Abstract
Objective. There is increasing interest in patients with metachronous (MBC) and synchronous breast cancer (SBC). The objective of this study was to evaluate the occurrence and outcome of MBCs and SBCs. Methods. A retrospective study on women operated in our department for breast cancer between 2002 and 2005 was carried out. Patients were divided into three groups: women with MBC, SBC, and unilateral breast cancer (UBC). Moreover, we performed a meta-analysis of the English literature about multiple breast cancers between 2000 and 2011 taking into consideration their prevalence and overall survival (OS). Results. We identified 584 breast cancer patients: 16 women (3%) presented SBC and 40 MBC (7%, second cancer after 72-month follow-up IQR 40–145). Although the meta-analysis showed significant OS differences between MBC or SBC and UBC, we did not observe any significant OS difference among the three groups of our population. Anyway, we found a significant worse disease-free survival in MBC than UBC and a significant higher prevalence of radical surgery in MBC and SBC than UBC. Conclusions. Despite the low prevalence of MBC and SBC, the presence of a long time risk of MBC confirms the crucial role of ipsi- and contralateral mammographies in the postoperative follow-up.
1. Introduction
The increasing incidence rate of breast cancer (BC) and its long term survival, due to both an improved prognosis and a growing life expectancy, have brought interest in patients with a second primary metachronous (MBC) or synchronous breast cancer (SBC) [1–3]. In particular, BC represents about the 30–50% of all second primary malignancies in women affected by primary BC, who have a two-to-sixfold increased risk of developing a new primary cancer in the contralateral breast during their life [4–6], corresponding to a risk of 0.3–1.0% per year [7–12].
There is uncertainty in the literature whether developing a MBC or SBC influences the outcome. In fact, some studies suggest poor survival while others report similar survival compared to patients with unilateral breast cancer (UBC). In particular, women affected by SBCs seem to have a lower long term survival [13–15], even if this difference is not always significant. Moreover, there is conflicting evidence about the impact of SBCs and MBCs on the management of patients with regard to surgical treatment options, such as the role of prophylactic mastectomy. In fact, these patients undergo more often bilateral mastectomies rather than breast conserving interventions, although there are reports confirming the efficacy of less invasive management in bilateral breast cancer as for unilateral tumors [14, 16].
The objective of this study is to evaluate the occurrence of MBCs or SBCs and their outcome.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Retrospective Study
A retrospective cross-sectional study on women operated in our department for BC between January 2001 and December 2004 was carried out, with a follow-up of at least 5 years, within May 2011. In addition, we selected only women with the first diagnosis of cancer occurring between January 2001 and December 2004. Patients were divided into three groups based on the presence of multiple breast cancers and the time interval between their detection. In particular, according to most of the authors, we considered synchronous all second BCs detected within 6 months from the first diagnosis and located in the contralateral breast [17–19] and metachronous those diagnosed after 6 months from the first BC diagnosis in the contralateral breast or in the same breast but with different histology. The remaining women with a diagnosis of UBCs were considered as a control cohort.
Tumor pathological characteristics include size, histological type, nuclear/histologic grading, multicentricity, eventual presence of peritumoral vascular invasion (PVI), extensive in situ component (EIC), axillary lymph node status, lymph nodes extracapsular invasion (ExCp), estrogen (ER) and progesterone receptor (PR) status, HER-2/Neu expression, Mib-1(Ki-67) expression. The surgical specimens were examined fresh and the maximum tumor diameter was recorded after these were fixed in 10% buffered formalin. Histologically, the tumors were classified according to the World Health Organization criteria [20], as modified by Rosen and Oberman [21]. Tumor grade was evaluated following the recommendations of Elston and Ellis [22]. The occurrence of PVI was assessed according to Rosen and Oberman [21]. The expression of ER, PR, Her-2/Neu, and the tumor proliferative fraction (Mib1/Ki67) was evaluated immunohistochemically. ER and PR status and cell proliferation were recorded as percentage value. HER-2/Neu was considered positive when Her-2/Neu test resulted 3+ or 2+ with fish amplification and negative if value was 1+. ExCp was defined as the extracapsular growth of tumor cells, invasion of perinodal fat, or extranodal location of tumor cells. Tumor stage was defined according to the TNM classification of 2009 VII ed. (AJCC/UICC).
Data about patients' familial history were also collected, and, for the purpose of our retrospective study, a positive familial history was defined by the presence of a first- or second-degree relative with breast cancer. Moreover, data was collected about the patients' age, at both the first and the second diagnosis, weight, breast size and density, tobacco smoking habits, the tumor localization (breast side and quadrant), the diagnostic tool (objective examination, mammography, or ultrasonography), and the specific finding at the first and the second diagnosis. Then, we retrieved information also about the treatment received for the first and the second tumor and type of surgery performed.
The three groups (MBC, SBC, and UBC) were compared, taking into consideration the following outcomes: overall survival (OS), disease-free survival (DFS), overall mortality and cancer-related mortality, and locoregional and distant disease recurrence. The study was approved by the local ethics committee.
2.2. Meta-Analysis
To perform our meta-analysis we searched in the following sources: Medline, Cochrane database, EBESCO, and Google Scholar. We included in our search only the English literature published between 2000 and 2011 and used the following search keywords: synchronous and metachronous breast cancer, bilateral breast cancer. We took into consideration in our analysis every retrospective or prospective study that evaluated survival in patients affected by MBC, SBC, and UBC. All included studies were observational and we took into consideration only those studies which utilized a Cox proportional hazards regression model for calculating the survival difference among MBC, SBC, and UBC. In addition, we included only articles of which the full text was available for data retrieval. Then, three reviewers independently extracted data from the included studies onto a standard form. The data abstracted were relevant to predetermined measures (prevalence of disease and hazards ratios with 95% confidence interval). The hazard ratio in our meta-analysis was calculated from data obtained from published reports, using methods previously described [23]. Geographic locations, sites of treatment, and time frame for breast cancer diagnosis were recorded, in order to avoid any possible population overlap, and when these features suggested a population overlap between two reports the study with longer follow-up or a larger data set was utilized, while the other was excluded from the pooled analysis. To perform this meta-analysis we took into consideration the MOOSE guidelines [24].
2.3. Statistical Analysis
Data was analysed by R (version 2.13.1), considering significant P < 0.05. All continuous variables were tested for distribution normality with Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. Monovariate analysis was performed by analysis of variance, Kruskall-Wallis test, t-test, or Wilcoxon test in case of continuous variables and chi-square test or Fisher exact test in case of categorical variables. The OS expressed in months was calculated from both the first malignancies and considered for MBCs from both the first and the second diagnosis, taking into consideration the one from the second diagnosis for OS and DFS analysis. The 5-year survival rates were also computed. Differences between the survival Kaplan-Meyer curves for MBC, SBC, and UBC were tested by means of the log-rank test. Moreover, the Cox proportional hazards model was used in the multivariate survival analysis, and the Cohen kappa value (1 indicates a perfect agreement, 0 denotes the lack of agreement, and the P value indicates whether the estimated kappa value differs from 0) was used to test the agreement of the investigated tumor characteristics within the same patient. We investigated the agreement also calculating the percentage of tumors within the same subject presenting the same characteristics. In the meta-analysis, a summary statistic was calculated considering, where appropriate, the prevalence or hazards ratio for survival analysis. The random effect model was applied to calculate the pooled estimate, as heterogeneity between studies was expected, a priori and confirmed by Q statistic and I2 index. Furthermore, we used rank correlation test of funnel plot asymmetry to test the presence of any publication bias.
3. Results
3.1. Population Description and Prevalence of MBC and SBC
Among 736 patients operated for a breast pathology in our department during the study period, we identified 584 breast cancer patients with the first BC diagnosis made during the same period: 16 women (3%) presented SBC and 40 presented MBC (7%). The median time interval between the first and the second primary cancer diagnosis in case of MBC resulted 72 months (IQR 40–120), being the 59% of metachronous cancers diagnosed after the 5th year of follow-up and the 40% after the 10th. We had also one case of SBC which was treated with conservative methods and subsequently developed a MBC with different histology.
Table 1 shows the characteristics of our population. SBCs appeared in a significantly elder population, as well as the second cancer in the MBC group. SBCs had a higher prevalence of familial history of breast cancer than other patients. Moreover, second synchronous and metachronous tumors were more frequently detected through the mammographic follow-up (P < 0.05). There was also a significant higher prevalence of hormonal therapies in SBCs than UBCs (P < 0.05).
Table 1.
Population characteristics: data is presented, where appropriate, as mean value (±standard deviation) and one way ANOVA*, median value (interquartile range) and Kruskall-Wallis test**, or prevalence and chi-square test.
| UBC | 1st MBC | 2nd MBC | 1st SBC | 2nd SBC | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Women age (years)* | 58.71 (±15.47) | 56.54 (±13.68) | 64.38 (±13.41) | 64.94 (±14.72) | 65.25 (±14.15) | <0.05 |
| BMI (kg/m2)* | 26.74 (±5.24) | 26.17 (±6.14) | 25.18 (±4.64) | 0.556 | ||
| Time interval between 1st and 2nd MBC (months)** | 72 (40–120) | N/A | ||||
| Follow-up time** | 79 (70–85) | 97 (82–120) | 66 (23–82) | 79 (72–90) | <0.05 | |
| Tobacco smoke | 2.46% (13/528) | 0% (0/39) | 0% (0/16) | 0.500 | ||
| Familial history | 0.95% (5/528) | 0% (0/39) | 6.25% (1/16) | 0.094 | ||
| Mode of diagnosis | ||||||
| Unknown | 4.55% (24/528) | 2.56% (1/39) | 2.5% (1/40) | 0% (0/16) | 0% (0/16) | 0.709 |
| Objective examination | 46.78% (247/528) | 69.23% (27/39) | 30% (12/40) | 31.25% (5/16) | 12.5% (2/16) | <0.05 |
| Mammography | 36.17% (191/528) | 20.51% (8/39) | 57.5% (23/40) | 43.75% (7/16) | 62.5% (10/16) | <0.05 |
| Ultrasound | 12.5% (66/528) | 7.69% (3/39) | 10% (4/40) | 25% (4/16) | 25% (4/16) | 0.236 |
| Radiotherapy | 56.44% (241/427) | 64.86% (24/37) | 46.67% (7/15) | 0.442 | ||
| Chemotherapy | 45.88% (195/425) | 47.22% (17/36) | 57.14% (8/14) | 0.703 | ||
| Hormonal therapy | 70.85% (299/422) | 80.56% (29/36) | 100% (14/14) | <0.05 | ||
| Tamoxifen therapy | 44.13% (233/528) | 53.85% (21/39) | 62.5% (10/16) | 0.187 |
3.2. Tumor Characteristics and Outcome
Table 2 describes the tumors characteristics and highlights a higher prevalence of lobular invasive histology among SBCs and MBCs than UBCs, but this is statistically significant only between SBCs and UBCs. No significant difference was observed among the considered groups about the TNM classification at diagnosis.
Table 2.
Histology and TNM staging (AJCC/UICC) of the tumors at the time of diagnosis: in this table we present prevalences and P values referring to chi-square test.
| UBC | 1st MBC | 2nd MBC | 1st SBC | 2nd SBC | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Histology | ||||||
| Ductal invasive carcinoma | 65.91% (348/528) | 69.23% (27/39) | 65% (26/40) | 43.75% (7/16) | 68.75% (11/16) | 0.447 |
| Lobular invasive carcinoma | 8.9% (47/528) | 15.38% (6/39) | 12.5% (5/40) | 37.5% (6/16) | 6.25% (1/16) | <0.05 |
| Ductal and lobular invasive carcinoma | 13.45% (71/528) | 7.69% (3/39) | 5% (2/40) | 12.5% (2/16) | 6.25% (1/16) | 0.418 |
| Other invasive carcinomas | 3.41% (18/528) | 2.56% (1/39) | 0% (0/40) | 0% (0/16) | 6.25% (1/16) | 0.645 |
| Ductal in situ carcinoma | 7.39% (39/528) | 5.13% (2/39) | 17.5% (7/40) | 6.25% (1/16) | 6.25% (1/16) | 0.212 |
| Lobular in situ carcinoma | 0.38% (2/528) | 0% (0/39) | 0% (0/40) | 0% (0/16) | 0% (0/16) | 0.981 |
| Unknown | 0.57% (3/528) | 0% (0/39) | 0% (0/40) | 0% (0/16) | 6.25% (1/16) | 0.067 |
| Tumor (UICC) | ||||||
| Tis-T1 | 67.94% (356/524) | 68.42% (26/38) | 70% (28/40) | 62.5% (10/16) | 75% (12/16) | 0.957 |
| T2 | 24.43% (128/524) | 26.32% (10/38) | 22.5% (9/40) | 37.5% (6/16) | 18.75% (3/16) | 0.755 |
| T3-T4 | 7.63% (40/524) | 5.26% (2/38) | 7.5% (3/40) | 0% (0/16) | 6.25% (1/16) | 0.806 |
| Lymph nodes (UICC) | ||||||
| N0 | 66.86% (347/519) | 75.68% (28/37) | 70% (28/40) | 56.25% (9/16) | 93.75% (15/16) | 0.122 |
| N1 | 19.27% (100/519) | 16.22% (6/37) | 15% (6/40) | 18.75% (3/16) | 6.25% (1/16) | 0.690 |
| N2 | 7.51% (39/519) | 2.7% (1/37) | 10% (4/40) | 12.5% (2/16) | 0% (0/16) | 0.476 |
| N3 | 6.36% (33/519) | 5.41% (2/37) | 5% (2/40) | 12.5% (2/16) | 0% (0/16) | 0.679 |
In Table 3 we see that the first and the second MBCs presented a higher prevalence of grading G3 than UBCs, but this difference was significant only between the first MBCs and UBCs (P < 0.05). Furthermore, we observed a nonsignificant lower prevalence of grading G3 in SBCs than UBCs. First MBCs expressed also less frequently estrogen and progesterone receptors than UBCs (P < 0.05), and they had a significantly lower prevalence of multifocality (P < 0.05). SBCs presented the same prevalence of estrogen and progesterone receptors expression as UBCs but a significantly higher prevalence of multifocality and lymph node extracapsular invasion than UBCs (P < 0.05).
Table 3.
Other characteristics of the tumors: in this table we present prevalences and P values referring to chi-square test.
| UBC | 1st MBC | 2nd MBC | 1st SBC | 2nd SBC | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grading | ||||||
| G1 | 7.16% (35/489) | 7.69% (3/39) | 7.5% (3/40) | 12.5% (2/16) | 18.75% (3/16) | 0.480 |
| G2 | 67.48% (330/489) | 41.03% (16/39) | 55% (22/40) | 81.25% (13/16) | 68.75% (11/16) | <0.05 |
| G3 | 25.36% (124/489) | 51.28% (20/39) | 37.5% (15/40) | 6.25% (1/16) | 12.5% (2/16) | <0.05 |
| ER positivity | 73.3% (387/528) | 51.28% (20/39) | 67.5% (27/40) | 75% (12/16) | 81.25% (13/16) | <0.05 |
| PR positivity | 68.94% (364/528) | 43.59% (17/39) | 60% (24/40) | 75% (12/16) | 75% (12/16) | <0.05 |
| HER-2/Neu positivity | 8.9% (47/528) | 7.69% (3/39) | 12.5% (5/40) | 6.25% (1/16) | 6.25% (1/16) | 0.912 |
| Mib-1/Ki-67 (%) | ||||||
| 1 to 20 | 34.98% (85/243) | 57.14% (4/7) | 32% (8/25) | 57.14% (4/7) | 60% (3/5) | 0.376 |
| 20 to 30 | 18.11% (44/243) | 0% (0/7) | 12% (3/25) | 0% (0/7) | 0% (0/5) | 0.331 |
| >30 | 46.91% (114/243) | 42.86% (3/7) | 56% (14/25) | 42.86% (3/7) | 40% (2/5) | 0.911 |
| Multifocality | 26.7% (141/528) | 5.13% (2/39) | 27.5% (11/40) | 50% (8/16) | 18.75% (3/16) | <0.05 |
| Extended in situ component | 22.16% (117/528) | 17.95% (7/39) | 32.5% (13/40) | 25% (4/16) | 0% (0/16) | 0.110 |
| Peritumoral vascular invasion | 6.82% (36/528) | 5.13% (2/39) | 7.5% (3/40) | 6.25% (1/16) | 0% (0/16) | 0.850 |
| Comedo-like necrosis | 8.9% (47/528) | 2.56% (1/39) | 12.5% (5/40) | 6.25% (1/16) | 6.25% (1/16) | 0.581 |
| Lymph node isolated tumor cells | 3.6% (19/528) | 0% (0/39) | 0% (0/40) | 0% (0/16) | 0% (0/16) | 0.390 |
| Lymph node extracapsular invasion | 2.27% (12/528) | 0% (0/39) | 0% (0/40) | 12.5% (2/16) | 0% (0/16) | <0.05 |
The first and the second SBCs presented the same histological type in 44% of cases (7/16) (kappa 0.138, P 0.225), grading in 69% (11/16) (kappa 0.223, P 0.232), ER positivity in 69% (11/16) (kappa 0.200, P 0.261), and PR positivity in 69% (11/16) (kappa 0.200, P 0.261). The first and the second MBCs presented the same histological type in 42% of cases (17/40) (kappa 0.069, P 0.151), grading in 42% (17/40) (kappa 0.006, P 0.483), ER positivity in 40% (16/40) (kappa 0.029, P 0.585), and PR positivity in 45% (18/40) (kappa 0.156, P 0.097). In addition, the second metachronous tumors were ipsilateral in 13% (5/40) of cases and contralateral in 85% (34/40), and one case happened after previous bilateral synchronous cancers 2% (1/40).
We found also a significantly higher prevalence of mastectomy for the second MBCs than UBCs (52% versus 36%, P < 0.05) and for any SBCs than UBCs (56% versus 36%, P < 0.05), being the 50% of SBCs treated with bilateral mastectomy.
Analyzing the OS, no statistically significant difference was observed between the three groups (Figure 1). Anyway, women affected by SBCs and MBCs had lower prevalences of death for neoplasm than UBCs. Considering the DFS, locoregional relapse or distant metastasis happened more frequently during follow-up of MBCs and SBCs than UBCs. Anyway, in the Kaplan-Meier curves of DFS the log-rank test was statistically significant only between MBCs and UBCs (P < 0.05) (Figure 1). This difference was also statistically significant using the monovariate, multivariate, and Cox proportional hazards model with adjustment for tumor dimensions, histology, lymph nodes status, age at diagnosis, and BMI (the HR are reported in Table 4). The 5-year OS in UBCs was 97% (95% CI: 95%–98%), while among MBCs and SBCs it was 100% (95% CI: 100%-100%). In addition, the 5-year DFS was 90% (95% CI: 88%–93%) in UBCs, 79% (95% CI: 66%–94%) in second MBCs, and 94% (95% CI: 83%–100%) in SBCs.
Figure 1.
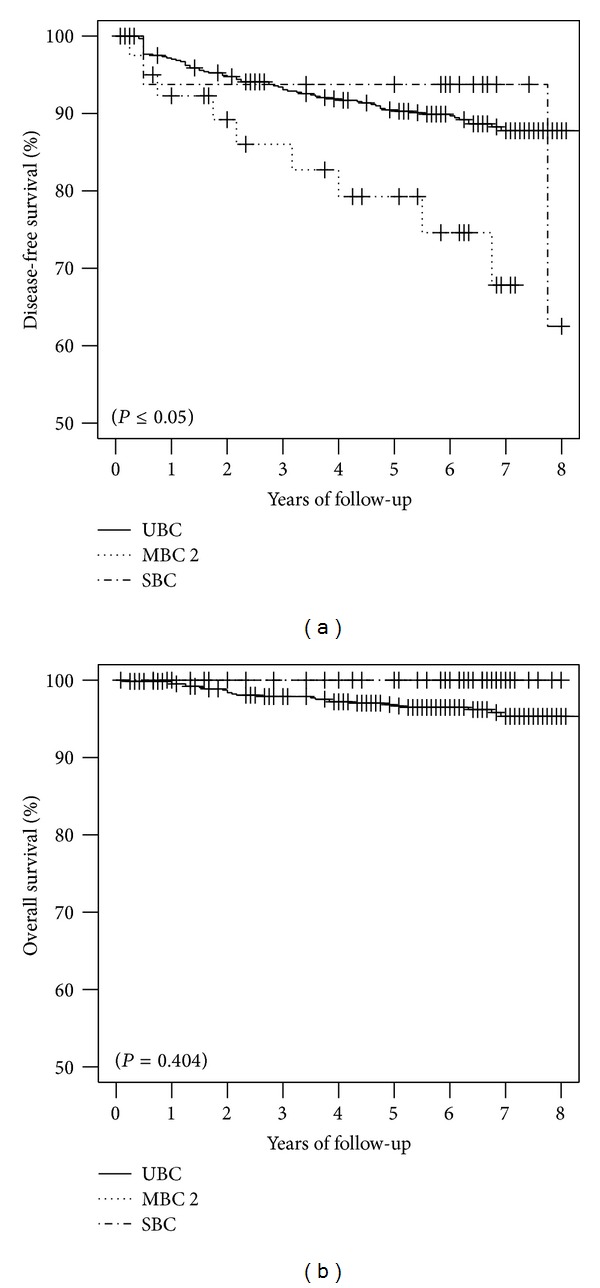
Kaplan-Meyer curves and P values calculated by log-rank test. We have on the left side the curves of disease free survival and on the right side the curves of overall survival.
Table 4.
Crude and adjusted* hazard ratios (HR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) for SBC and MBC and the risk of locoregional recurrence and distant metastasis in comparison with UBC (Cox proportional hazards model).
| HR (95% CI) | P | HR (95% CI)* | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UBC | 1 | 1 | ||
| MBC | 2.03 (1.01–4.08) | <0.05 | 2.70 (1.04–7.03) | <0.05 |
| SBC | 0.84 (0.21–3.43) | 0.809 | 1.42 (0.33–6.21) | 0.639 |
A shorter time interval between the first and the second tumor in women affected by MBCs did not predict a worse OS or DFS but resulted to be associated with a significantly lower hormone receptors positivity (P < 0.05) of the second MBC. Moreover, patients affected by MBCs, appearing within 47 months of follow-up, resulted to be older and to have a higher prevalence of lobular invasive cancers than patients with MBCs appearing after 47 months (P < 0.05) (Table 5). Furthermore, we observed a higher prevalence of G3 grading, peritumoral vascular invasion, extended in situ component, and multifocality among second MBCs appearing within 47 months of follow-up than UBCs (p n.s.) (Table 5).
Table 5.
Characteristics of second MBC stratified per time interval after diagnosis of first MBC. We considered as cutoff the median time interval that was 47 months. In this table we present mean values (±standard deviation) and one way ANOVA* or prevalences and chi-square test.
| ≤47 moths | >47 months | P | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Women age (years)* | 63.14 (±14.22) | 54.67 (±13.47) | <0.05 |
| BMI (kg/m2)* | 25.2 (±4.01) | 26.6 (±7.08) | 0.448 |
| Multifocality | 28.57% (6/21) | 26.32% (5/19) | 0.873 |
| Extended in situ component | 42.86% (9/21) | 21.05% (4/19) | 0.141 |
| Peritumoral vascular invasion | 9.52% (2/21) | 5.26% (1/19) | 0.609 |
| ER positivity | 57.14% (12/21) | 78.95% (15/19) | 0.141 |
| PR positivity | 42.86% (9/21) | 78.95% (15/19) | <0.05 |
| HER-2/Neu positivity | 14.29% (3/21) | 10.53% (2/19) | 0.720 |
| Histology | |||
| Ductal invasive carcinoma | 61.9% (13/21) | 68.42% (13/19) | 0.666 |
| Lobular invasive carcinoma | 23.81% (5/21) | 0% (0/19) | <0.05 |
| Ductal and lobular invasive carcinoma | 4.76% (1/21) | 5.26% (1/19) | 0.942 |
| Ductal in situ carcinoma | 9.52% (2/21) | 26.32% (5/19) | 0.163 |
| Grading | |||
| G1 | 14.29% (3/21) | 0% (0/19) | 0.087 |
| G2 | 47.62% (10/21) | 63.16% (12/19) | 0.324 |
| G3 | 38.1% (8/21) | 36.84% (7/19) | 0.935 |
| Mib-1/Ki-67 (%) | |||
| 1 to 20 | 43.75% (7/16) | 11.11% (1/9) | 0.093 |
| 20 to 30 | 12.5% (2/16) | 11.11% (1/9) | 0.918 |
| >30 | 43.75% (7/16) | 77.78% (7/9) | 0.100 |
3.3. Review of the Literature and Meta-Analysis
We found 1840 pertinent abstracts published between January 2000 and August 2011. Then, we selected and retrieved 24 full articles to be candidate for the analysis, 7 of which resulted to be appropriate for the meta-analysis comparing SBCs with UBCs and 6 comparing MBCs with UBCs. Table 6 summarized the data characteristics of the included studies [7, 15, 17–19, 25, 26]. Flow diagram depicting selection of articles for review is included as Supplemental Figure 1 in the Supplementary Materials available online at http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/250727 and more details about included and excluded studies are reported in Supplemental List 1.
Table 6.
Description of the studies included in our meta-analysis.*Mean, **median, and ¶follow-up divided between SBC, MBC, and UBC.
| Study | MBC/SBC | MBC after (months) | Follow-up years | Study design | Years considered | Follow-up until | Months between metachronous |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heron et al. 2000 [15] | MBC/SBC | 12 | 5/7/3∗∗¶ | Hosp.-based | 60/95 | ′95 | 44 |
| Polednak 2003 [26] | SBC | 3 | — | Pop.-based | 95/99 | ′00 | NA |
| Takahashi et al. 2005 [19] | MBC/SBC | 6 | 7* | Hosp.-based | 60/01 | ′01 | 113 |
| Verkooijen et al. 2007 [18] | MBC/SBC | 6 | 7** | Pop.-based | 70/02 | ′02 | 80 |
| Kuo et al. 2009 [17] | MBC/SBC | 6 | 8* | Hosp.-based | 90/99 | ′04 | 36 |
| Vuoto et al. 2010 [7] | MBC/SBC | 12 | 8/13/—∗¶ | Hosp.-based | 70/07 | ′07 | 81 |
| Beckmann et al. 2011 [25] | MBC/SBC | 3 | 6* | Pop.-based | 97/07 | ′09 | 34 |
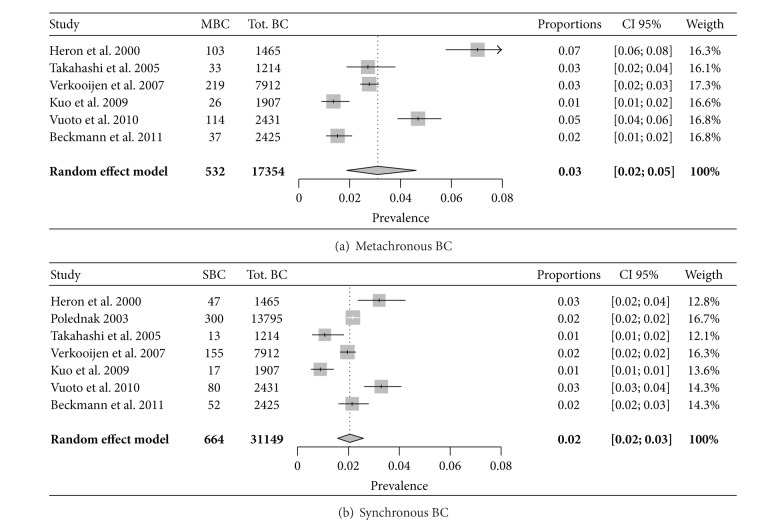
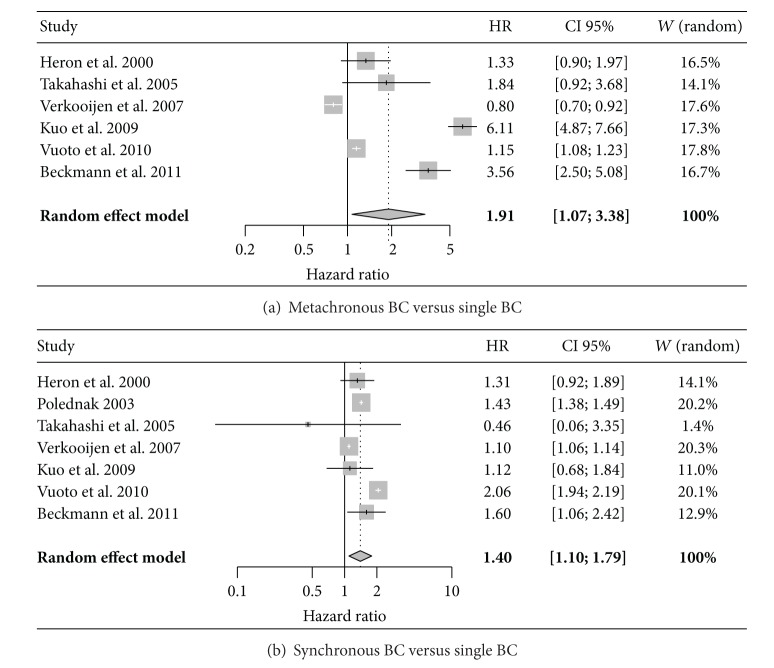
Through the meta-analysis, the prevalence of MBCs and SBCs was, respectively, 3% (CI 95%: 2–5%) and 2% (2-3%) (Figure 2). Moreover, considering the included studies, MBCs and SBCs presented a significantly unfavorable outcome (in terms of OS) in comparison to UBCs (Figure 3).
Figure 2.
Meta-analysis of SBCs and MBCs prevalence. (a) Heterogeneity: I2 = 95.9%, Q = 121.1, df = 5, and P < 0.0001; (b) heterogeneity: I2 = 87.7%, Q = 48.7, df = 6, and P < 0.0001.
Figure 3.
Meta-analysis of SBCs and MBCs overall survival statistics. (a) Heterogeneity: I2 = 99%, Q = 477.6, df = 5, and P < 0.0001; (b) heterogeneity: I2 = 98.3%, Q = 344.8, df = 6, and P < 0.0001.
4. Discussion
In our population, the prevalence of MBCs and SBCs resulted, respectively, 7% and 3%. We did not find significant differences in terms of OS among MBCs, SBCs, and UBCs. In particular no cancer-related mortality was observed among MBC and SBC patients, and there was no significant difference in death for other causes among the three groups. In our meta-analysis, a significantly more favourable outcome, in terms of longer survival, was observed in UBCs than in MBCs or SBCs. Rank correlation test of funnel plot asymmetry was not significant in all the performed analysis excluding possible publication bias.
4.1. MBC and SBC Prevalence
The incidence of MBC and SBC is relatively low, ranging in the literature from about 1% to as high as 21% [4, 27–30]. In our population, the SBCs prevalence resulted comparable to that described by other authors (Figure 2), but the meta-analysis of MBCs prevalence shows a great variability among the different studies (Figure 2), probably due to the significant difference of follow-up length and to the general disagreement about the definition of “metachronous” cancer (Table 6). In fact, the different authors defined as “metachronous” those tumors appearing after different time intervals from the first BC diagnosis, starting from a month and up to 5 years [31, 32]. In the more recent published studies, 3, 6, and 12 months are the most frequently considered time cutoffs to divide between SBCs and MBCs. The distinction between “metachronous” and “synchronous” is only time dependent and despite an evident synchronicity of the clinical appearance, which probably corresponds to a similarity in the time of cell transformation beginning, there may be a synchronicity of presence at the time of the first diagnosis even in the absence of any clinical or imaging evidence of the second tumor that leads this tumor to be defined clinically as “metachronous.” Therefore, although most of the authors define as “synchronous” breast cancers which present between the time of the primary tumor diagnosis and one year from it [7, 15, 17–19, 25, 26], Bloom and colleagues extended the “synchronous” BC definition to five years from the first diagnosis [32]. In our study, we chose the “synchronous” definition for every cancer presenting within 6 months from the original diagnosis.
In accordance with the literature, MBCs represented the majority of multiple breast cancers in our retrospective study (7% versus 3%) and affected women were younger at the time of the first diagnosis than others [7], whereas SBCs appeared in elderly women [33]. A possible explanation for such age difference may be the longer life expectancy of younger women with tumors of favorable prognosis who are therefore at high risk of developing a second breast malignancy [34]. Another consideration that could justify the older age in SBCs than MBCs or other cancers is that many older women neglect their health and find out their disease (or better accept the disease they already found out) in a more advanced stage, so that it may be just more statistically probable to detect another breast cancer (which in other circumstances would have been considered metachronous).
4.2. MBC and SBC Characteristics
MBCs presented higher grading and lower hormone receptors expression than UBCs. Meanwhile, SBCs presented higher hormone receptors expression than UBCs and lower grading than MBCs. The higher prevalence of estrogen receptors positivity in SBCs is confirmed also by the literature [33]. Anyway, both MBCs and SBCs had higher incidence of some histological negative prognostic factors (lobular invasive histology, high grading, multifocality, and lymph node extracapsular invasion).
Our data about the tumor hormonal status and histology demonstrate a lower concordance between the two tumors than the literature. In fact, Kheirelseid and colleagues found out a histological and ER-status concordance between the two BC diagnoses of, respectively, 79.2% and 49.5% [33]. Renz and colleagues demonstrated a histological concordance of 54.8%, ER and PR status concordance of 86.2% and 79.3%, and also a great similarity between the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) features of the two breast cancers [35]. The concordance in hormone receptor status of first and second breast cancers affecting the same patient could suggest that the two tumors may arise in a common milieu and that their subtypes are predetermined in the early stage of breast cancer development [36, 37].
The current literature suggests also the following predictive factors for bilateral breast cancer development: BC familial history [7, 25, 27], BRCA gene mutations [38], HER-2/Neu positivity [39], overweight [40], lobular histology [3, 41], and metropolitan residence, being this last probably due to a better access to the mammographic screening [25]. In fact, also in our study second MBCs and SBCs were more likely to be discovered by mammography.
4.3. Interval between First and Second MBC
In our study we confirmed the previous literature where the prevalence of MBCs after 10 years from the original diagnosis was around the 40% [33]. Such long time risk of MBC, which did not diminish with the pass of time, underlies the crucial role of prolonged ipsi- and contralateral mammographies in the postoperative follow-up of these patients [5, 33]. Moreover, some authors suggest that the annual breast ultrasonography could be a useful adjunctive tool to mammography for the detection of MBCs [42].
Hartman and colleagues demonstrated that the mortality rate of multiple breast cancers is inversely proportional to the age and to the time interval between the first and the second diagnosis in case of MBC [1]. In particular, it is even 120% higher in SBC women younger than 50, whereas it is only 40% higher in the same women after the 50th year of age, and, in case of MBC, it decreases with the passing of follow-up, so that women with a diagnosis of MBC more than 10 years after the first diagnosis result to have a 5-year cancer mortality not significantly different from that of women of the same age with a UBC. In our population, a shorter time interval between the first and the second tumor in women affected by MBC resulted to be associated with a significantly lower hormone receptors positivity (P < 0.05), higher grading, multifocality, extended in situ component, and peritumoral vascular invasion (p n.s.). And actually, in terms of biological aggressiveness, very close MBCs resemble SBCs, which the literature demonstrates to have a more aggressive histological type and to be poorly differentiated [37] and at greater risk for distant metastasis than UBCs [1, 15, 37]. Anyway, in our population, a shorter time interval between the two breast cancers did not predict a worse OS in MBC patients, as described also by other authors [33, 43].
4.4. MBC and SBC Survival
Most of the authors agree that no significant difference exists in survival for patients with unilateral compared to all bilateral breast cancers [39] or compared to MBC diagnosed after 5 years [7]. On the contrary, SBCs are associated with poorer survival in comparison to both MBCs and UBCs [7, 15, 27, 39], and only few studies describe an inverse tendency of better survival in case of SBC compared to MBC [19, 25].
Although our meta-analysis demonstrates a significant better outcome in UBCs than SBCs or MBCs, our retrospective study revealed no statistically significant difference in the OS among MBCs, SBCs, and UBCs, but we found better DFS in UBCs than MBCs or SBCs (Figure 1). This result could be justified by a more aggressive therapeutic management of women affected by multiple BC, who are more likely to receive a radical mastectomy, and by a more prompt imaging diagnosis of a second breast cancer in women followed up for a first breast lesion. In general, patients affected by MBCs or SCBs are more frequently treated with radical surgery, even if there is no clear demonstration of its usefulness [14, 16].
Finally, taking into consideration the impact of the different therapeutic approaches on SBC and MBC outcome, our data suggest a possible interesting role for the adjuvant hormonal therapies in the prevention or at least in the control of an eventual second primary BC. In fact, in our population, the higher hormone receptors positivity of SBCs and of the second MBCs allowed the women affected by multiple BCs to be more frequently treated with adjuvant hormonal therapies, and the second MBCs usually became evident sometime after stopping the hormonal treatment. Therefore, one could wonder if a radical surgery associated with an intensive, adjuvant chemotherapy or hormonal therapy may significantly improve MBC and SBC outcome. And we think that in order to overcome this question only a multicentric, prospective, clinical trial may try to give an answer.
4.5. Pros and Cons
Despite the number of patients we took into consideration is relatively smaller than that of the major, multicentric studies, a strength point of our work is the homogeneity of our population, as well as the reliability of the diagnostic and therapeutic management. Moreover, we chose to take into consideration only breast cancer diagnosed within 2004, in order to have an adequate follow-up length to more accurately evaluate patients outcome. Finally, in our study, we present for the first time a meta-analysis about survival statistics about MBCs and SBCs that are a rare entity which could not be easily investigated in single center studies.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, despite the MBCs and SBCs relatively low prevalence, the presence of a long time risk of MBC confirms the need of ipsi- and contralateral mammographies in the postoperative follow-up of BC patients. Although no significant difference in the OS among MBCs, SBCs, and UBCs was observed, SBCs and second tumors in case of MBCs appear to have a higher prevalence of histological negative prognostic factors, to have a worse DFS, and to receive more frequently radical surgery. In our meta-analysis UBCs had better outcomes than MBCs and SBCs. Furthermore, in our opinion, further studies are required in order to better understand the clinical impact of radical surgery and different medical and hormonal therapies on the outcome of these patients.
Supplementary Material
Supplemental Figure 1: we show the systematic review and meta-analysis flow diagram. And in Supplemental List 1: we show the included and excluded studies in the meta-analysis.
Abbreviations
- BC:
Breast cancer
- MBC:
Metachronous breast cancer
- SBC:
Synchronous breast cancer
- UBC:
Unilateral breast cancer
- OS:
Overall survival
- TNM:
Tumor, node, and metastasis
- AJCC/UICC:
American Joint Commission on Cancer/Union Internationale Contre le Cancer.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare that there is no potential conflict of interests relevant to this paper. This study had no financial support.
Authors' Contribution
Sergio Bernardi, Serena Bertozzi, and Ambrogio P. Londero planned the study and wrote the protocols. Sergio Bernardi, Antonio Minucci, and Serena Bertozzi collected the data. Sergio Bernardi, Ambrogio P. Londero, Serena Bertozzi, and Vito Angione carried out the literature research, collected data for the review, and drafted the paper. Ambrogio P. Londero, Sergio Bernardi, and Serena Bertozzi analyzed the data and drafted the paper. Antonio Minucci, Vito Angione, Giuliana Gentile, Cinzia Dri, Filippo Caponnetto, and Roberto Petri helped in drafting and the critical revision of the paper. All the authors read and approved the final paper. Ambrogio P. Londero, Sergio Bernardi, and Serena Bertozzi equally contributed to this work.
References
- 1.Hartman M, Czene K, Reilly M, et al. Incidence and prognosis of synchronous and metachronous bilateral breast cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2007;25(27):4210–4216. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2006.10.5056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bernstein JL, Lapinski R, Lynch C, Holford T, Thompson WD. Factors influencing mortality among young women with second primary breast carcinoma. Cancer. 2002;95(10):2051–2058. doi: 10.1002/cncr.10950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Chen Y, Thompson W, Semenciw R, Mao Y. Epidemiology of contralateral breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers and Prevention. 1999;8(10):855–861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chaudary MA, Millis RR, Hoskins EO, et al. Bilateral primary breast cancer: a prospective study of disease incidence. The British Journal of Surgery. 1984;71(9):711–714. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800710924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lu W, Schaapveld M, Jansen L, et al. The value of surveillance mammography of the contralateral breast in patients with a history of breast cancer. European Journal of Cancer. 2009;45(17):3000–3007. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2009.08.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Soerjomataram I, Louwman WJ, Lemmens VEPP, de Vries E, Klokman WJ, Coebergh JWW. Risks of second primary breast and urogenital cancer following female breast cancer in the south of The Netherlands, 1972–2001. European Journal of Cancer. 2005;41(15):2331–2337. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2005.01.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Vuoto HD, García AM, Candás GB, et al. Bilateral breast carcinoma: clinical characteristics and its impact on survival. Breast Journal. 2010;16(6):625–632. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-4741.2010.00976.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tilanus-Linthorst MMA, Bartels KCM, Alves C, et al. Selection bias influences reported contralateral breast cancer incidence and survival in high risk non-BRCA1/2 patients. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment. 2006;95(2):117–123. doi: 10.1007/s10549-005-9054-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hill-Kayser CE, Harris EER, Hwang WT, Solin LJ. Twenty-year incidence and patterns of contralateral breast cancer after breast conservation treatment with radiation. International Journal of Radiation Oncology Biology Physics. 2006;66(5):1313–1319. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.07.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Gao X, Fisher SG, Emami B. Risk of second primary cancer in the contralateral breast in women treated for early-stage breast cancer: a population-based study. International Journal of Radiation Oncology Biology Physics. 2003;56(4):1038–1045. doi: 10.1016/s0360-3016(03)00203-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Samant RS, Olivotto IA, Jackson JSH, Mates D. Diagnosis of metachronous contralateral breast cancer. Breast Journal. 2001;7(6):405–410. doi: 10.1046/j.1524-4741.2001.07605.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Broët P, de la Rochefordière A, Scholl SM, et al. Contralateral breast cancer: annual incidence and risk parameters. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 1995;13(7):1578–1583. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1995.13.7.1578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Levi F, Randimbison L, Te V, La Vecchia C. Prognosis of bilateral synchronous breast cancer in Vaud, Switzerland. Breast. 2003;12(2):89–91. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9776(02)00275-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Jobsen JJ, van der Palen J, Ong F, Meerwaldt JH. Synchronous, bilateral breast cancer: prognostic value and incidence. Breast. 2003;12(2):83–88. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9776(02)00278-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Heron DE, Komarnicky LT, Hyslop T, Schwartz GF, Mansfield CM. Bilateral breast carcinoma: risk factors and outcomes for patients with synchronous and metachronous disease. Cancer. 2000;88(12):2739–2750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lee MM, Heimann R, Powers C, Weichselbaum RR, Chen LM. Efficacy of breast conservation therapy in early stage bilateral breast cancer. Breast Journal. 1999;5(1):36–41. doi: 10.1046/j.1524-4741.1999.005001036.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kuo WH, Yen AMF, Lee PH, et al. Cumulative survival in early-onset unilateral and bilateral breast cancer: an analysis of 1907 Taiwanese women. The British Journal of Cancer. 2009;100(4):563–570. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6604898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Verkooijen HM, Chatelain V, Fioretta G, et al. Survival after bilateral breast cancer: results from a population-based study. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment. 2007;105(3):347–357. doi: 10.1007/s10549-006-9455-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Takahashi H, Watanabe K, Takahashi M, Taguchi K, Sasaki F, Todo S. The impact of bilateral breast cancer on the prognosis of breast cancer: a comparative study with unilateral breast cancer. Breast Cancer. 2005;12(3):196–202. doi: 10.2325/jbcs.12.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.The world health organization histological typing of breast tumors—second edition. The world organization. The American Journal of Clinical Pathology. 1982;78(6):806–816. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/78.6.806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Rosen P, Oberman H. Tumors of the Mammary Gland: Atlas of Tumor Pathology. Washington, DC, USA: AFIP; 1993. (3rd series). [Google Scholar]
- 22.Elston CW, Ellis IO. Pathological prognostic factors in breast cancer. I. The value of histological grade in breast cancer: experience from a large study with long-term follow-up. Histopathology. 1991;19(5):403–410. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1991.tb00229.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Parmar MK, Torri V, Stewart L. Extracting summary statistics to perform meta-analyses of the published literature for survival endpoints. Statistics in Medicine. 1998;17(24):2815–2834. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0258(19981230)17:24<2815::aid-sim110>3.0.co;2-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, et al. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting. The Journal of the American Medical Association. 2000;283(15):2008–2012. doi: 10.1001/jama.283.15.2008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Beckmann KR, Buckingham J, Craft P, et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of bilateral breast cancer in an Australian cohort. Breast. 2011;20(2):158–164. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2010.10.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Polednak AP. Bilateral synchronous breast cancer: a population-based study of characteristics, method of detection, and survival. Surgery. 2003;133(4):383–389. doi: 10.1067/msy.2003.110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Carmichael AR, Bendall S, Lockerbie L, Prescott R, Bates T. The long-term outcome of synchronous bilateral breast cancer is worse than metachronous or unilateral tumours. European Journal of Surgical Oncology. 2002;28(4):388–391. doi: 10.1053/ejso.2002.1266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Fracchia AA, Borgen PI. Bilateral breast cancer. Seminars in Surgical Oncology. 1991;7(5):300–305. doi: 10.1002/ssu.2980070513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Pomerantz RA, Murad T, Hines JR. Bilateral breast cancer. The American Surgeon. 1989;55(7):441–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Dixon JM, Anderson TJ, Page DL, Lee D, Duffy SW, Stewart HJ. Infiltrating lobular carcinoma of the breast: an evaluation of the incidence and consequence of bilateral disease. The British Journal of Surgery. 1983;70(9):513–516. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800700902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Yeatman TJ, Lyman GH, Smith SK, Reintgen DS, Cantor AB, Cox CE. Bilaterality and recurrence rates for lobular breast cancer: considerations for treatment. Annals of Surgical Oncology. 1997;4(3):198–202. doi: 10.1007/BF02306610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Bloom ND, Daluvoy V, Ceccarelli F, Degenshein GA. Bilateral mammary carcinoma. Immunologic implications. New York State Journal of Medicine. 1980;80(6):908–910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Díaz R, Munárriz B, Santaballa A, Palomar L, Montalar J. Synchronous and metachronous bilateral breast cancer: a long-term single-institution experience. Medical Oncology. 2012;29(1):16–24. doi: 10.1007/s12032-010-9785-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Rauschecker HF, Sauerbrei W, Gatzemeier W, et al. Eight-year results of a prospective non-randomised study on therapy of small breast cancer. European Journal of Cancer. 1998;34(3):315–323. doi: 10.1016/s0959-8049(97)10035-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Renz DM, Böttcher J, Baltzer PAT, et al. The contralateral synchronous breast carcinoma: a comparison of histology, localization, and magnetic resonance imaging characteristics with the primary index cancer. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment. 2010;120(2):449–459. doi: 10.1007/s10549-009-0718-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Huo D, Melkonian S, Rathouz PJ, Khramtsov A, Olopade OI. Concordance in histological and biological parameters between first and second primary breast cancers. Cancer. 2011;117(5):907–915. doi: 10.1002/cncr.25587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Bu-Ali H, Solh M, Kapur A, Mittal V. Receptor characteristics of the second tumor in synchronous versus metachronous breast cancer. The American Surgeon. 2008;74(8):702–705. doi: 10.1200/jco.2008.26.15_suppl.1107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Graeser MK, Engel C, Rhiem K, et al. Contralateral breast cancer risk in BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2009;27(35):5887–5892. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.19.9430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Kheirelseid EAH, Jumustafa H, Miller N, et al. Bilateral breast cancer: analysis of incidence, outcome, survival and disease characteristics. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment. 2011;126(1):131–140. doi: 10.1007/s10549-010-1057-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Majed B, Dozol A, Ribassin-Majed L, Senouci K, Asselain B. Increased risk of contralateral breast cancers among overweight and obese women: a time-dependent association. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment. 2011;126(3):729–738. doi: 10.1007/s10549-010-1153-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Kollias J, Gill PG, Coventry BJ, Malycha P, Chatterton B, Farshid G. Clinical and histological factors associated with sentinel node identification in breast cancer. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Surgery. 2000;70(7):485–489. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1622.2000.01861.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Kim MJ, Kim EK, Kwak JY, et al. Sonographic surveillance for the detection of contralateral metachronous breast cancer in an Asian population. The American Journal of Roentgenology. 2009;192(1):221–228. doi: 10.2214/AJR.07.4048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Alkner S, Bendahl P, Fernö M, Manjer J, Rydén L. Prediction of outcome after diagnosis of metachronous contralateral breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 2011;11, article 114 doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplemental Figure 1: we show the systematic review and meta-analysis flow diagram. And in Supplemental List 1: we show the included and excluded studies in the meta-analysis.