostov K. E. An Fc receptor structurally related to MHC class I antigens. Nature. 1989 Jan 12;337(6203):184–187. doi: 10.1038/337184a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D., Seed B. The Fc gamma receptor of natural killer cells is a phospholipid-linked membrane protein. Nature. 1988 Jun 9;333(6173):568–570. doi: 10.1038/333568a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stengelin S., Stamenkovic I., Seed B. Isolation of cDNAs for two distinct human Fc receptors by ligand affinity cloning. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):1053–1059. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02913.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart S. G., Trounstine M. L., Vaux D. J., Koch T., Martens C. L., Mellman I., Moore K. W. Isolation and expression of cDNA clones encoding a human receptor for IgG (Fc gamma RII). J Exp Med. 1987 Dec 1;166(6):1668–1684. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.6.1668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C., Scigliano E., Freedman V. H. Structure and function of human and murine receptors for IgG. Annu Rev Immunol. 1988;6:251–281. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.06.040188.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. F., Barclay A. N. The immunoglobulin superfamily--domains for cell surface recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. 1988;6:381–405. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.06.040188.002121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







