Abstract
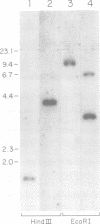
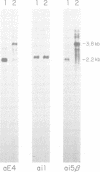
The nuclear PET54 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae was cloned and a pet54::LEU2 gene disruption strain was constructed. Analysis of the phenotype of this strain revealed a defect in expression of two mitochondrial genes: COX1, which encodes cytochrome c oxidase subunit I, and COX3, which encodes cytochrome c oxidase subunit III. The defect in COX1 gene expression in the pet54 mutant was shown to be the result of inefficient excision of COX1 intron aI5 beta. Two lines of evidence indicate that inefficient excision of intron aI5 beta is the sole defect in COX1 gene expression. First, a pet54::LEU2 cytoductant bearing the 'short' mitochondrial genome that lacks both COX1 introns aI5 alpha and aI5 beta is defective only in COX3 gene expression and not in COX1 mRNA splicing or mRNA translation. Second, Northern analysis of COX1 transcipts from the pet54 mutant showed that a 3.8 kb COX1 transcript containing unexcised intron aI5 beta and lacking intron aI5 alpha is accumulated while the amount of 2.2 kb mature COX1 mRNA is diminished. In an effort to relate the role of the PET54 gene product in splicing of COX1 pre-mRNA to the previously characterized role for PET54 in translation of mitochondrial COX3 mRNA, the sequence of the PET54-responsive portion of the COX3 5' untranslated leader region was compared to the COX1 intron aI5 beta sequence. Two blocks of RNA sequence present in COX3 have similar counterparts within intron aI5 beta of COX1. The possibility that the PET54 protein binds to one or the other of these blocks of RNA sequence and the potential consequences of this interaction are discussed.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akins R. A., Lambowitz A. M. A protein required for splicing group I introns in Neurospora mitochondria is mitochondrial tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase or a derivative thereof. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):331–345. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90488-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anziano P. Q., Hanson D. K., Mahler H. R., Perlman P. S. Functional domains in introns: trans-acting and cis-acting regions of intron 4 of the cob gene. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):925–932. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90297-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asher E. B., Groudinsky O., Dujardin G., Altamura N., Kermorgant M., Slonimski P. P. Novel class of nuclear genes involved in both mRNA splicing and protein synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae mitochondria. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Feb;215(3):517–528. doi: 10.1007/BF00427051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attardi G., Schatz G. Biogenesis of mitochondria. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:289–333. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benne R. Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases are involved in RNA splicing in fungal mitochondria. Trends Genet. 1988 Jul;4(7):181–182. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90072-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke J. M. Molecular genetics of group I introns: RNA structures and protein factors required for splicing--a review. Gene. 1988 Dec 20;73(2):273–294. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90493-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carignani G., Groudinsky O., Frezza D., Schiavon E., Bergantino E., Slonimski P. P. An mRNA maturase is encoded by the first intron of the mitochondrial gene for the subunit I of cytochrome oxidase in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):733–742. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90106-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R., Bass B. L. Biological catalysis by RNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:599–629. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conde J., Fink G. R. A mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae defective for nuclear fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3651–3655. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costanzo M. C., Fox T. D. Product of Saccharomyces cerevisiae nuclear gene PET494 activates translation of a specific mitochondrial mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3694–3703. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costanzo M. C., Fox T. D. Specific translational activation by nuclear gene products occurs in the 5' untranslated leader of a yeast mitochondrial mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2677–2681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costanzo M. C., Seaver E. C., Fox T. D. At least two nuclear gene products are specifically required for translation of a single yeast mitochondrial mRNA. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3637–3641. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04693.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costanzo M. C., Seaver E. C., Fox T. D. The PET54 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: characterization of a nuclear gene encoding a mitochondrial translational activator and subcellular localization of its product. Genetics. 1989 Jun;122(2):297–305. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.2.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R. W., Waring R. B., Ray J. A., Brown T. A., Scazzocchio C. Making ends meet: a model for RNA splicing in fungal mitochondria. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):719–724. doi: 10.1038/300719a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De La Salle H., Jacq C., Slonimski P. P. Critical sequences within mitochondrial introns: pleiotropic mRNA maturase and cis-dominant signals of the box intron controlling reductase and oxidase. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90051-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox T. D., Sanford J. C., McMullin T. W. Plasmids can stably transform yeast mitochondria lacking endogenous mtDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7288–7292. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grivell L. A., Schweyen R. J. RNA splicing in yeast mitochondria: taking out the twists. Trends Genet. 1989 Feb;5(2):39–41. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90018-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hensgens L. A., Arnberg A. C., Roosendaal E., van der Horst G., van der Veen R., van Ommen G. J., Grivell L. A. Variation, transcription and circular RNAs of the mitochondrial gene for subunit I of cytochrome c oxidase. J Mol Biol. 1983 Feb 15;164(1):35–58. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90086-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hensgens L. A., Bonen L., de Haan M., van der Horst G., Grivell L. A. Two intron sequences in yeast mitochondrial COX1 gene: homology among URF-containing introns and strain-dependent variation in flanking exons. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):379–389. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90457-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert C. J., Labouesse M., Dujardin G., Slonimski P. P. The NAM2 proteins from S. cerevisiae and S. douglasii are mitochondrial leucyl-tRNA synthetases, and are involved in mRNA splicing. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):473–483. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02835.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston S. A., Anziano P. Q., Shark K., Sanford J. C., Butow R. A. Mitochondrial transformation in yeast by bombardment with microprojectiles. Science. 1988 Jun 10;240(4858):1538–1541. doi: 10.1126/science.2836954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloeckener-Gruissem B., McEwen J. E., Poyton R. O. Identification of a third nuclear protein-coding gene required specifically for posttranscriptional expression of the mitochondrial COX3 gene is Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1399–1402. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1399-1402.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloeckener-Gruissem B., McEwen J. E., Poyton R. O. Nuclear functions required for cytochrome c oxidase biogenesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: multiple trans-acting nuclear genes exert specific effects on expression of each of the cytochrome c oxidase subunits encoded on mitochondrial DNA. Curr Genet. 1987;12(5):311–322. doi: 10.1007/BF00405753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancashire W. E., Mattoon J. R. Genetic manipulation of a latent defect in yeast cytochrome biosynthesis utilizing cytoduction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Oct 12;90(3):801–809. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91899-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazowska J., Claisse M., Gargouri A., Kotylak Z., Spyridakis A., Slonimski P. P. Protein encoded by the third intron of cytochrome b gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is an mRNA maturase. Analysis of mitochondrial mutants, RNA transcripts proteins and evolutionary relationships. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jan 20;205(2):275–289. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90341-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazowska J., Jacq C., Slonimski P. P. Sequence of introns and flanking exons in wild-type and box3 mutants of cytochrome b reveals an interlaced splicing protein coded by an intron. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):333–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90344-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEwen J. E., Ko C., Kloeckner-Gruissem B., Poyton R. O. Nuclear functions required for cytochrome c oxidase biogenesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Characterization of mutants in 34 complementation groups. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11872–11879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller P. P., Reif M. K., Zonghou S., Sengstag C., Mason T. L., Fox T. D. A nuclear mutation that post-transcriptionally blocks accumulation of a yeast mitochondrial gene product can be suppressed by a mitochondrial gene rearrangement. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jun 5;175(4):431–452. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90178-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K. A., Tatchell K. The structure of transposable yeast mating type loci. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):753–764. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80051-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmen J. D., Kloeckener-Gruissem B., McEwen J. E. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of the nuclear PET122 gene required for expression of the mitochondrial COX3 gene in S. cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 25;16(22):10783–10802. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.22.10783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M., Faye G. Steps in processing of the mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase subunit I pre-mRNA affected by a nuclear mutation in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):8–12. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Séraphin B., Simon M., Boulet A., Faye G. Mitochondrial splicing requires a protein from a novel helicase family. Nature. 1989 Jan 5;337(6202):84–87. doi: 10.1038/337084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Séraphin B., Simon M., Faye G. MSS18, a yeast nuclear gene involved in the splicing of intron aI5 beta of the mitochondrial cox1 transcript. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1455–1464. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02963.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thalenfeld B. E., Tzagoloff A. Assembly of the mitochondrial membrane system. Sequence of the oxi 2 gene of yeast mitochondrial DNA. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6173–6180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzagoloff A., Myers A. M. Genetics of mitochondrial biogenesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:249–285. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.001341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring R. B., Davies R. W. Assessment of a model for intron RNA secondary structure relevant to RNA self-splicing--a review. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):277–291. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss-Brummer B., Rödel G., Schweyen R. J., Kaudewitz F. Expression of the split gene cob in yeast: evidence for a precursor of a "maturase" protein translated from intron 4 and preceding exons. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):527–536. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90169-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]