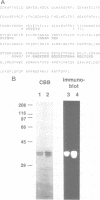
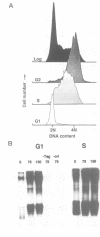
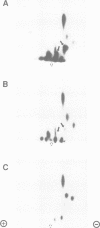
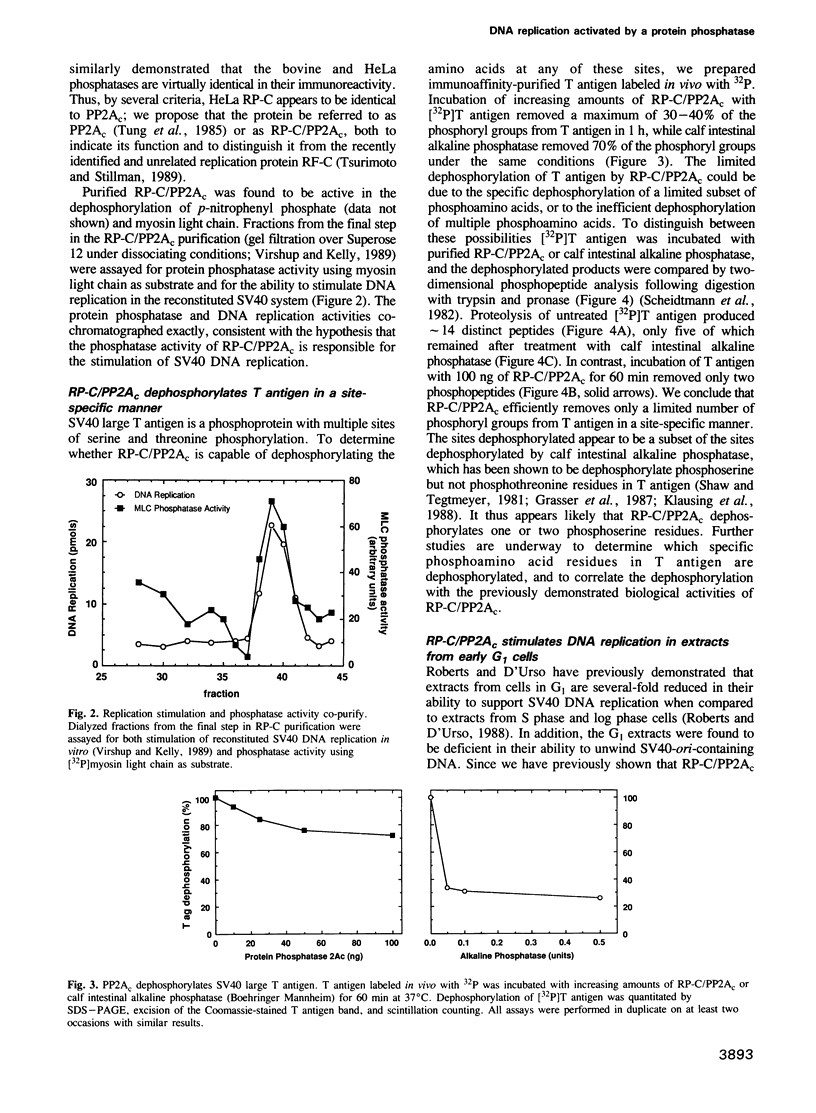
Abstract
We have made use of the cell-free SV40 DNA replication system to identify and characterize cellular proteins required for efficient DNA synthesis. One such protein, replication protein C (RP-C), was shown to be involved with SV40 large T antigen in the early stages of viral DNA replication in vitro. We demonstrate here that RP-C is identical to the catalytic subunit of cellular protein phosphatase 2A (PP2Ac). The purified protein dephosphorylates specific phosphoamino acid residues in T antigen, consistent with the hypothesis that SV40 DNA replication is regulated by modulating the phosphorylation state of the viral initiator protein. We also show that purified RP-C/PP2Ac preferentially stimulates SV40 DNA replication in extracts from early G1 phase cells. This finding suggests that the activity of a cellular factor that influences the net phosphorylation state of T antigen is cell cycle dependent.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aebersold R. H., Leavitt J., Saavedra R. A., Hood L. E., Kent S. B. Internal amino acid sequence analysis of proteins separated by one- or two-dimensional gel electrophoresis after in situ protease digestion on nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):6970–6974. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.6970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alemany S., Tung H. Y., Shenolikar S., Pilkis S. J., Cohen P. The protein phosphatases involved in cellular regulation. Antibody to protein phosphatase-2A as a probe of phosphatase structure and function. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Nov 15;145(1):51–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08520.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arino J., Woon C. W., Brautigan D. L., Miller T. B., Jr, Johnson G. L. Human liver phosphatase 2A: cDNA and amino acid sequence of two catalytic subunit isotypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4252–4256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann E. A. DNA-binding properties of phosphorylated and dephosphorylated D2-T antigen, a simian-virus-40 T-antigen-related protein. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Mar 15;147(3):495–501. doi: 10.1111/j.0014-2956.1985.00495.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowiec J. A., Hurwitz J. ATP stimulates the binding of simian virus 40 (SV40) large tumor antigen to the SV40 origin of replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):64–68. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowiec J. A., Hurwitz J. Localized melting and structural changes in the SV40 origin of replication induced by T-antigen. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3149–3158. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03182.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challberg M. D., Kelly T. J. Animal virus DNA replication. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:671–717. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.003323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. C., Kramer G., Hardesty B. Isolation and partial characterization of an Mr 60,000 subunit of a type 2A phosphatase from rabbit reticulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7267–7275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLucia A. L., Lewton B. A., Tjian R., Tegtmeyer P. Topography of simian virus 40 A protein-DNA complexes: arrangement of pentanucleotide interaction sites at the origin of replication. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):143–150. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.143-150.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean F. B., Bullock P., Murakami Y., Wobbe C. R., Weissbach L., Hurwitz J. Simian virus 40 (SV40) DNA replication: SV40 large T antigen unwinds DNA containing the SV40 origin of replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):16–20. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deb S. P., Tegtmeyer P. ATP enhances the binding of simian virus 40 large T antigen to the origin of replication. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3649–3654. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3649-3654.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Nathans D. Purification of simian virus 40 large T antigen by immunoaffinity chromatography. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):1001–1004. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.1001-1004.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodson M., Dean F. B., Bullock P., Echols H., Hurwitz J. Unwinding of duplex DNA from the SV40 origin of replication by T antigen. Science. 1987 Nov 13;238(4829):964–967. doi: 10.1126/science.2823389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Brizuela L., Beach D., Newport J. The Xenopus cdc2 protein is a component of MPF, a cytoplasmic regulator of mitosis. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):423–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90205-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairman M. P., Stillman B. Cellular factors required for multiple stages of SV40 DNA replication in vitro. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):1211–1218. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02933.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon J. V., Lane D. P. p53 and DNA polymerase alpha compete for binding to SV40 T antigen. Nature. 1987 Oct 1;329(6138):456–458. doi: 10.1038/329456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Norbury C., Lohka M., Nurse P., Maller J. Purified maturation-promoting factor contains the product of a Xenopus homolog of the fission yeast cell cycle control gene cdc2+. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):433–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90206-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green D. D., Yang S. I., Mumby M. C. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of the catalytic subunit of bovine type 2A protein phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4880–4884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grässer F. A., Mann K., Walter G. Removal of serine phosphates from simian virus 40 large T antigen increases its ability to stimulate DNA replication in vitro but has no effect on ATPase and DNA binding. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3373–3380. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3373-3380.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grässer F. A., Scheidtmann K. H., Tuazon P. T., Traugh J. A., Walter G. In vitro phosphorylation of SV40 large T antigen. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):13–22. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90653-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imaoka T., Imazu M., Usui H., Kinohara N., Takeda M. Resolution and reassociation of three distinct components from pig heart phosphoprotein phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1526–1535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly T. J. SV40 DNA replication. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):17889–17892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausing K., Scheidtmann K. H., Baumann E. A., Knippers R. Effects of in vitro dephosphorylation on DNA-binding and DNA helicase activities of simian virus 40 large tumor antigen. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1258–1265. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1258-1265.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. J., Kelly T. J. Simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6973–6977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohr I. J., Stillman B., Gluzman Y. Regulation of SV40 DNA replication by phosphorylation of T antigen. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):153–160. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04733.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumby M. C., Green D. D., Russell K. L. Structural characterization of cardiac protein phosphatase with a monoclonal antibody. Evidence that the Mr = 38,000 phosphatase is the catalytic subunit of the native enzyme(s). J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13763–13770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumby M. C., Russell K. L., Garrard L. J., Green D. D. Cardiac contractile protein phosphatases. Purification of two enzyme forms and their characterization with subunit-specific antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):6257–6265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami Y., Wobbe C. R., Weissbach L., Dean F. B., Hurwitz J. Role of DNA polymerase alpha and DNA primase in simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2869–2873. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Reilly D. R., Miller L. K. Expression and complex formation of simian virus 40 large T antigen and mouse p53 in insect cells. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3109–3119. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3109-3119.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oren M., Winocour E., Prives C. Differential affinities of simian virus 40 large tumor antigen for DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):220–224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottaviano Y., Gerace L. Phosphorylation of the nuclear lamins during interphase and mitosis. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):624–632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prelich G., Kostura M., Marshak D. R., Mathews M. B., Stillman B. The cell-cycle regulated proliferating cell nuclear antigen is required for SV40 DNA replication in vitro. Nature. 1987 Apr 2;326(6112):471–475. doi: 10.1038/326471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. M., D'Urso G. An origin unwinding activity regulates initiation of DNA replication during mammalian cell cycle. Science. 1988 Sep 16;241(4872):1486–1489. doi: 10.1126/science.2843984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidtmann K. H., Echle B., Walter G. Simian virus 40 large T antigen is phosphorylated at multiple sites clustered in two separate regions. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):116–133. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.116-133.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidtmann K. H., Hardung M., Echle B., Walter G. DNA-binding activity of simian virus 40 large T antigen correlates with a distinct phosphorylation state. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):1–12. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.1-12.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidtmann K. H. Phosphorylation of simian virus 40 large T antigen: cytoplasmic and nuclear phophorylation sites differ in their metabolic stability. Virology. 1986 Apr 15;150(1):85–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J., Fanning E. Mutations in the phosphorylation sites of simian virus 40 (SV40) T antigen alter its origin DNA-binding specificity for sites I or II and affect SV40 DNA replication activity. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1598–1605. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1598-1605.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw S. B., Tegtmeyer P. Binding of dephosphorylated A protein to SV40 DNA. Virology. 1981 Nov;115(1):88–96. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90091-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simanis V., Lane D. P. An immunoaffinity purification procedure for SV40 large T antigen. Virology. 1985 Jul 15;144(1):88–100. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90308-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. T., Chou W., Rodgers K. Phosphorylation downregulates the DNA-binding activity of simian virus 40 T antigen. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):888–894. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.888-894.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. T. Stepwise phosphorylation of the NH2-terminal region of the simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8633–8640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Tjian R. T-antigen-DNA polymerase alpha complex implicated in simian virus 40 DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):4077–4087. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.4077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurimoto T., Stillman B. Purification of a cellular replication factor, RF-C, that is required for coordinated synthesis of leading and lagging strands during simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):609–619. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tung H. Y., Alemany S., Cohen P. The protein phosphatases involved in cellular regulation. 2. Purification, subunit structure and properties of protein phosphatases-2A0, 2A1, and 2A2 from rabbit skeletal muscle. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Apr 15;148(2):253–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08833.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Roy F., Fransen L., Fiers W. Metabolic turnover of phosphorylation sites in simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):442–446. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.442-446.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virshup D. M., Kelly T. J. Purification of replication protein C, a cellular protein involved in the initial stages of simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3584–3588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold M. S., Kelly T. Purification and characterization of replication protein A, a cellular protein required for in vitro replication of simian virus 40 DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2523–2527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold M. S., Li J. J., Kelly T. J. Initiation of simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro: large-tumor-antigen- and origin-dependent unwinding of the template. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3643–3647. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold M. S., Weinberg D. H., Virshup D. M., Li J. J., Kelly T. J. Identification of cellular proteins required for simian virus 40 DNA replication. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):2801–2809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Roy F., Fransen L., Fiers W. Improved localization of phosphorylation sites in simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):315–331. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.315-331.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]