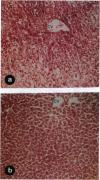
Abstract
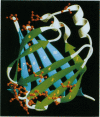
Molecular cloning of components of protective antigenic preparations has suggested that related parasite fatty acid-binding proteins could form the basis of the protective immune crossreactivity between the parasitic trematode worms Fasciola hepatica and Schistosoma mansoni. Molecular models of the two parasite proteins showed that both molecules adopt the same basic three-dimensional structure, consisting of a barrel-shaped molecule formed by 10 antiparallel beta-pleated strands joined by short loops, and revealed the likely presence of crossreactive, discontinuous epitopes principally derived from amino acids in the C-terminal portions of the molecules. A recombinant form of the S. mansoni antigen, rSm14, protected outbred Swiss mice by up to 67% against challenge with S. mansoni cercariae in the absence of adjuvant and without provoking any observable autoimmune response. The same antigen also provided complete protection against challenge with F. hepatica metacercariae in the same animal model. The results suggest that it may be possible to produce a single vaccine that would be effective against at least two parasites, F. hepatica and S. mansoni, of veterinary and human importance, respectively.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balloul J. M., Grzych J. M., Pierce R. J., Capron A. A purified 28,000 dalton protein from Schistosoma mansoni adult worms protects rats and mice against experimental schistosomiasis. J Immunol. 1987 May 15;138(10):3448–3453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banaszak L., Winter N., Xu Z., Bernlohr D. A., Cowan S., Jones T. A. Lipid-binding proteins: a family of fatty acid and retinoid transport proteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1994;45:89–151. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60639-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton G. J., Sternberg M. J. A strategy for the rapid multiple alignment of protein sequences. Confidence levels from tertiary structure comparisons. J Mol Biol. 1987 Nov 20;198(2):327–337. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90316-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker M. M., Kalinna B. H., Waine G. J., McManus D. P. Gene cloning, overproduction and purification of a functionally active cytoplasmic fatty acid-binding protein (Sj-FABPC) from the human blood fluke Schistosoma japonicum. Gene. 1994 Oct 21;148(2):321–325. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90706-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bleasby A. J., Wootton J. C. Construction of validated, non-redundant composite protein sequence databases. Protein Eng. 1990 Jan;3(3):153–159. doi: 10.1093/protein/3.3.153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillyer G. V., Haroun E. T., Hernandez A., de Galanes M. S. Acquired resistance to Fasciola hepatica in cattle using a purified adult worm antigen. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1987 Sep;37(2):363–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillyer G. V. Immunity of schistosomes using heterologous trematode antigens--a review. Vet Parasitol. 1984 Jun;14(3-4):263–283. doi: 10.1016/0304-4017(84)90096-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillyer G. V. Induction of immunity in mice to Fasciola hepatica with a Fasciola/Schistosoma cross-reactive defined immunity antigen. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1985 Nov;34(6):1127–1131. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1985.34.1127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. A., Bergfors T., Sedzik J., Unge T. The three-dimensional structure of P2 myelin protein. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1597–1604. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02985.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanar D. E., Pearce E. J., James S. L., Sher A. Identification of paramyosin as schistosome antigen recognized by intradermally vaccinated mice. Science. 1986 Oct 31;234(4776):593–596. doi: 10.1126/science.3094144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüthy R., Bowie J. U., Eisenberg D. Assessment of protein models with three-dimensional profiles. Nature. 1992 Mar 5;356(6364):83–85. doi: 10.1038/356083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser D., Tendler M., Griffiths G., Klinkert M. Q. A 14-kDa Schistosoma mansoni polypeptide is homologous to a gene family of fatty acid binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 5;266(13):8447–8454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Fahrnow A., Egner U., Jones T. A., Rüdel H., Spener F., Saenger W. Three-dimensional structure of fatty-acid-binding protein from bovine heart. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Jul 15;199(2):271–276. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16120.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Pérez J., Rodríguez-Medina J. R., García-Blanco M. A., Hillyer G. V. Fasciola hepatica: molecular cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression of a gene encoding a polypeptide homologous to a Schistosoma mansoni fatty acid-binding protein. Exp Parasitol. 1992 Jun;74(4):400–407. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(92)90202-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacchettini J. C., Gordon J. I., Banaszak L. J. Crystal structure of rat intestinal fatty-acid-binding protein. Refinement and analysis of the Escherichia coli-derived protein with bound palmitate. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jul 20;208(2):327–339. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90392-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacchettini J. C., Gordon J. I., Banaszak L. J. The structure of crystalline Escherichia coli-derived rat intestinal fatty acid-binding protein at 2.5-A resolution. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5815–5819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soisson L. A., Reid G. D., Farah I. O., Nyindo M., Strand M. Protective immunity in baboons vaccinated with a recombinant antigen or radiation-attenuated cercariae of Schistosoma mansoni is antibody-dependent. J Immunol. 1993 Nov 1;151(9):4782–4789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tendler M., Pinto R. M., Oliveira Lima A., Gebara G., Katz N. Schistosoma mansoni: vaccination with adult worm antigens. Int J Parasitol. 1986 Aug;16(4):347–352. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(86)90113-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornton J. M., Edwards M. S., Taylor W. R., Barlow D. J. Location of 'continuous' antigenic determinants in the protruding regions of proteins. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):409–413. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04226.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vriend G. WHAT IF: a molecular modeling and drug design program. J Mol Graph. 1990 Mar;8(1):52-6, 29. doi: 10.1016/0263-7855(90)80070-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westhof E., Altschuh D., Moras D., Bloomer A. C., Mondragon A., Klug A., Van Regenmortel M. H. Correlation between segmental mobility and the location of antigenic determinants in proteins. Nature. 1984 Sep 13;311(5982):123–126. doi: 10.1038/311123a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright M. D., Henkle K. J., Mitchell G. F. An immunogenic Mr 23,000 integral membrane protein of Schistosoma mansoni worms that closely resembles a human tumor-associated antigen. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 15;144(8):3195–3200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Z., Bernlohr D. A., Banaszak L. J. Crystal structure of recombinant murine adipocyte lipid-binding protein. Biochemistry. 1992 Apr 7;31(13):3484–3492. doi: 10.1021/bi00128a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanotti G., Scapin G., Spadon P., Veerkamp J. H., Sacchettini J. C. Three-dimensional structure of recombinant human muscle fatty acid-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 15;267(26):18541–18550. doi: 10.2210/pdb2hmb/pdb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]