Abstract
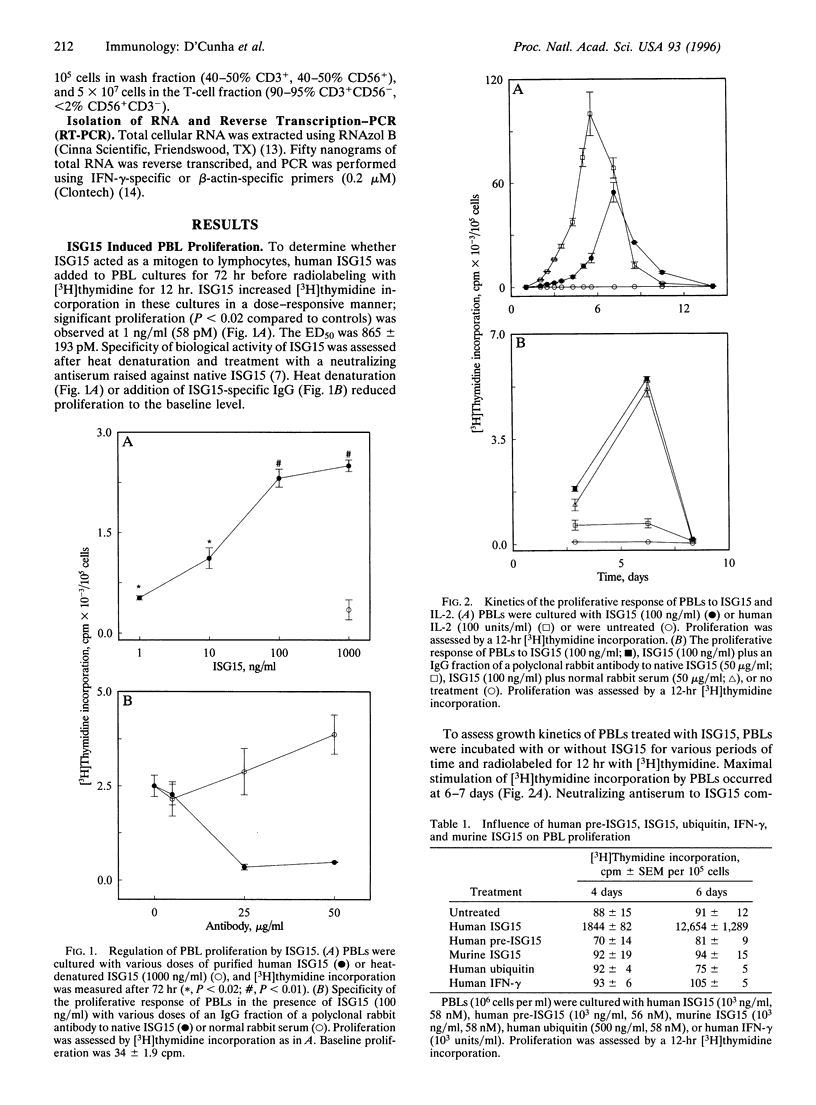
ISG15 is a 15-kDa protein of unique primary amino acid sequence, which is transcriptionally regulated by interferon (IFN) alpha and IFN-beta. Because it is synthesized in many cell types and secreted from human monocytes and lymphocytes, we postulated that ISG15 might act to modulate immune cell function. ISG15 stimulated B-depleted lymphocyte proliferation in a dose-dependent manner with significant proliferation induced by amounts of ISG15 as low as 1 ng/ml (58 pM). Maximal stimulation of [3H]thymidine incorporation by B-depleted lymphocytes occurred at 6-7 days. Immunophenotyping of ISG15-treated B-depleted lymphocyte cultures indicated a 26-fold expansion of natural killer (NK) cells (CD56+). In cytotoxicity assays, ISG15 was a potent inducer of cytolytic activity directed against both K562 (100 lytic units per 10(6) cells) and Daudi (80 lytic units per 10(6) cells) tumor cell targets, indicating that ISG15 enhanced lymphokine-activated killer-like activity. ISG15-induced NK cell proliferation required coculturing of T and NK cells, suggesting that soluble factor(s) were required. Measurement of ISG15-treated cell culture supernatants for cytokines indicated production of IFN-gamma (> 700 units/ml). No interleukin 2 or interleukin 12 was detected. IFN-gamma itself failed to stimulate lymphocyte proliferation and lymphokine-activated killer cell activation. Further, induced expression of IFN-gamma mRNA was detected by reverse transcription-PCR in T lymphocytes after ISG15 treatment but not in NK cells. Enhancement of NK cell proliferation, augmentation of non-major histocompatibility complex-restricted cytotoxicity, and induction of IFN-gamma from T cells identify ISG15 as a member of the cytokine cascade and suggest that it may be responsible for amplifying and directing some of the immunomodulatory effects of IFN-alpha or IFN-beta.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blomstrom D. C., Fahey D., Kutny R., Korant B. D., Knight E., Jr Molecular characterization of the interferon-induced 15-kDa protein. Molecular cloning and nucleotide and amino acid sequence. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8811–8816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. H., Perussia B., Gupta J. W., Kobayashi M., Pospísil M., Young H. A., Wolf S. F., Young D., Clark S. C., Trinchieri G. Induction of interferon gamma production by natural killer cell stimulatory factor: characterization of the responder cells and synergy with other inducers. J Exp Med. 1991 Apr 1;173(4):869–879. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.4.869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Jr, Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science. 1994 Jun 3;264(5164):1415–1421. doi: 10.1126/science.8197455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. J., Broeze R. J., Lengyel P. Accumulation of an mRNA and protein in interferon-treated Ehrlich ascites tumour cells. Nature. 1979 Jun 7;279(5713):523–525. doi: 10.1038/279523a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feltham N., Hillman M., Jr, Cordova B., Fahey D., Larsen B., Blomstrom D., Knight E., Jr A 15-kD interferon-induced protein and its 17-kD precursor: expression in Escherichia coli, purification, and characterization. J Interferon Res. 1989 Oct;9(5):493–507. doi: 10.1089/jir.1989.9.493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein G., Scheid M., Hammerling U., Schlesinger D. H., Niall H. D., Boyse E. A. Isolation of a polypeptide that has lymphocyte-differentiating properties and is probably represented universally in living cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):11–15. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handa K., Suzuki R., Matsui H., Shimizu Y., Kumagai K. Natural killer (NK) cells as a responder to interleukin 2 (IL 2). II. IL 2-induced interferon gamma production. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):988–992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Ciechanover A., Heller H., Haas A. L., Rose I. A. Proposed role of ATP in protein breakdown: conjugation of protein with multiple chains of the polypeptide of ATP-dependent proteolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1783–1786. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin system for protein degradation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:761–807. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.003553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasahara T., Hooks J. J., Dougherty S. F., Oppenheim J. J. Interleukin 2-mediated immune interferon (IFN-gamma) production by human T cells and T cell subsets. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1784–1789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight E., Jr, Cordova B. IFN-induced 15-kDa protein is released from human lymphocytes and monocytes. J Immunol. 1991 Apr 1;146(7):2280–2284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight E., Jr, Fahey D., Cordova B., Hillman M., Kutny R., Reich N., Blomstrom D. A 15-kDa interferon-induced protein is derived by COOH-terminal processing of a 17-kDa precursor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 5;263(10):4520–4522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi M., Fitz L., Ryan M., Hewick R. M., Clark S. C., Chan S., Loudon R., Sherman F., Perussia B., Trinchieri G. Identification and purification of natural killer cell stimulatory factor (NKSF), a cytokine with multiple biologic effects on human lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1989 Sep 1;170(3):827–845. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.3.827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korant B. D., Blomstrom D. C., Jonak G. J., Knight E., Jr Interferon-induced proteins. Purification and characterization of a 15,000-dalton protein from human and bovine cells induced by interferon. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14835–14839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb K. R., Haas A. L. The interferon-inducible 15-kDa ubiquitin homolog conjugates to intracellular proteins. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 15;267(11):7806–7813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recht M., Borden E. C., Knight E., Jr A human 15-kDa IFN-induced protein induces the secretion of IFN-gamma. J Immunol. 1991 Oct 15;147(8):2617–2623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich N., Evans B., Levy D., Fahey D., Knight E., Jr, Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon-induced transcription of a gene encoding a 15-kDa protein depends on an upstream enhancer element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6394–6398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romagnani S. Induction of TH1 and TH2 responses: a key role for the 'natural' immune response? Immunol Today. 1992 Oct;13(10):379–381. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90083-J. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger D. H., Goldstein G., Scheid M. P., Bitensky M. Chemical synthesis of a hexadecapeptide segment of ubiquitin that activates adenylate cyclase and induces lymphocytes to differentiate. Experientia. 1978 Jun 15;34(6):703–704. doi: 10.1007/BF01947269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen G. C., Lengyel P. The interferon system. A bird's eye view of its biochemistry. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5017–5020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G., Matsumoto-Kobayashi M., Clark S. C., Seehra J., London L., Perussia B. Response of resting human peripheral blood natural killer cells to interleukin 2. J Exp Med. 1984 Oct 1;160(4):1147–1169. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.4.1147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truitt R. L., Piaskowski V., Kirchner P., McOlash L., Camitta B. M., Casper J. T. Immunological evaluation of pediatric cancer patients receiving recombinant interleukin-2 in a phase I trial. J Immunother (1991) 1992 May;11(4):274–285. doi: 10.1097/00002371-199205000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf S. F., Temple P. A., Kobayashi M., Young D., Dicig M., Lowe L., Dzialo R., Fitz L., Ferenz C., Hewick R. M. Cloning of cDNA for natural killer cell stimulatory factor, a heterodimeric cytokine with multiple biologic effects on T and natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1991 May 1;146(9):3074–3081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




