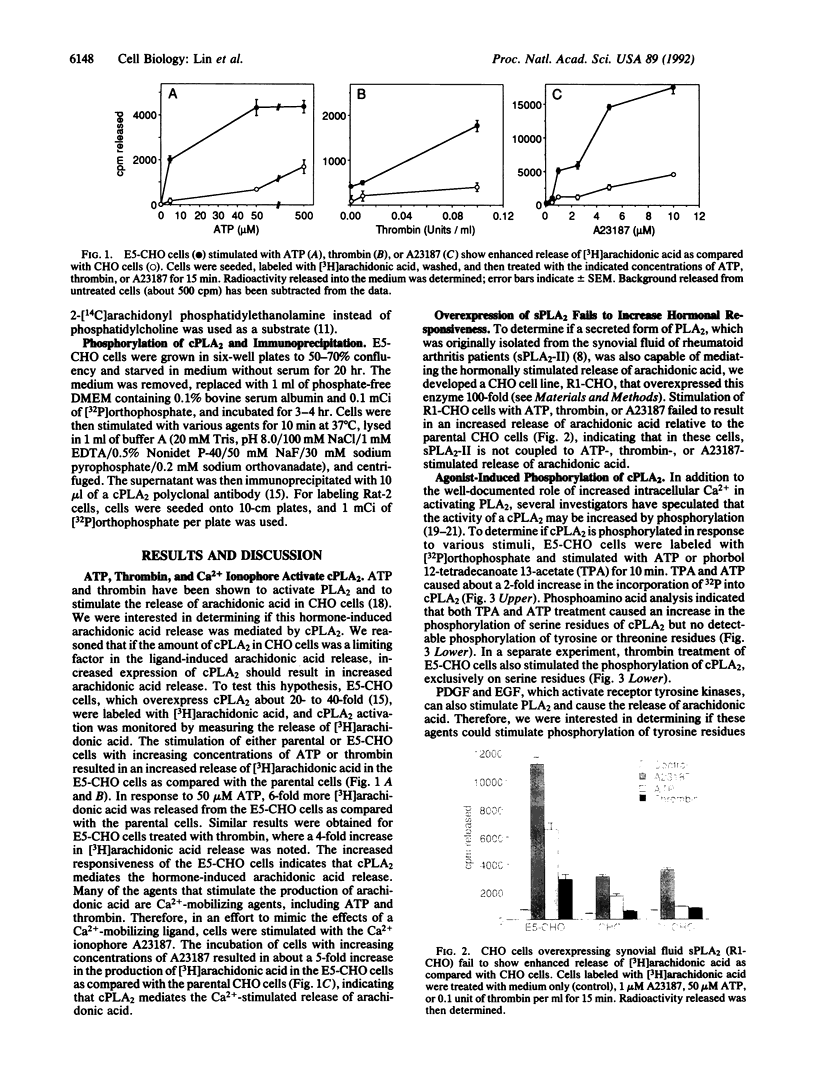
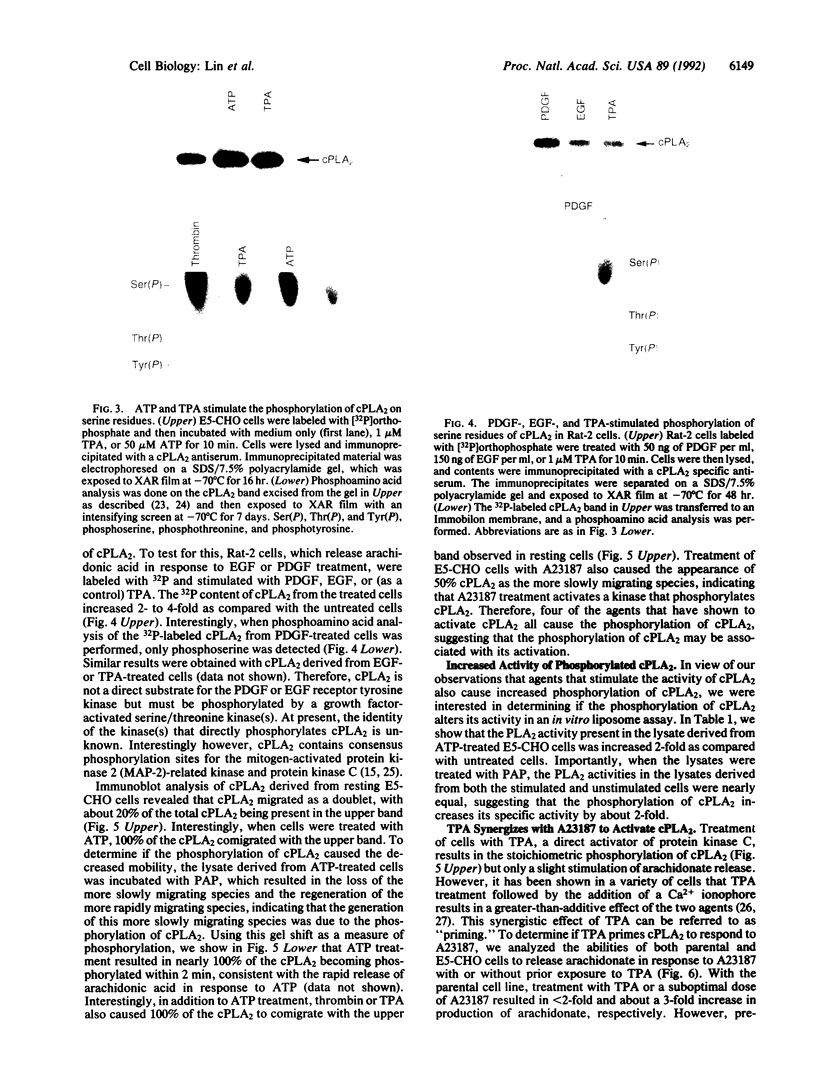
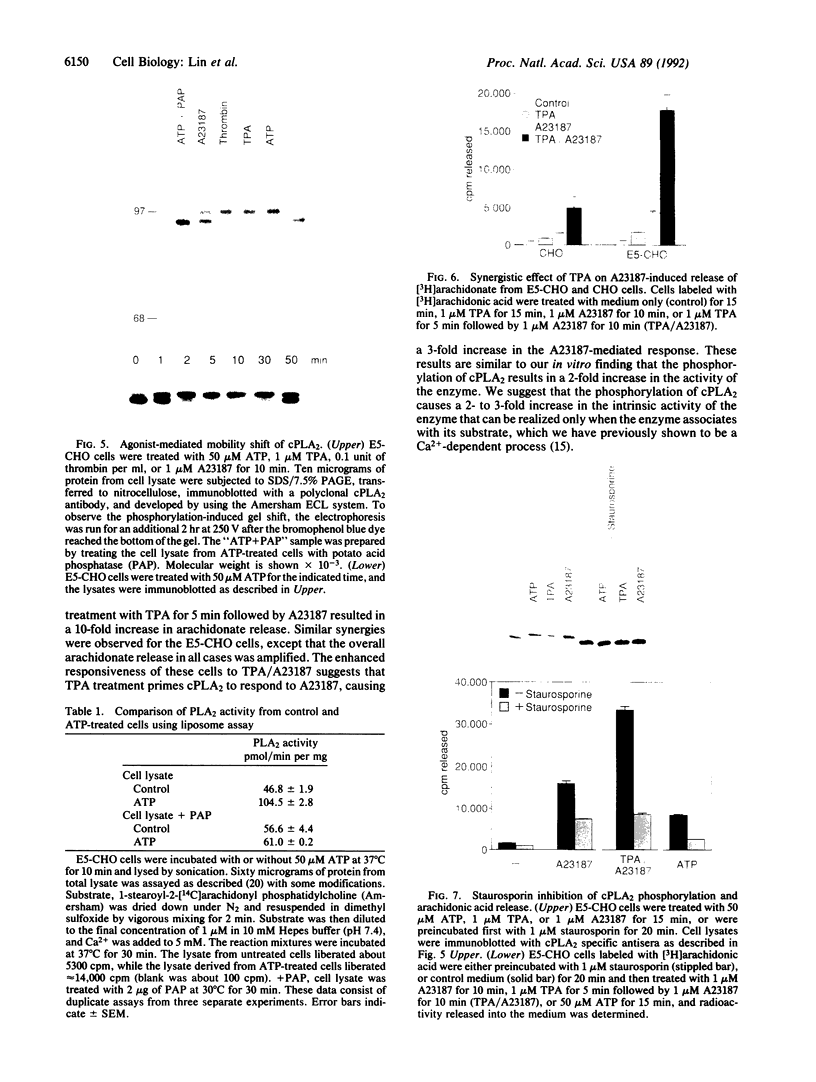
Abstract
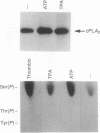
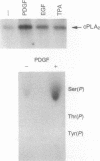
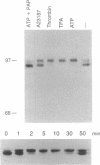
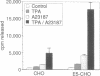
Cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2) binds to natural membrane vesicles in a Ca(2+)-dependent fashion, resulting in the selective release of arachidonic acid, thus implicating cPLA2 in the hormonally regulated production of eicosanoids. Here we report that the treatment of Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells overexpressing cPLA2 with ATP or thrombin resulted in an increased release of arachidonic acid as compared with parental CHO cells, demonstrating the hormonal coupling of cPLA2. In contrast, CHO cells overexpressing a secreted form of mammalian PLA2 (sPLA2-II) failed to show any increased hormonal responsiveness. Interestingly, we have noted that the activation of cPLA2 with a wide variety of agents stimulates the phosphorylation of cPLA2 on serine residues. Pretreatment of cells with staurosporin blocked the ATP-mediated phosphorylation of cPLA2 and strongly inhibited the activation of the enzyme. Increased cPLA2 activity was also observed in lysates prepared from ATP-treated cells and was sensitive to phosphatase treatment. These results suggest that in addition to Ca2+, the phosphorylation of cPLA2 plays an important role in the agonist-induced activation of cPLA2.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
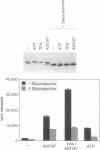
- Alvarez E., Northwood I. C., Gonzalez F. A., Latour D. A., Seth A., Abate C., Curran T., Davis R. J. Pro-Leu-Ser/Thr-Pro is a consensus primary sequence for substrate protein phosphorylation. Characterization of the phosphorylation of c-myc and c-jun proteins by an epidermal growth factor receptor threonine 669 protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15277–15285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonventre J. V., Gronich J. H., Nemenoff R. A. Epidermal growth factor enhances glomerular mesangial cell soluble phospholipase A2 activity. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 25;265(9):4934–4938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch R. M., Axelrod J. Dissociation of bradykinin-induced prostaglandin formation from phosphatidylinositol turnover in Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts: evidence for G protein regulation of phospholipase A2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6374–6378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. D., Lin L. L., Kriz R. W., Ramesha C. S., Sultzman L. A., Lin A. Y., Milona N., Knopf J. L. A novel arachidonic acid-selective cytosolic PLA2 contains a Ca(2+)-dependent translocation domain with homology to PKC and GAP. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1043–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90556-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. D., Milona N., Knopf J. L. Purification of a 110-kilodalton cytosolic phospholipase A2 from the human monocytic cell line U937. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7708–7712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson F. F., Dennis E. A. Evolutionary relationships and implications for the regulation of phospholipase A2 from snake venom to human secreted forms. J Mol Evol. 1990 Sep;31(3):228–238. doi: 10.1007/BF02109500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg H. J., Viegas M. M., Margolis B. L., Schlessinger J., Skorecki K. L. The tyrosine kinase activity of the epidermal-growth-factor receptor is necessary for phospholipase A2 activation. Biochem J. 1990 Apr 15;267(2):461–465. doi: 10.1042/bj2670461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronich J. H., Bonventre J. V., Nemenoff R. A. Identification and characterization of a hormonally regulated form of phospholipase A2 in rat renal mesangial cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16645–16651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronich J. H., Bonventre J. V., Nemenoff R. A. Purification of a high-molecular-mass form of phospholipase A2 from rat kidney activated at physiological calcium concentrations. Biochem J. 1990 Oct 1;271(1):37–43. doi: 10.1042/bj2710037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S. K., Diez E., Heasley L. E., Osawa S., Johnson G. L. A G protein mutant that inhibits thrombin and purinergic receptor activation of phospholipase A2. Science. 1990 Aug 10;249(4969):662–666. doi: 10.1126/science.2166341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. J. Platelet activating factor: a biologically active phosphoglyceride. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:483–509. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho A. K., Klein D. C. Activation of alpha 1-adrenoceptors, protein kinase C, or treatment with intracellular free Ca2+ elevating agents increases pineal phospholipase A2 activity. Evidence that protein kinase C may participate in Ca2+-dependent alpha 1-adrenergic stimulation of pineal phospholipase A2 activity. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11764–11770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Sefton B. M. Transforming gene product of Rous sarcoma virus phosphorylates tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1311–1315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F. How is the level of free arachidonic acid controlled in mammalian cells? Biochem J. 1982 Apr 15;204(1):3–16. doi: 10.1042/bj2040003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Sefton B. M. Acid and base hydrolysis of phosphoproteins bound to immobilon facilitates analysis of phosphoamino acids in gel-fractionated proteins. Anal Biochem. 1989 Jan;176(1):22–27. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90266-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim D. K., Kudo I., Inoue K. Purification and characterization of rabbit platelet cytosolic phospholipase A2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 24;1083(1):80–88. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(91)90127-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. M., Hession C., Johansen B., Hayes G., McGray P., Chow E. P., Tizard R., Pepinsky R. B. Structure and properties of a human non-pancreatic phospholipase A2. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5768–5775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. M., Roberts E. F., Manetta J., Putnam J. E. The Ca2(+)-sensitive cytosolic phospholipase A2 is a 100-kDa protein in human monoblast U937 cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 15;266(8):5268–5272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre T. M., Reinhold S. L., Prescott S. M., Zimmerman G. A. Protein kinase C activity appears to be required for the synthesis of platelet-activating factor and leukotriene B4 by human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15370–15376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murayama T., Kajiyama Y., Nomura Y. Histamine-stimulated and GTP-binding proteins-mediated phospholipase A2 activation in rabbit platelets. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4290–4295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuelsson B., Dahlén S. E., Lindgren J. A., Rouzer C. A., Serhan C. N. Leukotrienes and lipoxins: structures, biosynthesis, and biological effects. Science. 1987 Sep 4;237(4819):1171–1176. doi: 10.1126/science.2820055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalkwijk C. G., Märki F., Van den Bosch H. Studies on the acyl-chain selectivity of cellular phospholipases A2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 1;1044(1):139–146. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(90)90229-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D. L., White S. P., Otwinowski Z., Yuan W., Gelb M. H., Sigler P. B. Interfacial catalysis: the mechanism of phospholipase A2. Science. 1990 Dec 14;250(4987):1541–1546. doi: 10.1126/science.2274785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seilhamer J. J., Pruzanski W., Vadas P., Plant S., Miller J. A., Kloss J., Johnson L. K. Cloning and recombinant expression of phospholipase A2 present in rheumatoid arthritic synovial fluid. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5335–5338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaoki T., Nomoto H., Takahashi I., Kato Y., Morimoto M., Tomita F. Staurosporine, a potent inhibitor of phospholipid/Ca++dependent protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 13;135(2):397–402. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thunnissen M. M., Ab E., Kalk K. H., Drenth J., Dijkstra B. W., Kuipers O. P., Dijkman R., de Haas G. H., Verheij H. M. X-ray structure of phospholipase A2 complexed with a substrate-derived inhibitor. Nature. 1990 Oct 18;347(6294):689–691. doi: 10.1038/347689a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]