Abstract
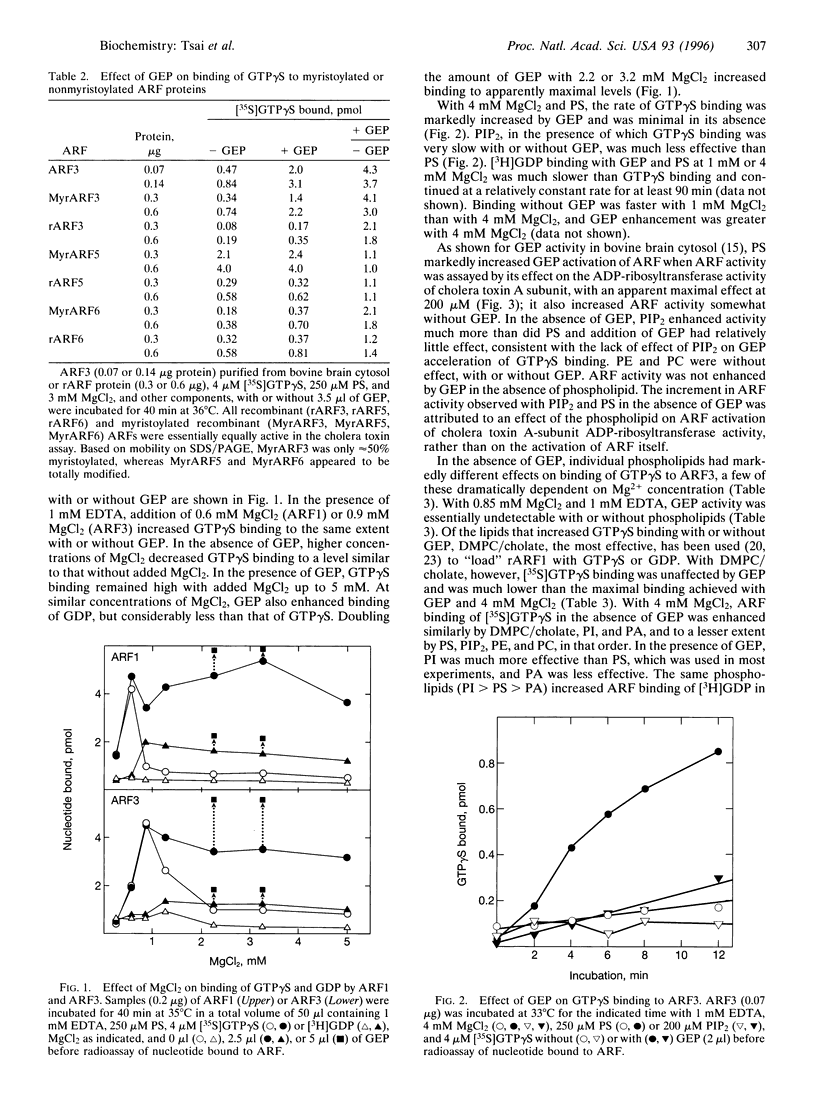
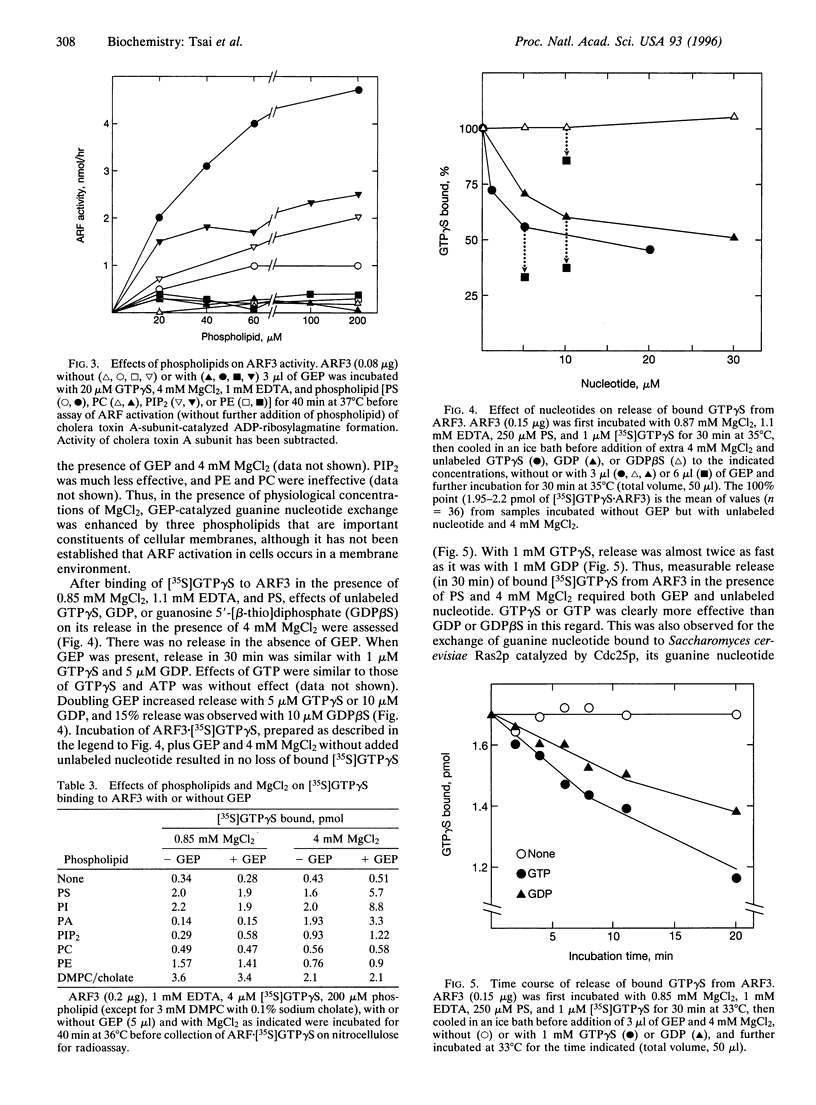
ADP-ribosylation factors (ARFs) are 20-kDa guanine nucleotide-binding proteins and are active in the GTP-bound state and inactive with GDP bound. ARF-GTP has a critical role in vesicular transport in several cellular compartments. Conversion of ARF-GDP to ARF-GTP is promoted by a guanine nucleotide-exchange protein (GEP). We earlier reported the isolation from bovine brain cytosol of a 700-kDa protein complex containing GEP activity that was inhibited by brefeldin A (BFA). Partial purification yielded an approximately 60-kDa BFA-insensitive GEP that enhanced binding of ARF1 and ARF3 to Golgi membranes. GEP has now been purified extensively from rat spleen cytosol in a BFA-insensitive, approximately 55-kDa form. It activated class I ARFs (ARFs 1 and 3) that were N-terminally myristoylated, but not nonmyristoylated ARFs from class-I, II, or III. GEP activity required MgCl2. In the presence of 0.6-0.8 mM MgCl2 and 1 mM EDTA, binding of guanosine 5'-[gamma[35S]thio]triphosphate ([35S]GTP gamma S) by ARF1 and ARF3 was equally high without and with GEP. At higher Mg2+ concentrations, binding without GEP was much lower; with 2-5 mM MgCl2, GEP-stimulated binding was maximal. The rate of GDP binding was much less than that of GTP gamma S with and without GEP. Phospholipids were necessary for GEP activity; phosphatidylinositol was more effective than phosphatidylserine, and phosphatidic acid was less so. Other phospholipids tested were ineffective. Maximal effects required approximately 200 microM phospholipid, with half-maximal activation at 15-20 microM. Release of bound [35S]GTP gamma S from ARF3 required the presence of both GEP and unlabeled GTP or GTP gamma S; GDP was much less effective. This characterization of the striking effects of Mg2+ concentration and specific phospholipids on the purified BFA-insensitive ARF GEP should facilitate experiments to define its function in vesicular transport.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balch W. E., Kahn R. A., Schwaninger R. ADP-ribosylation factor is required for vesicular trafficking between the endoplasmic reticulum and the cis-Golgi compartment. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):13053–13061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boman A. L., Taylor T. C., Melançon P., Wilson K. L. A role for ADP-ribosylation factor in nuclear vesicle dynamics. Nature. 1992 Aug 6;358(6386):512–514. doi: 10.1038/358512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown H. A., Gutowski S., Moomaw C. R., Slaughter C., Sternweis P. C. ADP-ribosylation factor, a small GTP-dependent regulatory protein, stimulates phospholipase D activity. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1137–1144. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90323-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson J. G., Finazzi D., Klausner R. D. Brefeldin A inhibits Golgi membrane-catalysed exchange of guanine nucleotide onto ARF protein. Nature. 1992 Nov 26;360(6402):350–352. doi: 10.1038/360350a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franco M., Chardin P., Chabre M., Paris S. Myristoylation of ADP-ribosylation factor 1 facilitates nucleotide exchange at physiological Mg2+ levels. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jan 20;270(3):1337–1341. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.3.1337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haney S. A., Broach J. R. Cdc25p, the guanine nucleotide exchange factor for the Ras proteins of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, promotes exchange by stabilizing Ras in a nucleotide-free state. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 17;269(24):16541–16548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haun R. S., Tsai S. C., Adamik R., Moss J., Vaughan M. Effect of myristoylation on GTP-dependent binding of ADP-ribosylation factor to Golgi. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 5;268(10):7064–7068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helms J. B., Rothman J. E. Inhibition by brefeldin A of a Golgi membrane enzyme that catalyses exchange of guanine nucleotide bound to ARF. Nature. 1992 Nov 26;360(6402):352–354. doi: 10.1038/360352a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn R. A., Goddard C., Newkirk M. Chemical and immunological characterization of the 21-kDa ADP-ribosylation factor of adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):8282–8287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn R. A., Randazzo P., Serafini T., Weiss O., Rulka C., Clark J., Amherdt M., Roller P., Orci L., Rothman J. E. The amino terminus of ADP-ribosylation factor (ARF) is a critical determinant of ARF activities and is a potent and specific inhibitor of protein transport. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):13039–13046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenhard J. M., Kahn R. A., Stahl P. D. Evidence for ADP-ribosylation factor (ARF) as a regulator of in vitro endosome-endosome fusion. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):13047–13052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liscovitch M., Chalifa V., Pertile P., Chen C. S., Cantley L. C. Novel function of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate as a cofactor for brain membrane phospholipase D. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 26;269(34):21403–21406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makler V., Cukierman E., Rotman M., Admon A., Cassel D. ADP-ribosylation factor-directed GTPase-activating protein. Purification and partial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 10;270(10):5232–5237. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.10.5232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Vaughan M. Structure and function of ARF proteins: activators of cholera toxin and critical components of intracellular vesicular transport processes. J Biol Chem. 1995 May 26;270(21):12327–12330. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.21.12327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randazzo P. A., Kahn R. A. GTP hydrolysis by ADP-ribosylation factor is dependent on both an ADP-ribosylation factor GTPase-activating protein and acid phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 8;269(14):10758–10763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randazzo P. A., Terui T., Sturch S., Fales H. M., Ferrige A. G., Kahn R. A. The myristoylated amino terminus of ADP-ribosylation factor 1 is a phospholipid- and GTP-sensitive switch. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jun 16;270(24):14809–14815. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.24.14809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randazzo P. A., Terui T., Sturch S., Kahn R. A. The amino terminus of ADP-ribosylation factor (ARF) 1 is essential for interaction with Gs and ARF GTPase-activating protein. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 25;269(47):29490–29494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randazzo P. A., Yang Y. C., Rulka C., Kahn R. A. Activation of ADP-ribosylation factor by Golgi membranes. Evidence for a brefeldin A- and protease-sensitive activating factor on Golgi membranes. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9555–9563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleifer L. S., Kahn R. A., Hanski E., Northup J. K., Sternweis P. C., Gilman A. G. Requirements for cholera toxin-dependent ADP-ribosylation of the purified regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 10;257(1):20–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terui T., Kahn R. A., Randazzo P. A. Effects of acid phospholipids on nucleotide exchange properties of ADP-ribosylation factor 1. Evidence for specific interaction with phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 11;269(45):28130–28135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. C., Adamik R., Haun R. S., Moss J., Vaughan M. Effects of brefeldin A and accessory proteins on association of ADP-ribosylation factors 1, 3, and 5 with Golgi. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):10820–10825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. C., Adamik R., Moss J., Vaughan M. Identification of a brefeldin A-insensitive guanine nucleotide-exchange protein for ADP-ribosylation factor in bovine brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 12;91(8):3063–3066. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.8.3063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. C., Noda M., Adamik R., Chang P. P., Chen H. C., Moss J., Vaughan M. Stimulation of choleragen enzymatic activities by GTP and two soluble proteins purified from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):1768–1772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya M., Price S. R., Tsai S. C., Moss J., Vaughan M. Molecular identification of ADP-ribosylation factor mRNAs and their expression in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):2772–2777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker M. W., Bobak D. A., Tsai S. C., Moss J., Vaughan M. GTP but not GDP analogues promote association of ADP-ribosylation factors, 20-kDa protein activators of cholera toxin, with phospholipids and PC-12 cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3230–3235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss O., Holden J., Rulka C., Kahn R. A. Nucleotide binding and cofactor activities of purified bovine brain and bacterially expressed ADP-ribosylation factor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):21066–21072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeuzem S., Feick P., Zimmermann P., Haase W., Kahn R. A., Schulz I. Intravesicular acidification correlates with binding of ADP-ribosylation factor to microsomal membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6619–6623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



