CASE SUMMARY
History
A 78-year-old Bulgarian woman presented to the National Institutes of Health (NIH) with a diagnosis of poorly differentiated metastatic carcinoma of unknown origin. The prior month she had been seen at a hospital in Bulgaria for weight loss and a right inguinal mass. NIH pathology review confirmed a poorly differentiated carcinoma with extensive necrosis suggesting squamous cell carcinoma. She was enrolled in a treatment trial at NIH with metastatic disease invading the lungs and lymph nodes (mediastinum, abdomen, and pelvis) and started on a chemotherapy regimen of gemcitabine, carboplatin and lenalidomide with dexamethasone as an antiemetic. The patient returned on day 8, and a rash of two days duration was noted. Immediately, before arriving at the dermatology clinic, she developed altered mental status with aphasia and was admitted for neurologic observation. The altered mental status resolved and evaluation revealed only small vessel ischemia. The patient was also experiencing diarrhea and was found to have elevated transaminases (4–7 fold over normal). Chemotherapy was held due to the transaminase abnormalities and altered mental status. The following day, the patient was seen by dermatology for a progressive asymptomatic eruption.
Physical Examination
This elderly woman had multiple thin, urticarial, pink papules and plaques, ranging in size from 0.5–1.5 cm, and linear pink to red thread-like lesions arrayed over her trunk and extremities. Some lesions were arcuate. Across chest, breasts, the areolae and thighs were striking, linear pink, palpable threads ranging from 2–6 cm in length (Figure 1A, B). The total number of lesions was approximately 75, and none had epidermal change.
Figure 1.
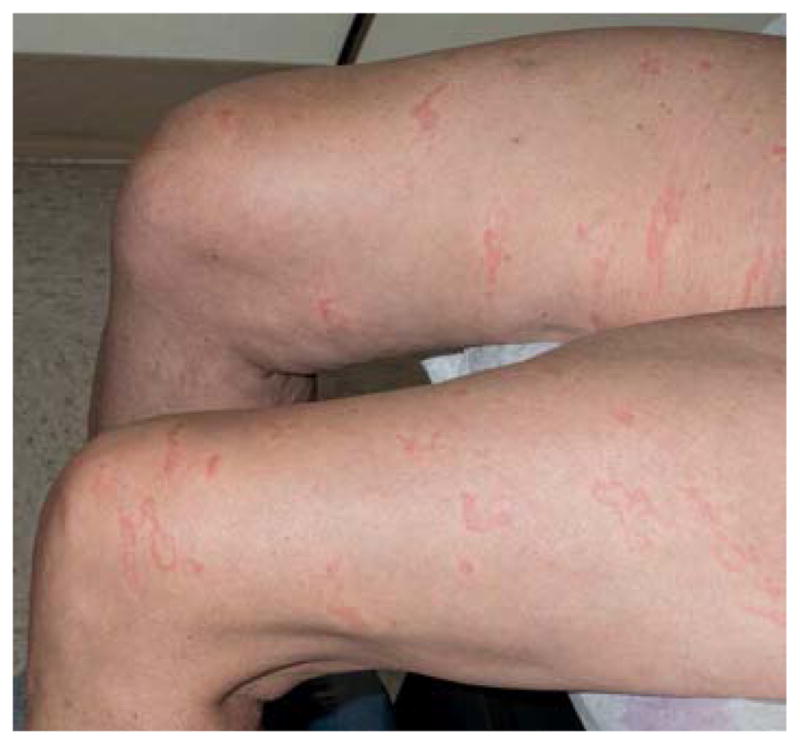
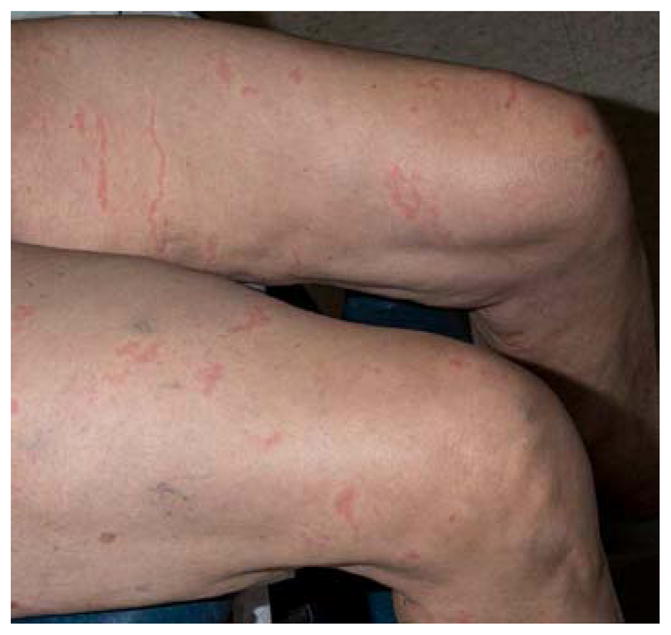
A, B. Larva currens. Linear and serpiginous, migratory pink thread-like lesions.
Histopathology
A punch biopsy was obtained from a pink linear lesion on the right shoulder and showed very mild superficial perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate and numerous eosinophils in the dermis.
Significant Diagnostic Studies
Prior to the chemotherapy and systemic glucocorticoid treatment, the patient had an elevated white blood count of 10.14 (Nl to 10.04 K/uL) and an elevated absolute eosinophil count of 0.81 (Nl to 0.36 K/uL), but at the time of dermatology consultation her absolute eosinophil count was normal (0.22 K/uL). Aspartate aminotransferase was 144 U/L and alanine aminotransferase was 300 U/L. Microscopic evaluation of the stool revealed numerous rhabditiform larvae of Strongyloides stercoralis (Figure 2). Stool inoculated in the center of a blood agar plate (Figure 3) demonstrated stool bacterial colonies in numerous serpiginous tracts, consistent with the presence of multiple live, motile larvae.
Figure 2.
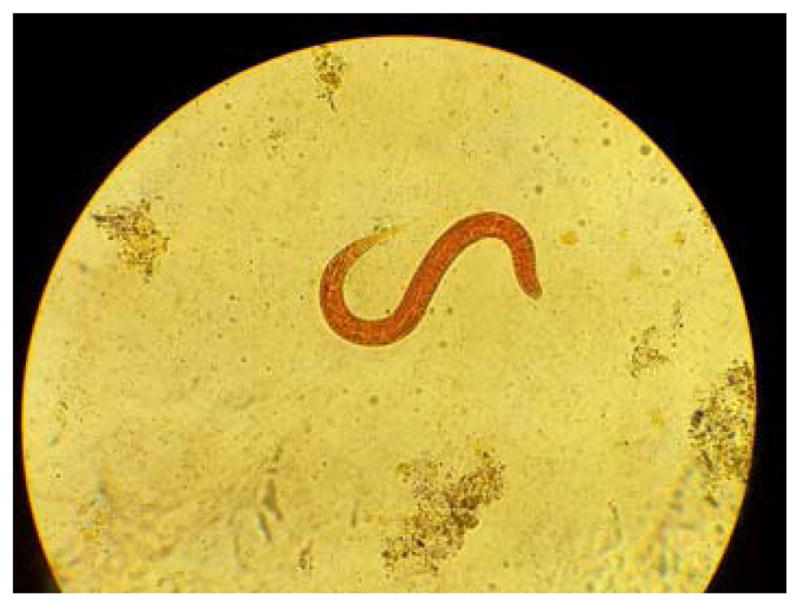
Strongyloides stercoralis. Microscopic evaluation of the stool revealed rhabditiform larvae.
Figure 3.
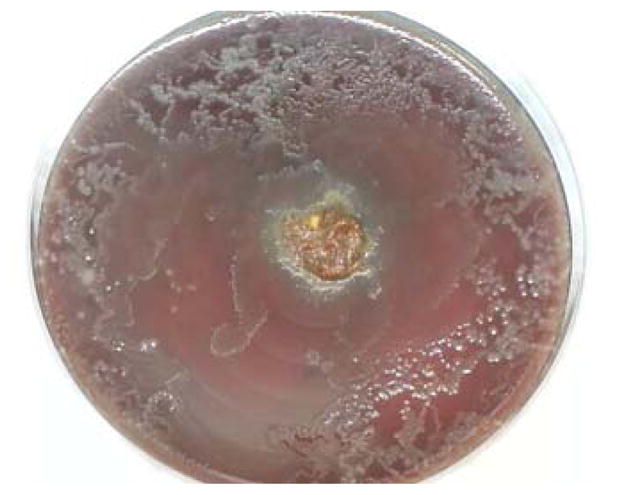
Strongyloides stercoralis. Stool inoculated in the center of a blood agar plate shows stool bacterial colonies in numerous serpiginous tracts, consistent with the presence of multiple live, motile larvae.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of Strongyloides stercoralis hyperinfection syndrome was made.
FOLLOW-UP
The patient received a seven-day course of ivermectin. Within four days the rash resolved and the transaminase elevations improved. Repeat stool cultures were performed on days 4 and 7 of treatment, and both were negative for larvae. She resumed her chemotherapy and antiemetic dexamethasone after ivermectin treatment and confirmation of negative stool examinations for larvae.
DISCUSSION
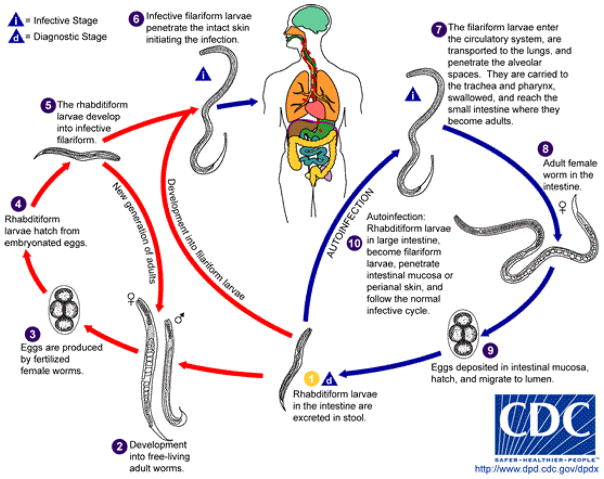
Strongyloides stercoralis is a parasitic nematode (roundworm) with a worldwide distribution that includes the southeastern United States and southern Europe.1 Infection is often asymptomatic in the absence of immunosuppression. Among nematodes, Strongyloides stercoralis is unique in its ability to complete its entire life cycle in humans through autoinfection and multiplication (Figure 4). Infection most commonly occurs through contact with infested soil. Free-living filariform larvae penetrate the skin, enter the circulatory system and migrate through the lung before being coughed up and swallowed. In the small intestine, the larvae mature into adult worms. A female worm can produce up to forty eggs per day. The eggs hatch into noninfective rhabditiform larvae, which are excreted in the stool. In a normal host, small numbers of rhabditiform larvae become filariform larvae in the large intestine. These filariform larvae can penetrate the perianal skin or migrate through the intestinal mucosa, reentering the circulatory system. This autoinfection cycle may persist for decades.
Figure 4.
Strongyloides stercoralis. Life cycle of the nematode (roundworm) from Centers for Disease Control & Prevention website (http://www.dpd.cdc.gov/dpdx/HTML/Strongyloidiasis.htm , accessed 10/18/2013) .3 Autoinfection can occur if the rhabditiform larvae in the large intesting become filariform larvae and penetrate the intestinal mucosa or perianal skin, and then follow the normal infective cycle.
In immunosuppressed patients, parasite numbers can increase, accelerating the autoinfection cycle and causing clinical signs and symptoms termed the hyperinfection syndrome. 2 Larvae may spread widely, and disseminated strongyloidiasis is characterized by parasitic invasion into organs beyond the skin, gastrointestinal tract, and lungs. Disseminated strongyloidiasis has a mortality of up to 90%.3 Although hyperinfection syndrome has been associated with a variety of conditions, including hematologic malignancy, organ transplantation and HIV infection, the vast majority of cases occur after corticosteroid therapy and/or HTLV-1 infection. Central nervous system (CNS) infection can be seen in disseminated strongyloidiasis and can manifest as transient altered mental status, aseptic meningitis, or more profound neurologic alterations.4–6 The high mortality in these cases is secondary to gram negative bacteremia that results from the larvae disseminating bacteria from the gastrointestinal tract as they migrate into different organs.7
Common cutaneous manifestations of Strongyloides, including urticaria and larva currens (a hypersensitivity reaction to larvae migrating in the skin), may be present at any time during infection, but are florid in cases of hyperinfection. Lesions of larva currens have a characteristic appearance as seen in this patient, with evanescent pink, urticarial plaques and thread-like lesions. The lesions may advance up to 10 cm per day.8 Plaques can be linear, serpiginous, annular, and arcuate and should be distinguished from cutaneous larva migrans (creeping eruption), which refers to infection with animal nematodes, most commonly Ancylostoma braziliense.9 Although cutaneous larva migrans is also characterized by serpiginous tracks lesions are solitary or few in number and occur within days of exposure. The tracks of larva migrans extend at a rate of only several millimeters per day and can persist for weeks. Arthur and Shelly, in 1958, distinguished between larva migrans from larva currens, and credited the first full account to Fülleborn in 1926, who reproduced larva currens in himself by application of larvae to his lower arm.10
Persistent Strongyloides infection is of increasing relevance as populations age, emigrate from endemic areas, travel to endemic areas for work or pleasure, and may be subsequently immunosuppressed. Although immigrants from highly endemic areas in the tropics and subtropics represent the highest risk group in the United States, veterans who served in World War II, Vietnam, Korea, and other South East Asian countries are also at risk.11, 12 The infection is endemic in the southern U.S., with Strongyloides stercoralis detected in stool samples from 6.1% of 229 randomly selected hospitalized patients in rural Tennessee.13 A recent CDC Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report notified that of 102 patients attending a public, weekend, general clinic, in southeastern Kentucky who agreed to be tested, 5 patients (born in the U.S. with no travel history to tropical countries) were positive for S. stercoralis antibody.14
Patients with chronic Strongyloides infection may demonstrate persistent eosinophilia. Consequently, unexplained eosinophilia should raise suspicion for occult strongyloidiasis in a patient with an appropriate exposure history. Stool ova and parasite evaluation has low sensitivity in chronic infection in normal hosts, due to intermittent excretion of small numbers of larvae, but is useful in hyperinfection syndrome.1 Stool samples can also be assessed by placing an unrefrigerated, fresh stool sample on a heme containing agar plate. Larvae migrate dragging stool bacteria with them, creating characteristic serpiginous tracts of bacterial colonies. A similar finding can be demonstrated using sputum samples from individuals with hyperinfection syndrome.15 Alerting the laboratory to suspect Strongyloides will allow them to take the necessary measures including inoculating fresh stool onto a blood plate, observing the plate for at least 48 hours, and examining multiple slides for larvae. Immunodiagnostic tests, particularly enzyme immunoassay, can identify antibodies, but antibody tests do not distinguish past from current infections. Diagnosis and treatment of active Strongyloides infection before iatrogenic immunosuppression is important in order to reduce mortality.
KEY TEACHING POINTS.
Strongyloides is a genus of obligate gastrointestinal nematodes (roundworms) of vertebrates. The species stercoralis, the usual cause of human infection, has the potential for autoinfection and multiplication in humans.
Peripheral eosinophilia without a known cause may represent chronic, persistent infection with Strongyloides stercoralis.
Undiagnosed disease is prevalent, especially among immigrants and military veterans who served in highly endemic areas in the tropics and subtropics.
Immunosuppression of individuals with persistent Strongyloides stercoralis infection can lead to hyperinfection syndrome or disseminated infection, which can be fatal in up to 90% of cases.
First line therapy for acute and chronic strongyloidiasis is ivermectin, 200 mcg/kg orally in a single daily dose for 1–2 days. Treatment of hyperinfection syndrome includes reduction of immunosuppression, if possible, and administration of ivermectin (200 mcg/kg daily) until larvae are no longer detected in stool for at least 2 weeks. 3, 16 The spectrum of clinical disease is wide, however, and shorter courses of ivermectin may be sufficient.
Larva currens is a hypersensitivity reaction that refers to the cutaneous manifestation of Strongyloides and should be distinguished from cutaneous larva migrans which is due to abortive human infection with an animal hookworm.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Chyi-Chia Richard Lee, M.D., Ph.D. for histologic interpretation and Mary King , Patient Support Services, Clinical Center, for patient photography.
This research was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the NCI, NIH.
Footnotes
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
We will not request reprints
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Reference List
- 1.Genta RM. Global prevalence of strongyloidiasis: critical review with epidemiologic insights into the prevention of disseminated disease. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Sep;11(5):755–67. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.5.755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ganesh S, Cruz RJ., Jr Strongyloidiasis: a multifaceted disease. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y ) 2011 Mar;7(3):194–6. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Strongyloides. Vol. 2013. Center for Disease Control and Prevention; Oct 18, 2013. Ref Type: Internet Communication. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Schindzielorz A, Edberg SC, Bia FJ. Strongyloides stercoralis hyperinfection and central nervous system involvement in a patient with relapsing polychondritis. South Med J. 1991 Aug;84(8):1055–7. doi: 10.1097/00007611-199108000-00030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Feely NM, Waghorn DJ, Dexter T, Gallen I, Chiodini P. Strongyloides stercoralis hyperinfection: difficulties in diagnosis and treatment. Anaesthesia. 2010 Mar;65(3):298–301. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.2009.06196.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Rodriguez M, Flores P, Ahumada V, Vazquez-Vazquez L, Alvarado-de la Barrera C, Reyes-Teran G. Central Nervous System Strongyloidiasis and Cryptococcosis in an HIV-Infected Patient Starting Antiretroviral Therapy. Case Rep Med. 2012;2012:575470. doi: 10.1155/2012/575470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kassalik M, Monkemuller K. Strongyloides stercoralis hyperinfection syndrome and disseminated disease. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y ) 2011 Nov;7(11):766–8. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Smith JD, Goette DK, Odom RB. Larva currens. Cutaneous strongyloidiasis. Arch Dermatol. 1976 Aug;112(8):1161–3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Caumes E, Danis M. From creeping eruption to hookworm-related cutaneous larva migrans. Lancet Infect Dis. 2004 Nov;4(11):659–60. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(04)01178-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Arthur RP, Shelley WB. Larva currens; a distinctive variant of cutaneous larva migrans due to Strongyloides stercoralis. AMA Arch Derm. 1958 Aug;78(2):186–90. doi: 10.1001/archderm.1958.01560080044007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Nuesch R, Zimmerli L, Stockli R, Gyr N, Christoph Hatz FR. Imported strongyloidosis: a longitudinal analysis of 31 cases. J Travel Med. 2005 Mar;12(2):80–4. doi: 10.2310/7060.2005.12204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Genta RM, Weesner R, Douce RW, Huitger-O'Connor T, Walzer PD. Strongyloidiasis in US veterans of the Vietnam and other wars. JAMA. 1987 Jul 3;258(1):49–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Berk SL, Verghese A, Alvarez S, Hall K, Smith B. Clinical and epidemiologic features of strongyloidiasis. A prospective study in rural Tennessee. Arch Intern Med. 1987 Jul;147(7):1257–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Notes from the field: strongyloidiasis in a rural setting - southeastern kentucky 2013. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2013 Oct 25;62(42):843. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Keystone JS. Can one afford not to screen for parasites in high-risk immigrant populations? Clin Infect Dis. 2007 Nov 15;45(10):1316–8. doi: 10.1086/522530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Mejia R, Nutman TB. Screening, prevention, and treatment for hyperinfection syndrome and disseminated infections caused by Strongyloides stercoralis. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2012 Aug;25(4):458–63. doi: 10.1097/QCO.0b013e3283551dbd. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]