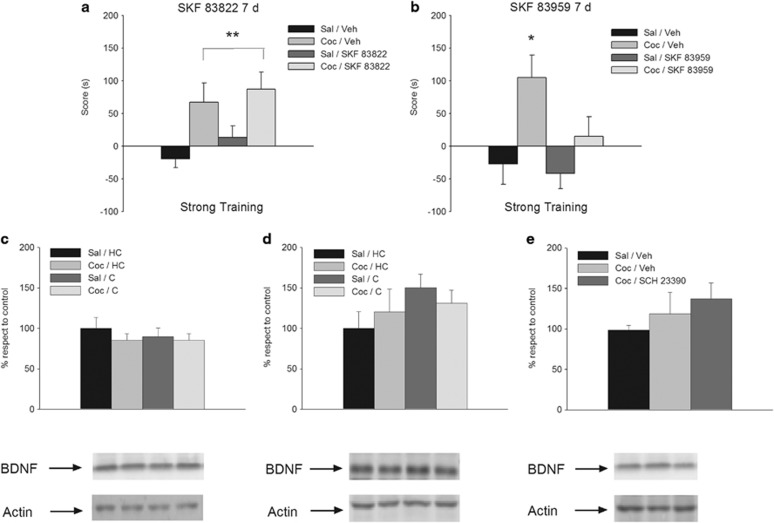
Figure 3.
Persistence of cocaine-related memories is regulated by dopaminergic receptors coupled to phospholipase C (PLC) cascade and is not mediated by brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). (a) Delayed (12 h after conditioning trial) infusion of the adenylyl cyclase (AC)-selective D1-type agonist SKF 83822 had no effect on the 7-day retention of the memory for cocaine–place associations established by three-trial training (n=9–10 per group). (b) Delayed (12 h after conditioning trial) infusion of the PLC-selective D1-type agonist SKF 83959 significantly attenuated 7-day retention of the memory for cocaine–place associations established by three-trial training (n=7–9 per group). Post hoc analyses demonstrated that the group conditioned with cocaine, infused with SKF 83959 12 h later, and tested at 7 days showed a higher score when compared with the other groups (Newman–Keuls, *p<0.05). Asterisks upon bracket indicate a significant difference between saline- and cocaine-injected animals, collapsed across intracerebral infusion treatments (Newman–Keuls, **p<0.01). (c–e) Dorsal hippocampal levels of BDNF of animals administered either saline or 20 mg/kg cocaine. Animals were injected and returned to their home cages (HC groups) or were conditioned as described (C groups). In all the figures, control group is represented by animals injected with saline and left undisturbed in their home cages (Sal/HC groups). (c) Levels of dorsal hippocampal BDNF measured at 12 h after one-trial training. BDNF levels did not vary across treatments (n=5 per group). (d) Levels of dorsal hippocampal BDNF measured at 12 h after three-trial training. BDNF levels did not vary across treatments (n=3–4 per group). (e) SCH 23390 administration did not modify the dorsal hippocampal levels of BDNF measured at 12 h after one-trial training. Animals were conditioned with either saline or cocaine; 11.5 h later they were infused with SCH 23390 or its vehicle and were killed 30 min later (n=15 per group). Coc, cocaine; Sal, saline; Veh, vehicle.