Abstract
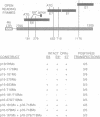
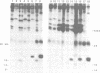
The human papillomavirus types (HPVs) most often associated with cancer of the cervix, such as HPV16, have been reported previously to immortalize normal human foreskin keratinocytes in vitro, while the types that are primarily associated with benign cervical lesions failed to do so. In this study we have determined the HPV16 genes that are responsible for the immortalizing activity of the viral genome. Transfection with a plasmid in which E6 and E7 were the only intact open reading frames (ORFs) induced an indefinite life-span in the keratinocytes with an efficiency similar to that of the entire early region of the viral DNA. Mutants in the E6E7 clone with inactivating lesions in E6 or E7 failed to induce immortalization. When transfected alone, E7 could induce hyperproliferation, but these cells eventually senesced. By itself, E6 exhibited no activity, Co-transfection of a plasmid with an intact E6 ORF and a second plasmid with an intact E7 ORF generated keratinocyte lines with indefinite growth potential. The E6 and E7 proteins were detected in the lines induced by the E6E7 DNA and by co-transfection of the E6 and E7 plasmids. Therefore, we conclude that HPV16 E6 and E7 cooperative to immortalize human keratinocytes in vitro. Changes in cellular gene expression are probably also required for immortalization since all of the keratinocyte lines examined were aneuploid. Serum and calcium resistant sublines were isolated from the E6E7 induced lines, indicating that other HPV genes do not play an obligatory role in the generation of resistance to differentiation.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Androphy E. J., Hubbert N. L., Schiller J. T., Lowy D. R. Identification of the HPV-16 E6 protein from transformed mouse cells and human cervical carcinoma cell lines. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):989–992. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04849.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. C., Phelps W. C., Lindgren V., Braun M. J., Gonda M. A., Howley P. M. Structural and transcriptional analysis of human papillomavirus type 16 sequences in cervical carcinoma cell lines. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):962–971. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.962-971.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa M. S., Lowy D. R., Schiller J. T. Papillomavirus polypeptides E6 and E7 are zinc-binding proteins. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1404–1407. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1404-1407.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedell M. A., Jones K. H., Grossman S. R., Laimins L. A. Identification of human papillomavirus type 18 transforming genes in immortalized and primary cells. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1247–1255. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1247-1255.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Gissmann L., Ikenberg H., Kleinheinz A., Scheurlen W., zur Hausen H. A new type of papillomavirus DNA, its presence in genital cancer biopsies and in cell lines derived from cervical cancer. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1151–1157. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01944.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerni C., Binétruy B., Schiller J. T., Lowy D. R., Meneguzzi G., Cuzin F. Successive steps in the process of immortalization identified by transfer of separate bovine papillomavirus genes into rat fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3266–3270. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole S. T., Danos O. Nucleotide sequence and comparative analysis of the human papillomavirus type 18 genome. Phylogeny of papillomaviruses and repeated structure of the E6 and E7 gene products. J Mol Biol. 1987 Feb 20;193(4):599–608. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90343-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crook T., Morgenstern J. P., Crawford L., Banks L. Continued expression of HPV-16 E7 protein is required for maintenance of the transformed phenotype of cells co-transformed by HPV-16 plus EJ-ras. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):513–519. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03405.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crook T., Storey A., Almond N., Osborn K., Crawford L. Human papillomavirus type 16 cooperates with activated ras and fos oncogenes in the hormone-dependent transformation of primary mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8820–8824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyson N., Howley P. M., Münger K., Harlow E. The human papilloma virus-16 E7 oncoprotein is able to bind to the retinoblastoma gene product. Science. 1989 Feb 17;243(4893):934–937. doi: 10.1126/science.2537532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürst M., Dzarlieva-Petrusevska R. T., Boukamp P., Fusenig N. E., Gissmann L. Molecular and cytogenetic analysis of immortalized human primary keratinocytes obtained after transfection with human papillomavirus type 16 DNA. Oncogene. 1987;1(3):251–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürst M., Gissmann L., Ikenberg H., zur Hausen H. A papillomavirus DNA from a cervical carcinoma and its prevalence in cancer biopsy samples from different geographic regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3812–3815. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds C., Vousden K. H. A point mutational analysis of human papillomavirus type 16 E7 protein. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2650–2656. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2650-2656.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu Y. S., Reagan J. W., Richart R. M. Definition of precursors. Gynecol Oncol. 1981 Oct;12(2 Pt 2):S220–S231. doi: 10.1016/0090-8258(81)90076-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gius D., Grossman S., Bedell M. A., Laimins L. A. Inducible and constitutive enhancer domains in the noncoding region of human papillomavirus type 18. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):665–672. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.665-672.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman S. R., Mora R., Laimins L. A. Intracellular localization and DNA-binding properties of human papillomavirus type 18 E6 protein expressed with a baculovirus vector. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):366–374. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.366-374.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanda T., Furuno A., Yoshiike K. Human papillomavirus type 16 open reading frame E7 encodes a transforming gene for rat 3Y1 cells. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):610–613. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.610-613.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaur P., McDougall J. K. Characterization of primary human keratinocytes transformed by human papillomavirus type 18. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):1917–1924. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.1917-1924.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. Inhibition of SV40 replication in simian cells by specific pBR322 DNA sequences. Nature. 1981 Sep 3;293(5827):79–81. doi: 10.1038/293079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsukura T., Kanda T., Furuno A., Yoshikawa H., Kawana T., Yoshiike K. Cloning of monomeric human papillomavirus type 16 DNA integrated within cell DNA from a cervical carcinoma. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):979–982. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.979-982.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCance D. J. Human papillomaviruses and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986;823(3):195–205. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(86)90002-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pater M. M., Pater A. Human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 sequences in carcinoma cell lines of the cervix. Virology. 1985 Sep;145(2):313–318. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90164-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pecoraro G., Morgan D., Defendi V. Differential effects of human papillomavirus type 6, 16, and 18 DNAs on immortalization and transformation of human cervical epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):563–567. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfister H. Human papillomaviruses and genital cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 1987;48:113–147. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60691-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps W. C., Yee C. L., Münger K., Howley P. M. The human papillomavirus type 16 E7 gene encodes transactivation and transformation functions similar to those of adenovirus E1A. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):539–547. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90570-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirisi L., Creek K. E., Doniger J., DiPaolo J. A. Continuous cell lines with altered growth and differentiation properties originate after transfection of human keratinocytes with human papillomavirus type 16 DNA. Carcinogenesis. 1988 Sep;9(9):1573–1579. doi: 10.1093/carcin/9.9.1573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirisi L., Yasumoto S., Feller M., Doniger J., DiPaolo J. A. Transformation of human fibroblasts and keratinocytes with human papillomavirus type 16 DNA. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1061–1066. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1061-1066.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid R., Crum C. P., Herschman B. R., Fu Y. S., Braun L., Shah K. V., Agronow S. J., Stanhope C. R. Genital warts and cervical cancer. III. Subclinical papillomaviral infection and cervical neoplasia are linked by a spectrum of continuous morphologic and biologic change. Cancer. 1984 Feb 15;53(4):943–953. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19840215)53:4<943::aid-cncr2820530421>3.0.co;2-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato H., Furuno A., Yoshiike K. Expression of human papillomavirus type 16 E7 gene induces DNA synthesis of rat 3Y1 cells. Virology. 1989 Jan;168(1):195–199. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90423-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato H., Watanabe S., Furuno A., Yoshiike K. Human papillomavirus type 16 E7 protein expressed in Escherichia coli and monkey COS-1 cells: immunofluorescence detection of the nuclear E7 protein. Virology. 1989 May;170(1):311–315. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90386-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller J. T., Vass W. C., Lowy D. R. Identification of a second transforming region in bovine papillomavirus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7880–7884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Phelps W. C., Zhang Y. L., Barbosa M. Quantitative keratinocyte assay detects two biological activities of human papillomavirus DNA and identifies viral types associated with cervical carcinoma. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3181–3187. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03185.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider-Gädicke A., Schwarz E. Different human cervical carcinoma cell lines show similar transcription patterns of human papillomavirus type 18 early genes. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2285–2292. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04496.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smotkin D., Prokoph H., Wettstein F. O. Oncogenic and nononcogenic human genital papillomaviruses generate the E7 mRNA by different mechanisms. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1441–1447. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1441-1447.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smotkin D., Wettstein F. O. The major human papillomavirus protein in cervical cancers is a cytoplasmic phosphoprotein. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1686–1689. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1686-1689.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smotkin D., Wettstein F. O. Transcription of human papillomavirus type 16 early genes in a cervical cancer and a cancer-derived cell line and identification of the E7 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4680–4684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storey A., Pim D., Murray A., Osborn K., Banks L., Crawford L. Comparison of the in vitro transforming activities of human papillomavirus types. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1815–1820. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03013.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka A., Noda T., Yajima H., Hatanaka M., Ito Y. Identification of a transforming gene of human papillomavirus type 16. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1465–1469. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1465-1469.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vousden K. H., Doniger J., DiPaolo J. A., Lowy D. R. The E7 open reading frame of human papillomavirus type 16 encodes a transforming gene. Oncogene Res. 1988 Sep;3(2):167–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vousden K. H., Jat P. S. Functional similarity between HPV16E7, SV40 large T and adenovirus E1a proteins. Oncogene. 1989 Feb;4(2):153–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe S., Kanda T., Yoshiike K. Human papillomavirus type 16 transformation of primary human embryonic fibroblasts requires expression of open reading frames E6 and E7. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):965–969. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.965-969.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodworth C. D., Bowden P. E., Doniger J., Pirisi L., Barnes W., Lancaster W. D., DiPaolo J. A. Characterization of normal human exocervical epithelial cells immortalized in vitro by papillomavirus types 16 and 18 DNA. Cancer Res. 1988 Aug 15;48(16):4620–4628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodworth C. D., Doniger J., DiPaolo J. A. Immortalization of human foreskin keratinocytes by various human papillomavirus DNAs corresponds to their association with cervical carcinoma. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):159–164. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.159-164.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee C., Krishnan-Hewlett I., Baker C. C., Schlegel R., Howley P. M. Presence and expression of human papillomavirus sequences in human cervical carcinoma cell lines. Am J Pathol. 1985 Jun;119(3):361–366. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yutsudo M., Okamoto Y., Hakura A. Functional dissociation of transforming genes of human papillomavirus type 16. Virology. 1988 Oct;166(2):594–597. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90532-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Knebel Doeberitz M., Oltersdorf T., Schwarz E., Gissmann L. Correlation of modified human papilloma virus early gene expression with altered growth properties in C4-1 cervical carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 1988 Jul 1;48(13):3780–3786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]