Abstract
Penetration of intestinal epithelial cells is an important step in the pathogenesis of Salmonella infections. We have characterized a gene, invE, that is necessary for Salmonella invasion of cultured epithelial cells. The predicted amino acid sequence of InvE showed significant homology to the Yersinia outer membrane protein YopN (LcrE). Strains of Salmonella carrying mutations in invE were unable to penetrate Henle-407 human intestinal cells and Madin-Darby canine kidney cells, although they were fully capable of attaching to the same cells. Unlike wild-type Salmonella typhimurium, invE mutants failed to change the intracellular free calcium levels or the distribution of polymerized actin in cultured epithelial cells; neither did they alter the normal architecture of the microvilli of polarized Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. Wild-type S. typhimurium was able to rescue the invasive phenotype of the invE mutants in simultaneous infections of cultured epithelial cells although it did not rescue the Escherichia coli strain RDEC-1. We hypothesize that invE mutants are deficient in triggering the intracellular events that lead to bacterial internalization.
Full text
PDF

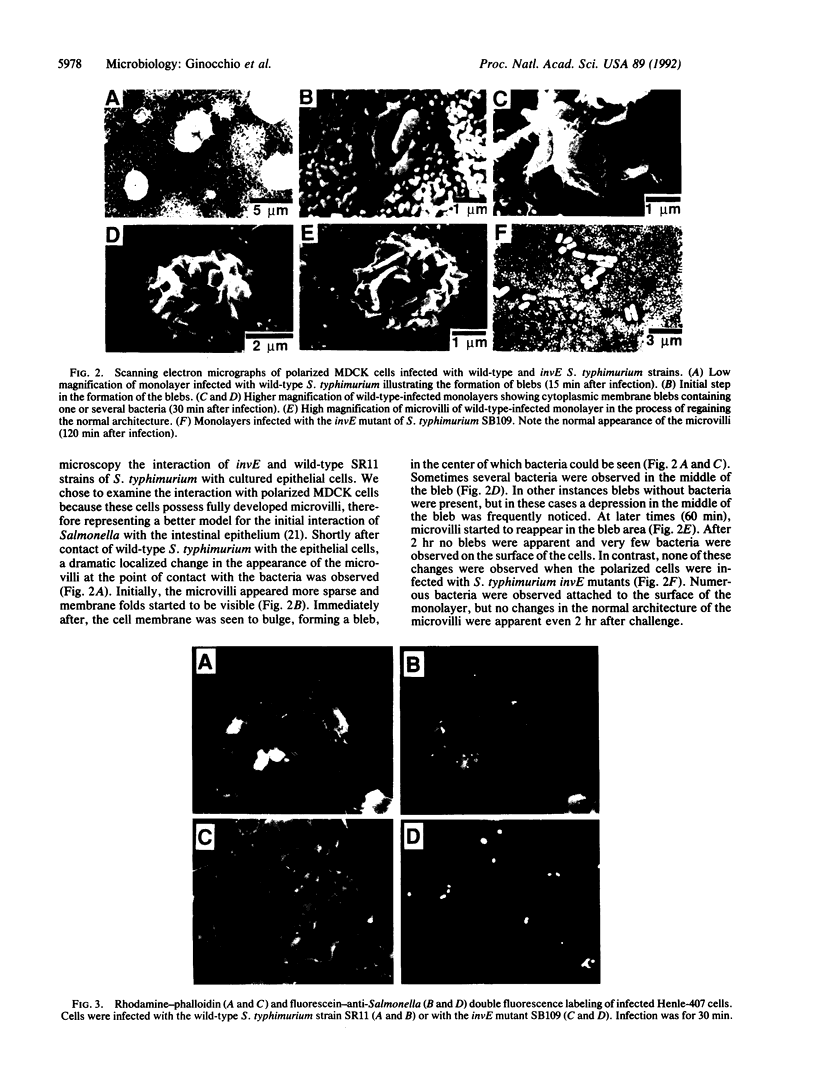


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brundage R. A., Fogarty K. E., Tuft R. A., Fay F. S. Calcium gradients underlying polarization and chemotaxis of eosinophils. Science. 1991 Nov 1;254(5032):703–706. doi: 10.1126/science.1948048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukholm G. Effect of cytochalasin B and dihydrocytochalasin B on invasiveness of entero-invasive bacteria in HEp-2 cell cultures. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1984 Jun;92(3):145–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1984.tb02809.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheney C. P., Schad P. A., Formal S. B., Boedeker E. C. Species specificity of in vitro Escherichia coli adherence to host intestinal cell membranes and its correlation with in vivo colonization and infectivity. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):1019–1027. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.1019-1027.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Close T. J., Rodriguez R. L. Construction and characterization of the chloramphenicol-resistance gene cartridge: a new approach to the transcriptional mapping of extrachromosomal elements. Gene. 1982 Dec;20(2):305–316. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90048-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsinghorst E. A., Baron L. S., Kopecko D. J. Penetration of human intestinal epithelial cells by Salmonella: molecular cloning and expression of Salmonella typhi invasion determinants in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5173–5177. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Falkow S. Salmonella interactions with polarized human intestinal Caco-2 epithelial cells. J Infect Dis. 1990 Nov;162(5):1096–1106. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.5.1096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Gumbiner B., Falkow S. Penetration of Salmonella through a polarized Madin-Darby canine kidney epithelial cell monolayer. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;107(1):221–230. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.1.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Starnbach M. N., Francis C. L., Stocker B. A., Chatfield S., Dougan G., Falkow S. Identification and characterization of TnphoA mutants of Salmonella that are unable to pass through a polarized MDCK epithelial cell monolayer. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Nov;2(6):757–766. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00087.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsberg A., Viitanen A. M., Skurnik M., Wolf-Watz H. The surface-located YopN protein is involved in calcium signal transduction in Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Apr;5(4):977–986. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00773.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galán J. E., Curtiss R., 3rd Cloning and molecular characterization of genes whose products allow Salmonella typhimurium to penetrate tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6383–6387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galán J. E., Curtiss R., 3rd Distribution of the invA, -B, -C, and -D genes of Salmonella typhimurium among other Salmonella serovars: invA mutants of Salmonella typhi are deficient for entry into mammalian cells. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):2901–2908. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.2901-2908.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galán J. E., Curtiss R., 3rd Expression of Salmonella typhimurium genes required for invasion is regulated by changes in DNA supercoiling. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1879–1885. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1879-1885.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III in DNA sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:156–165. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchin B. W., Dobson P. R., Brown B. L., Hardcastle J., Hardcastle P. T., Taylor C. J. Measurement of intracellular mediators in enterocytes isolated from jejunal biopsy specimens of control and cystic fibrosis patients. Gut. 1991 Aug;32(8):893–899. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.8.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kihlström E., Nilsson L. Endocytosis of Salmonella typhimurium 395 MS and MR10 by HeLa cells. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1977 Oct;85B(5):322–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1977.tb01982.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohbata S., Yokoyama H., Yabuuchi E. Cytopathogenic effect of Salmonella typhi GIFU 10007 on M cells of murine ileal Peyer's patches in ligated ileal loops: an ultrastructural study. Microbiol Immunol. 1986;30(12):1225–1237. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1986.tb03055.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. A., Jones B. D., Falkow S. Identification of a Salmonella typhimurium invasion locus by selection for hyperinvasive mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1847–1851. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S. L., Ezaki T., Miura H., Matsui K., Yabuuchi E. Intact motility as a Salmonella typhi invasion-related factor. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1967–1973. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1967-1973.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARMUR J., DOTY P. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its thermal denaturation temperature. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jul;5:109–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks P. W., Maxfield F. R. Local and global changes in cytosolic free calcium in neutrophils during chemotaxis and phagocytosis. Cell Calcium. 1990 Feb-Mar;11(2-3):181–190. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(90)90069-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straley S. C. The low-Ca2+ response virulence regulon of human-pathogenic Yersiniae. Microb Pathog. 1991 Feb;10(2):87–91. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(91)90069-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi A. Electron microscope studies of experimental Salmonella infection. I. Penetration into the intestinal epithelium by Salmonella typhimurium. Am J Pathol. 1967 Jan;50(1):109–136. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. L., Blinks J. R., Reynolds G. Contractile basis of ameboid movement. VII. Aequorin luminescence during ameboid movement, endocytosis, and capping. J Cell Biol. 1980 Aug;86(2):599–607. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.2.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viitanen A. M., Toivanen P., Skurnik M. The lcrE gene is part of an operon in the lcr region of Yersinia enterocolitica O:3. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3152–3162. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3152-3162.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





