Abstract
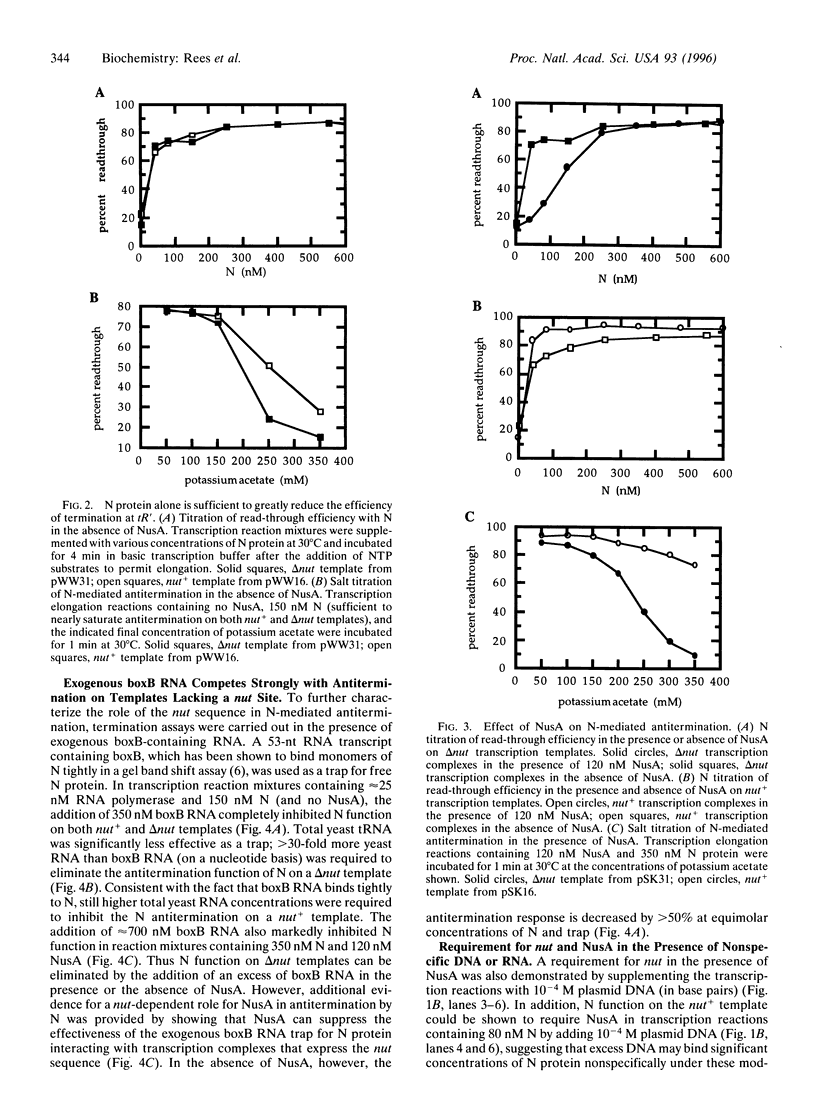
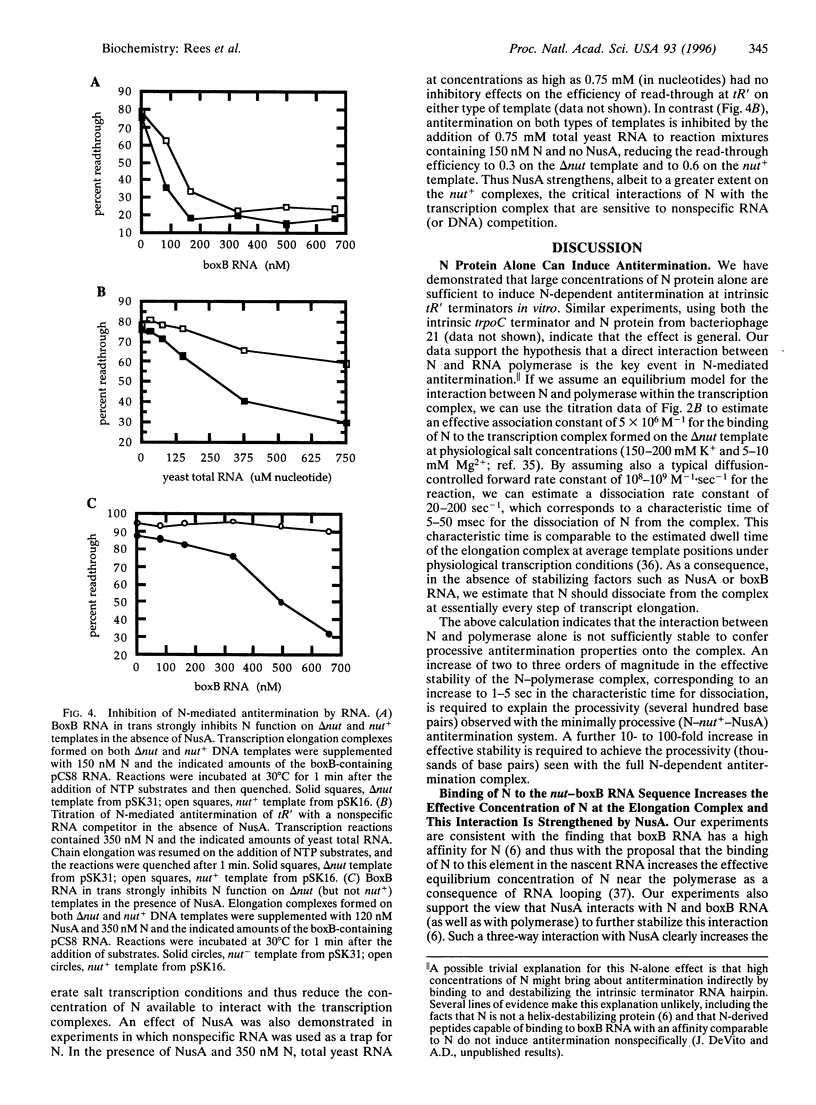
Specific and processive antitermination by bacteriophage lambda N protein in vivo and in vitro requires the participation of a large number of Escherichia coli proteins (Nus factors), as well as an RNA hairpin (boxB) within the nut site of the nascent transcript. In this study we show that efficient, though nonprocessive, antitermination can be induced by large concentrations of N alone, even in the absence of a nut site. By adding back individual components of the system, we also show that N with nut+ nascent RNA is much more effective in antitermination than is N alone. This effect is abolished if N is competed away from the nut+ RNA by adding, in trans, an excess of boxB RNA. The addition of NusA makes antitermination by the N-nut+ complex yet more effective. This NusA-dependent increase in antitermination is lost when delta nut transcripts are used. These results suggest the formation of a specific boxB RNA-N-NusA complex within the transcription complex. By assuming an equilibrium model, we estimate a binding constant of 5 x 10(6) M-1 for the interaction of N alone with the transcription complex. This value can be used to estimate a characteristic dissociation time of N from the complex that is comparable to the dwell time of the complex at an average template position, thus explaining the nonprocessivity of the antitermination effect induced by N alone. On this basis, the effective dissociation rate of N should be approximately 1000-fold slower from the minimally processive (100-600 bp) N-NusA-nut+ transcription complex and approximately 10(5)-fold slower from the maximally processive (thousands of base pairs) complex containing all of the components of the in vivo N-dependent antitermination system.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barik S., Ghosh B., Whalen W., Lazinski D., Das A. An antitermination protein engages the elongating transcription apparatus at a promoter-proximal recognition site. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):885–899. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S., Garcia-Mena J., DeVito J., Wolska K., Das A. Bipartite function of a small RNA hairpin in transcription antitermination in bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Apr 25;92(9):4061–4065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.9.4061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dambly C., Couturier M. A minor Q-independent pathway for the expression of the late genes in bacteriophage lambda. Mol Gen Genet. 1971;113(3):244–250. doi: 10.1007/BF00339545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das A. Control of transcription termination by RNA-binding proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:893–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.004333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das A. How the phage lambda N gene product suppresses transcription termination: communication of RNA polymerase with regulatory proteins mediated by signals in nascent RNA. J Bacteriol. 1992 Nov;174(21):6711–6716. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.21.6711-6716.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeVito J., Das A. Control of transcription processivity in phage lambda: Nus factors strengthen the termination-resistant state of RNA polymerase induced by N antiterminator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 30;91(18):8660–8664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.18.8660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin N. C., Doelling J. H. Overexpression of N antitermination proteins of bacteriophages lambda, 21, and P22: loss of N protein specificity. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2513–2522. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2513-2522.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. I., Olson E. R., Johnson L. L., Alessi D., Craven M. G. Transcription-dependent competition for a host factor: the function and optimal sequence of the phage lambda boxA transcription antitermination signal. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12A):2210–2222. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12a.2210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. I., Wilgus G. S., Mural R. J. Gene N regulator function of phage lambda immun21: evidence that a site of N action differs from a site of N recognition. J Mol Biol. 1973 Dec 25;81(4):505–516. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90519-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill S. C., Weitzel S. E., von Hippel P. H. Escherichia coli sigma 70 and NusA proteins. I. Binding interactions with core RNA polymerase in solution and within the transcription complex. J Mol Biol. 1991 Jul 20;220(2):307–324. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90015-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill S. C., Yager T. D., von Hippel P. H. Escherichia coli sigma 70 and NusA proteins. II. Physical properties and self-association states. J Mol Biol. 1991 Jul 20;220(2):325–333. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90016-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill S. C., von Hippel P. H. Calculation of protein extinction coefficients from amino acid sequence data. Anal Biochem. 1989 Nov 1;182(2):319–326. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90602-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt J., Li J. Interaction of the sigma factor and the nusA gene protein of E. coli with RNA polymerase in the initiation-termination cycle of transcription. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):421–428. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90332-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt J., Li J. The nusA gene protein of Escherichia coli. Its identification and a demonstration that it interacts with the gene N transcription anti-termination protein of bacteriophage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1981 Mar 25;147(1):11–23. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt J., Malnoe P., Li J. Purification of the gene N transcription anti-termination protein of bacteriophage lambda. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1465–1470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt J., Nodwell J. R., Mason S. W. Transcriptional antitermination. Nature. 1993 Jul 29;364(6436):401–406. doi: 10.1038/364401a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt J. Positive control of endolysin synthesis in vitro by the gene N protein of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3606–3610. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gribskov M., Devereux J., Burgess R. R. The codon preference plot: graphic analysis of protein coding sequences and prediction of gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):539–549. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz R. J., Li J., Greenblatt J. An elongation control particle containing the N gene transcriptional antitermination protein of bacteriophage lambda. Cell. 1987 Nov 20;51(4):631–641. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90132-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao-Huang Y., Revzin A., Butler A. P., O'Conner P., Noble D. W., von Hippel P. H. Nonspecific DNA binding of genome-regulating proteins as a biological control mechanism: measurement of DNA-bound Escherichia coli lac repressor in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4228–4232. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazinski D., Grzadzielska E., Das A. Sequence-specific recognition of RNA hairpins by bacteriophage antiterminators requires a conserved arginine-rich motif. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):207–218. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90882-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J., Horwitz R., McCracken S., Greenblatt J. NusG, a new Escherichia coli elongation factor involved in transcriptional antitermination by the N protein of phage lambda. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):6012–6019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason S. W., Greenblatt J. Assembly of transcription elongation complexes containing the N protein of phage lambda and the Escherichia coli elongation factors NusA, NusB, NusG, and S10. Genes Dev. 1991 Aug;5(8):1504–1512. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.8.1504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason S. W., Li J., Greenblatt J. Direct interaction between two Escherichia coli transcription antitermination factors, NusB and ribosomal protein S10. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jan 5;223(1):55–66. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90715-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason S. W., Li J., Greenblatt J. Host factor requirements for processive antitermination of transcription and suppression of pausing by the N protein of bacteriophage lambda. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19418–19426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nodwell J. R., Greenblatt J. Recognition of boxA antiterminator RNA by the E. coli antitermination factors NusB and ribosomal protein S10. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):261–268. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90665-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nodwell J. R., Greenblatt J. The nut site of bacteriophage lambda is made of RNA and is bound by transcription antitermination factors on the surface of RNA polymerase. Genes Dev. 1991 Nov;5(11):2141–2151. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.11.2141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds R., Bermúdez-Cruz R. M., Chamberlin M. J. Parameters affecting transcription termination by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. I. Analysis of 13 rho-independent terminators. J Mol Biol. 1992 Mar 5;224(1):31–51. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90574-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes G., Chamberlin M. J. Ribonucleic acid chain elongation by Escherichia coli ribonucleic acid polymerase. I. Isolation of ternary complexes and the kinetics of elongation. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 25;249(20):6675–6683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salstrom J. S., Szybalski W. Coliphage lambdanutL-: a unique class of mutants defective in the site of gene N product utilization for antitermination of leftward transcription. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 5;124(1):195–221. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90156-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. C., Chamberlin M. J. Amplification and isolation of Escherichia coli nusA protein and studies of its effects on in vitro RNA chain elongation. Biochemistry. 1984 Jan 17;23(2):197–203. doi: 10.1021/bi00297a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalen W. A., Das A. Action of an RNA site at a distance: role of the nut genetic signal in transcription antitermination by phage-lambda N gene product. New Biol. 1990 Nov;2(11):975–991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalen W., Ghosh B., Das A. NusA protein is necessary and sufficient in vitro for phage lambda N gene product to suppress a rho-independent terminator placed downstream of nutL. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2494–2498. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson K. S., von Hippel P. H. Stability of Escherichia coli transcription complexes near an intrinsic terminator. J Mol Biol. 1994 Nov 18;244(1):36–51. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson K. S., von Hippel P. H. Transcription termination at intrinsic terminators: the role of the RNA hairpin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Sep 12;92(19):8793–8797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.19.8793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]